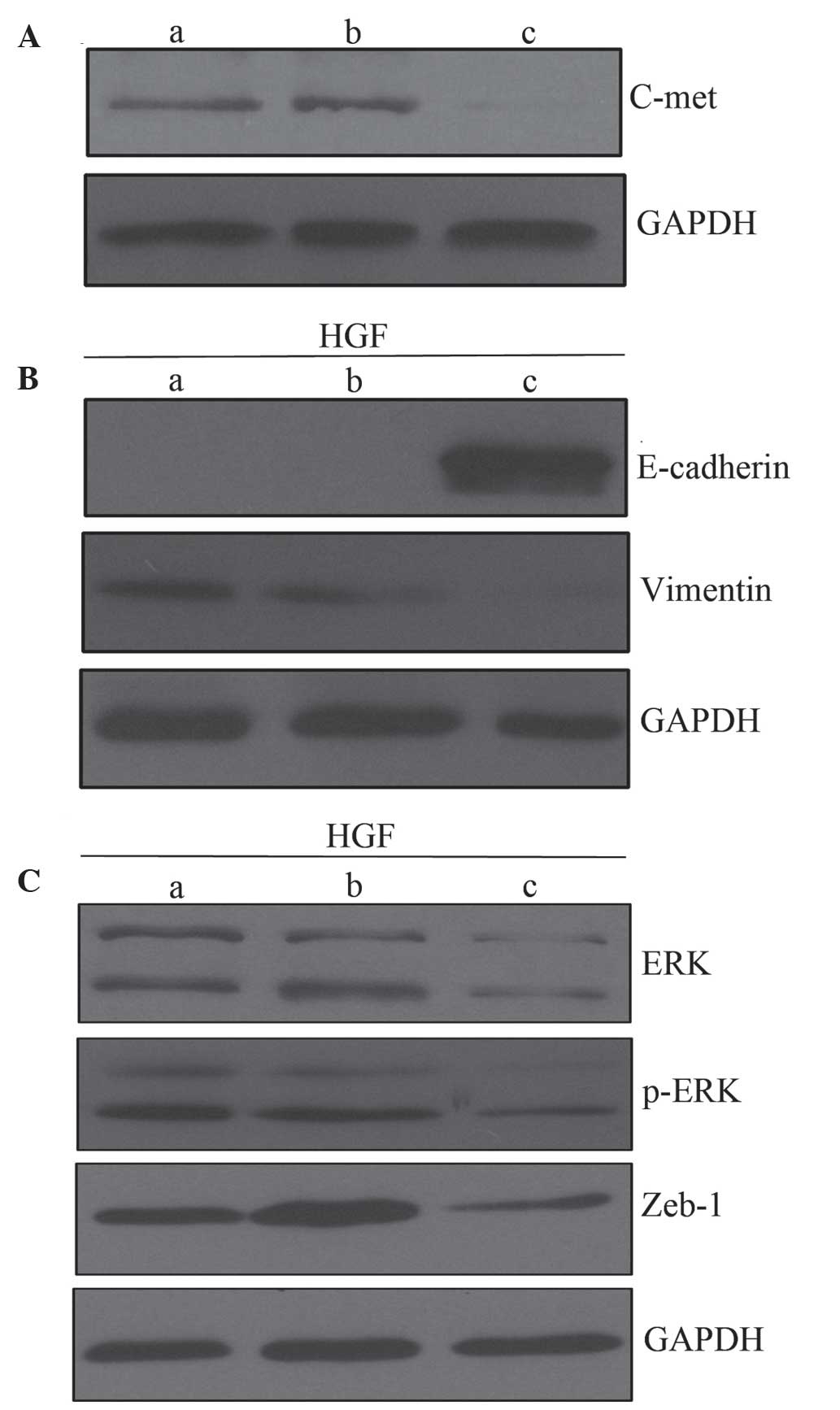
|
1
|
Jin JK, Dayyani F and Gallick GE: Steps in
prostate cancer progression that lead to bone metastasis. Int J
Cancer. 128:2545–2561. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jacobs SC: Spread of prostatic cancer to
bone. Urology. 21:337–344. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shah RB, Mehra R, Chinnaiyan AM, Shen R,
Ghosh D, Zhou M, Macvicar GR, Varambally S, Harwood J, Bismar TA,
et al: Androgen-independent prostate cancer is a heterogeneous
group of diseases: Lessons from a rapid autopsy program. Cancer
Res. 64:9209–9216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K,
Bronner-Fraser M and Nieto MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions:
The importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J
Clin Invest. 119:1438–1449. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scheel C and Weinberg RA: Cancer stem
cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Concepts and molecular
links. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:396–403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morel AP, Lievre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G,
Ansieau S and Puisieux A: Generation of breast cancer stem cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 3:e28882008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matsuoka J, Yashiro M, Doi Y, Fuyuhiro Y,
Kato Y, Shinto O, Noda S, Kashiwagi S, Aomatsu N, Hirakawa T, et
al: Hypoxia stimulates the EMT of gastric cancer cells through
autocrine TGFβ signaling. PLoS One. 8:e623102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo Y, He DL, Ning L, Shen SL, Li L, Li X,
Zhau HE and Chung LW: Over-expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha increases the invasive potency of LNCaP cells in
vitro. BJU Int. 98:1315–1319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lamouille S, Subramanyam D, Blelloch R and
Derynck R: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal and
mesenchymal-epithelial transitions by microRNAs. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 25:200–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chung LW, Huang WC, Sung SY, Wu D,
Odero-Marah V, Nomura T, Shigemura K, Miyagi T, Seo S, Shi C, et
al: Stromal-epithelial interaction in prostate cancer progression.
Clin Genitourin Cancer. 5:162–170. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hashem M and Essam T: Hepatocyte growth
factor as a tumor marker in the serum of patients with prostate
