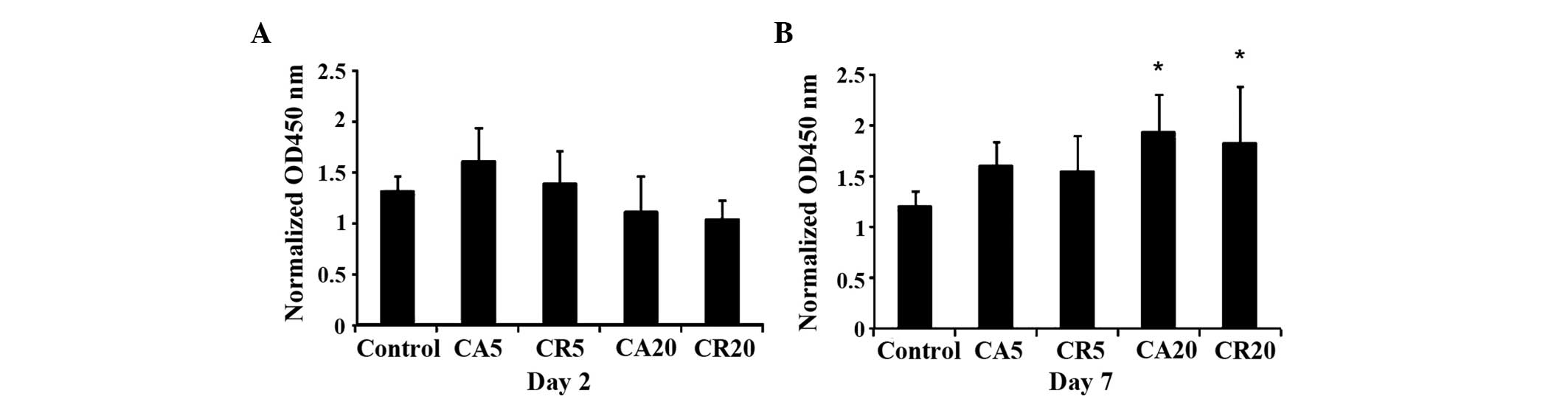
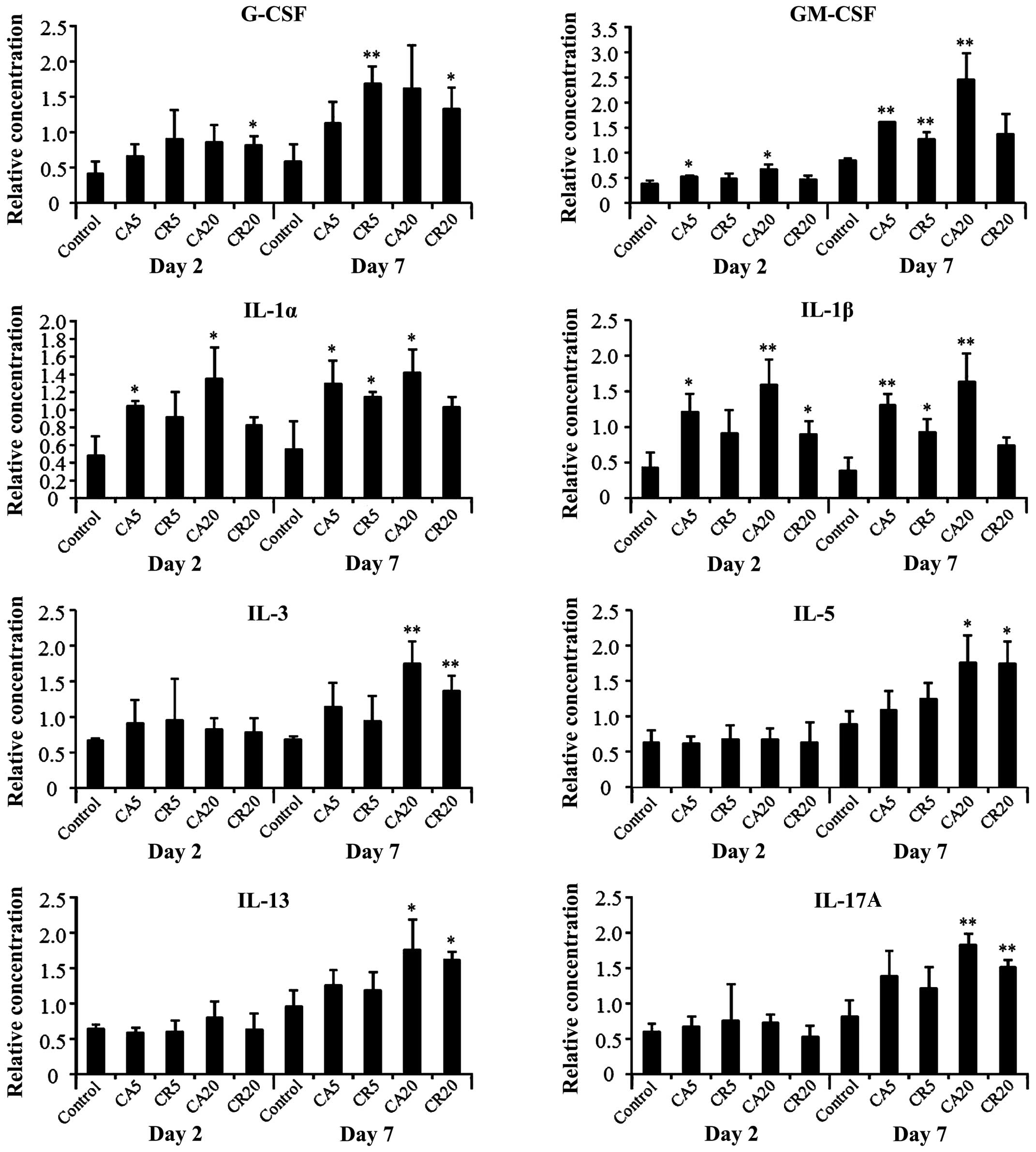
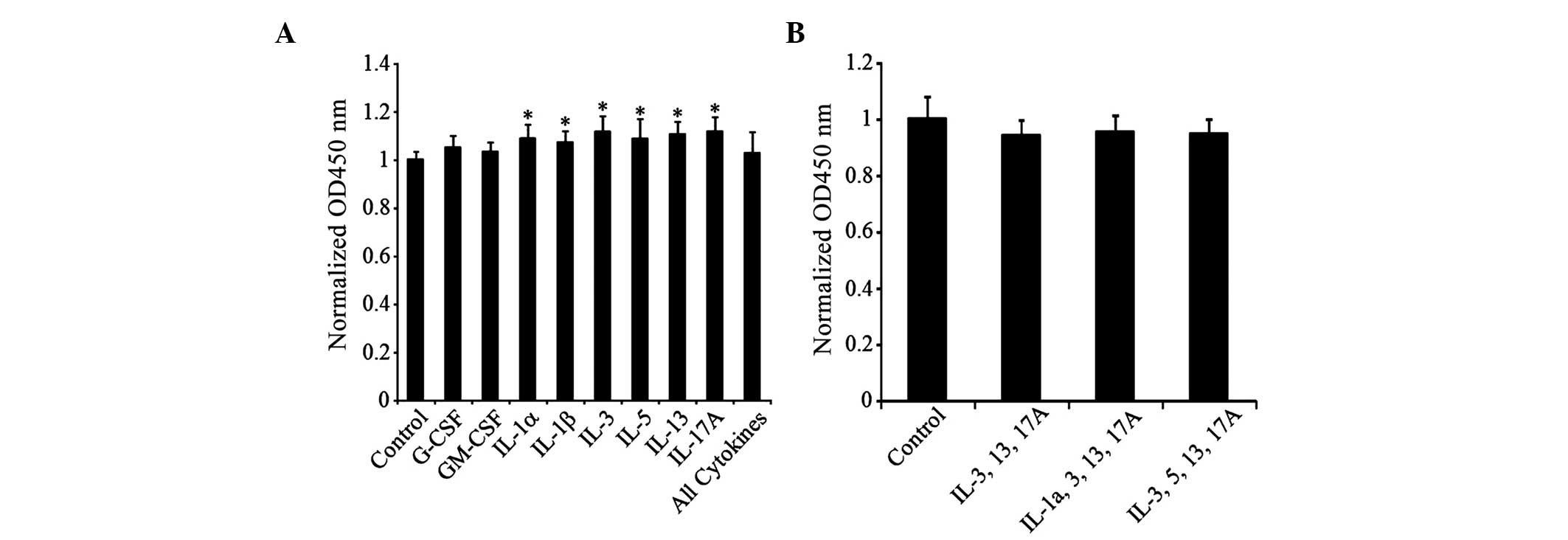
|
1
|
Becklake MR, Bagatin E and Neder JA:
Asbestos-related diseases of the lungs and pleura: Uses, trends and
management over the last century. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis.
