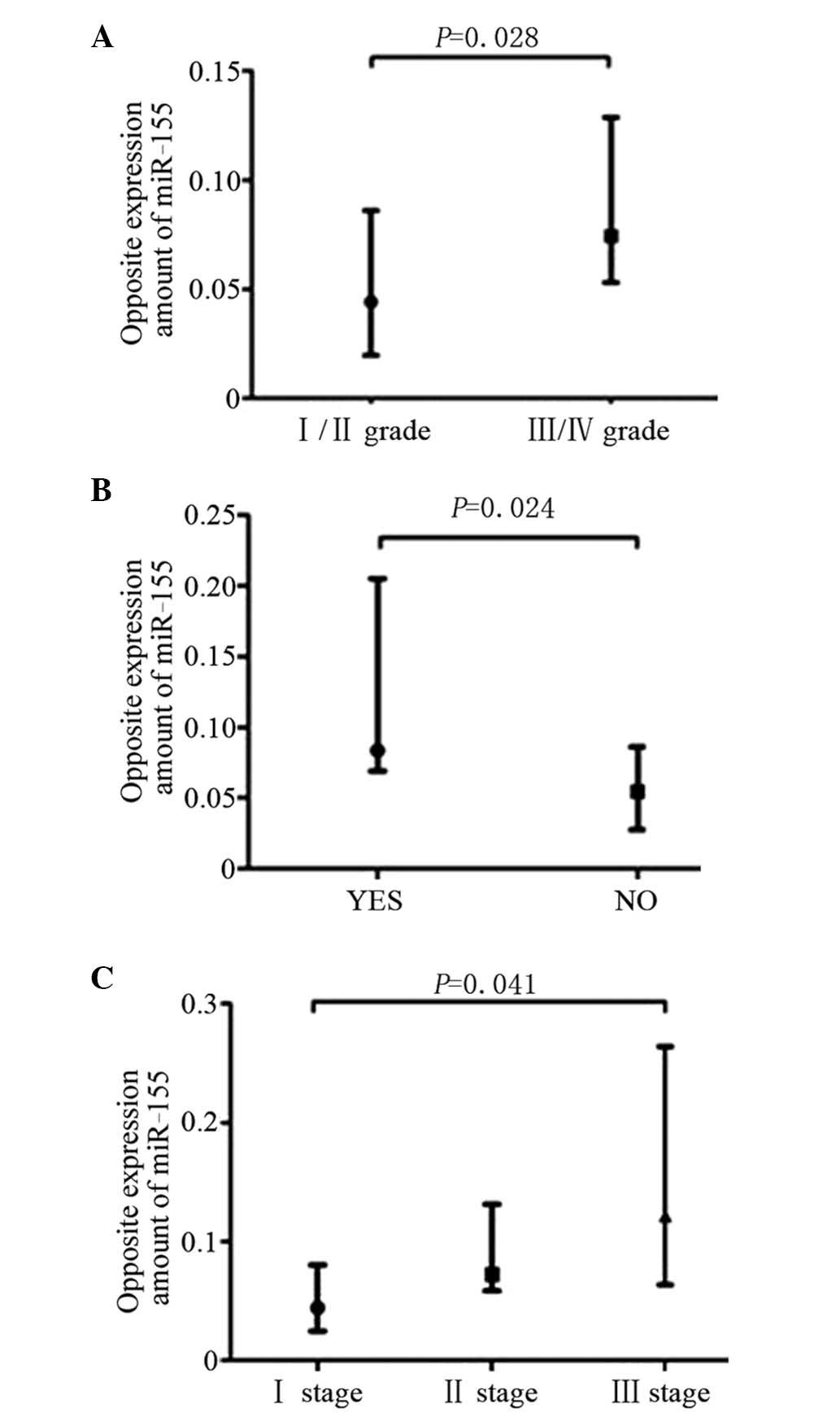
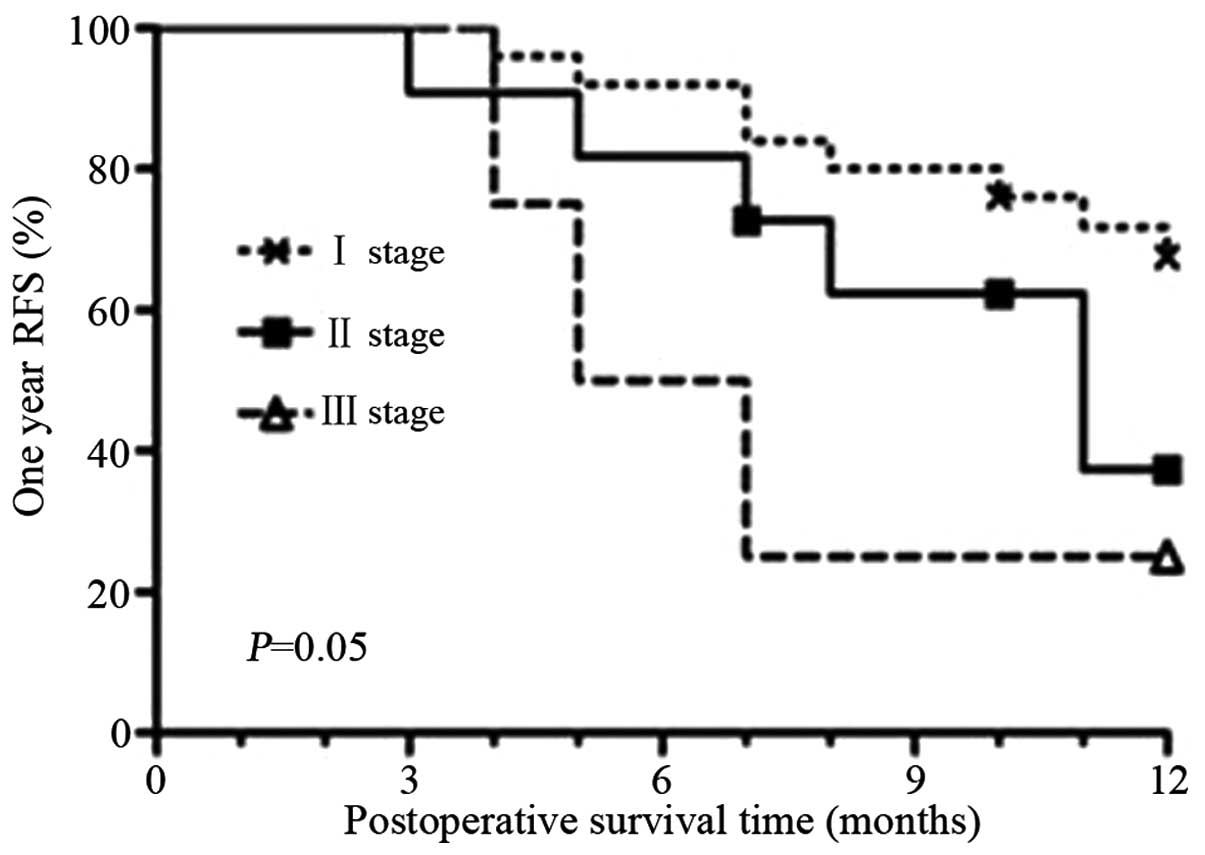
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al:
Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int
J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lencioni R, Chen XP, Dagher L and Venook
AP: Treatment of intermediate/advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in
the clinic, How can outcomes be improved? Oncologist. 15((Suppl
4)): S42–S52. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Suh SJ and Yim HJ: Current status of
molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J
Gastroenterol. 61:136–146. 2013.(In Korean). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qin S: Primary Liver Cancer Diagnosis and
Treatment Expert Panel of the Chinese Ministry of Health:
Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer
(2011 edition). Chin Clin Oncol. 1:102012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanyal AJ, Yoon SK and Lencioni R: The
etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma and consequences for
treatment. Oncologist. 15(Suppl 4): 14–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kumar M, Zhao X and Wang XW: Molecular
carcinogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma, One step closer to personalized medicine? Cell
Biosci. 1:52011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The
Celegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, et
al: Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr
Biol. 12:735–739. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Merhautova, J, Hezova R, Poprach A, et al:
miR-155 and miR-484 are associated with time to progression in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:9419802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ling N, Gu J, Lei Z, et al: microRNA-155
regulates cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FOXO3a in
glioma. Oncol Rep. 30:2111–2118. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang GJ, Xiao HX, Tian HP, et al:
Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of claudin-1
expression. Int J Mol Med. 31:1375–1380. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Faraoni I, Antonetti FR, Cardone J and
