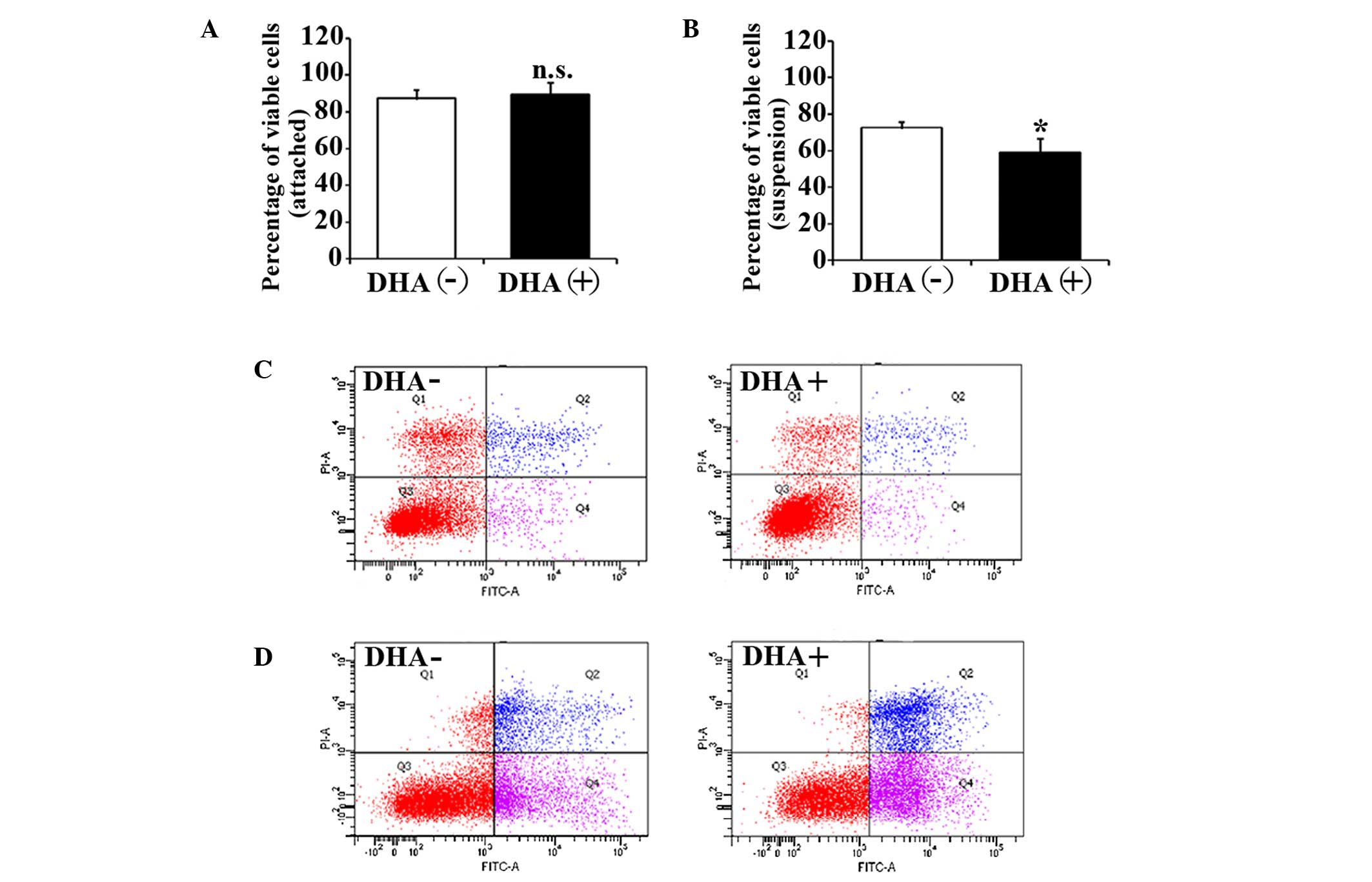
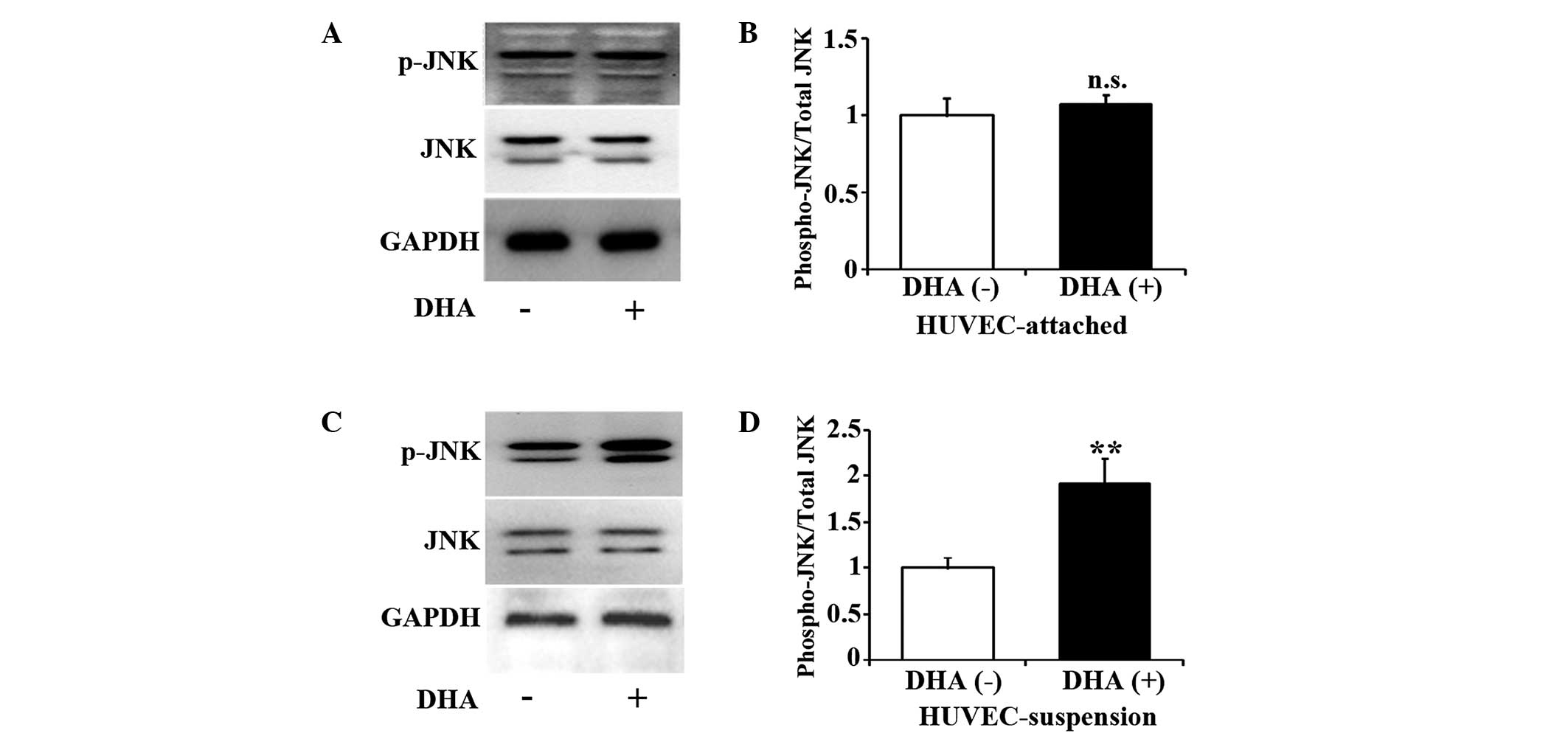
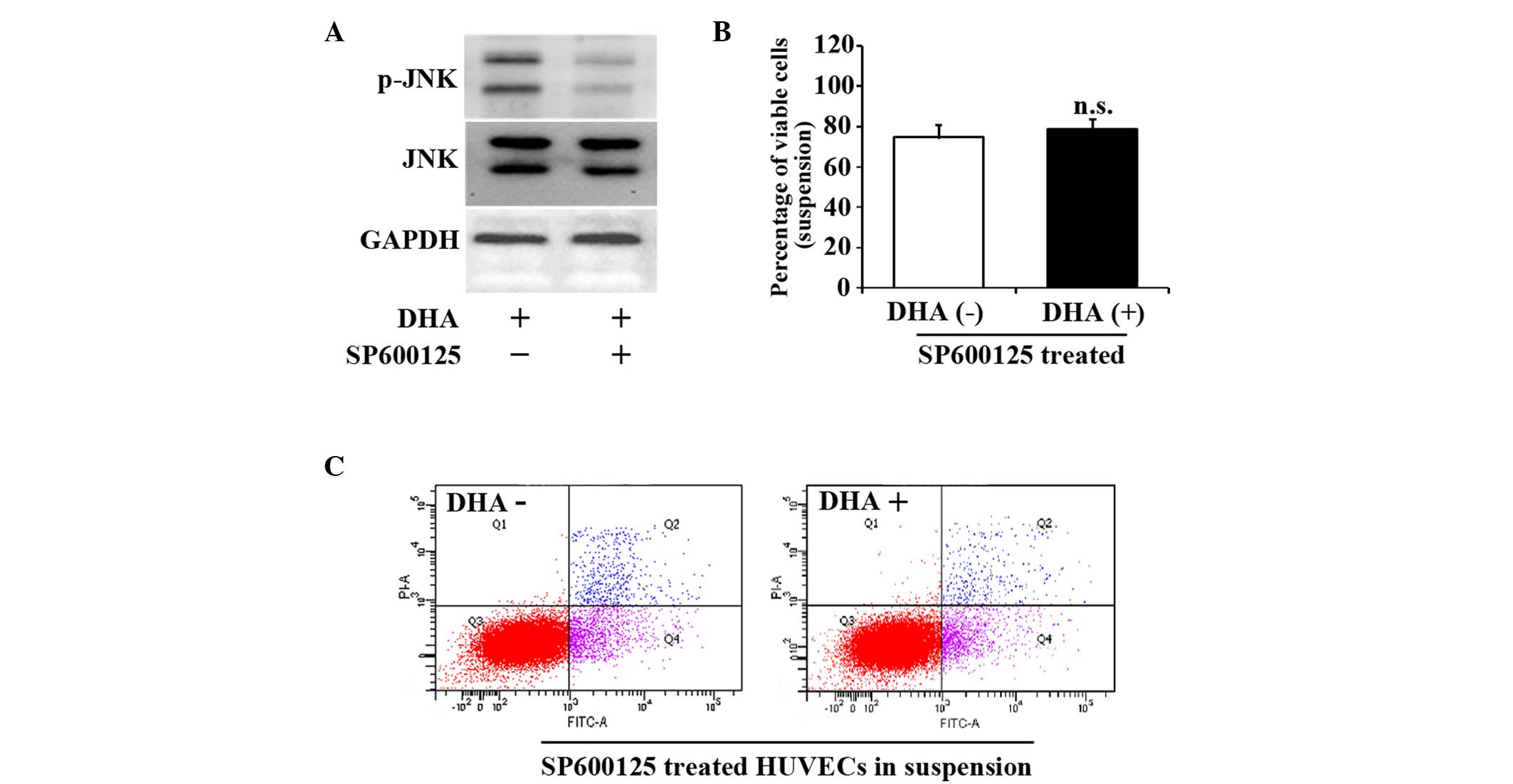
|
1
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu J, Deutsch U, Jeong J and Lobe CG:
Constitutive notch signaling in adult transgenic mice inhibits
bFGF-induced angiogenesis and blocks ovarian follicle development.
Genesis. 52:809–816. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett
N, Phillips HS and Ferrara N: Inhibition of vascular endothelial
growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in
vivo. Nature. 362:841–844. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanahan D: Signaling vascular
morphogenesis and maintenance. Science. 277:48–50. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aoudjit F and Vuori K: Matrix attachment
regulates Fas-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells: A role for
c-flip and implications for anoikis. J Cell Biol. 152:633–643.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Green DR and Llambi F: Cell death
signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7:pii: a006080. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gilmore AP: Anoikis. Cell Death Differ.
12(Suppl 2): 1473–1477. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee J, Zhou HJ and Wu XH:
Dihydroartemisinin downregulates vascular endothelial growth factor
expression and induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia K562
cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 57:213–220. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ho WE, Peh HY, Chan TK and Wong WS:
Artemisinins: Pharmacological actions beyond anti-malarial.
