Introduction
Milia appear on the face as multiple white globoid
papules, and is usually treated by evacuation with a comedone
extractor (1). It has been suggested
that milia may be derived from the lowest portion of the
infundibulum of vellus hairs at the level of the sebaceous duct
(2). However, the histogenesis and
origin of milia remain unclear. Milia typically appear on the face,
particularly in aged women, and may be formed by an obstruction of
the follicular infundibulum (1). A
previous study demonstrated that keratin, particularly K1, K10, K14
and K16, is expressed in milia (3).
In addition, it has been reported that milia occur due to the
cystic alteration of trichoepitheliomatous bulge proliferation
(4). In experimental
autotransplantation, milia may attach to the outer root sheath near
the insertion point of the arrector pili muscle (2). Therefore, milia may be originated from
hair bulge of the outer root sheath. The aim of our study is to
identify the origin of milia with immunohistochemical methods using
keratin and filaggrin.
Keratin is a useful marker to evaluate the origin of
epithelial tumors and filaggrin is a marker of terminal
differentiation (5). In normal hair
follicles, K10 and K1 are expressed in the infundibulum and
suprabasal epidermis (5). K14 is
expressed in all layers of the outer root sheath and infundibulum
and in the basal layer of the epidermis. K15 is expressed in the
outermost cells of the hair bulge, while K16 is expressed in the
outer root sheath beneath the opening of the sebaceous duct
(5). K17 is expressed in all layers
of the outer root sheath and in the infra-infundibulum (5). By contrast, filaggrin is expressed in
the superficial layer of the infundibulum (5). Therefore, it was hypothesized that milia
may originate from the hair bulge of outer root sheath. To
elucidate the histogenesis of milia, immunohistochemistry was
performed using anti-keratin and anti-filaggrin antibodies to
determine the expression of keratin and filaggrin.
Case report
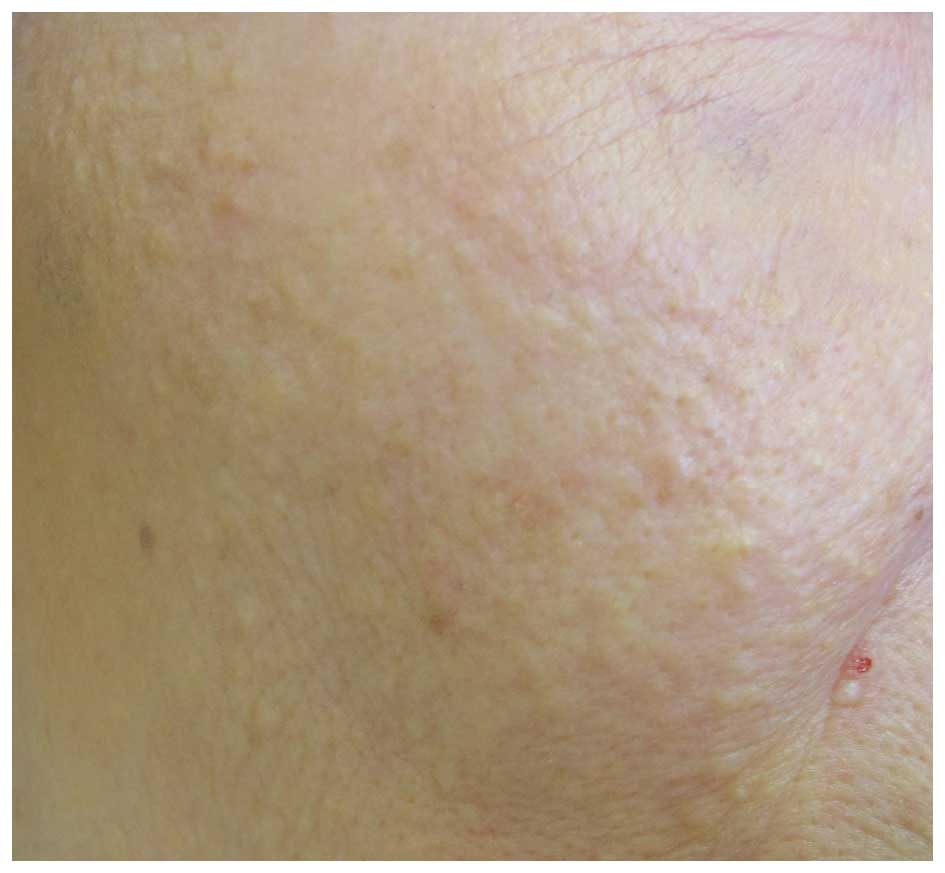
A 74-year-old woman presented to the Department of
Dermatology, Meiwa Hospital (Nishinomiya, Japan) on May 2015 with
multiple white papules on the face, which had persisted for 10
years (Fig. 1). Milia were diagnosed
by the clinical feature of facial white papules.
