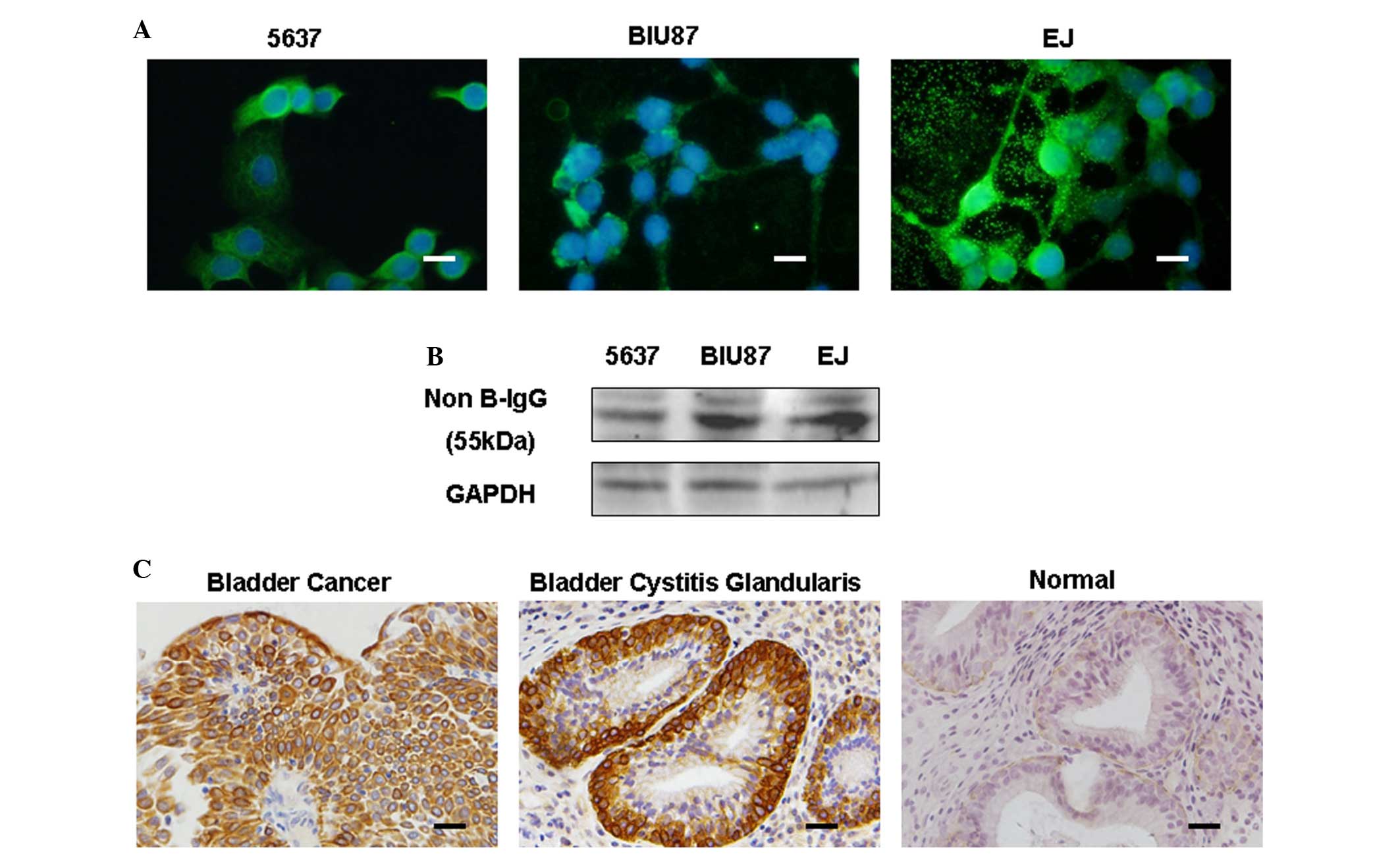
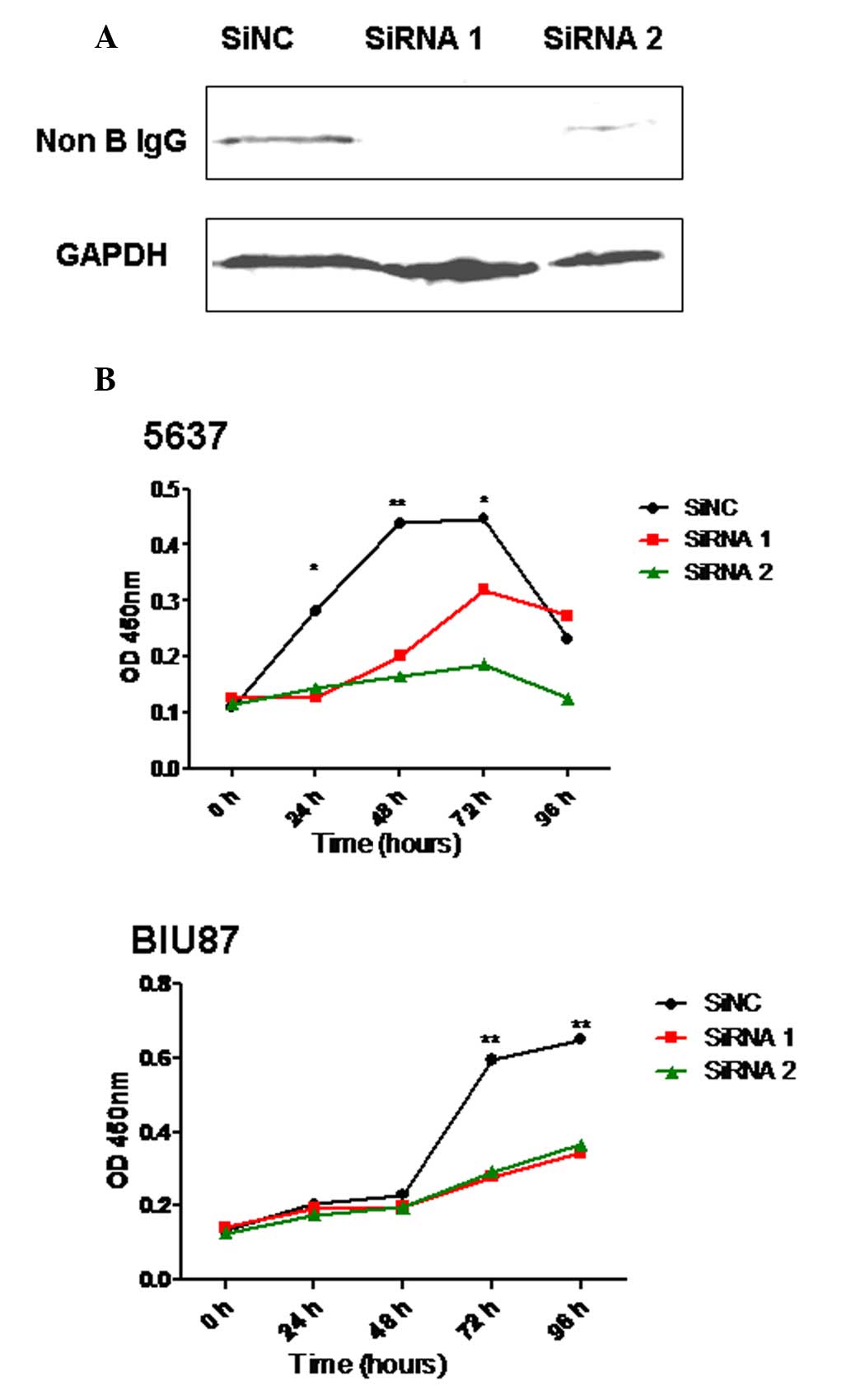
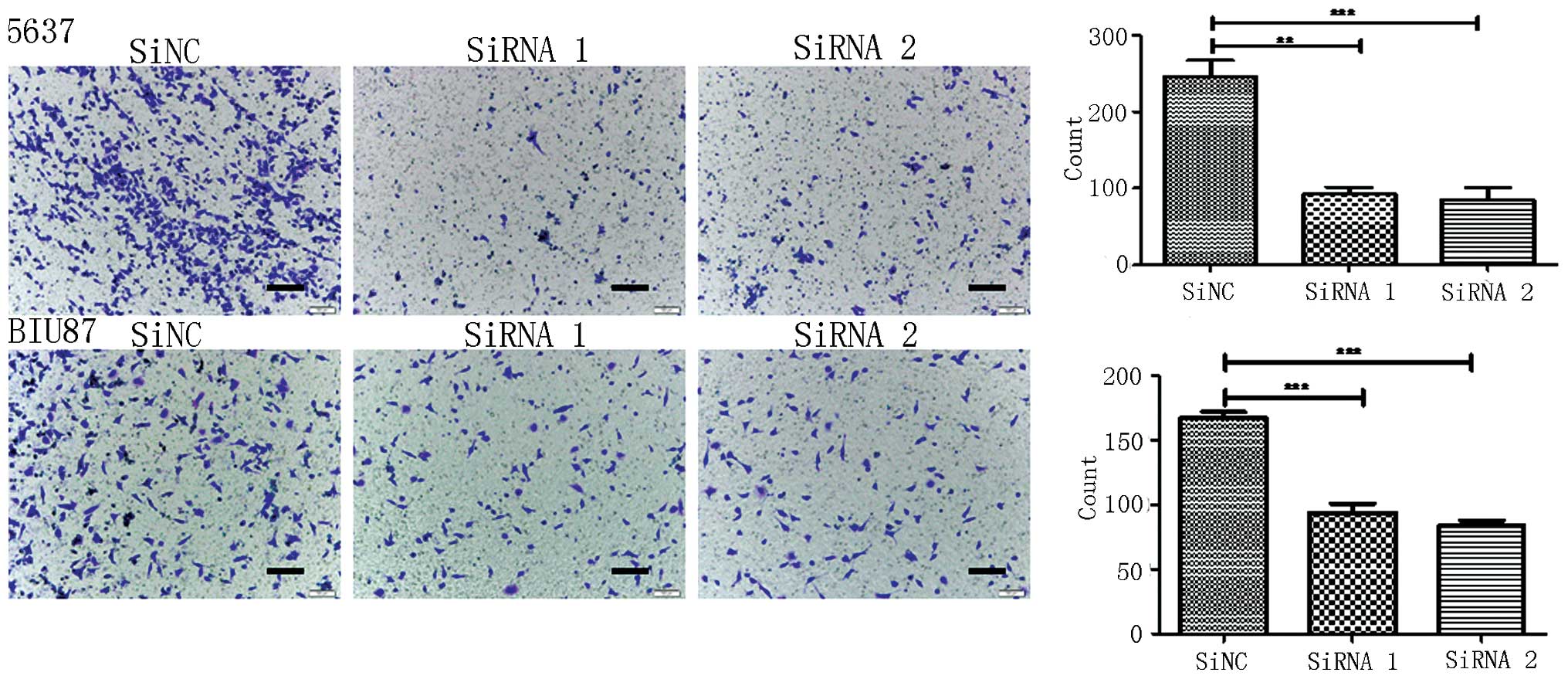
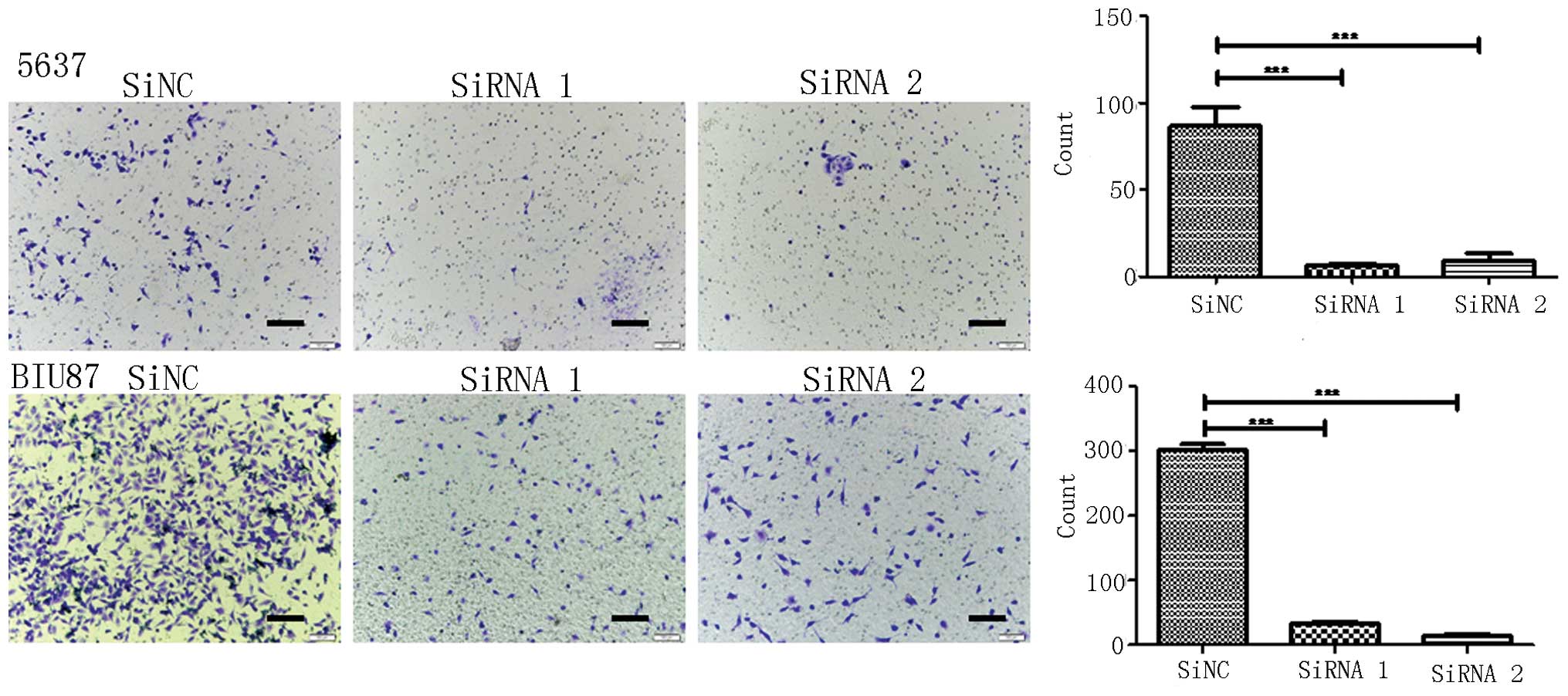
|
1
|
Bos MK, Marmolejo RO, Rasch CR and Pieters
BR: Bladder preservation with brachytherapy compared to cystectomy
for T1-T3 muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review. J
Contemp Brachytherapy. 6:191–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seitz M, Zaak D, Knuchel-Clarke R and
Stief C: Urinary bladder tumours. The new 2004 WHO classification.
Urologe A. 44:1073–1086. 2005.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Das S, Hirano M, Tako R, McCallister C and
