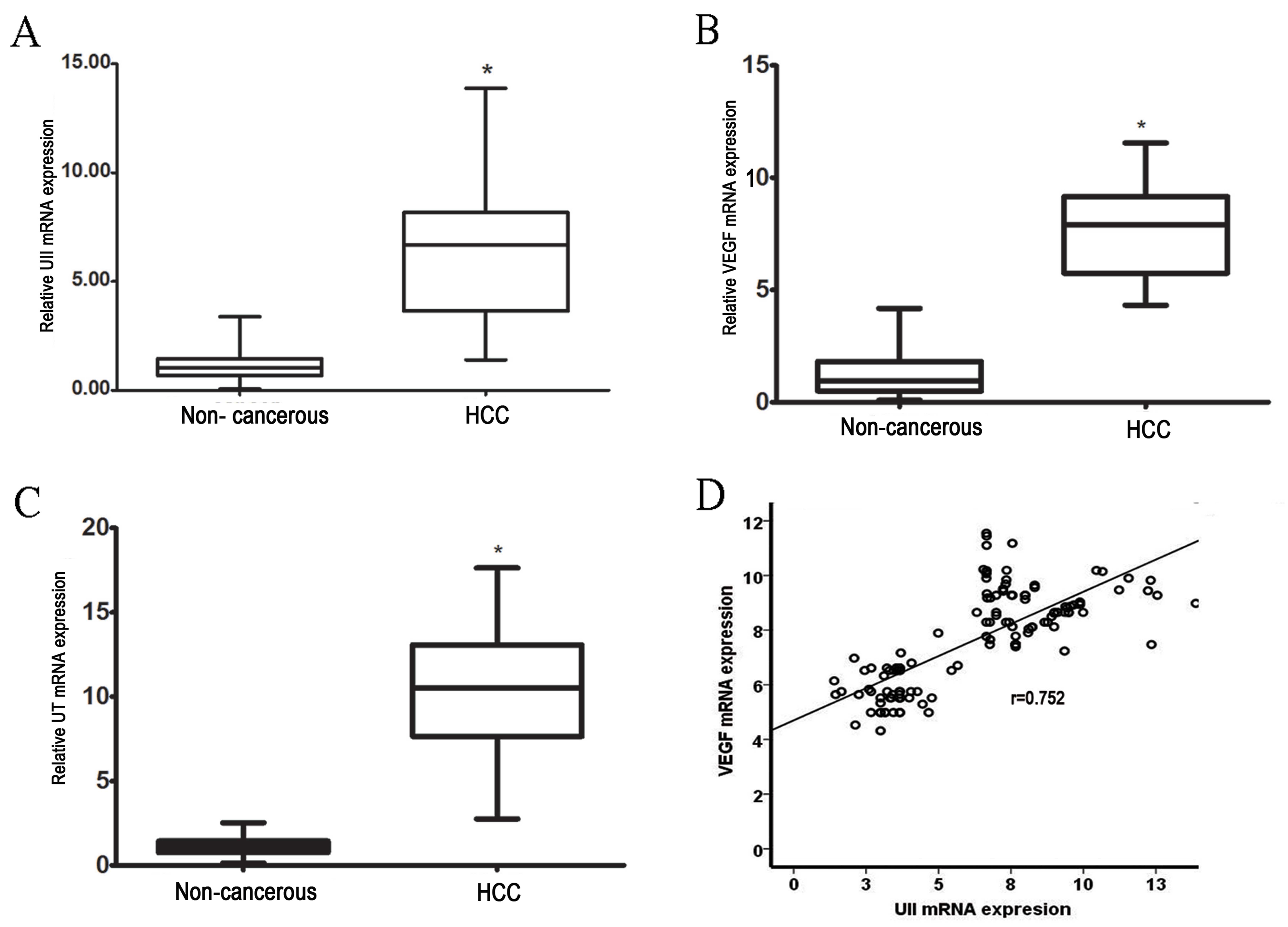
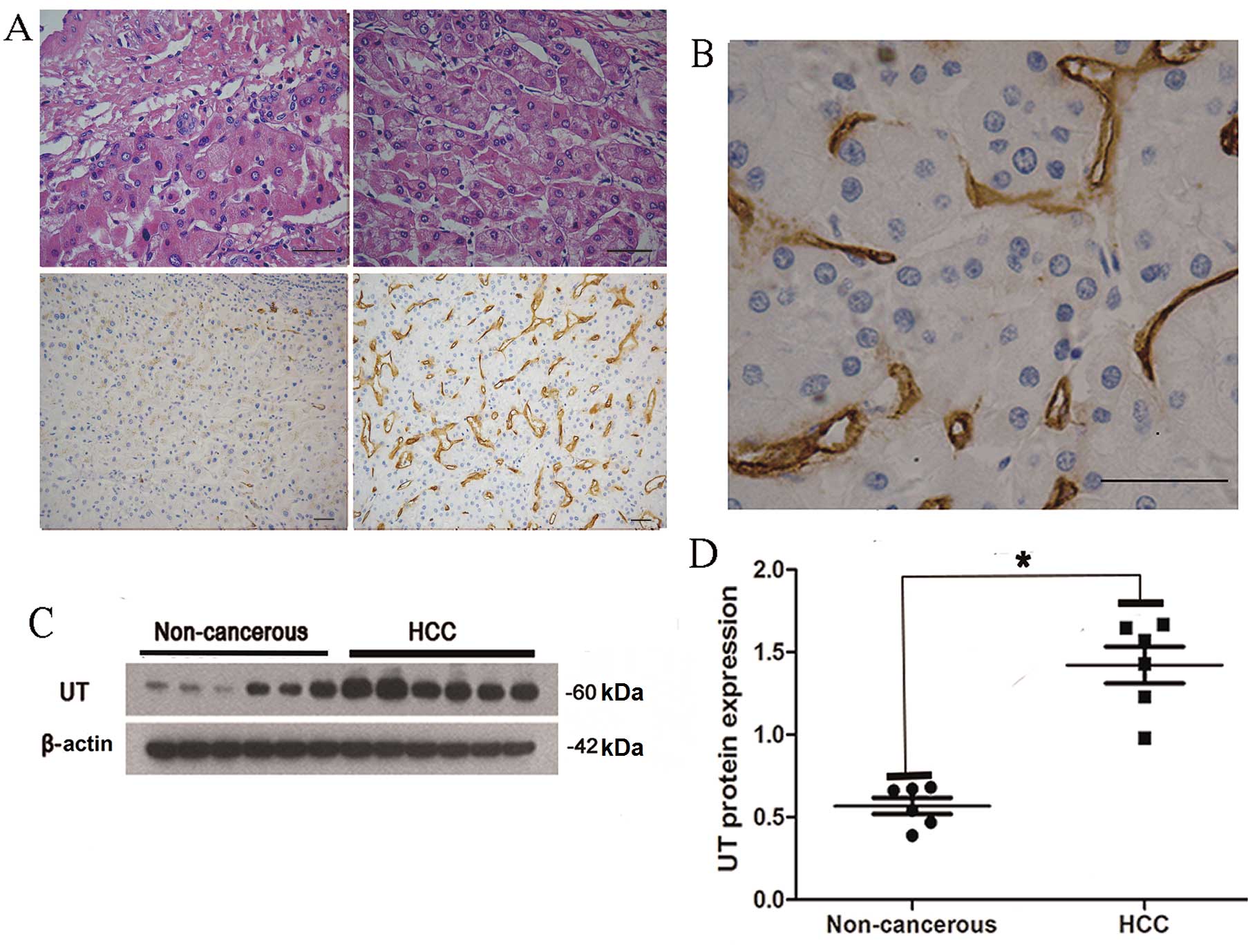
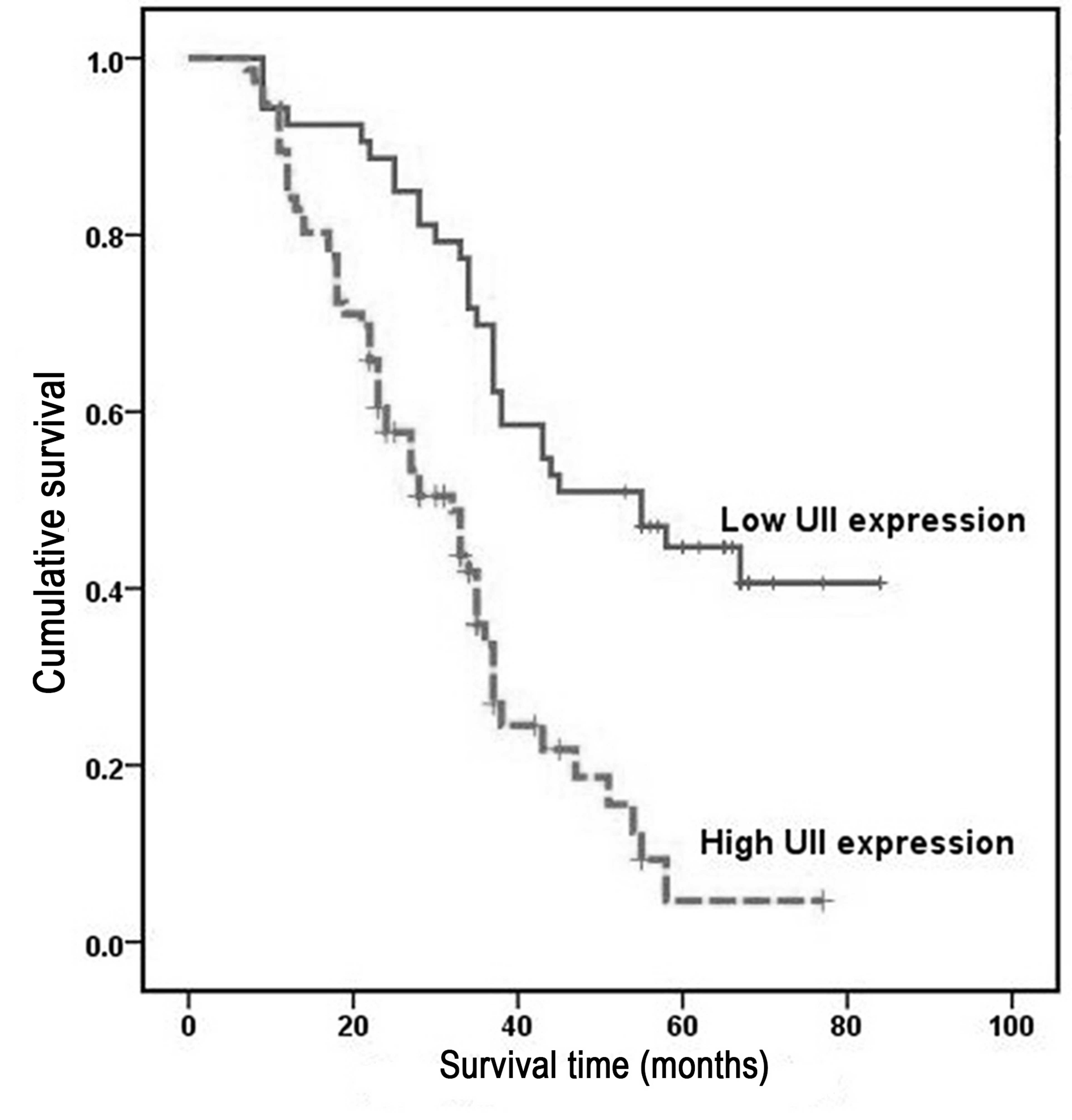
|
1
|
Chow PK, Choo SP, Ng DC, Lo RH, Wang ML,
Toh HC, Tai DW, Goh BK, Wong JS, Tay KH, et al: National cancer
centre singapore consensus guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Liver Cancer. 5:97–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig
AB, Fleshman JM and Matrisian LM: Projecting cancer incidence and
deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and
pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74:2913–2921.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bodzin AS and Busuttil RW: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Advances in diagnosis, management, and long term
