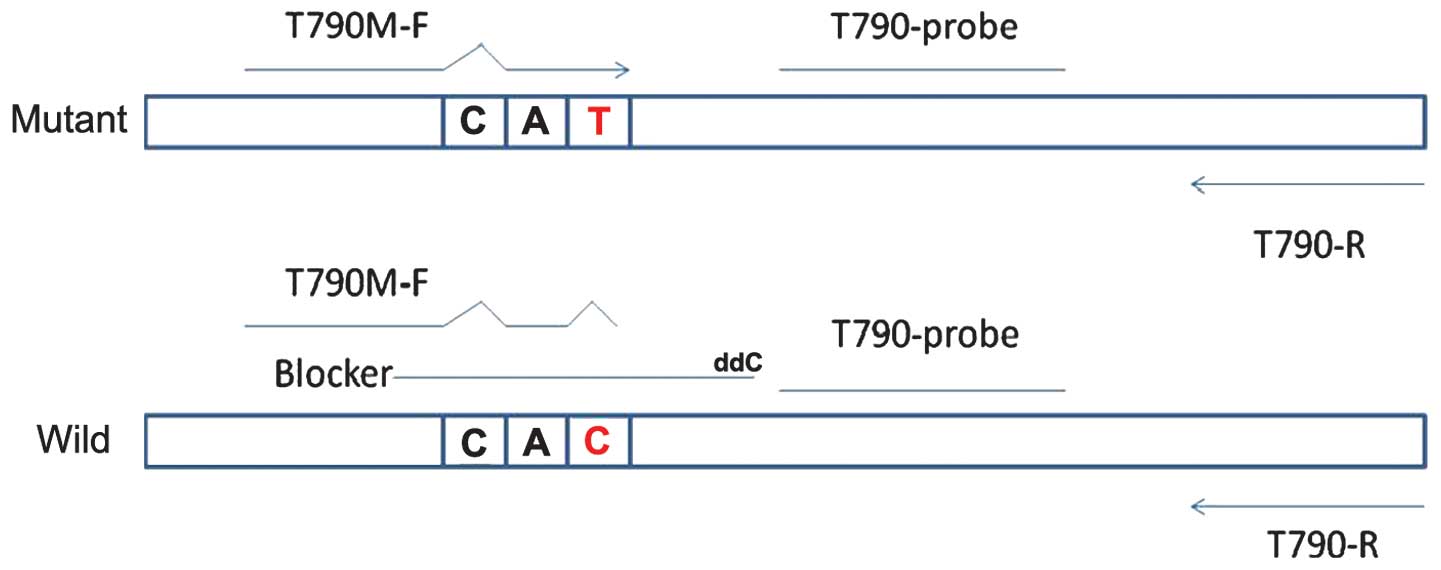
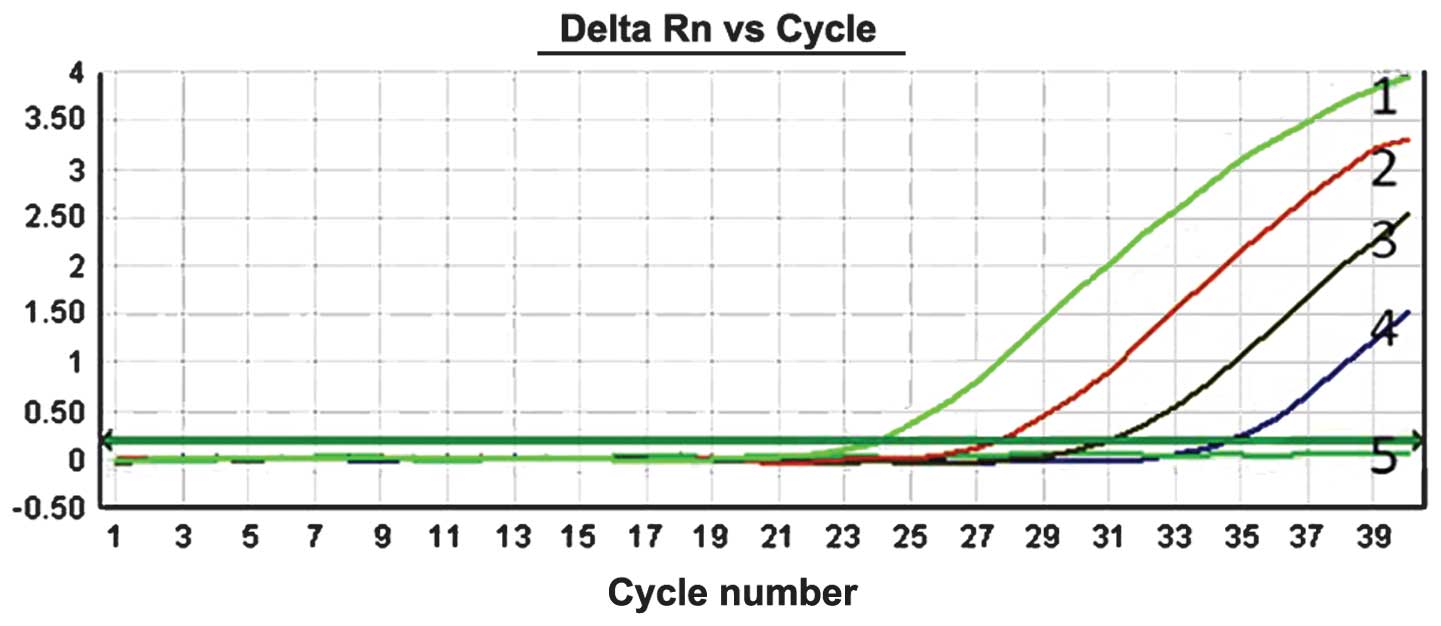
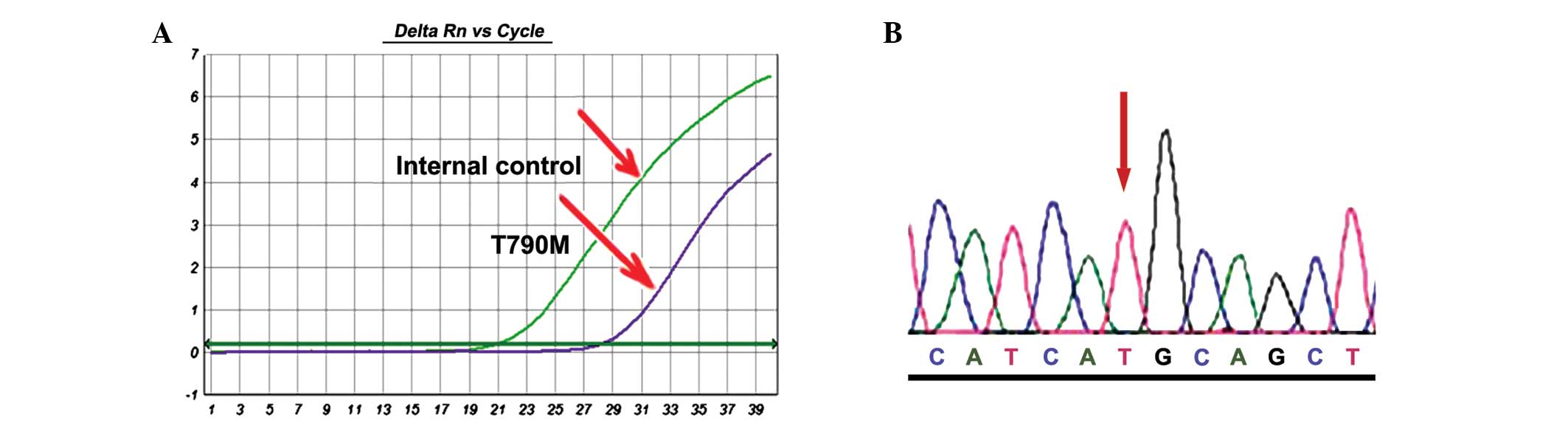
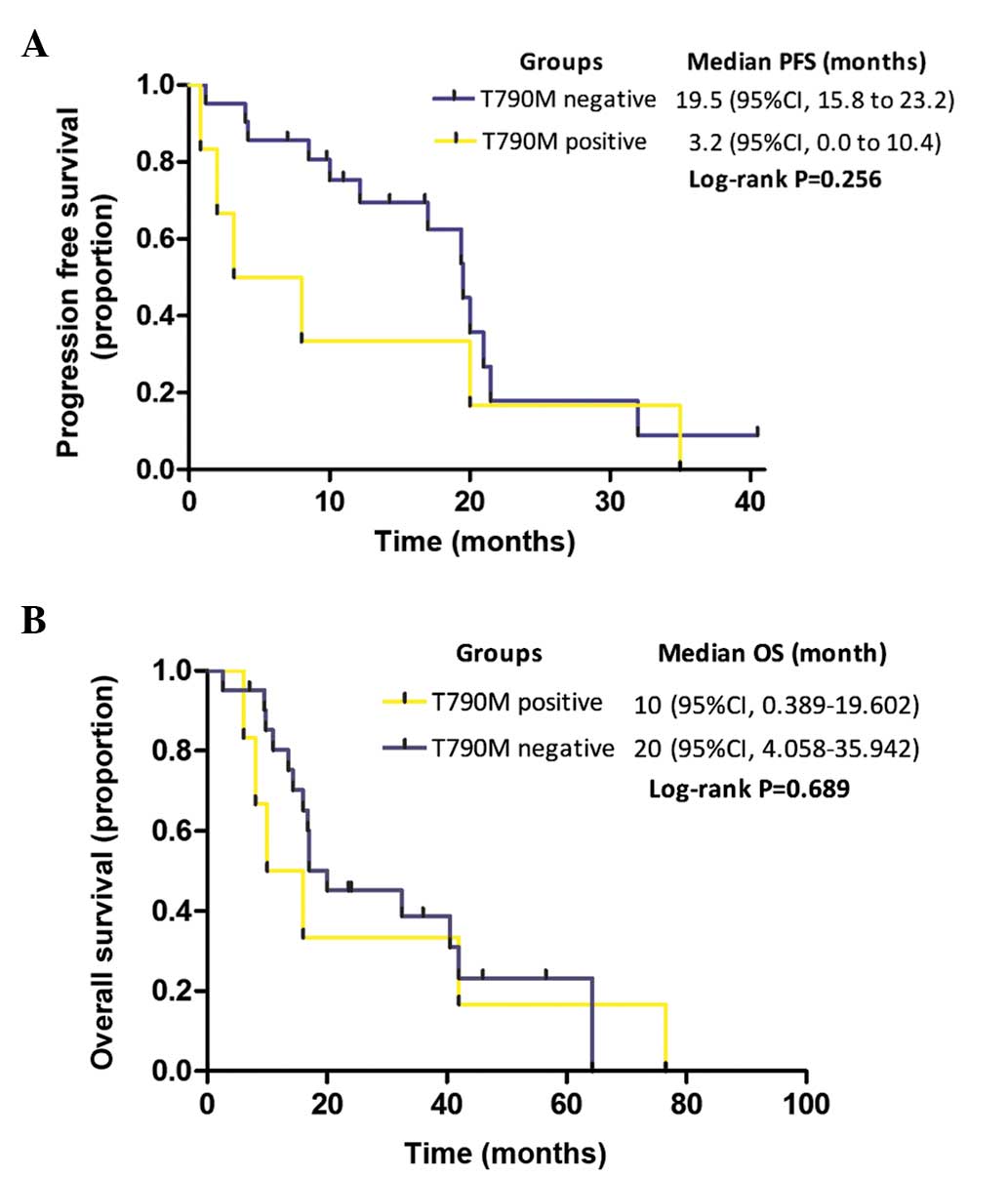
|
1
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger
S, Cosper AK, et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung
cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Su KY, Chen HY, Li KC, Kuo ML, Yang JC,
Chan WK, Ho BC, Chang GC, Shih JY, Yu SL and Yang PC: Pretreatment
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation predicts
shorter EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response duration in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30:433–440.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosell R, Molina MA, Costa C, Simonetti S,
Gimenez-Capitan A, Bertran-Alamillo J, Mayo C, Moran T, Mendez P,
Cardenal F, et al: Pretreatment EGFR T790M mutation and BRCA1 mRNA