11:356–369. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Straif K, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Baan R,
Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Guha N, Freeman C,
Galichet L and Cogliano V: WHO International Agency for Research on
Cancer Monograph Working Group: A review of human carcinogen - Part
C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 10:453–454.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Upadhyay D and Kamp DW: Asbestos-induced
pulmonary toxicity: Role of DNA damage and apoptosis. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 228:650–659. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lanphear BP and Buncher CR: Latent period
for malignant mesothelioma of occupational origin. J Occup Med.
34:718–721. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miura Y, Nishimura Y, Katsuyama H, Maeda
M, Hayashi H, Dong M, Hyodoh F, Tomita M, Matsuo Y, Uesaka A, et
al: Involvement of IL-10 and Bcl-2 in resistance against an
asbestos-induced apoptosis of T cells. Apoptosis. 11:1825–1835.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Murakami S, Nishimura Y, Maeda M, Kumagai
N, Hayashi H, Chen Y, Kusaka M, Kishimoto T and Otsuki T: Cytokine
alteration and speculated immunological pathophysiology in
silicosis and asbestos-related diseases. Environ Health Prev Med.
14:216–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Otsuki T, Maeda M, Murakami S, Hayashi H,
Miura Y, Kusaka M, Nakano T, Fukuoka K, Kishimoto T, Hyodoh F, et
al: Immunological effects of silica and asbestos. Cell Mol Immunol.
4:261–268. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kumagai-Takei N, Nishimura Y, Maeda M,
Hayashi H, Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Hiratsuka J and Otsuki T: Effect of
asbestos exposure on differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in
mixed lymphocyte reaction of human peripheral blood mononuclear
cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:28–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nishimura Y, Kumagai-Takei N, Matsuzaki H,
Lee S, Maeda M, Kishimoto T, Fukuoka K, Nakano T and Otsuki T:
Functional alteration of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T
lymphocytes upon asbestos exposure and in malignant mesothelioma
patients. BioMed Res Int. 2015:2384312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nishimura Y, Maeda M, Kumagai-Takei N, Lee
S, Matsuzaki H, Wada Y, Nishiike-Wada T, Iguchi H and Otsuki T:
Altered functions of alveolar macrophages and NK cells involved in
asbestos-related diseases. Environ Health Prev Med. 18:198–204.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nishimura Y, Maeda M, Kumagai-Takei N,
Matsuzaki H, Lee S, Fukuoka K, Nakano T, Kishimoto T and Otsuki T:
Effect of asbestos on anti-tumor immunity and immunological
alteration in patients with mesothelioma. Malignant Mesothelioma.
Belli C and Anand S: InTech. (Rijeka). 31–48. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Miller J and Shukla A: The role of
inflammation in development and therapy of malignant mesothelioma.
