Introduction
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal
myeloproliferative disorder of pluripotent stem cells. CML is
caused by reciprocal translocation between the long arms of
chromosomes 9 and 22, t(9;22)(q34;q11), termed the Philadelphia
chromosome (Ph) (1,2). The translocation consists of the
combination of the break-point cluster region (BCR) and Abelson
(ABL) genes to form the fusion gene BCR/ABL, which produces a
chimeric protein with deregulated tyrosine kinase activity. The
tyrosine kinase activity is responsible for regulating the
maintenance of adult tissues, aiding signaling pathways and
regulating cell division (3–5). The fusion gene BCR/ABL is associated
with increased levels of erythrocytes, monocytes, megakaryocytes,
myelocytes and platelets in the peripheral blood and marked myeloid
hyperplasia in the bone marrow (6).
The Ph-positive translocation that results from
reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 (q34;q11) is
present in 90–95% of CML cases. However variant or complex
translocations involving one or more additional chromosomes
compared with (9;22)(q34;q11) may be observed in 5–8% CML patients
(1,7,8).
Gleevec imatinib mesylate (Novartis Pharmaceuticals,
Basel, Switzerland) is an orally-designed selective BCR/ABL protein
tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which may induce a complete cytogenetic
response in 65–90% of CML patients (9,10). The
therapy is the first line treatment for >90% of CML patients,
and the key function of imatinib mesylate is to hinder
proliferation and induce apoptosis in cells that express the
BCR/ABL gene (7). There is evidence
to suggest that imatinib mesylate may prolong survival and improve
the quality of life for patients with CML (6,11,12).
The present study reports of the case of a
45-year-old male patient diagnosed with CML in the chronic phase of
disease, who demonstrated a rare Ph-positive three-way complex
variant translocation involving chromosome 46XY,t(9;11;22)(q34;
p15; q11.2)[10]. Written informed consent was obtained from the
patient.
Case report
A 45-year-old male patient was diagnosed with CML at
the Sundayman Civil Hospital (Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan) on
August 5, 2008. The patient was referred to the hospital due to a
15 week history of weight loss, sleep disturbance, fever, anxiety,
depression, dry skin, sweating, swelling on body and high
cholesterol levels. The hematological parameters of the patient
were as follows: White blood cell (WBC) count, 186.5×103
cells/µl (normal range, 4–11×103 cells/µl); hemoglobin,
11.1 g/dl (normal range, 14–18 g/dl); platelet (PLT) count,
235×103 PLTs/µl (normal range, 150–400×103
PLTs/µl); neutrophils, 66% (normal range, 40–75%); lymphocytes, 2%
(normal range, 20–45%); eosinophils, 1% (normal range, 1–6%);
monocytes, 6% (normal range, 2–10%); myelocytes, 15% (normal range,
0%); metamyelocytes, 4% (normal range, 0%); promyelocytes, 6%
(normal range, 0%); and basophils, 0% (normal range,0–1%). Due to
the high WBC count and low hemoglobin levels identified, the
patient was subsequently administered ongoing treatment with
imatinib mesylate (400 mg/day).
For complete blood cell analysis, a hematological
analyzer (Celltac F MEK-8222; Nihon Kohden Corporation, Tokyo,
Japan) was used to assess the total leukocyte, WBC, neutrophil,
lymphocyte, eosinophil, monocyte, myelocyte, promyelocyte, basophil
and platelet counts. CML patients tend to exhibit high WBC and
platelet counts. The aforementioned assessments were used to
determine if the patient was suffering from leukemia. The patient
was advised to undergo additional tests.
A cytogenetic analysis was performed using the
GTG-banding technique. Bone marrow specimens were examined on
direct or short-term (24 h) cultures and >10 metaphases were
analyzed. The karyotypes were classified using the International
System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (13,14).
