|
1
|
Hargrave D, Bartels U and Bouffet E:
Diffuse brainstem glioma in children: Critical review of clinical
trials. Lancet Oncol. 7:241–248. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Puget S, Philippe C, Bax DA, Job B, Varlet
P, Junier MP, Andreiuolo F, Carvalho D, Reis R, Guerrini-Rousseau
L, et al: Mesenchymal transition and PDGFRA amplification/mutation
are key distinct oncogenic events in pediatric diffuse intrinsic
pontine gliomas. PLoS One. 7:e303132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Donaldson SS, Laningham F and Fisher PG:
Advances toward an understanding of brainstem gliomas. J Clin
Oncol. 24:1266–1272. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
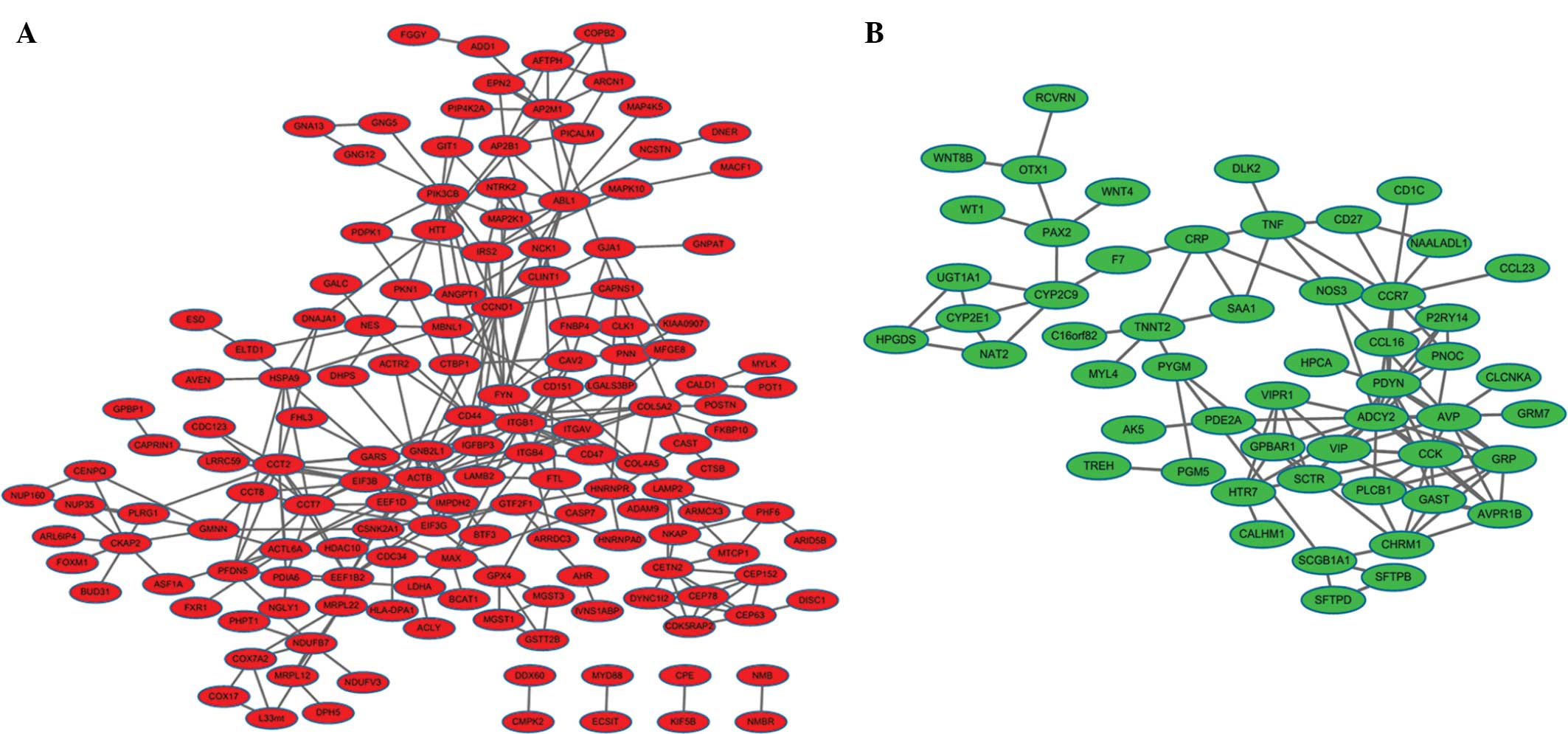
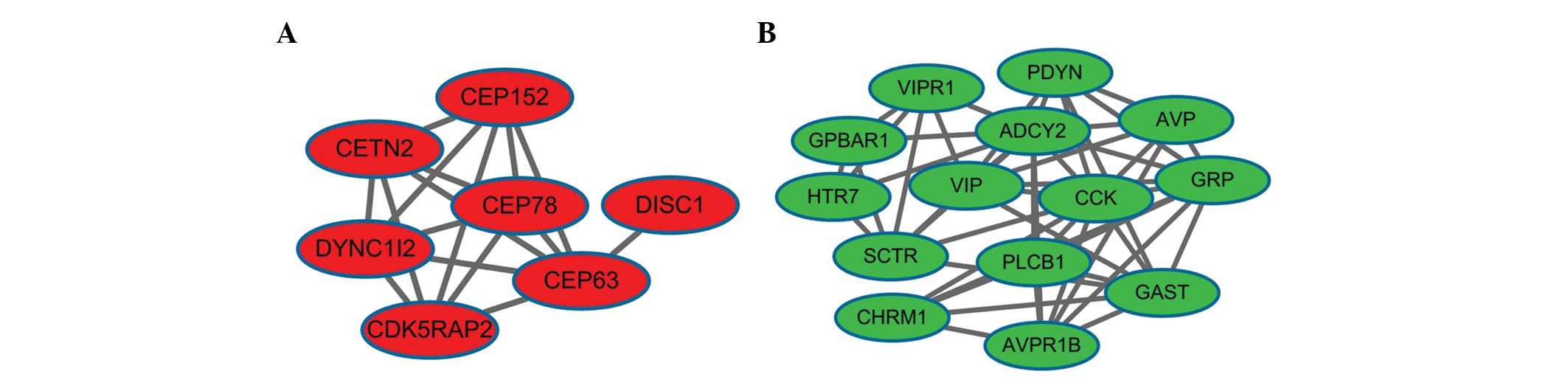
|
Paugh BS, Broniscer A, Qu C, Miller CP,
Zhang J, Tatevossian RG, Olson JM, Geyer JR, Chi SN, da Silva NS,
et al: Genome-wide analyses identify recurrent amplifications of
receptor tyrosine kinases and cell-cycle regulatory genes in
diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Clin Oncol. 29:3999–4006. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu G, Broniscer A, McEachron TA, Lu C,
Paugh BS, Becksfort J, Qu C, Ding L, Huether R, Parker M, et al:
Project SJCsRHWUPCG: Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric
diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas.
Nat Genet. 44:251–253. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buczkowicz P, Hoeman C, Rakopoulos P,
Pajovic S, Letourneau L, Dzamba M, Morrison A, Lewis P, Bouffet E,
Bartels U, et al: Genomic analysis of diffuse intrinsic pontine
gliomas identifies three molecular subgroups and recurrent
activating ACVR1 mutations. Nat Genet. 46:451–456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kurooka H, Nakahiro T, Mori K, Sano K and
Yokota Y: BMP signaling is responsible for serum-induced Id2
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 420:281–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kowanetz M, Valcourt U, Bergström R,
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Id2 and Id3 define the potency of cell