The skin biopsy was obtained from a white papule
under local anesthesia. The specimens were fixed with formalin,
embedded in paraffin, and cut into sections of 5-7-µm thickness.
Selected sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Analysis
of a skin biopsy resulted in the diagnosis of primary milia, with
hematoxylin and eosin staining indicating the presence of dilated
follicular cysts. The epithelial lining of the cyst walls consisted
of two sections: The more superficial and the deeper sections.
Keratohyalin granules were detected in the more superficial section
of the epithelial lining, but were not detected in the deeper
section. Hair germ structures were identified in the deeper section
of the epithelial lining.
On immunohistochemical examination for keratin and
filaggrin expression, the labeled streptavidin-biotin (LSAB) method
was used (Dako North America, Inc., Carpinteria, CA, USA). The
following mouse anti-human keratin antibodies were used in the
present study: 34βB4 (anti-K1; dilution 1:50), LP5K (anti-K7;
dilution 1:10), LP3K (anti-K8; dilution 1:50), HP1 (anti-K10;
dilution 1:50), LL002 (anti-K14; dilution 1:200), LHK15 (anti-K15;
dilution 1:40), LL025 (anti-K16; dilution 1:20), E3 (anti-K17;
dilution 1:25), 5D3 (anti-K18; dilution 1:20), b170 (anti-K19;
dilution 1:100), Ks 20.8 (anti-K20; dilution 1:25), and 15C10
(anti-filaggrin; dilution 1:50), all from Novocastra Laboratories
Ltd. (New castle upon Tyne, UK). The LSAB method was applied
according to the manufacturer's protocol. The levels of keratin
expression were assessed using anti-keratin antibodies against K1,
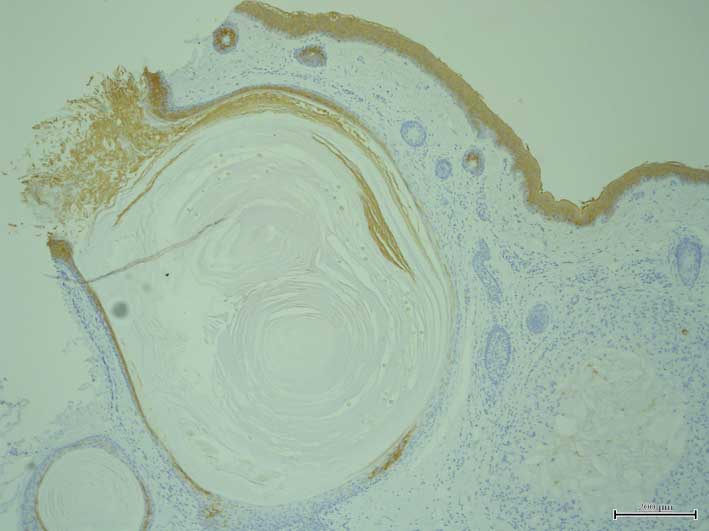
K7, K8, K10, K14, K15, K16, K17, K18, K19, K20 and filaggrin. K1
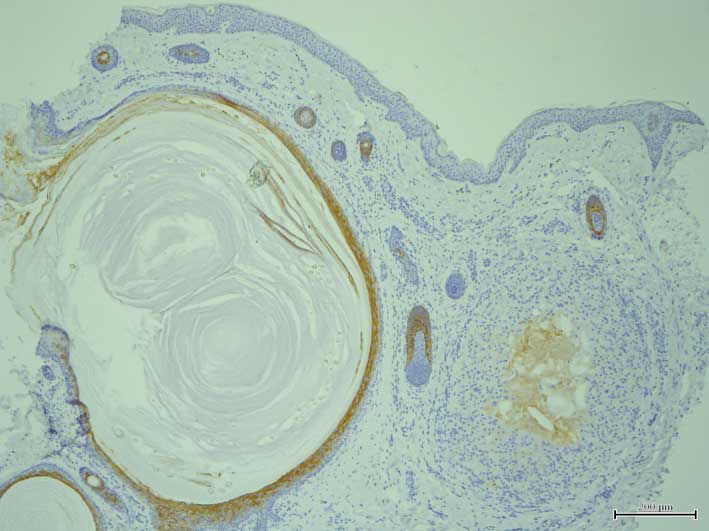
(Fig. 2) and K10 expression was
detected in the suprabasal layers of the more superficial section
of the cyst walls and their expression was attenuated in the deeper
sections. By contrast, K14 expression was observed in all layers of
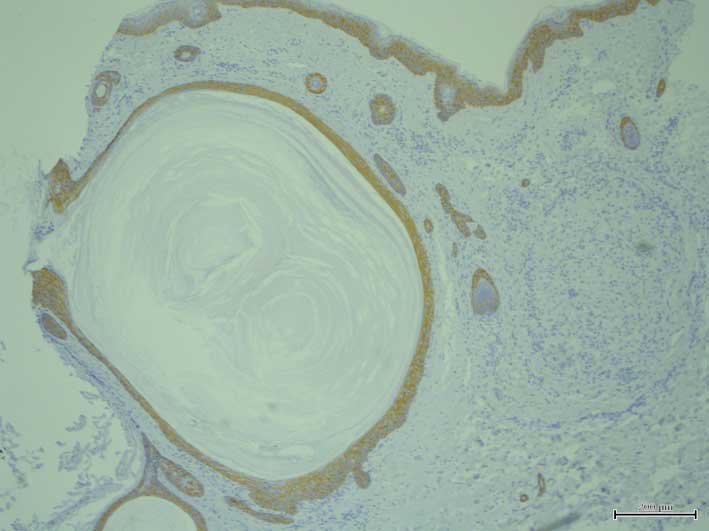
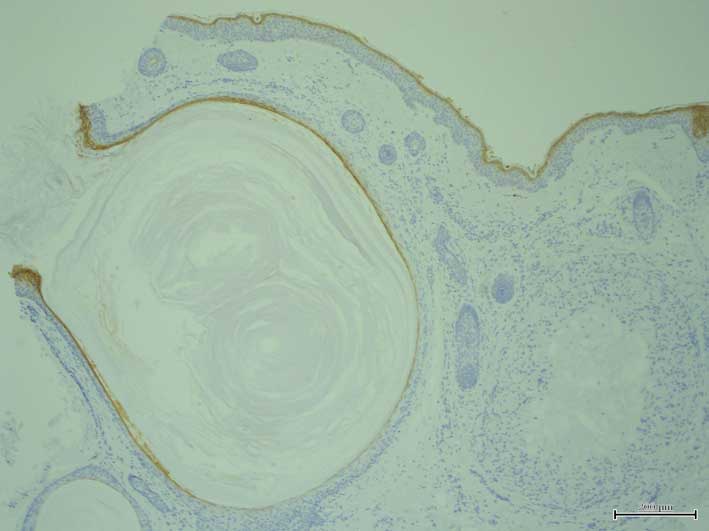
the cyst walls (Fig. 3). Notably, K15
was expressed in the outermost layer of the deeper area of the cyst
walls and hair germ structures (Fig.
