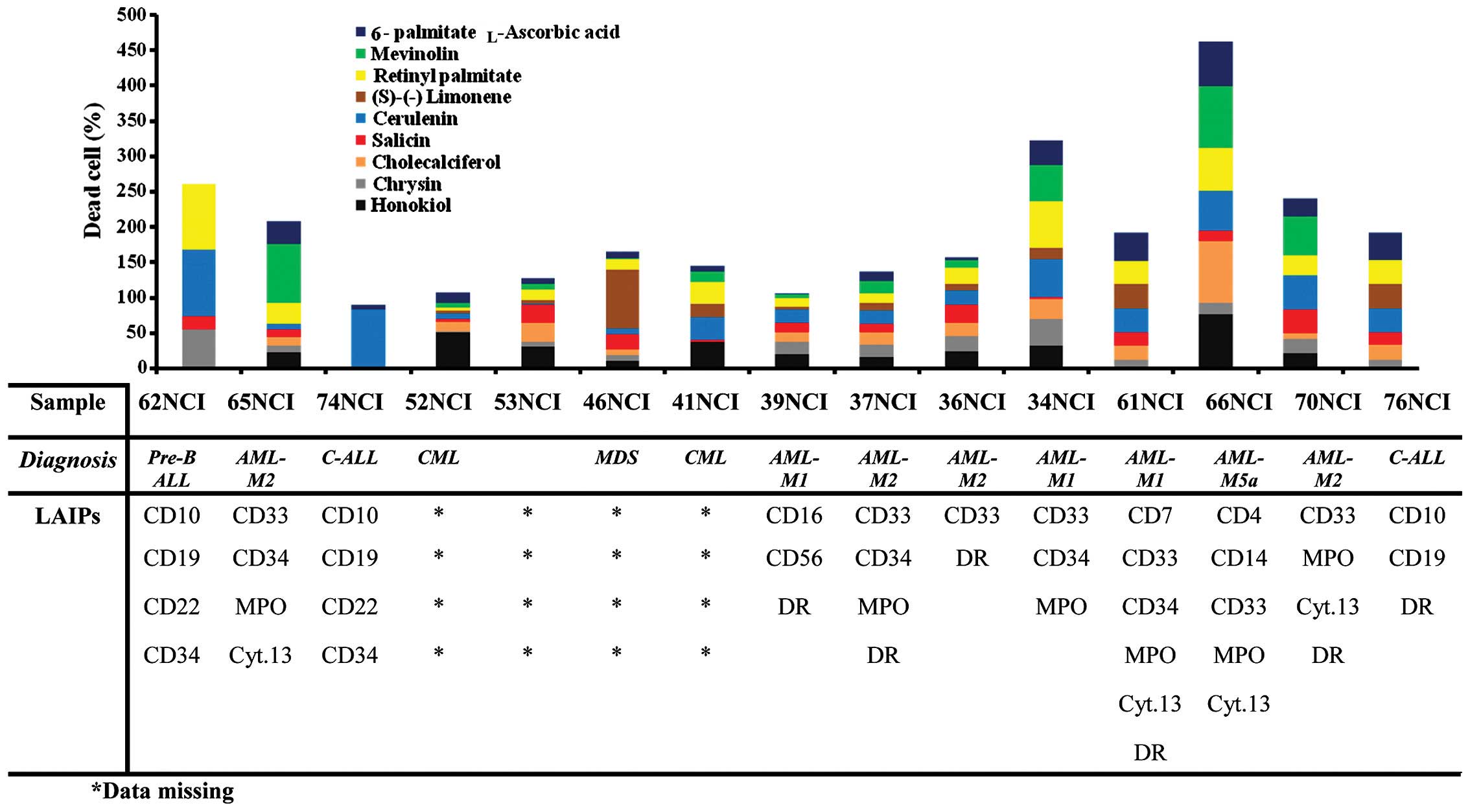
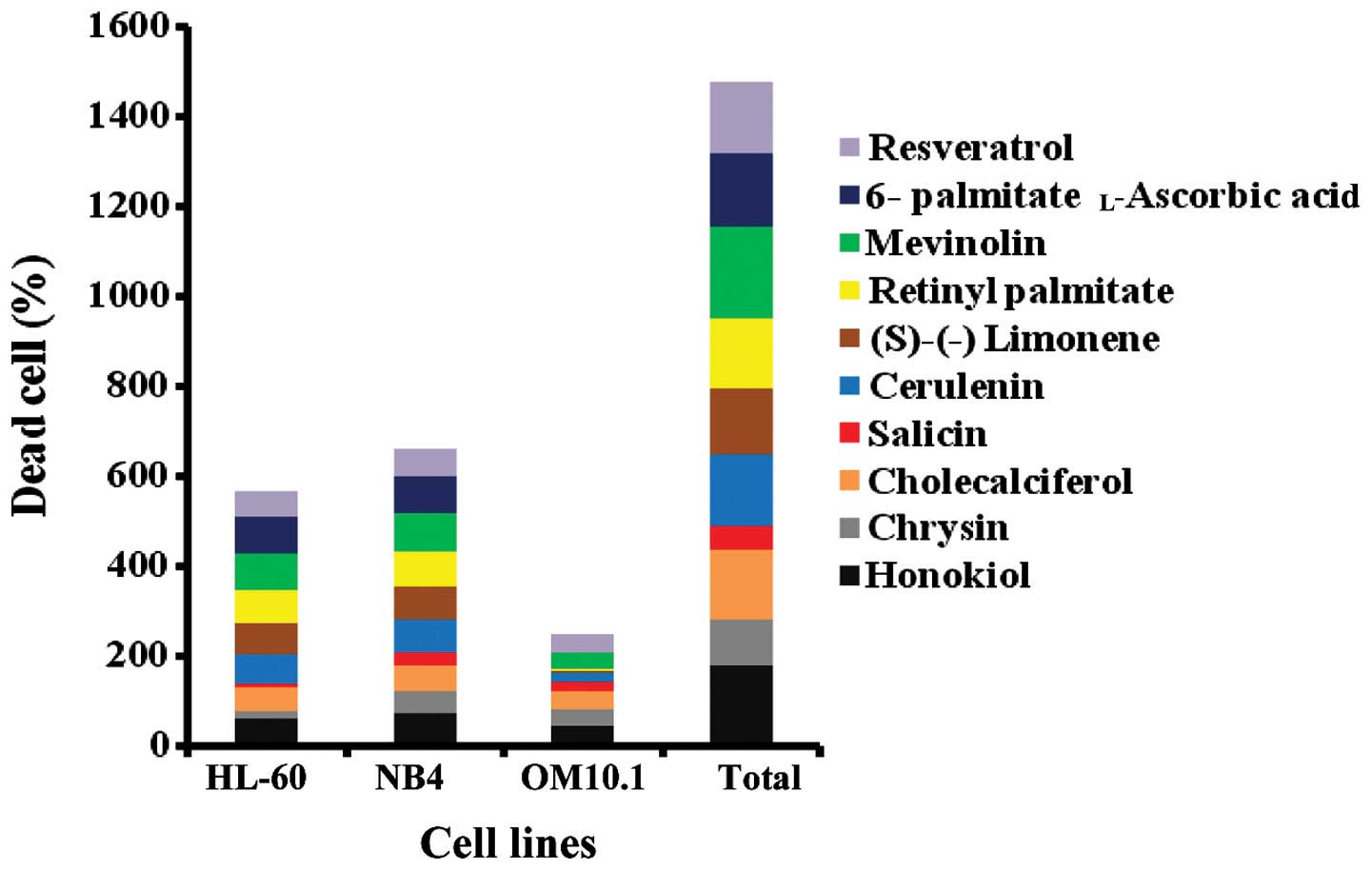
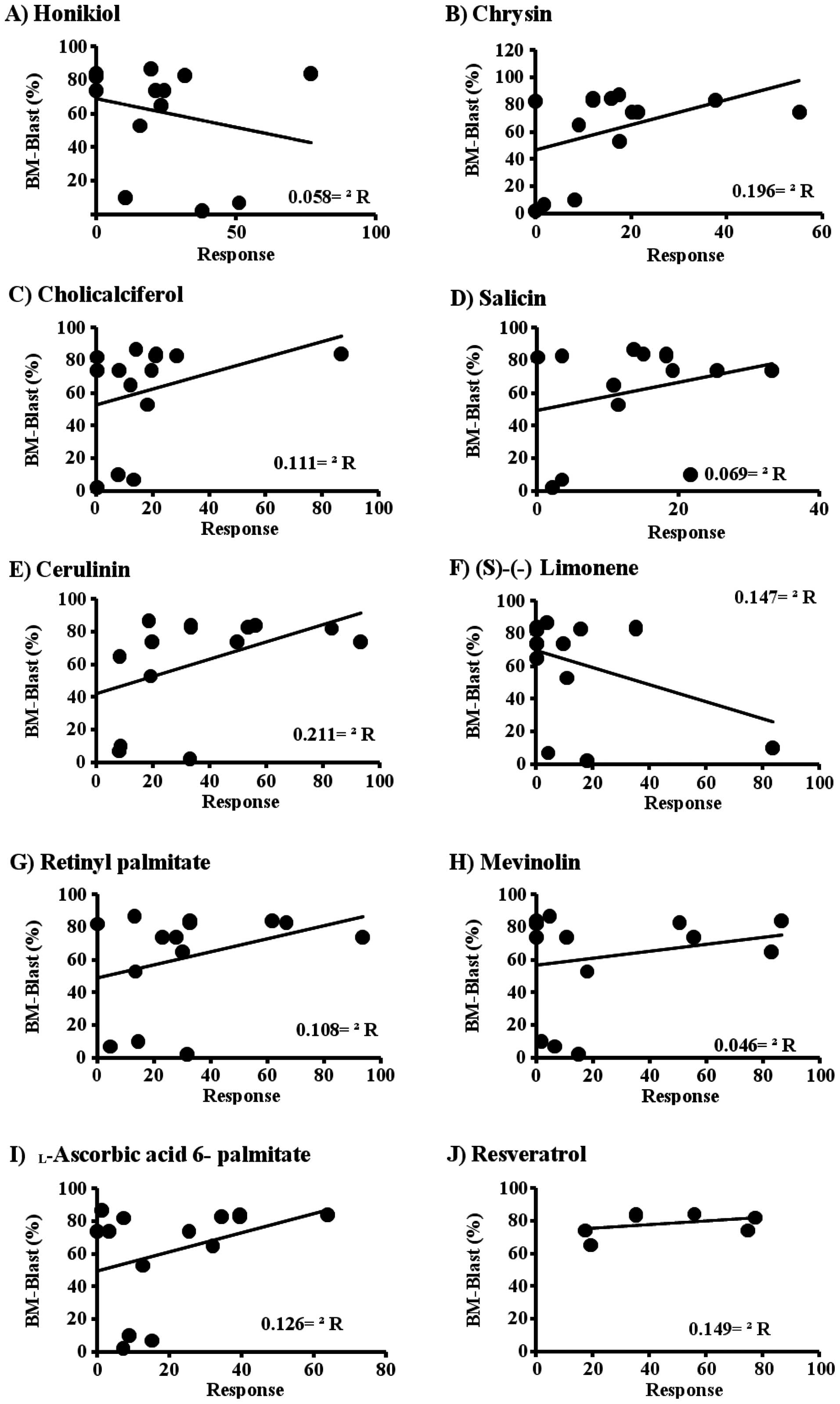
|
1
|
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT,
Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR and Sultan C: Proposals for the
classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British
(FAB) co-operative group. Br J Haematol. 33:451–458. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bain BJ: Acute leukemia cytology,
cytochemistry and the FAB classification. Leukemia Diagnosis. Bain
J: Chapter 2. (2nd). (Oxford, UK). Blackwell Science. 1–52.
1999.
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Jemal A, Grey N, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global cancer transitions according to the Human
Development Index (2008–2030): a population-based study. Lancet
Oncol. 13:790–801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
American Cancer Society: Global Cancer
Facts & Figures (3rd). Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society.