Am Med J. 3:240–248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang H, Bocchetta M, Kroczynska B,
Elmishad AG, Chen Y, Liu Z, Bubici C, Mossman BT, Pass HI, Testa
JR, et al: TNF-alpha inhibits asbestos-induced cytotoxicity via a
NF-kappaB-dependent pathway, a possible mechanism for
asbestos-induced oncogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:10397–10402. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mossman BT, Shukla A, Heintz NH,
Verschraegen CF, Thomas A and Hassan R: New insights into
understanding the mechanisms, pathogenesis, and management of
malignant mesotheliomas. Am J Pathol. 182:1065–1077. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hillegass JM, Shukla A, Lathrop SA,
MacPherson MB, Beuschel SL, Butnor KJ, Testa JR, Pass HI, Carbone
M, Steele C and Mossman BT: Inflammation precedes the development
of human malignant mesotheliomas in a SCID mouse xenograft model.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1203:7–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kasuga I, Ishizuka S, Minemura K, Utsumi
K, Serizawa H and Ohyashiki K: Malignant pleural mesothelioma
produces functional granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Chest.
119:981–983. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maeda M, Miura Y, Nishimura Y, Murakami S,
Hayashi H, Kumagai N, Hatayama T, Katoh M, Miyahara N, Yamamoto S,
et al: Immunological changes in mesothelioma patients and their
experimental detection. Clin Med Circ Respirat Pulm Med. 2:11–17.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakano T, Chahinian AP, Shinjo M, Tonomura
A, Miyake M, Togawa N, Ninomiya K and Higashino K: Interleukin 6
and its relationship to clinical parameters in patients with
malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br J Cancer. 77:907–912. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Riddell SR and Greenberg PD: The use of
anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies to clone and expand
human antigen-specific T cells. J Immunol Methods. 128:189–201.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nishimura Y, Miura Y, Maeda M, Kumagai N,
Murakami S, Hayashi H, Fukuoka K, Nakano T and Otsuki T: Impairment
in cytotoxicity and expression of NK cell-activating receptors on
human NK cells following exposure to asbestos fibers. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 22:579–590. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Otsuki T, Hata H, Harada N, Matsuzaki H,
Yata K, Wada H, Yawata Y, Ueki A and Yamada O: Cellular biological
differences between human myeloma cell lines KMS-12-PE and
KMS-12-BM established from a single patient. Int J Hematol.
72:216–222. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dinarello CA: Proinflammatory cytokines.
Chest. 118:503–508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rakoff-Nahoum S: Why cancer and
inflammation? Yale J Biol Med. 79:123–130. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hamilton RF Jr, Thakur SA and Holian A:
Silica binding and toxicity in alveolar macrophages. Free Radic
Biol Med. 44:1246–1258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Multhoff G, Molls M and Radons J: Chronic
inflammation in cancer development. Front Immunol. 2:982012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Lee TC, Guillemin B, Yu MC and
Rom WN: Enhanced IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release
and messenger RNA expression in macrophages from idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis or after asbestos exposure. J Immunol.
150:4188–4196. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dostert C, Pétrilli V, Van Bruggen R,
Steele C, Mossman BT and Tschopp J: Innate immune activation
through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science.
320:674–677. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Franchi L, Eigenbrod T, Muñoz-Planillo R
and Nuñez G: The inflammasome: A caspase-1-activation platform that
regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat Immunol.
10:241–247. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alam R, Pazdrak K, Stafford S and Forsythe
P: The lnterleukin-5/receptor interaction activates Lyn and Jak2
tyrosine kinases and propagates signals via the Ras-Raf-1-MAP
kinase and the Jak-STAT pathways in eosinophils. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 107:226–227. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sabo-Attwood T, Ramos-Nino M, Bond J,
Butnor KJ, Heintz N, Gruber AD, Steele C, Taatjes DJ, Vacek P and
Mossman BT: Gene expression profiles reveal increased mClca3 (Gob5)
expression and mucin production in a murine model of
asbestos-induced fibrogenesis. Am J Pathol. 167:1243–1256. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sabo-Attwood T, Ramos-Nino ME,
Eugenia-Ariza M, Macpherson MB, Butnor KJ, Vacek PC, McGee SP,
Clark JC, Steele C and Mossman BT: Osteopontin modulates
inflammation, mucin production, and gene expression signatures
after inhalation of asbestos in a murine model of fibrosis. Am J
Pathol. 178:1975–1985. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee SJ, Lee EJ, Kim SK, Jeong P, Cho YH,
Yun SJ, Kim S, Kim GY, Choi YH, Cha EJ, et al: Identification of
pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with muscle invasive bladder
cancer; The roles of IL-5, IL-20, and IL-28A. PLoS One.