FISH was performed using directly labeled dual color
locus-specific indicator/centromere enumeration probes, according
to the manufacturer's protocol (Oncor; Ventana Medical Systems,
Tucson, AZ, USA) in order to detect BCR/ABL translocation. In
total, 500 metaphase or interphase cells were counted in order to
calculate the percentage of BCR/ABL cells. The main steps in the
methodology included the hypotonic treatment and fixation of direct
demecolcine-treated cultures, dehydration, codenaturation,
overnight hybridization, washing and the mounting of slides using
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-antifade (15,16). The
slides were viewed using an Axioskop 2 microscope (Zeiss AG,
Oberkochen, Germany) with a HBO 100 mercury lamp (Osram, Munich,
Germany). The slides were analyzed through a fluorescent microscope
(BMX60; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) with DAPI, rhodamine, fluorescein
isothiocyanate and triple band pass filters (Chromo Technology,
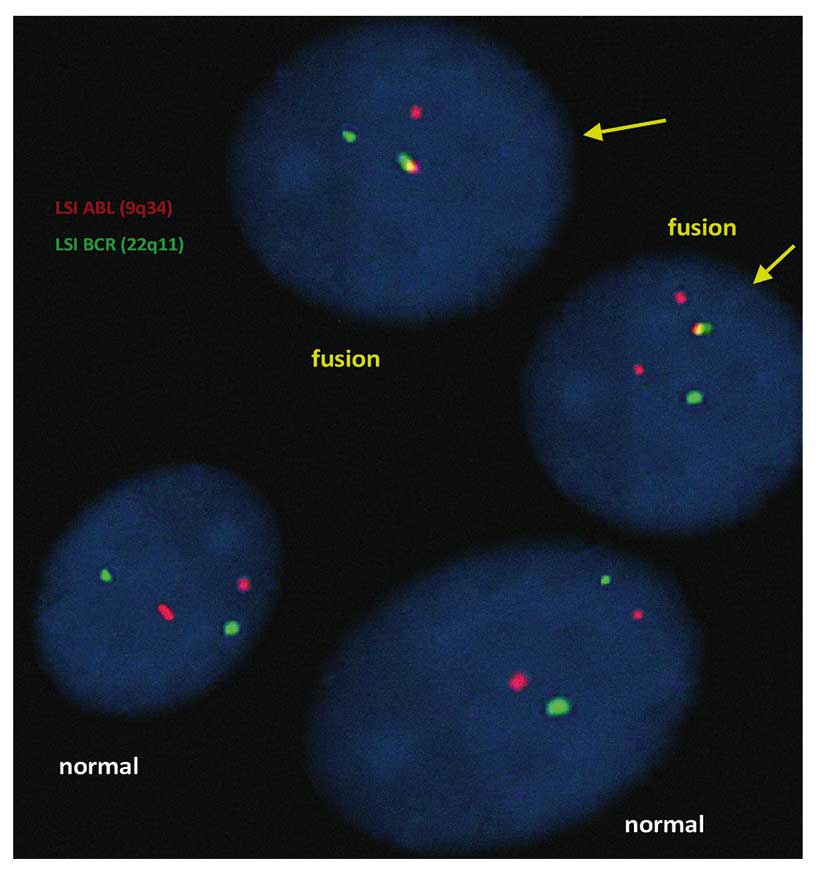
Bellows Falls, VT, USA). The slides showed fluorescent red dots
(rhodamine) that corresponded to the ABL (9q34.1) gene and green
dots (fluorescein) that corresponded to the BCR (22q11) gene.
Therefore, a cell exhibiting two isolated orange and green dots was
counted as normal, or without translocation. A cell exhibiting one
isolated orange dot, one isolated green dot and one fused orange
and green signal was considered to be presenting the irregular
translocation of CML. Morphological and hematological analyses were
performed on the bone marrow of the CML patient every 6 months for
a year. Follow-up revealed a reduction in fatigue, anxiety and
swelling of the body on June 5th, 2009. In total the patient was
followed-up for 84 months.