Nikolaidis N: Evolutionary genomics of immunoglobulin-encoding Loci
in vertebrates. Curr Genomics. 13:95–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hirano M, Guo P, McCurley N, Schorpp M,
Das S, Boehm T and Cooper MD: Evolutionary implications of a third
lymphocyte lineage in lampreys. Nature. 501:435–438. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qiu X, Zhu X, Zhang L, Mao Y, Zhang J, Hao
P, Li G, Lv P, Li Z, Sun X, et al: Human epithelial cancers secrete
immunoglobulin g with unidentified specificity to promote growth
and survival of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 63:6488–6495.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang J, Sun X, Mao Y, Zhu X, Zhang P,
Zhang L, Du J and Qiu X: Expression of immunoglobulin gene with
classical V-(D)-J rearrangement in mouse brain neurons. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1604–1615. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Welinder C, Baldetorp B, Blixt O, Grabau D
and Jansson B: Primary breast cancer tumours contain high amounts
of IgA1 immunoglobulin: An immunohistochemical analysis of a
possible carrier of the tumour-associated Tn antigen. PLoS One.
8:e617492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Upender MB, Dunn JA, Wilson SM and Naegele
JR: Immunoglobulin molecules are present in early-generated
neuronal populations in the rat cerebral cortex and retina. J Comp
Neurol. 384:271–282. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang J, Zhang L, Ma T, Zhang P and Qiu X:
Expression of immunoglobulin gene with classical V-(D)-J
rearrangement in mouse testis and epididymis. J Histochem Cytochem.
57:339–349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng S, Cao J and Geng L: Structure and
expression of colorectal cancer related Immunoglobulin novel gene
SNC73. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 81:485–488. 2001.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Z and Gu J: Immunoglobulin G
expression in carcinomas and cancer cell lines. FASEB J.
