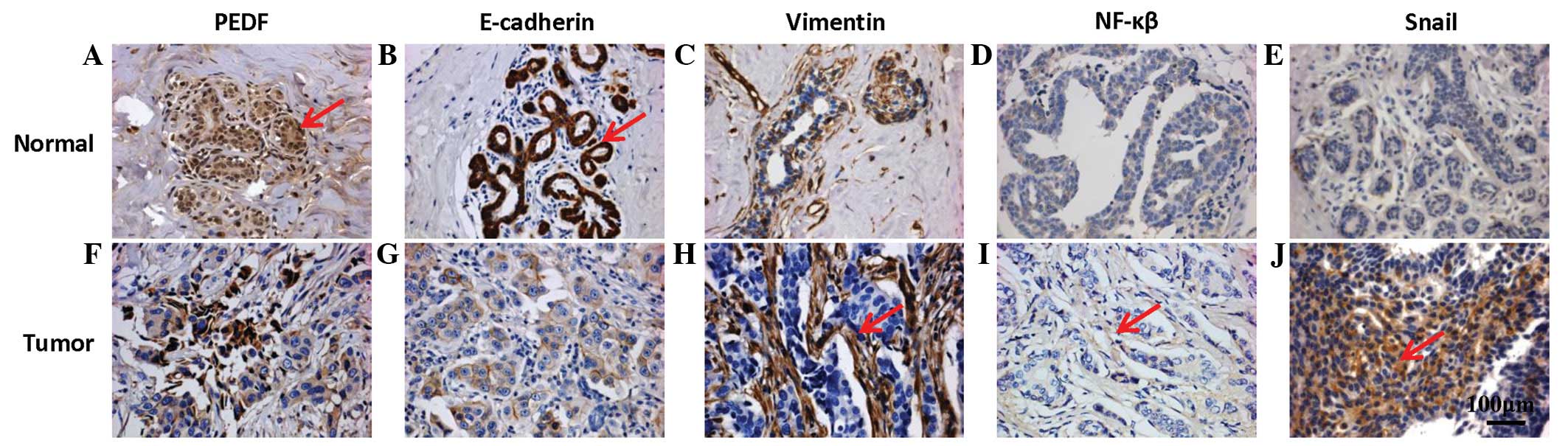
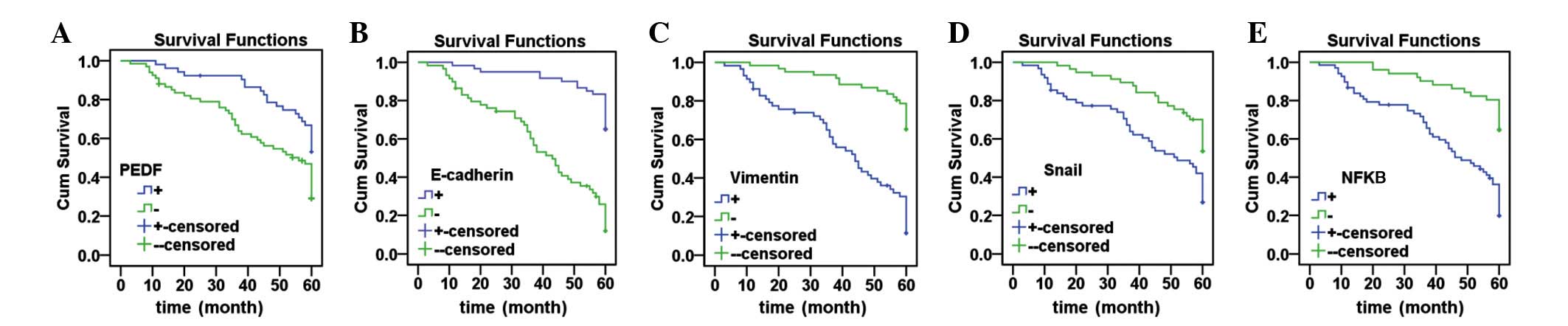
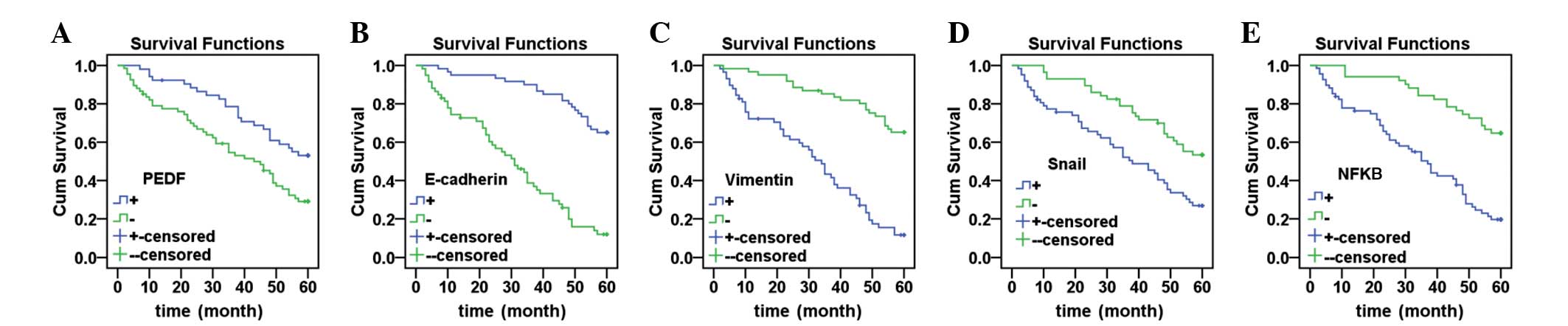
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Linos E, Spanos D, Rosner BA, et al:
Effects of reproductive and demographic changes on breast cancer
incidence in China: A modeling analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:1352–1360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang X, Li X, Zhang N, Yang Q and Moran
MS: Low doses ionizing radiation enhances the invasiveness of
breast cancer cells by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 412:188–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kalluri R: EMT: When epithelial cells
decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest.
119:1417–1419. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Emadi Baygi M, Soheili ZS, Schmitz I, et
al: Snail regulates cell survival and inhibits cellular senescence
in human metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Biol Toxicol.
26:553–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Kuiatse I, Lee AV, et al:
Sustained c-Jun-NH2-kinase activity promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, invasion and survival of breast cancer cells by
regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Mol
Cancer Res. 8:266–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tryndyak VP, Beland FA and Pogribny IP:
E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and
microRNA-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and
drug-resistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 126:2575–2583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zavadil J and Böttinger EP: TGF-beta and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 29:5764–5774.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH and Sonenshein
GE: NF-kappaB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 104:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huber MA, Beug H and Wirth T:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: NF-kappaB takes center stage.