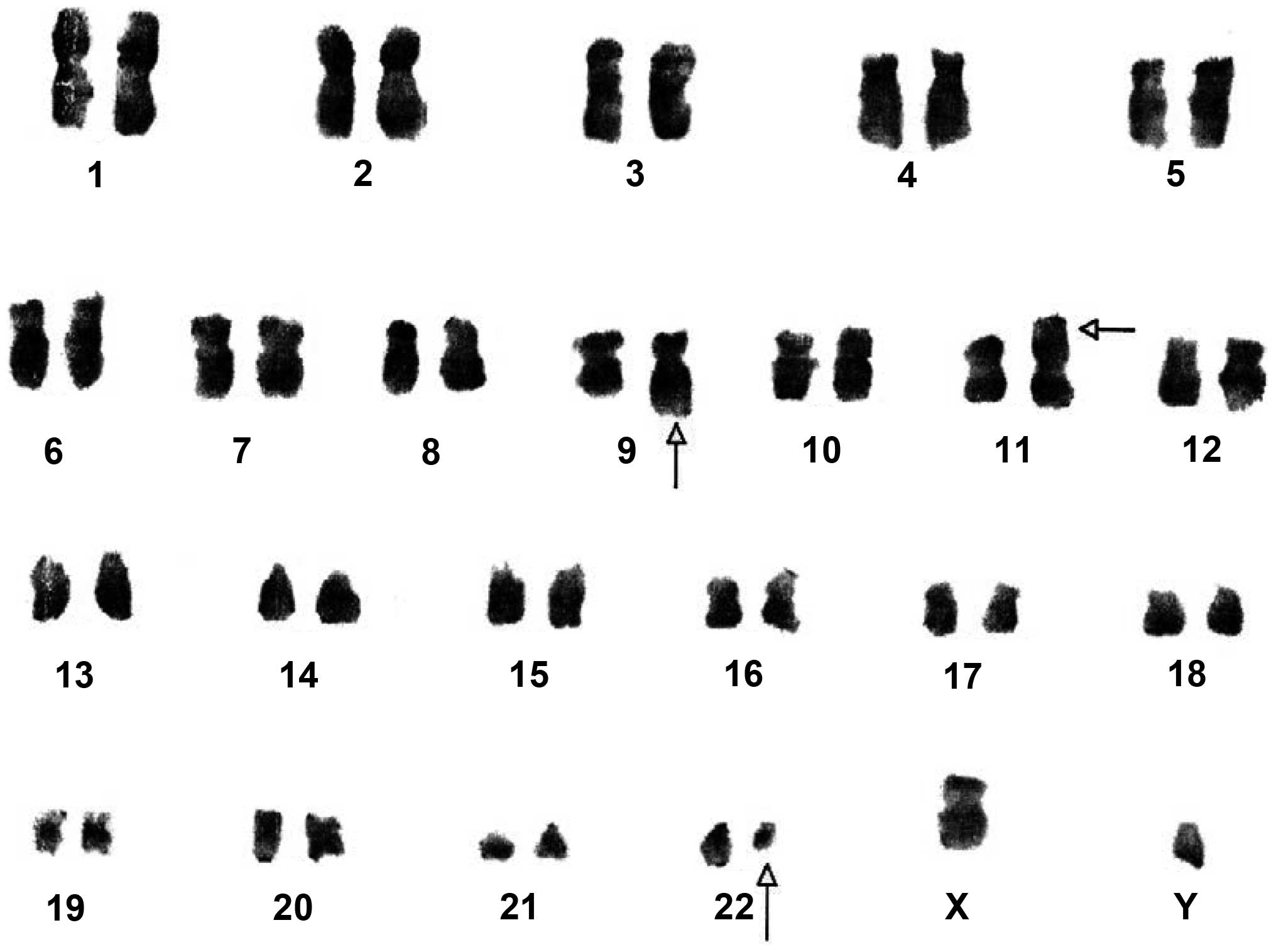
The cytogenetic analysis revealed that 10 of the
cells that were examined expressed the Ph chromosome and
demonstrated the 46XY,t(9;11;22)(p15;q34;q11.2)[10] translocation
(Fig. 1). BCR/ABL translocations were
detected in 67% of the 500 nuclei counted using the FISH test
(Fig. 2). The hematological analyses
revealed that the WBC count was 186.5×103 cells/µl, the
PLT count was 235×103 PLTs/µl and the hemoglobin level
was 11.1 mg/dl, which indicated that the patient had anemia.
