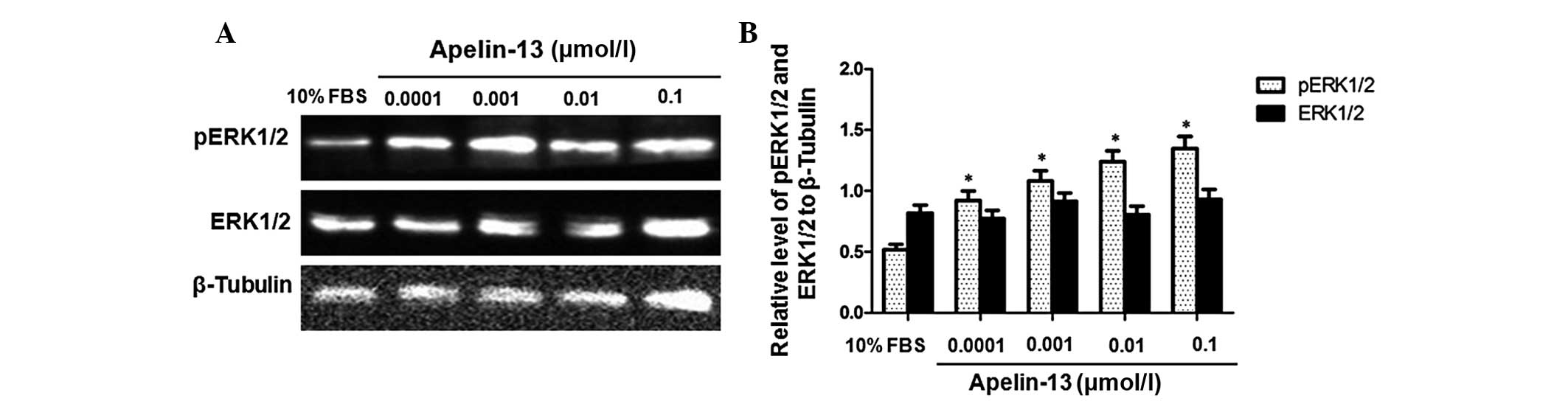
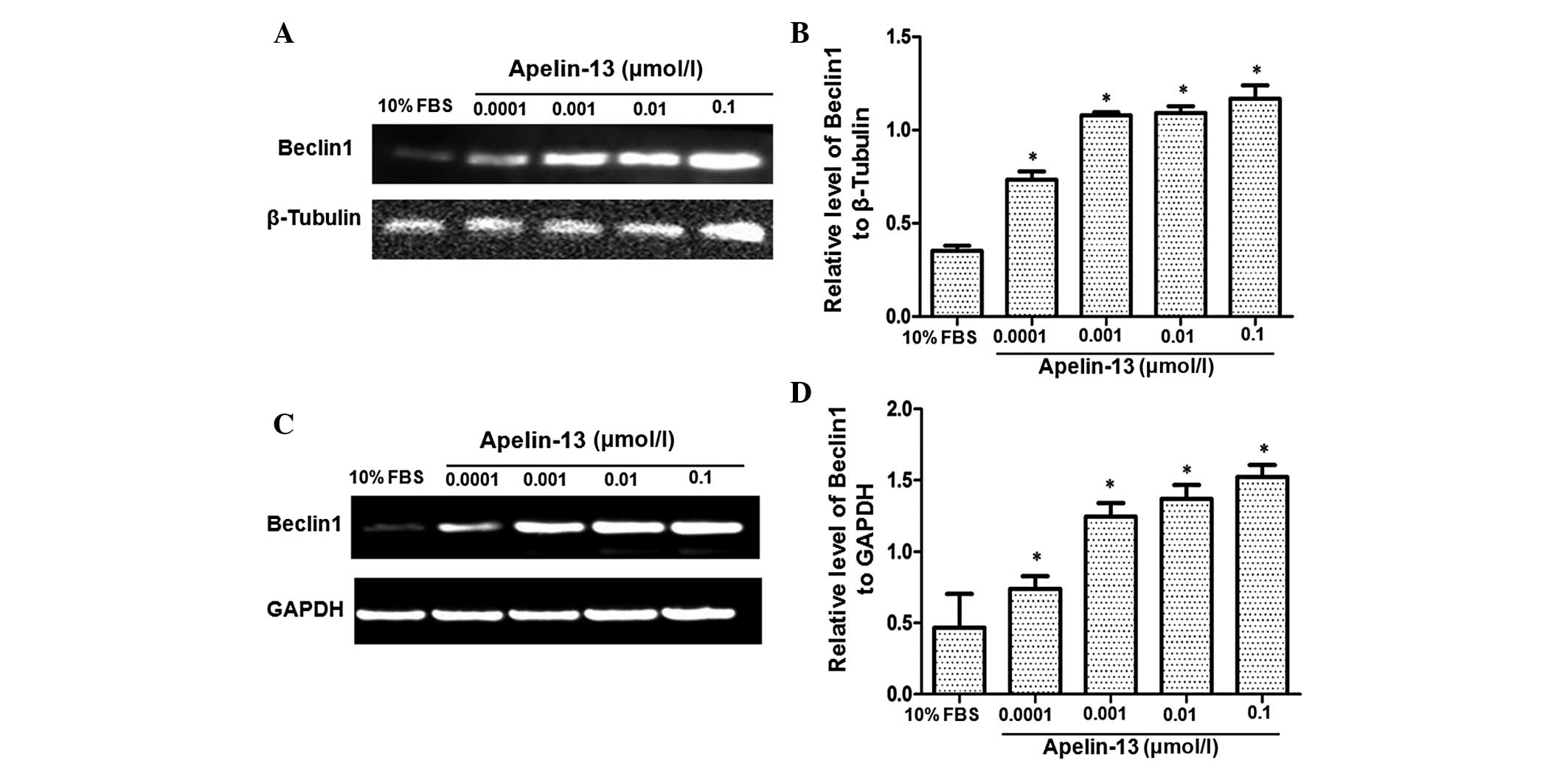
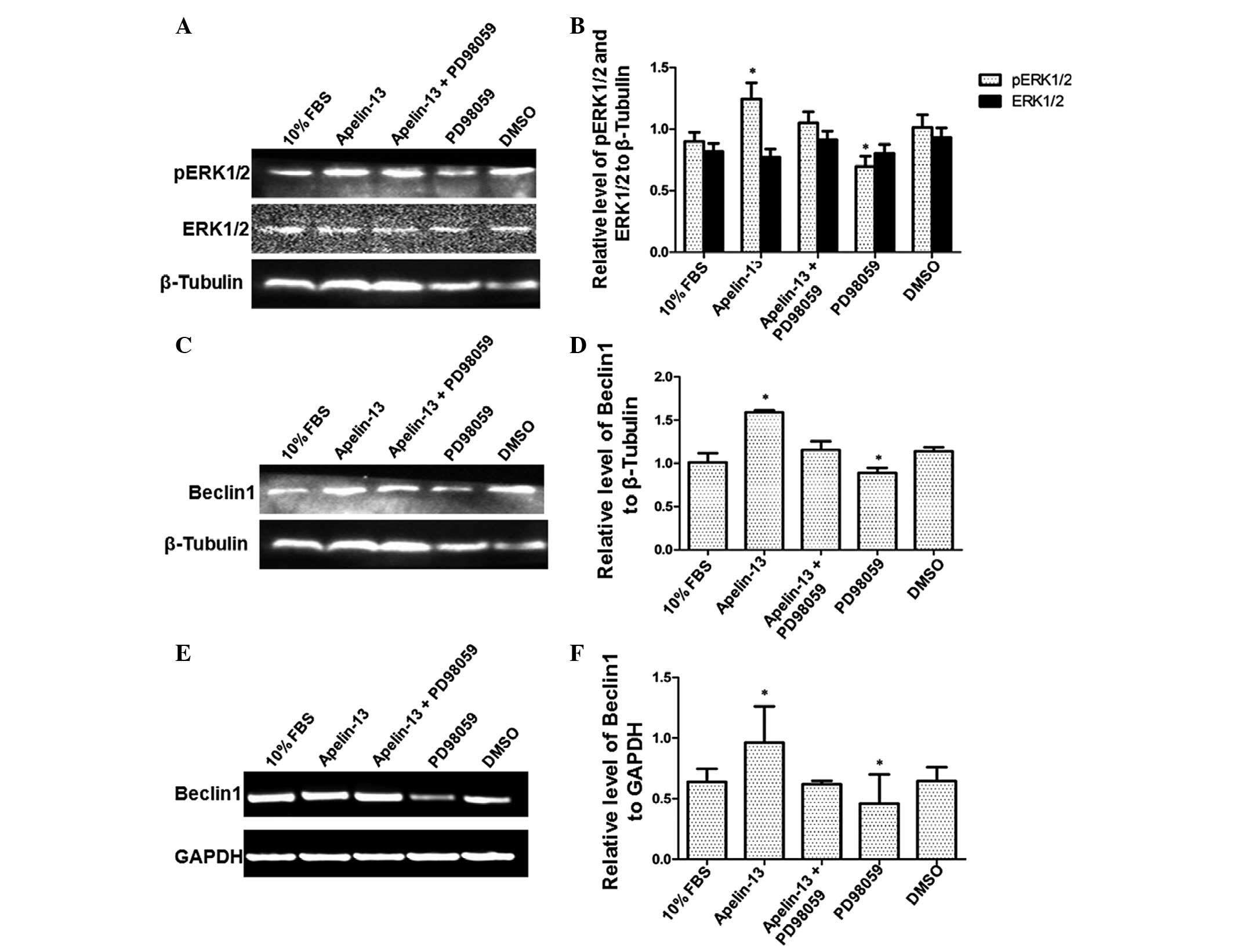
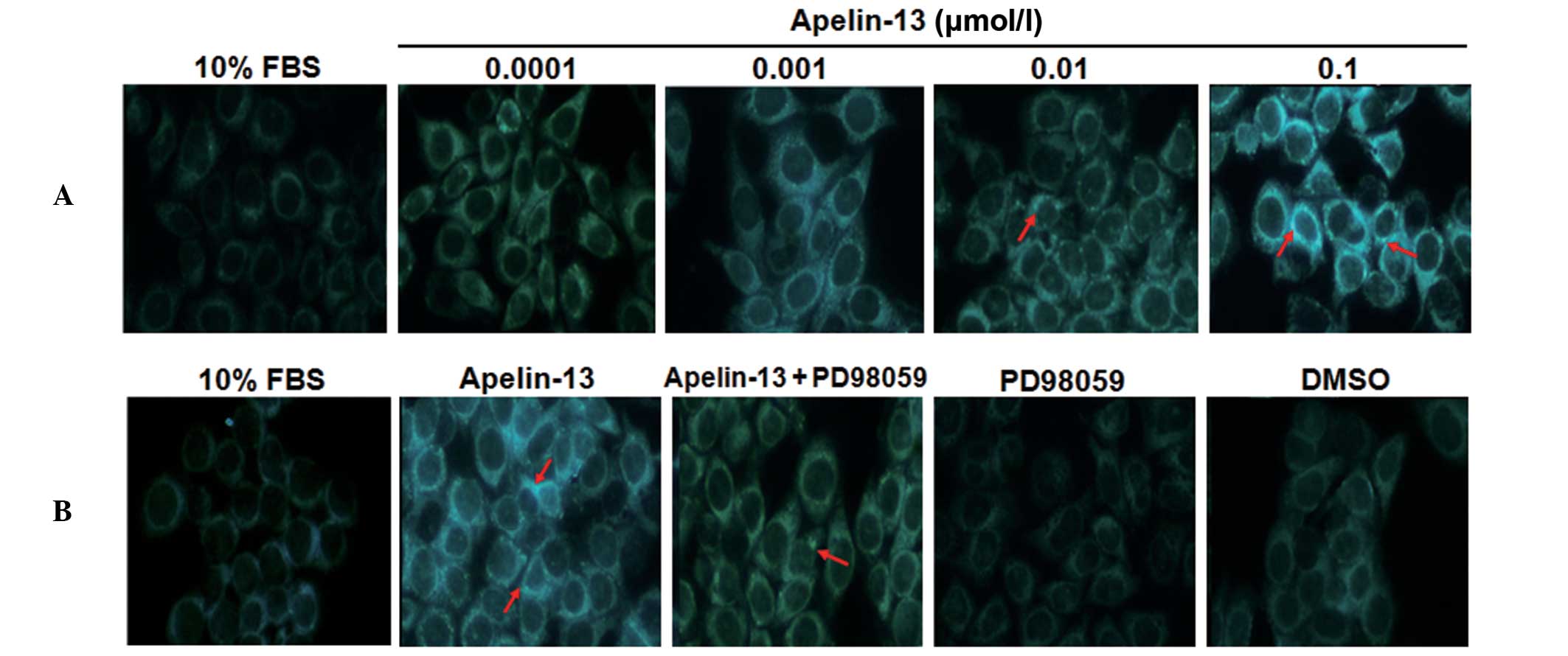
|
1
|
Meijer AJ and Codogno P: Regulation and
role of autophagy in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2445–2462. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K,
Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H and Levine B: Induction of autophagy and
inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 402:672–676. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shoji-Kawata S, Sumpter R, Leveno M,
Campbell GR, Zou Z, Kinch L, Wilkins AD, Sun Q, Pallauf K, MacDuff
D, et al: Identification of a candidate therapeutic
autophagy-inducing peptide. Nature. 494:201–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Furuya N, Yu J, Byfield M, Pattingre S and
Levine B: The evolutionarily conserved domain of Beclin 1 is
required for Vps34 binding, autophagy and tumor suppressor
function. Autophagy. 1:46–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pattingre S, Bauvy C and Codogno P: Amino
acids interfere with the ERK1/2-dependent control of macroautophagy
by controlling the activation of Raf-1 in human colon cancer HT-29