proliferation and differentiation responses to transforming growth
factor beta and bone morphogenetic protein. Mol Cell Biol.
24:4241–4254. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shin M, Ohte S, Fukuda T, Sasanuma H,
Yoneyama K, Kokabu S, Miyamoto A, Tsukamoto S, Hohjoh H, Jimi E and
Katagiri T: Identification of a novel bone morphogenetic protein
(BMP)-inducible transcript, BMP-inducible transcript-1, by
utilizing the conserved BMP-responsive elements in the Id genes. J
Bone Miner Metab. 31:34–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Piccirillo S, Reynolds B, Zanetti N,
Lamorte G, Binda E, Broggi G, Brem H, Olivi A, Dimeco F and Vescovi
AL: Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential
of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature. 444:761–765. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K, Donin NM, Li A,
Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, et al:
Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein
pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:69–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu G, Diaz AK, Paugh BS, Rankin SL, Ju B,
Li Y, Zhu X, Qu C, Chen X, Zhang J, et al: St. Jude Children's
Research Hospital - Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome
Project: The genomic landscape of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
and pediatric non-brainstem high-grade glioma. Nat Genet.
46:444–450. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taylor KR, Mackay A, Truffaux N,
Butterfield YS, Morozova O, Philippe C, Castel D, Grasso CS, Vinci
M, Carvalho D, et al: Recurrent activating ACVR1 mutations in
diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Nat Genet. 46:457–461. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zarghooni M, Bartels U, Lee E, Buczkowicz
P, Morrison A, Huang A, Bouffet E and Hawkins C: Whole-genome
profiling of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas highlights
platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and poly (ADP-ribose)
polymerase as potential therapeutic targets. J Clin Oncol.