2015.
|
|
5
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts
& Figures 2014. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society. 2014.
|
|
6
|
Tadmouri GO, Nair P, Obeid T and Gallala
S: Genetics Made Easy 2: Cancers. Center for Arab Genomic Studies.
http://www.cags.org.ae/gme2cancersenleukemia.pdfAccessed.
Feb 22–2015
|
|
7
|
El-Shemy HA, Aboul-Enein AM, Aboul-Enein
MI, Issa SI and Fujita K: The effect of willow leaf extracts on
human leukemic cells in vitro. J Biochem Mol Biol. 36:387–389.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Shemy HA, Aboul-Enein AM, Aboul-Enein
KM and Fujita K: Willow leaves' extracts contain anti-tumor agents
effective against three cell types. PLoS One. 2:e1782007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elgendi HM, Mekawy MA, Abdel Wahab SE,
Tawfik LM, Ismail EA and Adly AA: AC133 expression in egyptian
children with acute leukemia: impact on treatment response and
disease outcome. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 32:286–293. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
No authors listed: All natural. Nat Chem
Biol. 3:3512007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krause J and Tobin G: Discovery,
Development, and Regulation of Natural Products. Using Old
Solutions to New Problems - Natural Drug Discovery in the 21st
Century. Marianna Kulka: InTech. 424(Rijeka, Croatia). 2013.
|
|
12
|
Schwartsmann G: Marine organisms and other
novel natural sources of new cancer drugs. Ann Oncol. 11(Suppl 3):
235–243. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McChesney JD, Venkataraman SK and Henri
JT: Plant natural products: back to the future or into extinction?
Phytochemistry. 68:2015–2022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rout SP, Choudary KA, Kar DM, Das L and
Jain A: Plants in traditional medicinal system - Future source of
new drugs. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 1:1–23. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Beutler JA: Natural Products as a
Foundation for Drug Discovery. Curr Protoc Pharmacol.
46:9.11.1–9.11.21. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Cragg GM and Newman DJ: Plants as a source
of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol. 100:72–79. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raskin I, Ribnicky DM, Komarnytsky S, Ilic
N, Poulev A, Borisjuk N, Brinker A, Moreno DA, Ripoll C, Yakoby N,
et al: Plants and human health in the twenty-first century. Trends
Biotechnol. 20:522–531. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kishimoto T, Kikutani H, Von dem Borne AEG
Jr, Goyert SM, Mason DY, Miyasaka M, Moretta L, Okumura K, Shaw S,
Springer TA, Sugamura K and Zola H: Leukocyte Typing VI. White Cell
Differentiation Antigens (New York, NY). Garland Publishing, Inc.
1997.
|
|
19
|
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin
G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J, Lister TA and Bloomfield CD:
World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of
the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: Report of the Clinical
Advisory Committee meeting-Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J
Clin Oncol. 17:3835–3849. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Borowitz MJ and Chan JK: Precursor
lymphoid neoplasms. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic
and lymphoid tissues. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al:
(4th). (Lyon). International Agency for Research on Cancer.
167–178. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Xu F, Yin CX, Wang CL, et al:
Immunophenotypes and Immune Markers Associated with Acute
Promyelocytic Leukemia Prognosis. Dis Markers. 2014:4219062014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robbins SL, Kumar V and Cotran RS: Robbins
and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
2010.
|
|
23
|
Fielding AK: Current treatment of
Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program). 2011:231–237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen B, Wang YY, Shen Y, Zhang WN, He HY,
Zhu YM, Chen HM, Gu CH, Fan X, Chen JM, et al: Newly diagnosed
acute lymphoblastic leukemia in China (I): abnormal genetic
patterns in 1346 childhood and adult cases and their comparison
with the reports from Western countries. Leukemia. 26:1608–1616.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mi JQ, Wang X, Yao Y, Lu HJ, Jiang XX,
Zhou JF, Wang JH, Jiao B, Shen SH, Tang JY, et al: Newly diagnosed
acute lymphoblastic leukemia in China (II): prognosis related to
genetic abnormalities in a series of 1091 cases. Leukemia.
26:1507–1516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brüggemann M, Droese J, Bolz I, Lüth P,
Pott C, von Neuhoff N, Scheuering U and Kneba M: Improved
assessment of minimal residual disease in B cell malignancies using
fluorogenic consensus probes for real-time quantitative PCR.