cells. J Biol Chem. 278:16667–16674. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang YC, Hung WC, Chen WT, Yu HS and Chai
CY: Sodium arsenite-induced DAPK promoterhypermethylation and
autophagy via ERK1/2 phosphorylation in humanuroepithelial cells.
Chem Biol Interact. 181:254–262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R,
Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, et
al: Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide
ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
251:471–476. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li F, Li L, Qin X, Pan W, Feng F, Chen F,
Zhu B, Liao D, Tanowitz H, Albanese C, et al: Apelin-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation: The regulation of cyclin
D1. Front Biosci. 13:3786–3792. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Biederbick A, Kern HF and Elsässer HP:
Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for
autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol. 66:3–14. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
D'Alessandro LA, Meyer R and Klingmüller
U: Hepatocellular carcinoma A systems biology perspective. Front
Physiol. 4:282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He J, Gu D, Wu X, Reynolds K, Duan X, Yao
C, Wang J, Chen CS, Chen J, Wildman RP, et al: Major causes of
death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 353:1124–1134.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klionsky DJ: The molecular machinery of
autophagy: U nanswered questions. J Cell Sci. 118:7–18. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Massey AC, Zhang C and Cuervo AM:
Chaperone-mediated autophagy in aging and disease. Curr Top Dev
Biol. 73:205–235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang ZH, Xu L, Duan ZL, Zeng LQ, Yan NH
and Peng ZL: Beclin 1 mediated macroautophagy involves regulation
of caspase-9 expression in cervical cancer HeLa cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 107:107–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duan ZL, Peng ZL and Wang ZH: Expression
and involved sign alransduction pathway of autophagy gene Beclin 1
in epithelial ovarian cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
38:239–242. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miracco C, Cosci E, Oliveri G, Luzi P,
Pacenti L, Monciatti I, Mannucci S, De Nisi MC, Toscano M,
Malagnino V, et al: Protein and mRNA expression of autophagy gene
Beclin 1 in human brain tumours. Int J Oncol. 30:429–436.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roesly HB, Khan MR, Chen HD, Hill KA,
Narendran N, Watts GS, Chen X and Dvorak K: The decreased
expression of Beclin-1 correlates with progression to esophageal
adenocarcinoma, The role of deoxycholic acid. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G864–G872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou WH, Tang F, Xu J, Wu X, Yang SB, Feng
ZY, Ding YG, Wan XB, Guan Z, Li HG, et al: Low expression of Beclin
1, associated with high Bcl-XL, predicts a malignant phenotype and
poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Autophagy. 8:389–400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: A
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Apel A, Zentgraf H, Büchler MW and Herr I:
Autophagy - a double-edged sword in oncology. Int J Cancer.
125:991–995. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee SJ, Kim HP, Jin Y, Choi AM and Ryter
SW: Beclin 1 deficiency is associated with increased
hypoxia-induced angiogenesis. Autophagy. 7:829–839. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|