Bonmassar E: miR-155 gene, A typical multifunctional microRNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:497–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Macfarlane LA and Murphy PR: MicroRNA:
Biogenesis function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics. 11:537–561.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Papaconstantinou IG, Manta A, Gazouli M,
et al: Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer
and its prognostic significance. Pancreas. 42:67–71. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shibuya H, Iinuma H, Shimada R, Horiuchi A
and Watanabe T: Clinicopathological and prognostic value of
microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in colorectal cancer. Oncology.
79:313–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W
and Du X: Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early
detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:118–126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
World Medical: Association: Declaration of
Helsinki. Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human
Subjects. http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/b3/17c.pdfAccessed.
December 25–2011
|
|
20
|
Tsai HC and Baylin SB: Cancer epigenetics:
Linking basic biology to clinical medicine. Cell Res. 21:502–517.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu YH, Cai Q and Lan QY: Expression of
miR-155 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effect on the
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:1737–1741. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Song CG, Wu XY, Fu FM, et al: Correlation
of miR-155 on formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissues with
invasiveness and prognosis of breast cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 50:1011–1014. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han ZB, Chen HY, Fan JW, et al:
Up-regulation of microRNA-155 promotes cancer cell invasion and
predicts poor survival of hepatocellular carcinoma following liver
transplantation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:153–161. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Michieli P, Chedid M, Lin D, Pierce JH,