cancer. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 17:114–120. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yasuda K, Nagakawa O, Akashi T, Fujiuchi
Y, Koizumi K, Komiya A, Saiki I and Fuse H: Serum active hepatocyte
growth factor (AHGF) in benign prostatic disease and prostate
cancer. Prostate. 69:346–351. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo Y, He DL and Ning L: Expression of
‘epithelial-mesenchymal transition’ associated proteins in prostate
cancer cell lines with different metastatic potentials and its
significance. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 12:696–700. 2006.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu X, Zerbini LF, Otu HH, Bhasin M, Yang
Q, Joseph MG, Grall F, Onatunde T, Correa RG and Libermann TA:
Reduced PDEF expression increases invasion and expression of
mesenchymal genes in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:4219–4226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Veveris-Lowe TL, Lawrence MG, Collard RL,
Bui L, Herington AC, Nicol DL and Clements JA: Kallikrein 4 (hK4)
and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) are associated with the loss of
E-cadherin and an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like
effect in prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:631–643.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Whitbread AK, Veveris-Lowe TL, Lawrence
MG, Nicol DL and Clements JA: The role of kallikrein-related
peptidases in prostate cancer: Potential involvement in an
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biol Chem. 387:707–714. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Yue D, Li K, Liu YL, Ren CS and
Wang P: The role of TRPC6 in HGF-induced cell proliferation of
human prostate cancer DU145 and PC3 cells. Asian J Androl.
12:841–852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Martin TA, Mason MD and Jiang WG:
Hepatocyte growth factor signaling in cancer metastasis. Curr
Signal Transduct Ther. 6:180–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Naughton M, Picus J, Zhu X, Catalona WJ,
Vollmer RT and Humphrey PA: Scatter factor-hepatocyte growth factor
elevation in the serum of patients with prostate cancer. J Urol.
165:1325–1328. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Humphrey PA, Halabi S, Picus J, Sanford B,
Vogelzang NJ, Small EJ and Kantoff PW: Prognostic significance of
plasma scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor levels in patients
with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer: Results from
cancer and leukemia group B 150005/9480. Clin Genitourin Cancer.