21:2931–2938. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Z, Huang X, Ye J, Pan P, Cao Q, Yang
B, Li Z, Su M, Huang C and Gu J: Immunoglobulin G is present in a
wide variety of soft tissue tumors and correlates well with
proliferation markers and tumor grades. Cancer. 116:1953–1963.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang C, Huang T, Wang Y, Huang G, Wan X
and Gu J: Immunoglobulin G expression in lung cancer and its
effects on metastasis. PLoS One. 9:e973592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Liu D, Wang C, Liao Q, Huang J,
Jiang D, Shao W, Yin CC, Zhang Y, Lee G and Qiu X: Binding of the
monoclonal antibody RP215 to immunoglobulin G in metastatic lung
adenocarcinomas is correlated with poor prognosis. Histopathology.
67:645–653. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gritzmacher CA: Molecular aspects of
heavy-chain class switching. Crit Rev Immunol. 9:173–200.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng J, Huang J, Mao Y, Liu S, Sun X, Zhu
X, Ma T, Zhang L, Ji J, Zhang Y, et al: Immunoglobulin gene
transcripts have distinct VHDJH recombination characteristics in
human epithelial cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:13610–13619. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang S, Mao Y, Huang J, Ma T, Zhang L,
Zhu X, Zheng J, Wu L, Yin CC and Qiu X: Immunoglobulin gene locus
events in epithelial cells of lactating mouse mammary glands. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 67:985–994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang J, Sun X, Gong X, He Z, Chen L, Qiu
X and Yin CC: Rearrangement and expression of the immunoglobulin
µ-chain gene in human myeloid cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 11:94–104.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee G, Laflamme E, Chien CH and Ting HH:
Molecular identity of a pan cancer marker, CA215. Cancer Biol Ther.
7:2007–2014. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee G: Cancer cell-expressed
immunoglobulins: CA215 as a pan cancer marker and its diagnostic
applications. Cancer Biomark. 5:137–142. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee G, Chu RA and Ting HH: Preclinical
assessment of anti-cancer drugs by using RP215 monoclonal antibody.
Cancer Biol Ther. 8:161–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee G and Ge B: Cancer cell expressions of
immunoglobulin heavy chains with unique carbohydrate-associated
biomarker. Cancer Biomark. 5:177–188. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang PY, Li HY, Zhou ZY, Jin YX, Wang SX,
Peng XH and Ou SJ: Overexpression of immunoglobulin G prompts cell
proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in human urothelial
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:1783–1791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Connor KC, Nguyen K and Stollar BD:
Recognition of DNA by VH and Fv domains of an IgG anti-poly(dC)
antibody with a singly mutated VH domain. J Mol Recognit. 14:18–28.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li W, Yu R, Ma B, Yang Y, Jiao X, Liu Y,
Cao H, Dong W, Liu L, Ma K, et al: Core fucosylation of IgG B cell
receptor is required for antigen recognition and antibody
production. J Immunol. 194:2596–2606. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoshimi K, Woo M, Son Y, Baudry M and
Thompson RF: IgG-immunostaining in the intact rabbit brain:
Variable but significant staining of hippocampal and cerebellar
neurons with anti-IgG. Brain Res. 956:53–66. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hozumi N and Tonegawa S: Evidence for
somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes coding for variable
and constant regions. 1976 [classical article]. J Immunol.
173:4260–4264. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Adamovic T, McAllister D, Guryev V, Wang
X, Andrae JW, Cuppen E, Jacob HJ and Sugg SL: Microalterations of
inherently unstable genomic regions in rat mammary carcinomas as
revealed by long oligonucleotide array-based comparative genomic
hybridization. Cancer Res. 69:5159–5167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer, . World Cancer Report 2014. Stewart BW and Wild CP: WHO
Press; Geneva, Switzerland: pp. 418–419. 2015
|
|
31
|
Chung CK, Stryker JA, Ward SP, Nahhas WA
and Mortel R: Histologic grade and prognosis of carcinoma of the
cervix. bstet Gynecol. 57:636–642. 1981.
|
|
32
|
Lodde M, Mian C, Mayr R, Comploj E, Trenti
E, Melotti R, Campodonico F, Maffezzini M, Fritsche HM and Pycha A:
Recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle invasive
bladder cancer: prognostic models including multicolor fluorescence
in situ hybridization molecular grading. Int J Urol. 21:968–972.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Droller MJ: Tumor size predicts the
survival of patients with pathologic stage T2 bladder carcinoma: A
critical evaluation of the depth of muscle invasion. J Urol.
163:665–666. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|