Mercer WE and Givol D: Induction of WAF1/CIP1 by a p53-independent
pathway. Cancer Res. 54:3391–3395. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie Q, Chen X, Lu F, et al: Aberrant
expression of microRNA 155 may accelerate cell proliferation by
targeting sex-determining region Y box 6 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer. 118:2431–2442. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yan XL, Jia YL, Chen L, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem cells promote
hepatocarcinoma progression: Role of the S100A4-miR155-SOCS1-MMP9
axis. Hepatology. 57:2274–2286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi J, Lai EC, Li N, et al: A new
classification for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor
thrombus. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 18:74–80. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, et al: Different
risk factors and prognosis for early and late intrahepatic
recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
89:500–507. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun J, Jian ZX, Ou YL, Hou BH and Qu JR:
Ensured the early recurrent time and model of liver cancer after
radical resection. Shi Yong Yi Xue Za Zhi. 10:1748–1750. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Cai XR, Huang CY, Zhou LY and Zhou HH:
Study on risk factors and therapeutic effect of different
recurrence period after resection of primary hepatocellular
carcinoma. Shi Yong Yi Xue Za Zhi. 5:560–563. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Braconi C, Henry JC, Kogure T, Schmittgen
T and Patel T: The role of microRNAs in human liver cancers. Semin
Oncol. 38:752–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shrivastava S, Steele R, Ray R and Ray RB:
MicroRNAs Role in hepatitis C virus pathogenesis. Genes Dis.
2:35–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang YH, Lin KH, Chen HC, et al:
Identification of postoperative prognostic microRNA predictors in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e371882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|