expression in erlotinib-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
patients with EGFR mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1160–1168. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maheswaran S, Sequist LV, Nagrath S, Ulkus
L, Brannigan B, Collura CV, Inserra E, Diederichs S, Iafrate AJ,
Bell DW, et al: Detection of mutations in EGFR in circulating
lung-cancer cells. N Engl J Med. 359:366–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujita Y, Suda K, Kimura H, Matsumoto K,
Arao T, Nagai T, Saijo N, Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T and Nishio K:
Highly sensitive detection of EGFR T790M mutation using colony
hybridization predicts favorable prognosis of patients with lung
cancer harboring activating EGFR mutation. J Thorac Oncol.
7:1640–1644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Janne PA, Ramalingam SS, Yang JC, et al:
Clinical activity of the mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor AZD9291 in
patients (pts) with EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol. 32(Suppl 15): 508s Abstract
80092014.
|
|
7
|
Sequist LV, Soria J, Gadgeel SM, et al:
First-in-human evaluation of CO-1686, an irreversible, highly
selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor of mutations of EGFR
(activating and T790M). J Clin Oncol. 32(Suppl 15): 508s Abstract
80102014.
|
|
8
|
Kim D, Lee D, Kang J, et al: Clinical
activity and safety of HM61713, an EGFR-mutant selective inhibitor,
in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (pts) with
EGFR mutations who had received EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
(TKIs). J Clin Oncol. 32(Suppl 15): 508s Abstract 80112014.