7:e402672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zurawski G and de Vries JE: Interleukin
13, an interleukin 4-like cytokine that acts on monocytes and B
cells, but not on T cells. Immunol Today. 15:19–26. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hamilton RF Jr, Holian A and Morandi MT: A
comparison of asbestos and urban particulate matter in the in vitro
modification of human alveolar macrophage antigen-presenting cell
function. Exp Lung Res. 30:147–162. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hillegass JM, Shukla A, MacPherson MB,
Bond JP, Steele C and Mossman BT: Utilization of gene profiling and
proteomics to determine mineral pathogenicity in a human
mesothelial cell line (LP9/TERT-1). J Toxicol Environ Health A.
73:423–436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takenouchi M, Hirai S, Sakuragi N, Yagita
H, Hamada H and Kato K: Epigenetic modulation enhances the
therapeutic effect of anti-IL-13R(alpha)2 antibody in human
mesothelioma xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2819–2829. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barderas R, Bartolomé RA,
Fernandez-Aceñero MJ, Torres S and Casal JI: High expression of
IL-13 receptor α2 in colorectal cancer is associated with invasion,
liver metastasis and poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 72:2780–2790.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kolls JK and Lindén A: Interleukin-17
family members and inflammation. Immunity. 21:467–476. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lo Re S, Dumoutier L, Couillin I, Van Vyve
C, Yakoub Y, Uwambayinema F, Marien B, van den Brûle S, Van Snick
J, Uyttenhove C, et al: IL-17A-Producing gammadelta T and Th17
lymphocytes mediate lung inflammation but not fibrosis in
experimental silicosis. J Immunol. 184:6367–6377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B,
Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, Berger A, Bruneval P, Fridman WH,
Pagès F and Galon J: Clinical impact of different classes of
infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, Th2, Treg, Th17) in
patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 71:1263–1271. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kryczek I, Wei S, Szeliga W, Vatan L and
Zou W: Endogenous IL-17 contributes to reduced tumor growth and
metastasis. Blood. 114:357–359. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dodson RF, Williams MG Jr, Corn CJ, Brollo
A and Bianchi C: A comparison of asbestos burden in lung
parenchyma, lymph nodes, and plaques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 643:53–60.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miserocchi G, Sancini G, Mantegazza F and
Chiappino G: Translocation pathways for inhaled asbestos fibers.
Environ Health. 7:42008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lemaire I, Beaudoin H and Dubois C:
Cytokine regulation of lung fibroblast proliferation. Pulmonary and
systemic changes in asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev
Respir Dis. 134:653–658. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Geist LJ, Powers LS, Monick MM and
Hunninghake GW: Asbestos stimulation triggers differential cytokine
release from human monocytes and alveolar macrophages. Exp Lung
Res. 26:41–56. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shurin MR, Lu L, Kalinski P, Stewart-Akers
AM and Lotze MT: Th1/Th2 balance in cancer, transplantation and
pregnancy. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 21:339–359. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lauerova L, Dusek L, Simickova M, Kocák I,
Vagundová M, Zaloudík J and Kovarík J: Malignant melanoma
associates with Th1/Th2 imbalance that coincides with disease
progression and immunotherapy response. Neoplasma. 49:159–166.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pellegrini P, Berghella AM, Del Beato T,
Cicia S, Adorno D and Casciani CU: Disregulation in TH1 and TH2
subsets of CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood of
colorectal cancer patients and involvement in cancer establishment
and progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 42:1–8. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sato M, Goto S, Kaneko R, Ito M, Sato S
and Takeuchi S: Impaired production of Th1 cytokines and increased
frequency of Th2 subsets in PBMC from advanced cancer patients.
Anticancer Res. 18(5D): 3951–3955. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schulze-Koops H and Kalden JR: The balance
of Th1/Th2 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin
Rheumatol. 15:677–691. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kidd P: Th1/Th2 balance: The hypothesis,
its limitations, and implications for health and disease. Altern
Med Rev. 8:223–246. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|