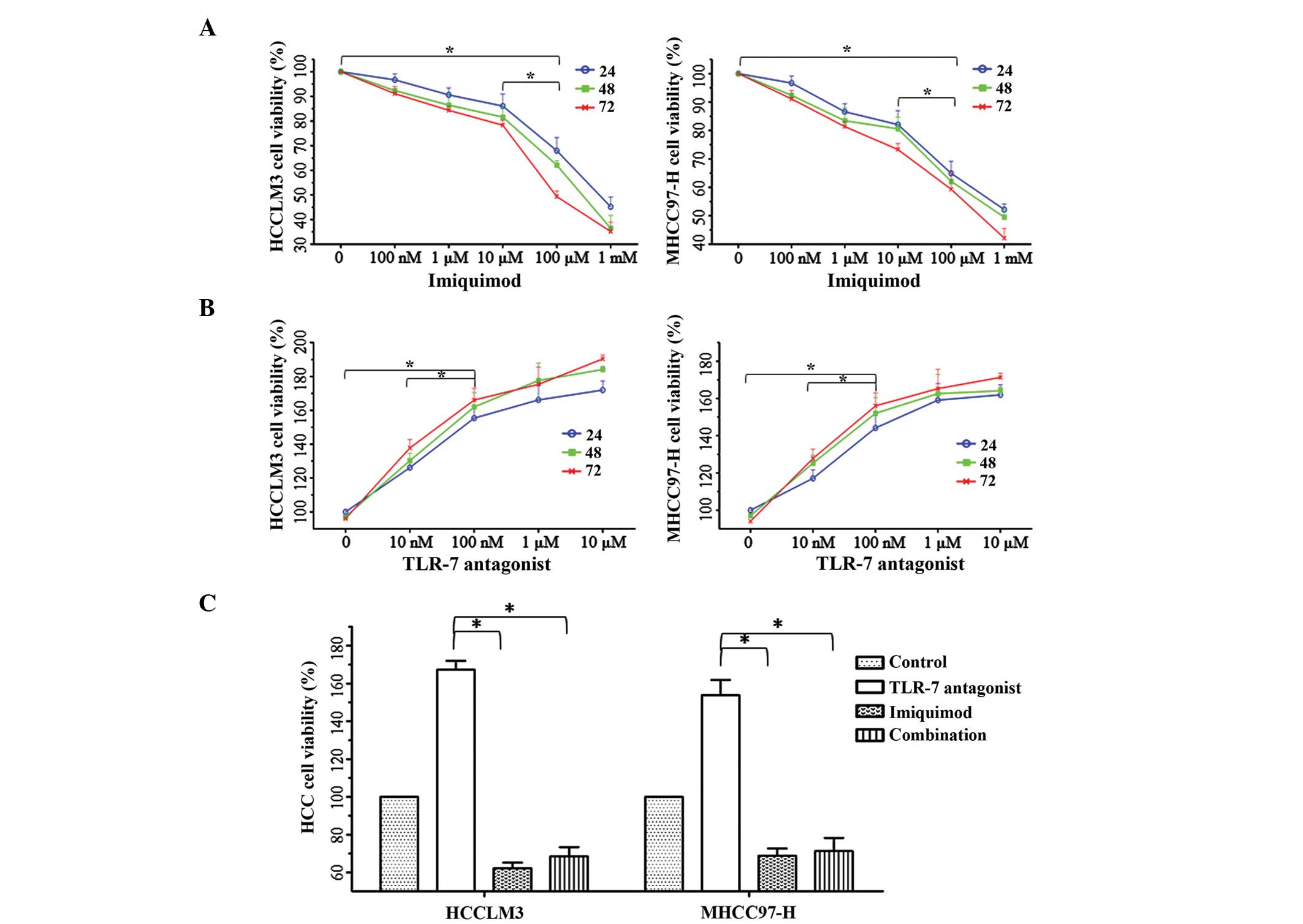
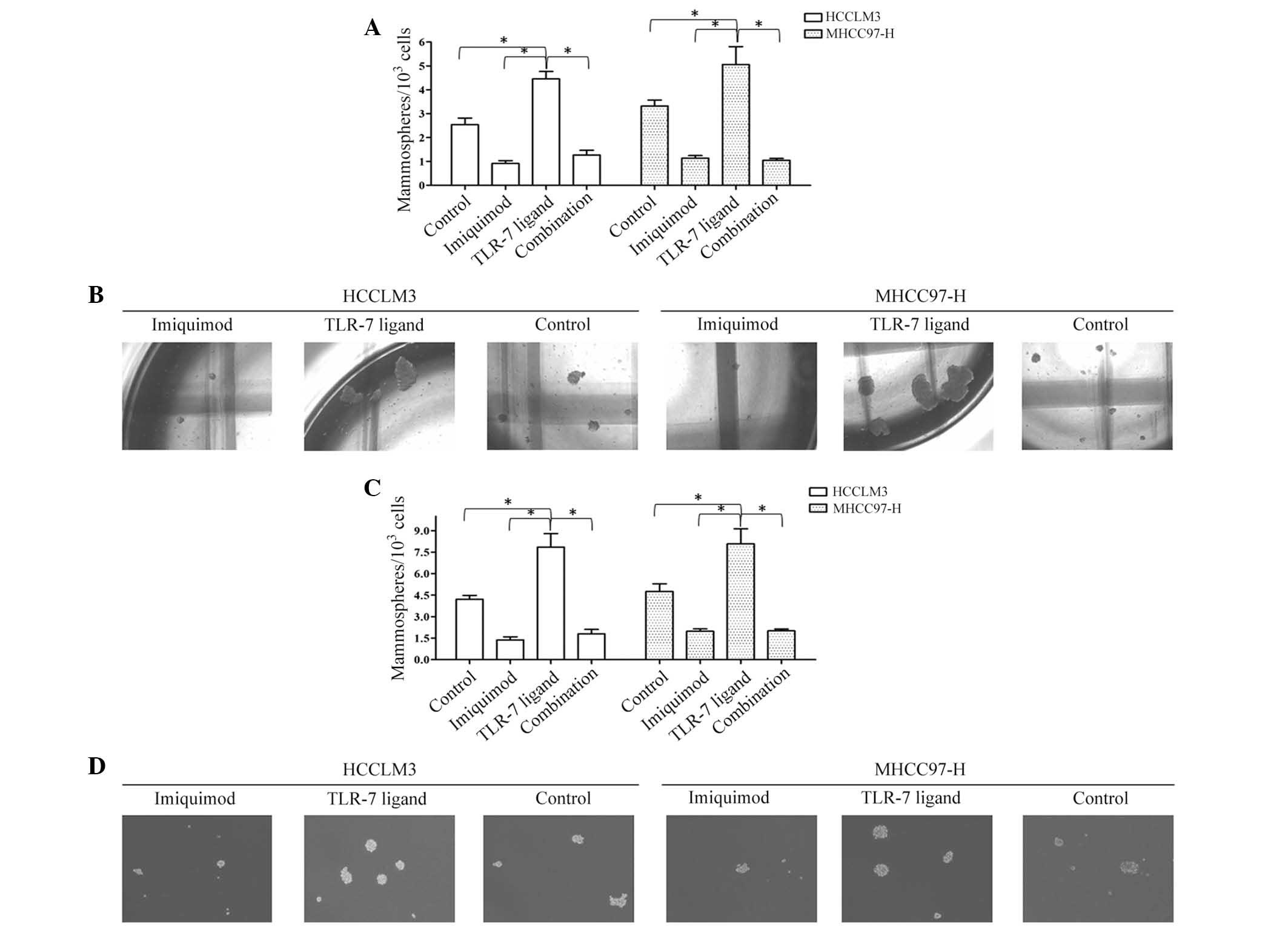
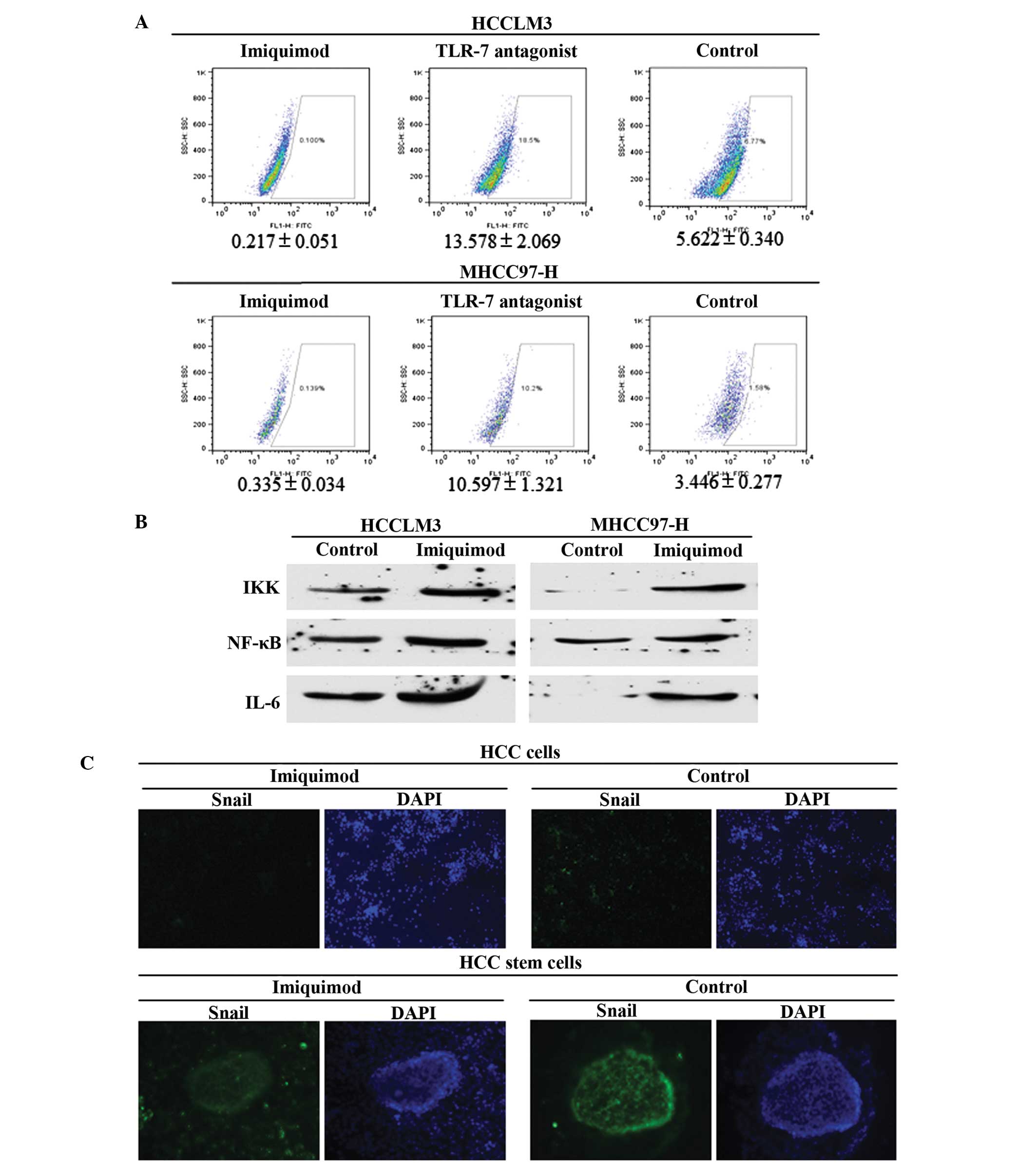
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thun MJ, DeLancey JO, Center MM, Jemal A
and Ward EM: The global burden of cancer: Priorities for
prevention. Carcinogenesis. 31:100–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu HC and Santella R: The role of
aflatoxins in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 12:e72382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dennison U, McKernan DP, Scully P, Clarke
G, Cryan J and Dinan T: Menstrual cycle influences toll-like
receptor responses. Neuroimmunomodulation. 19:171–179. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kesar V and Odin JA: Toll-like receptors
and liver disease. Liver Int. 34:184–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mencin A, Kluwe J and Schwabe RF:
Toll-like receptors as targets in chronic liver diseases. Gut.