Cell Cycle. 3:1477–1480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huber MA, Azoitei N, Baumann B, et al:
NF-kappaB is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
metastasis in a model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest.
114:569–581. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai J, Parr C, Watkins G, Jiang WG and
Boulton M: Decreased pigment epithelium-derived factor expression
in human breast cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3510–3517.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou D, Cheng SQ, Ji HF, et al: Evaluation
of protein pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) and microvessel
density (MVD) as prognostic indicators in breast cancer. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 136:1719–1727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yasui N, Mori T, Morito D, et al:
Dual-site recognition of different extracellular matrix components
by antiangiogenic/neurotrophic serpin, PEDF. Biochemistry.
42:3160–3167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aurora AB, Biyashev D, Mirochnik Y, et al:
NF-kappaB balances vascular regression and angiogenesis via
chromatin remodeling and NFAT displacement. Blood. 116:475–484.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zaichuk TA, Shroff EH, Emmanuel R, et al:
Nuclear factor of activated T cells balances angiogenesis
activation and inhibition. J Exp Med. 199:1513–1522. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoshina D, Abe R, Yamagishi SI and Shimizu
H: The role of PEDF in tumor growth and metastasis. Curr Mol Med.
10:292–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fitzgerald DP, Subramanian P, Deshpande M,
et al: Opposing effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor on
breast cancer cell versus neuronal survival: Implication for brain
metastasis and metastasis-induced brain damage. Cancer Res.