28:1337–1344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W, Irizarry
RA and Dudoit S: Springer-Verlag; New York: pp. 397–420. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology constortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Croft D, O'Kelly G, Wu G, Haw R, Gillespie
M, Matthews L, Caudy M, Garapati P, Gopinath G, Jassal B, et al:
Reactome: A database of reactions, pathways and biological
processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:(Database Issue). D691–D697. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huangda W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao M, Sun J and Zhao Z: TSGene: A web
resource for tumor suppressor genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D970–D976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen JS, Hung WS, Chan HH, Tsai SJ and Sun
HS: In silico identification of oncogenic potential of fyn-related
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 29:420–427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9. 1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maraziotis IA, Dimitrakopoulou K and
Bezerianos A: An in silico method for detecting overlapping
functional modules from composite biological networks. BMC Syst
Biol. 2:932008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saratsis AM, Yadavilli S, Magge S, Rood
BR, Perez J, Hill DA, Hwang E, Kilburn L, Packer RJ and Nazarian J:
Insights into pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma through
proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. Neuro Oncol. 14:547–560.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rehfeld JF, Friis-Hansen L, Goetze JP and
Hansen TV: The biology of cholecystokinin and gastrin peptides.
Curr Top Med Chem. 7:1154–1165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lefranc F, Camby I, Belot N, Bruyneel E,
Chaboteaux C, Brotchi J, Mareel M, Salmon I and Kiss R: Gastrin
significantly modifies the migratory abilities of experimental
glioma cells. Lab Invest. 82:1241–1252. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oikonomou E, Buchfelder M and Adams EF:
Cholecystokinin (CCK) and CCK receptor expression by human gliomas:
Evidence for an autocrine/paracrine stimulatory loop.
Neuropeptides. 42:255–265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dmitrenko V, Bojko O, Shostak K, Vitak NY,
Bukreeva T, Rozumenko V, Malysheva T, Shamayev M, Zozulya YP and
Kavsan VM: Characterization of genes, down-regulated in human
glioma, potential tumor suppressor genes. Biopolym Cell.
23:347–362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Harmar AJ: Family-B G-protein-coupled
receptors. Genome Biol. 2:REVIEWS30132001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shu M, Zhou Y, Zhu W, Zhang H, Wu S, Chen
J and Yan G: MicroRNA 335 is required for differentiation of
malignant glioma cells induced by activation of cAMP/protein kinase
A pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 81:292–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Smith AM and Watson SA: Gastrin and
gastrin receptor activation: An early event in the
adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Gut. 47:820–824. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paillasse MR, de Medina P, Amouroux G,
Mhamdi L, Poirot M and Silvente-Poirot S: Signaling through
cholesterol esterification: A new pathway for the cholecystokinin 2
receptor involved in cell growth and invasion. J Lipid Res.
50:2203–2211. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oswald P, Souery D and Mendlewicz J:
Molecular genetics of affective disorders. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 6:155–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jones C, Perryman L and Hargrave D:
Paediatric and adult malignant glioma: Close relatives or distant
cousins? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 9:400–413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chan KM, Fang D, Gan H, Hashizume R, Yu C,
Schroeder M, Gupta N, Mueller S, James CD, Jenkins R, et al: The
histone H3.3K27M mutation in pediatric glioma reprograms H3K27
methylation and gene expression. Genes Dev. 27:985–990. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Monteith GR, McAndrew D, Faddy HM and
Roberts-Thomson SJ: Calcium and cancer: Targeting Ca2+ transport.
Nat Rev Cancer. 7:519–530. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kang SS, Han KS, Ku BM, Lee YK, Hong J,
Shin HY, Almonte AG, Woo DH, Brat DJ, Hwang EM, et al:
Caffeine-mediated inhibition of calcium release channel inositol
1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor subtype 3 blocks glioblastoma invasion
and extends survival. Cancer Res. 70:1173–1183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ludwig MG and Seuwen K: Characterization
of the human adenylyl cyclase gene family: cDNA, gene structure,
and tissue distribution of the nine isoforms. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 22:79–110. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hagan JJ, Price GW, Jeffrey P, Deeks NJ,
Stean T, Piper D, Smith MI, Upton N, Medhurst AD, Middlemiss DN, et
al: Characterization of SB-269970-A, a selective 5-HT(7) receptor
antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 130:539–548. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang HT, Huang Y, Jin SL, Frith SA,
Suvarna N, Conti M and O'Donnell JM: Antidepressant-like profile
and reduced sensitivity to rolipram in mice deficient in the PDE4D
phosphodiesterase enzyme. Neuropsychopharmacology. 27:587–595.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schmidt M, Evellin S, Weernink PA, von
Dorp F, Rehmann H, Lomasney JW and Jakobs KH: A new
phospholipase-C-calcium signalling pathway mediated by cyclic AMP
and a Rap GTPase. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1020–1024. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|