58:704–720. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mittal D, Saccheri F, Vénéreau E, Pusterla
T, Bianchi ME and Rescigno M: TLR4-mediated skin carcinogenesis is
dependent on immune and radioresistant cells. EMBO J. 29:2242–2252.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dapito DH, Mencin A, Gwak GY, Pradere JP,
Jang MK, Mederacke I, Caviglia JM, Khiabanian H, Adeyemi A,
Bataller R, et al: Promotion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by the
Intestinal Microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell. 21:504–516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ji R, Tian S, Lu HJ and Lu Q, Zheng Y,
Wang X, Ding J, Li Q and Lu Q: TAM receptors affect adult brain
neurogenesis by negative regulation of microglial cell activation.
J Immunol. 191:6165–6177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Larangé A, Antonios D, Pallardy M and
Kerdine-Römer S: TLR7 and TLR8 agonists trigger different signaling
pathways for human dendritic cell maturation. J Leukoc Biol.
85:673–683. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Abel K, Lantz K, Krieg AM,
McChesney MB and Miller CJ: The Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)
agonist, Imiquimod and the TLR9 agonist, CpG ODN, induce antiviral
cytokines and chemokines but do not prevent vaginal transmission of
simian immunodeficiency virus when applied intravaginally to rhesus
macaques. J Virol. 79:14355–14370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oosterhoff D, Heusinkveld M, Lougheed SM,
Kosten I, Lindstedt M, Bruijns SC, van Es T, van Kooyk Y, van der
Burg SH and de Gruijl TD: Intradermal delivery of TLR agonists in a
human explant skin model: Preferential activation of migratory
dendritic cells by polyribosinic-polyribocytidylic acid and
peptidoglycans. J Immunol. 190:3338–3345. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O'Neill LA, Bryant CE and Doyle SL:
Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and
inflammatory diseases and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 61:177–197. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun X, Jiao X, Pestell TG, Fan C, Qin S,
Mirabelli E, Ren H and Pestell RG: MicroRNAs and cancer stem cells:
The sword and the shield. Oncogene. 33:4967–4977. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kreso A and Dick JE: Evolution of the
cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 14:275–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun X, Qin S, Fan C, Xu C, Du N and Ren H:
Let-7: A regulator of the ERα signaling pathway in human breast
tumors and breast cancer stem cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2079–2087.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cicalese A, Bonizzi G, Pasi CE, Faretta M,
Ronzoni S, Giulini B, Brisken C, Minucci S, Di Fiore PP and Pelicci
PG: The tumor suppressor p53 regulates polarity of self-renewing
divisions in mammary stem cells. Cell. 138:1083–1095. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdel-Raouf TA, Ahmed A, Zaki WK, Abdella
HM and Zid MA: Study of toll-like receptor 7 expression and
interferon α in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C
infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Egypt J Med Hum Genet.
15:387–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mohamed FE, Al-Jehani RM, Minogue SS,
Andreola F, Winstanley A, Olde Damink SW, Habtesion A, Malagó M,
Davies N, Luong TV, et al: Effect of toll-like receptor 7 and 9
targeted therapy to prevent the development of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 35:1063–1076. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guiducci C, Tripodo C, Gong M, Sangaletti
S, Colombo MP, Coffman RL and Barrat FJ: Autoimmune skin
inflammation is dependent on plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation
by nucleic acids via TLR7 and TLR9. J Exp Med. 207:2931–2942. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tazzyman S, Barry ST, Ashton S, Wood P,
Blakey D, Lewis CE and Murdoch C: Inhibition of neutrophil
infiltration into A549 lung tumors in vitro and in
vivo using a CXCR2-specific antagonist is associated with
reduced tumor growth. Int J Cancer. 129:847–858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adams S, Kozhaya L, Martiniuk F, Meng TC,
Chiriboga L, Liebes L, Hochman T, Shuman N, Axelrod D, Speyer J, et
al: Topical TLR7 agonist imiquimod can induce immune-mediated
rejection of skin metastases in patients with breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:6748–6757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|