outcome. World J Hepatol. 7:1157–1167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1312–1327.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peck-Radosavljevic M: Drug therapy for
advanced-stage liver cancer. Liver cancer. 3:125–131. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Albertin G, Guidolin D, Sorato E,
Oselladore B, Tortorella C and Ribatti D: Urotensin-II-stimulated
expression of pro-angiogenic factors in human vascular endothelial
cells. Regul Pept. 172:16–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yumrutas O, Oztuzcu S, Büyükhatipoglu H,
Bozgeyik I, Bozgeyik E, Igci YZ, Bagis H, Cevik MO, Kalender ME,
Eslik Z and Arslan A: The role of the UTS2 gene polymorphisms and
plasma Urotensin-II levels in breast cancer. Tumor Bio.
36:4427–4432. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Franco R, Zappavigna S, Gigantino V, Luce
A, Cantile M, Cerrone M, Facchini G, Perdonà S, Pignata S, Di
Lorenzo G, et al: Urotensin II receptor determines prognosis of
bladder cancer regulating cell motility/invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 33:482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Federico A, Zappavigna S, Romano M, Grieco
P, Luce A, Marra M, Gravina AG, Stiuso P, D'Armiento FP, Vitale G,
et al: Urotensin-II receptor is over-expressed in colon cancer cell
lines and in colon carcinoma in humans. Eur J Clin Invest.
44:285–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grieco P, Franco R, Bozzuto G, Toccacieli
L, Sgambato A, Marra M, Zappavigna S, Migaldi M, Rossi G, Striano
S, et al: Urotensin II receptor predicts the clinical outcome of
prostate cancer patients and is involved in the regulation of
motility of prostate adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem.