4:269–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duhon D, Bigelow RL, Coleman DT, Steffan
JJ, Yu C, Langston W, Kevil CG and Cardelli JA: The polyphenol
epigallocatechin-3-gallate affects lipid rafts to block activation
of the c-Met receptor in prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
49:739–749. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Previdi S, Maroni P, Matteucci E, Broggini
M, Bendinelli P and Desiderio MA: Interaction between human-breast
cancer metastasis and bone microenvironment through activated
hepatocyte growth factor/Met and b-catenin/Wnt pathways. Eur J
Cancer. 46:1679–1691. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ogunwobi OO and Liu C: Hepatocyte growth
factor upregulation promotes carcinogenesis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellularcarcinoma via
Akt and COX-2 pathways. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:721–731. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fram ST, Wells CM and Jones GE:
HGF-induced DU145 cell scatter assay. Methods Mol Biol. 769:31–40.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S, Sahakyan A,
Karagiannides I, Bakirtzi K, Jazirehi A and Bonavida B: Mechanisms
of nitric oxide-mediated inhibition of EMT in cancer: Inhibition of
the metastasis-inducer Snail and induction of the
metastasis-suppressor RKIP. Cell Cycle. 9:4931–4940. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yates CC, Shepard CR, Stolz DB and Wells
A: Co-culturing human prostate carcinoma cells with hepatocytes
leads to increased expression of E-cadherin. Br J Cancer.
96:1246–1252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locasioa A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shimada S, Mimata A, Sekine M, Mogushi K,
Akiyama Y, Fukamachi H, Jonkers J, Tanaka H, Eishi Y and Yuasa Y:
Synergistic tumour suppressor activity of E-cadherin and p53 in a
conditional mouse model for metastatic diffuse-type gastric cancer.
Gut. 61:344–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Odero-Marah VA, Wang R, Chu G, Zayzafoon
M, Xu J, Shi C, Marshall FF, Zhau HE and Chung LW: Receptor
activator of NF-kappaB Ligand (RANKL) expression is associated with
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer
cells. Cell Rese. 18:858–870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chung LW, Baseman A, Assikis V and Zhau
HE: Molecular insights into prostate cancer progression: The
missing link of tumor microenvironment. J Urol. 173:10–20. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jiang WG, Davies G, Martin TA, Parr C,
Watkins G, Mason MD, Mokbel K and Mansel RE: Targeting matrilysin
and its impact on tumor growth in vivo: The potential
implications in breast cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6012–6019. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
You WK and McDonald DM: The hepatocyte
growth factor/c-Met signaling pathway as a therapeutic target to
inhibit angiogenesis. BMB Rep. 41:833–839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boccaccio C and Comoglio PM: Invasive
growth: A MET-driven genetic programme for cancer and stem cells.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:637–645. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Migliore C and Giordano S: Molecular
cancer therapy: Can our expectation be MET? Eur J Cancer.
44:641–651. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ogunwobi OO and Liu C: Hepatocyte growth
factor upregulation promotes carcinogenesis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via
Akt and COX-2 pathways. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:721–731. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nieto MA and Cano A: The epithelial -
mesenchymal transition under control: Global programs to regulate
epithelial plasticity. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:361–368. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kwok WK, Ling MT, Lee TW, Lau TC, Zhou C,
Zhang X, Chua CW, Chan KW, Chan FL, Glackin C, et al: Upregulation
of TWIST in prostate cancer and its implication as a therapeutic
target. Cancer Res. 65:5153–5162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Grotegut S, von Schweinitz D, Christofori
G and Lehembre F: Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering
through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J.
25:3534–3545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Peña C, García JM, García V, Silva J,
Domínguez G, Rodríguez R, Maximiano C, de Herreros García A, Muñoz
A and Bonilla F: The expression levels of the transcriptional
regulators p300 and CtBP modulate the correlations between SNAIL,
ZEB1, E-cadherin and vitamin D receptor in human colon carcinomas.
Int J Cancer. 119:2098–2104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hlubek F, Berx
G, Eger A, Merkel S, Jung A, Kirchner T and Brabletz T: A
transient, EMT-linked loss of basement membranes indicates
metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 131:830–840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|