Discussion
CML is a cancer of the blood that occurs when two
proteins on chromosomes 9 and 22 translocate to create the novel Ph
chromosome. CML is responsible for the production of the BCR/ABL
gene. BCR/ABL interferes with the function of white blood cells,
making it challenging for the body to fight off infections. The Ph
chromosome (9;22)(q34;q11) is found in 90–95% of CML patients;
however, only 5–8% of CML patients demonstrate a variant that
involves a third chromosome other than (9;22) in a three-way Ph
chromosome complex (1,8,17).
To the best of our knowledge, the present study is
the second case of a three-way complex variant involving chromosome
46XY,t(9;11;22)(q34;p15;q11.2) to be reported, with one case
reported previously, which was identified by searching the Mitelman
Database of Chromosome Aberrations and Gene Fusions in Cancer
(http://cgap.nci.nih.gov/Chromosomes/Mitelman) using
the terms ‘Chronic myeloid leukemia’ and ‘complex variant
translocation (9;11;22)(q34;p15;q11)’ (18).
The formation of the variant Ph translocations is a
controversial matter. The studies by Morel et al (2003) and
Emberger et al (2001) on complex variant Ph translocations
concluded that the variant may occur as a result of a single event,
which involves the simultaneous breaking of the chromosomal regions
involved, followed by a mismatched rejoining of the broken ends,
termed concerted genomic rearrangement (18,19). The
studies by Sessarego et al (1995) and Reddy and Sulcova
(2001) stated that the mechanism behind variant translocation is a
two-step process, which includes the initial formation of a
standard t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation, followed by a
translocation that usually involves one derivative chromosome from
the Ph translocation and a third chromosome (20,21).
In the present study the patient was successfully
treated with 400 mg/day imatinib mesylate. Imatinib mesylate is an
orally designed tyrosine kinase protein inhibitor that inhibits
BCR/ABL gene translocation and the constitutive abnormal tyrosine
kinase produced by the Ph chromosome. The drug also inhibits the
platelet-derived growth factor and stem cell factor receptor
tyrosine kinases. The treatment of CML with imatinib has
demonstrated notable success, by prolonging the survival time and
improving the quality of life for the patient (2,11,17).
In conclusion, the present study reports a rare case
of a CML patient in the chronic phase of disease, who demonstrates
the BCR/ABL translocation that involves the three-way translocation
variant 46XY,t(9;11;22)(q34;p15;q11.2)[10].
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Faculty of Life
Sciences BUITEMS, Quetta, Pakistan. (registration ID no.
27934).
References
|
1
|
Kuru D, Tarkan-Argüden Y, Ar MC, Çırakoğlu
A, Öngören Ş, Yılmaz Ş, Eşkazan AE, Deviren A, Soysal T,
Hacıhanefioğlu S and Ülkü B: Variant Philadelphia translocations
with different breakpoints in six chronic myeloid leukemia
patients. Turk J Hematol. 28:186–192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Aliano S, Cirmena G, Fugazza G, Bruzzone
R, Palermo C and Sessarego M: Standard and variant Philadelphia
translocation in a CML patient with different sensitivity to
imatinib therapy. Leuk Res Rep. 2:75–78. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quintás-Cardama A and Cortes JE: Chronic
myeloid leukemia: Diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc.