Pharmacol Ther. 142:126–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong F, Zhou X, Li C, Yan S, Deng X, Cao
Z, Li L, Tang B, Allen TD and Liu J: Dihydroartemisinin targets
VEGFR2 via the NF-κB pathway in endothelial cells to inhibit
angiogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:1479–1488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong F, Tian H, Yan S, Li L, Dong X, Wang
F, Li J, Li C, Cao Z, Liu X and Liu J: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits
endothelial cell proliferation through the suppression of the ERK
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 35:1381–1387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo L, Dong F, Hou Y, Cai W, Zhou X, Huang
AL, Yang M, Allen TD and Liu J: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell
migration by a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent
pathway. Exp Ther Med. 8:1707–1712. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen HH, Zhou HJ, Wang WQ and Wu GD:
Antimalarial dihydroartemisinin also inhibits angiogenesis. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 53:423–432. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J and Kapron CM: Differential
induction of MAP kinase signalling pathways by cadmium in primary
cultures of mouse embryo limb bud cells. Reprod Toxicol.
29:286–291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frisch SM, Vuori K, Kelaita D and Sicks S:
A role for Jun-N-terminal kinase in anoikis; suppression by bcl-2
and crmA. J Cell Biol. 135:1377–1382. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cardone MH, Salvesen GS, Widmann C,
Johnson G and Frisch SM: The regulation of anoikis: MEKK-1
activation requires cleavage by caspases. Cell. 90:315–323. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary
EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, et
al: SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal
kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13681–13686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oh S, Jeong IH, Shin WS and Lee S: Growth
inhibition activity of thioacetal artemisinin derivatives against
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
13:3665–3668. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leppa S and Bohmann D: Diverse functions
of JNK signaling and c-Jun in stress response and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 18:6158–6162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Rivera Rosado LA, Moon SY and
Zhang B: Silencing of D4-GDI inhibits growth and invasive behavior
in MDA-MB-231 cells by activation of Rac-dependent p38 and JNK
signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:12956–12965. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krestow JK, Rak J, Filmus J and Kerbel RS:
Functional dissociation of anoikis-like cell death and activity of
stress activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
260:48–53. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khwaja A and Downward J: Lack of
correlation between activation of Jun-NH2-terminal kinase and
induction of apoptosis after detachment of epithelial cells. J Cell
Biol. 139:1017–1023. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li AE, Ito H, Rovira II, Kim KS, Takeda K,
Yu ZY, Ferrans VJ and Finkel T: A role for reactive oxygen species
in endothelial cell anoikis. Circ Res. 85:304–310. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kong R, Jia G, Cheng ZX, Wang YW, Mu M,
Wang SJ, Pan SH, Gao Y, Jiang HC, Dong DL and Sun B:
Dihydroartemisinin enhances Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in
pancreatic cancer cells via ROS-mediated up-regulation of death
receptor 5. PloS One. 7:e372222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim SJ, Kim MS, Lee JW, Lee CH, Yoo H,
Shin SH, Park MJ and Lee SH: Dihydroartemisinin enhances
radiosensitivity of human glioma cells in vitro. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 132:129–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng R, Li C, Wei L, Li L, Zhang Y, Yao
Y, Gu X, Cai W, Yang Z, Ma J, et al: The artemisinin derivative
artesunate inhibits corneal neovascularization by inducing
ROS-dependent apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:3400–3409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu Q and Rounds S: Focal adhesion kinase
and endothelial cell apoptosis. Microvasc Res. 83:56–63. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sundberg LJ, Galante LM, Bill HM, Mack CP
and Taylor JM: An endogenous inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase
blocks Rac1/JNK but not Ras/ERK-dependent signaling in vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 278:29783–29791. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu G, Meng X, Jin Y, Bai J, Zhao Y, Cui
X, Chen F and Fu S: Inhibitory role of focal adhesion kinase on
anoikis in the lung cancer cell A549. Cell Biol Int. 32:663–670.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu B, Hu K, Li S, Zhu J, Gu L, Shen H,
Hambly BD, Bao S and Di W: Dihydroartiminisin inhibits the growth
and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 27:101–108.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|