72:144–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Manalo KB, Choong PF and Dass CR: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor as an impending therapeutic agent against
vascular epithelial growth factor-driven tumor-angiogenesis. Mol
Carcinog. 50:67–72. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
World Health Organization: World Health
Organization family of international classifications. The meeting
for heads of WHO collaborating centres for the family of
internation classifications (Cologne, Germany). October
19–25–2003.
|
|
24
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors (Fifth). New York, NY:
Wiley-Liss. 1997.
|
|
25
|
Elston EW and Ellis IO: Method for grading
breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 46:189–190. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang M, Liu NY, Wang XE, et al: Activin B
promotes epithelial wound healing in vivo through Rhoa-JNK
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 6:e251432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haybittle JL, Blamey RW, Elston CW, et al:
A prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
45:361–366. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Filleur S, Nelius T, de Riese W and
Kennedy RC: Characterization of PEDF: A multi-functional serpin
family protein. J Cell Biochem. 106:769–775. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Setten GV and Abdiu O: Possible role of
pigment epithelium derived factor in angiogenesis. European
Opthalmic Rev. 10:64–67. 2009.
|
|
31
|
Kawaguchi T, Yamagishi SI and Sata M:
Structure-function relationships of PEDF. Curr Mol Med. 10:302–311.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Broadhead ML, Dass CR and Choong PF:
Cancer cell apoptotic pathways mediated by PEDF: Prospects for
therapy. Trends Mol Med. 15:461–467. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jan R, Huang M and Lewis-Wambi J: Loss of
pigment epithelium-derived factor: A novel mechanism for the
development of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res. 14:R1462012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Uehara H, Miyamoto M, Kato K, et al:
Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor decreases liver
metastasis and correlates with favorable prognosis for patients
with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 64:3533–3537.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guan M, Yam HF, Su B, et al: Loss of
pigment epithelium derived factor expression in glioma progression.
J Clin Pathol. 56:277–282. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheung LW, Au SC, Cheung AN, et al:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor is estrogen sensitive and
inhibits the growth of human ovarian cancer and ovarian surface
epithelial cells. Endocrinology. 147:4179–4191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ning Q, Liu C, Hou L, et al: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 activation promotes migration
and invasion of breast cancer cells through epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. PLoS One. 8:e652172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seki R, Yamagishi S, Matsui T, et al:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) inhibits survival and
proliferation of VEGF-exposed multiple myeloma cells through its
anti-oxidative properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 431:693–697.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang J, Chen S, Huang X, et al: Growth
suppression of cervical carcinoma by pigment epithelium-derived
factor via anti-angiogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:967–974. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Han J, Yang X, et al: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis and growth of
gastric carcinoma by down-regulation of VEGF. Oncol Rep.
26:681–686. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cai J, Jiang WG, Grant MB and Boulton M:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis via
regulated intracellular proteolysis of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 1. J Biol Chem. 281:3604–3613. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kokkinos MI, Wafai R, Wong MK, et al:
Vimentin and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast
cancer-observations in vitro and in vivo. Cells Tissues Organs.
185:191–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee J, Hahm ER, Marcus AI and Singh SV:
Withaferin A inhibits experimental epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in MCF-10A cells and suppresses vimentin protein level
in vivo in breast tumors. Mol Carcinog. 30:102013.
|
|
44
|
Blanco MJ, Moreno-Bueno G, Sarrio D, et
al: Correlation of Snail expression with histological grade and
lymph node status in breast carcinomas. Oncogene. 21:3241–3246.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luo WR, Li SY, Cai LM and Yao KT: High
expression of nuclear Snail, but not cytoplasmic staining, predicts
poor survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
19:2971–2979. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alkatout I, Wiedermann M, Bauer M, et al:
Transcription factors associated with epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cancer stem cells in the tumor centre and margin of
invasive breast cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 94:168–173. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hirsch J, Johnson CL, Nelius T, Kennedy R,
Riese WD and Filleur S: PEDF inhibits IL8 production in prostate
cancer cells through PEDF receptor/phospholipase A2 and regulation
of NFκB and PPARγ. Cytokine. 55:202–210. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|