81:973–988. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aguayo A, García-Álvarez E,
Cázarez-Ordónez Y, Crespo-Solís E, Martínez-Baños D,
Guadarrama-Beltrán E, Cervera-Ceballos EE and López-Karpovicth X:
Chronic myeloid leukemia: A clinicoepidemiologic and therapeutic
description of a single institution in México City. Clinical
Leukemia. 2:261–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Au WY, Caguioa PB, Chuah C, Hsu SC, Jootar
S, Kim DW, Kweon IY, O'Neil WM, Saikia TK and Wang J: Chronic
myeloid leukemia in Asia. Int J Hematol. 89:14–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sawyers CL: Chronic myeloid leukemia. N
Engl J Med. 340:1330–1340. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Al-Achkar W, Wafa A and Liehr T: A new
t(9;11;20;22)(q34;p11.2;q11.21;q11) in a Philadelphia-positive
chronic myeloid leukemia case. Oncol Lett. 5:605–608.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sessarego M, Fugazza G, Bruzzone R,
Ballestrero A, Miglino M and Bacigalupo A: Complex chromosome
rearrangements may locate the bcr/abl fusion gene sites other than
22q11. Haematologica. 85:35–39. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
O'Brien SG, Meinhardt P, Bond E, Beck J,
Peng B, Dutreix C, Mehring G, Milosavljev S, Huber C, Capdeville R
and Fischer T: Effects of imatinib mesylate (STI571, Glivec) on the
pharmacokinetics of simvastatin, a cytochrome p450 3A4 substrate,
in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Cancer.
89:1855–1859. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Todaro J, Ferreira E, Hamerschlak N, Simon
SD, Kutner JM, Pietrocola M and Borovik CL: Imatinib improves
survival of CML patients in accelerated phase: A 48-month
follow-up. Einstein. 4:16–21. 2006.
|
|
11
|
Cohen MH, Williams G, Johnson JR, Duan J,
Gobburu J, Rahman A, Benson K, Leighton J, Kim SK, Wood R, et al:
Approval summary for imatinib mesylate capsules in the treatment of
chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 8:935–942.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cohen MS, Hussain HB and Moley JF:
Inhibition of medullary thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation and
RET phosphorylation by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Surgery.
132:960–966. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Simons A, Shaffer LG and Hastings RJ:
Cytogenetic nomenclature: Changes in the ISCN 2013 compared to the
2009 edition. Cytogenet Genome Res. 141:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Claussen U, Michel S, Mühlig P, Westermann
M, Grummt UW, Kromeyer-Hauschild K and Liehr T: Demystifying
chromosome preparation and the implications for the concept of
chromosome condensation during mitosis. Cytogenet Genome Res.
98:136–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Froncillo MC, Maffei L, Cantonetti M, Del
Poeta G, Lentini R, Bruno A, Masi M, Tribalto M and Amadori S: FISH
analysis for CML monitoring? Ann Hematol. 73:113–119. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Buño I, Wyatt WA, Zinsmeister AR,
Dietz-Band J, Silver RT and Dewald GW: A special fluorescent in
situ hybridization technique to study peripheral blood and assess
the effectiveness of interferon therapy in chronic myeloid
leukemia. Blood. 92:2315–2321. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
La Starza R, Testoni N, Lafage-Pochitaloff
M, Ruggeri D, Ottaviani E, Perla G, Martelli MF, Marynen P and
Mecucci C: Complex variant Philadelphia translocations involving
the short arm of chromosome 6 in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Haematologica. 87:143–147. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morel F, Herry A, Le Bris MJ, Morice P,
Bouquard P, Abgrall JF, Berthou C and De Braekeleer M: Contribution
of fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses to the
characterization of masked and complex Philadelphia chromosome
translocations in chronic myelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 147:115–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Emberger W, Behmel A, Tschernigg M,
Seewann HL, Petek E, Kroisel PM and Wagner K: Chronic myeloid
leukemia with a rare variant Philadelphia translocation:
t(9;10;22)(q34;q22;q11). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 129:76–79. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reddy KS and Sulcova V: A FISH study of
variant Philadelphia rearrangements. Cancer Genet Cytogenet.
118:121–131. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sessarego M, Fugazza G, Canepa L,
Bacigalupo A, Bruzzone R and Patrone F: Fluorescence in situ
hybridization provides evidence for two step rearrangement in a
masked Ph chromosome formation. Leuk Res. 19:921–925. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|