112:341–353. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ames RS, Sarau HM, Chambers JK, Willette
RN, Aiyar NV, Romanic AM, Louden CS, Foley JJ, Sauermelch CF,
Coatney RW, et al: Human urotensin-II is a potent vasoconstrictor
and agonist for the orphan receptor GPR14. Nature. 401:282–286.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takahashi K, Totsune K, Murakami O,
Arihara Z, Noshiro T, Hayashi Y and Shibahara S: Expression of
urotensin II and its receptor in adrenal tumors and stimulation of
proliferation of cultured tumor cells by urotensin II. Peptides.
24:301–306. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takahashi K, Totsune K, Murakami O and
Shibahara S: Expression of urotensin II and urotensin II receptor
mRNAs in various human tumor cell lines and secretion of urotensin
II-like immunoreactivity by SW-13 adrenocortical carcinoma cells.
Peptides. 22:1175–1179. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang H, Dong K, Xue X, Feng P and Wang X:
Elevated expression of urotensin II and its receptor in
diethylnitrosamine-mediated precancerous lesions in rat liver.
Peptides. 32:382–387. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu D, Chen J, Wang J, Zhang Z, Ma X, Jia
J and Wang Y: Increased expression of urotensin II and GPR14 in
patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Int J Mol Med.
25:845–851. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu XT, Wang PY, Shi ZM, Dong K, Feng P,
Wang HX and Wang XJ: Up-regulation of urotensin ii and its receptor
contributes to human hepatocellular carcinoma growth via activation
of the PKC, ERK1/2, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Molecules.
19:20768–20779. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shariff MI, Cox IJ, Gomaa AI, Khan SA,
Gedroyc W and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and
therapeutics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:353–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lei HJ, Chau GY, Lui WY, Tsay SH, King KL,
Loong CC and Wu CW: Prognostic value and clinical relevance of the
6th Edition 2002 American joint committee on cancer staging system
in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll
Surg. 203:426–435. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pirisi M, Leutner M, Pinato DJ, Avellini
C, Carsana L, Toniutto P, Fabris C and Boldorini R: Reliability and
reproducibility of the edmondson grading of hepatocellular
carcinoma using paired core biopsy and surgical resection
specimens. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 134:1818–1822. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang SB, Wang JH, Chen J, Giri RK and Chen
MH: Natural history of liver cirrhosis in south China based on a
large cohort study in one center: A follow-up study for up to 5
years in 920 patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:2157–2162.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bagnato A and Catt KJ: Endothelins as
autocrine regulators of tumor cell growth. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
9:378–383. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou CH, Wan YY, Chu XH, Song Z, Xing SH,
Wu YQ and Yin XX: Urotensin II contributes to the formation of lung
adenocarcinoma inflammatory microenvironment through the NF-κB
pathway in tumor-bearing nude mice. Oncol Lett. 4:1259–1263.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dai J and Rabie AB: VEGF: An essential
mediator of both angiogenesis and endochondral ossification. J Dent
Res. 86:937–950. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shibuya M: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and its receptor system: Physiological functions in
angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J Biochem.
153:13–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mukozu T, Nagai H, Matsui D, Kanekawa T
and Sumino Y: Serum VEGF as a tumor marker in patients with
HCV-related liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 33:1013–1021. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marra M, Sordelli IM, Lombardi A, Lamberti
M, Tarantino L, Giudice A, Stiuso P, Abbruzzese A, Sperlongano R,
Accardo M, et al: Molecular targets and oxidative stress biomarkers
in hepatocellular carcinoma: An overview. J Transl Med. 9:1712011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Colombino M, Sperlongano P, Izzo F,
Tatangelo F, Botti G, Lombardi A, Accardo M, Tarantino L, Sordelli
I, Agresti M, et al: BRAF and PIK3CA genes are somatically mutated
in hepatocellular carcinoma among patients from South Italy. Cell
Death Dis. 3:e2592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Caraglia M, Giuberti G, Marra M, Addeo R,
Montella L, Murolo M, Sperlongano P, Vincenzi B, Naviglio S, Prete
SD, et al: Oxidative stress and ERK1/2 phosphorylation as
predictors of outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated
with sorafenib plus octreotide LAR. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1502011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Scognamiglio PL, Di Natale C, Perretta G
and Marasco D: From peptides to small molecules: An intriguing but
intricated way to new drugs. Curr Med Chem. 20:3803–3817. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|