Leukemia. 14:1419–1425. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kerst G, Kreyenberg H, Roth C, Well C,
Dietz K, Coustan-Smith E, Campana D, Koscielniak E, Niemeyer C,
Schlegel PG, et al: Concurrent detection of minimal residual
disease (MRD) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by flow
cytometry and real-time PCR. Br J Haematol. 128:774–782. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Salem DA and Abd El-Aziz SM:
Flowcytometric immunophenotypic profile of acute leukemia: mansoura
experience. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 28:89–96. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Denys B, van der Sluijs-Gelling AJ,
Homburg C, van der Schoot CE, de Haas V, Philippé J, Pieters R, van
Dongen JJ and van der Velden VH: Improved flow cytometric detection
of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Leukemia. 27:635–641. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
El-Shemy HA, Aboul-Soud MA, Nassr-Allah
AA, Aboul-Enein KM, Kabash A and Yagi A: Antitumor properties and
modulation of antioxidant enzymes' activity by Aloe vera
leaf active principles isolated via supercritical carbon dioxide
extraction. Curr Med Chem. 17:129–138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han SS, Keum YS, Seo HJ and Surh YJ:
Curcumin suppresses activation of NF-kappaB and AP-1 induced by
phorbol ester in cultured human promyelocytic leukemia cells. J
Biochem Mol Biol. 35:337–342. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shanab SM, Shalaby EA, Lightfoot DA and
El-Shemy HA: Allelopathic effects of water hyacinth (Eichhornia
crassipes). PLoS One. 5:e132002010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ieven M, Van den Berghe DA, Mertens F,
Vlietinck A and Lammens E: Screening of higher plants for
biological activities. I. Antimicrobial activity. Planta Med.
36:311–321. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV,
Thomas CF, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Farnsworth NR, Kinghorn AD, Mehta
RG, et al: Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a
natural product derived from grapes. Science. 275:218–220. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lawson K: Botanical and Plant-derived
Drugs: Global Markets. BCC Research. 2013.
|
|
36
|
Shaked Y, Emmenegger U, Francia G, Chen L,
Lee CR, Man S, Paraghamian A, Ben-David Y and Kerbel RS: Low-dose
metronomic combined with intermittent bolus-dose cyclophosphamide
is an effective long-term chemotherapy treatment strategy. Cancer
Res. 65:7045–7051. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Onodera T, Poe JC, Tedder TF and Tsubata
T: CD22 regulates time course of both B cell division and antibody
response. J Immunol. 180:907–913. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Forsyth RG, De Boeck G, Baelde JJ,
Taminiau AH, Uyttendaele D, Roels H, Praet MM and Hogendoorn PC:
CD33+ CD14- phenotype is characteristic of multinuclear
osteoclast-like cells in giant cell tumor of bone. J Bone Miner
Res. 24:70–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gorin NC, Labopin M, Reiffers J, Milpied
N, Blaise D, Witz F, de Witte T, Meloni G, Attal M, Bernal T, et
al: Acute Leukemia Working Party, European Cooperative Group for
Blood and Marrow Transplantation: Higher incidence of relapse in
patients with acute myelocytic leukemia infused with higher doses
of CD34+ cells from leukapheresis products autografted during the
first remission. Blood. 116:3157–3162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kamel AM, Assem MM, Jaffe ES, Magrath I,
Enein Aboul MI and Hindawy DS: Immunological phenotypic pattern of
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in Egypt. Leuk Res. 13:519–525. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McDermott U and Settleman J: Personalized
cancer therapy with selective kinase inhibitors: an emerging
paradigm in medical oncology. J Clin Oncol. 27:5650–5659. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tantawy AA, El-Bostany EA, Adly AA, El
Abou Asrar M, El-Ghouroury EA and Abdulghaffar EE: Methylene
tetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism in Egyptian children
with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis.
21:28–34. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Herzog CM, Dey S, Hablas A, et al:
Geographic distribution of hematopoietic cancers in the Nile delta
of Egypt. Ann Oncol. 23:2748–2755. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|