|
|
9
|
He C, Zheng L, Xu Y, Liu M, Li Y and Xu J:
Highly sensitive and noninvasive detection of epidermal growth
factor receptor T790M mutation in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Chim Acta. 425:119–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Inukai M, Toyooka S, Ito S, Asano H,
Ichihara S, Soh J, Suehisa H, Ouchida M, Aoe K, Aoe M, et al:
Presence of epidermal growth factor receptor gene T790M mutations
as a minor clone in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
66:7854–7858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen HJ, Mok TS, Chen ZH, Guo AL, Zhang
XC, Su J and Wu YL: Clinicopathologic and molecular features of
epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation and c-MET
amplification in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant Chinese
non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 15:651–658. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arcila ME, Oxnard GR, Nafa K, Riely GJ,
Solomon SB, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Pao W, Miller VA and Ladanyi M:
Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR
inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a
locked nucleic acid-based assay. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1169–1180.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miyazawa H, Tanaka T, Nagai Y, Matsuoka M,
Huqun Sutani A, Udagawa K, Zhang J, Hirama T, Murayama Y, et al:
Peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid polymerase chain reaction
clamp-based detection test for gefitinib-refractory T790M epidermal
growth factor receptor mutation. Cancer Sci. 99:595–600. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oh JE, An CH, Yoo NJ and Lee SH: Detection
of low-level EGFR T790M mutation in lung cancer tissues. APMIS.
119:403–411. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guha M, Castellanos-Rizaldos E and
Makrigiorgos GM: Dissect method using PNA-LNA clamp improves
detection of EGFR T790m mutation. PLoS One. 8:e677822013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuang Y, Rogers A, Yeap BY, Wang L,
Makrigiorgos M, Vetrand K, Thiede S, Distel RJ and Jänne PA:
Noninvasive detection of EGFR T790M in gefitinib or erlotinib
resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:2630–2636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li J, Wang L, Jänne PA and Makrigiorgos
GM: Coamplification at lower denaturation temperature-PCR increases
mutation-detection selectivity of TaqMan-based real time PCR. Clin
Chem. 55:748–756. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oh YH, Kim Y, Kim YP, Seo SW, Mitsudomi T,
Ahn MJ, Park K and Kim HS: Rapid detection of the epidermal growth
factor receptor mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer for analysis
of acquired resistance using molecular beacons. J Mol Diagn.
12:644–652. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taniguchi K, Uchida J, Nishino K, Kumagai
T, Okuyama T, Okami J, Higashiyama M, Kodama K, Imamura F and Kato
K: Quantitative detection of EGFR mutations in circulating tumor
DNA derived form lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res.
17:7808–7815. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Board RE, Thelwell NJ, Ravetto PF, Little
S, Ranson M, Dive C, Hughes A and Whitcombe D: Multiplexed assays
for detection of mutations in PIK3CA. Clin Chem. 54:757–760. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L:
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions: The
IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sequist LV, Martins RG, Spigel D, Grunberg
SM, Spira A, Jänne PA, Joshi VA, McCollum D, Evans TL, Muzikansky
A, et al: First-line gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small
cell lung cancer harboring somatic EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol.
26:2442–2449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim HJ, Oh SY, Kim WS, Kim SJ, Yoo GH, Kim
WD and Lee KY: Clinical investigation of EGFR mutation detection by
pyrosequencing in lung cancer patients. Oncol Lett. 5:271–276.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Newton CR, Graham A, Heptinstall LE,
Powell SJ, Summers C, Kalsheker N, Smith JC and Markham AF:
Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory
mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res. 17:2503–2516. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, Riely GJ,
Chmielecki J, Kris MG, Pao W, Ladanyi M and Miller VA: Acquired
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung
cancer: Distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring
the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1616–1622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bai H, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhuo M, Zhou Q,
Duan J, Yang L, Wu M, An T, Zhao J and Wang J: Detection and
clinical significance of intratumoral EGFR mutational heterogeneity
in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e541702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim HR, Cho BC, Shim HS, Lim SM, Kim SK,
Chang J, Kim DJ and Kim JH: Prediction for response duration to
epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR
mutated never smoker lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 83:374–782.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hata A, Katakami N, Yoshioka H, Takeshita
J, Tanaka K, Nanjo S, Fujita S, Kaji R, Imai Y, Monden K, et al:
Rebiopsy of non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired
resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase
inhibitor: Comparison between T790M mutation-positive and
mutation-negative populations. Cancer. 119:4325–4332. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee Y, Lee GK, Lee YS, Zhang W, Hwang JA,
Nam BH, Kim SH, Kim JH, Yun T, Han JY, et al: Clinical outcome
according to the level of preexisting epidermal growth factor
receptor T790M mutation in patients with lung cancer harboring
sensitive epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Cancer.
120:2090–2098. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chmielecki J, Foo J, Oxnard GR, Hutchinson
K, Ohashi K, Somwar R, Wang L, Amato KR, Arcila M, Sos ML, et al:
Optimization of dosing for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
with evolutionary cancer modeling. Sci Transl Med. 3:90ra592011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|