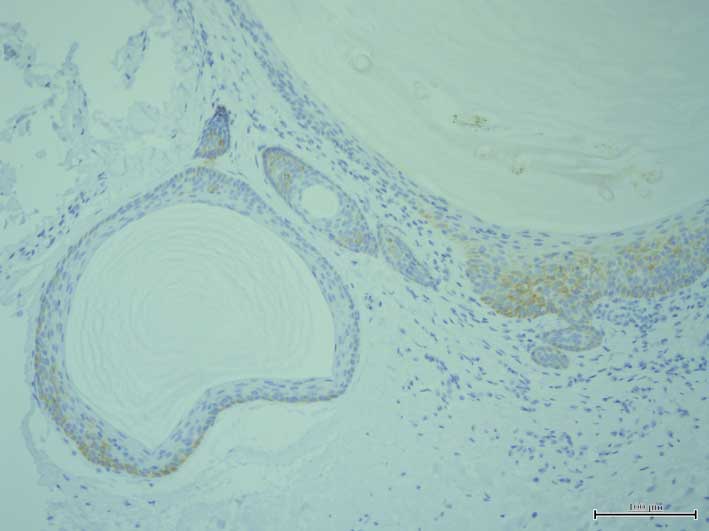
4), while K17 was expressed in all layers of the cyst walls
(Fig. 5). The expression of other
keratins was not detected in the cyst walls. Filaggrin was
expressed in the superficial layer of the more superficial sections
of the cyst walls (Fig. 6). The milia
were treated with adapalene. However, no remarkable change was
observed and the treatment was discontinued.
Discussion
Milia are derived from the lowest portion of the
infundibulum of vellus hairs at the level of the sebaceous duct
(1). The current study demonstrated
that K1 and K10 were expressed in the more superficial sections of
the cyst walls, and that filaggrin expression was detected in the
more superficial part of the cyst walls, while K15 and K17 were
expressed in the deeper sections of the cyst walls. K14 expression
was detected in all cyst wall layers. In addition, it was observed
that K16 was not expressed in milia. This is different from the
results of a previous study (3) and
may be explained by the diversified heterogeneity of milia
differentiation. It is possible that the present case may not be a
conventional example of milia and that individual differences
between various cases of milia may exist.
Regarding the previously described pattern of
keratin expression in normal hair follicles (5), the current study revealed that keratin
expression in the more superficial section of the cyst wall is the
same as that of the infundibulum, and that its expression in the
deeper section is the same as that of the hair bulge of the outer
root sheath. These results suggested that keratin and filaggrin
expression in milia correspond to the more superficial section of
the infundibulum and the outermost layer of the hair bulge,
respectively. Furthermore, K15, a stem pluripotent cell marker, is
expressed in the outermost layer in normal hair follicles (5). K15 was present in the outermost layer of
the deeper section of cyst walls and hair germ structures in the
present study. In trichoepithelioma, K15 expression is observed
(6). A previous study demonstrated
that milia were the result of cystic alteration of the
trichoepitheliomatous bulge proliferation (4).
In conclusion, the present study reported a case of
milia with an immunohistological evaluation of keratin and
filaggrin expression. According to the pattern of keratin and
filaggrin expression observed in the current study, milia may
originate from the outermost cells of the hair bulge of the outer
root sheath. Further studies concerning keratin and filaggrin
expression in milia are necessary to confirm this hypothesis.
References
|
1
|
Berk DR and Bayliss SJ: Milia: A review
and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 59:1050–1063. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Epstein W and Kligman AM: The pathogenesis
of milia and benign tumors of the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 26:1–11.
1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Broekaert D, Leigh IM, Lane EB, Van Muijen
GN, Ramaekers FC, De Bersaques J and Coucke P: An
immunohistochemical and histochemical study of cytokeratin,
involucrin and transglutaminase in seborrhoeic keratosis. Arch
Dermatol Res. 285:482–490. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van der Putte SC: The pathogenesis of
familial multiple cylindromas, trichoepitheliomas, milia, and
spiradenomas. Am J Dermatopathol. 17:271–280. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kurokawa I, Takahashi K, Moll I and Moll
R: Expression of keratins in cutaneous epithelial tumors and
related disorders-distribution and clinical significance. Exp
Dermatol. 20:217–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanitakis J, Bourchany D, Faure M and
Claudy A: Expression of the hair stem cell-specific keratin 15 in
pilar tumors of the skin. Eur J Dermatol. 9:363–365.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|