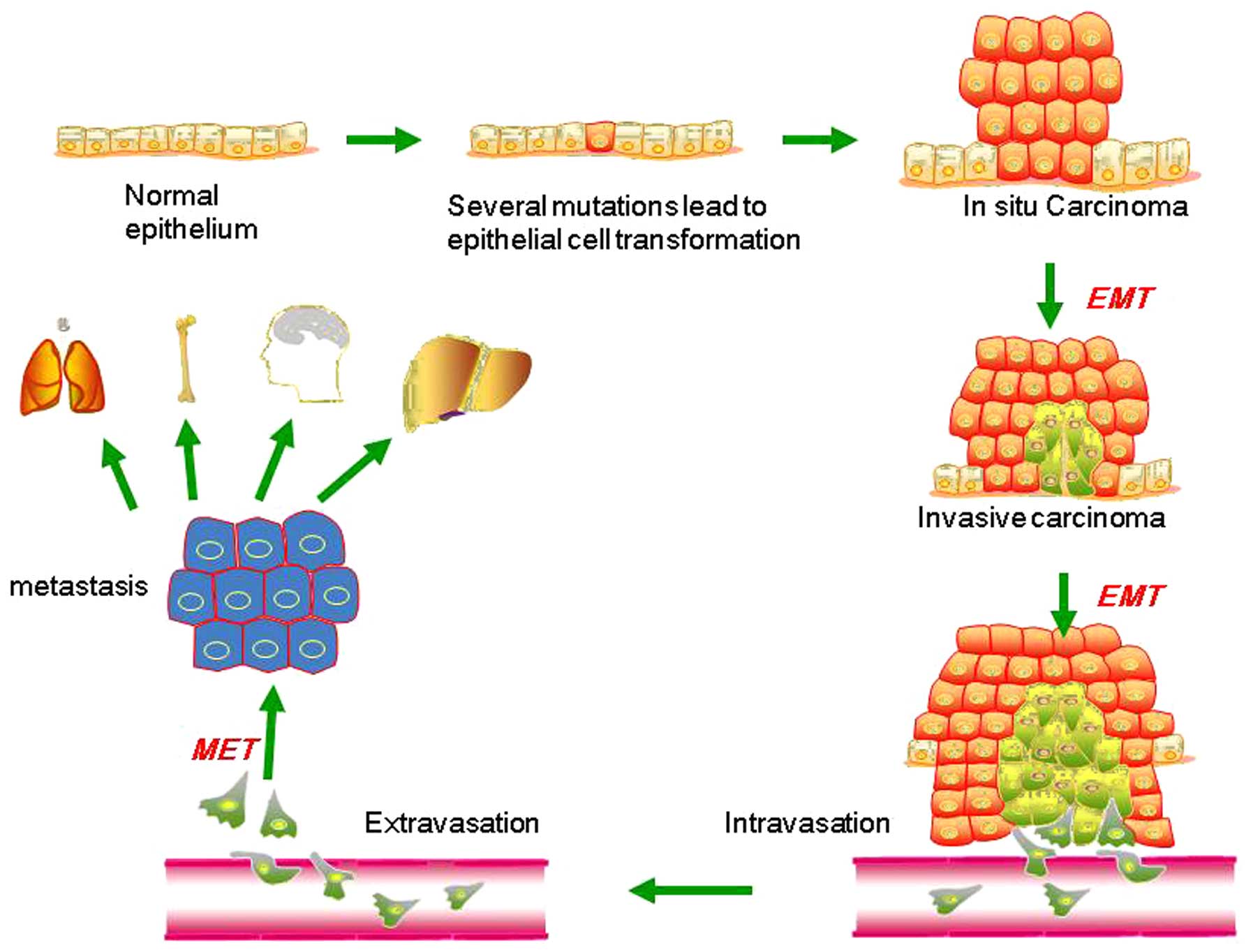
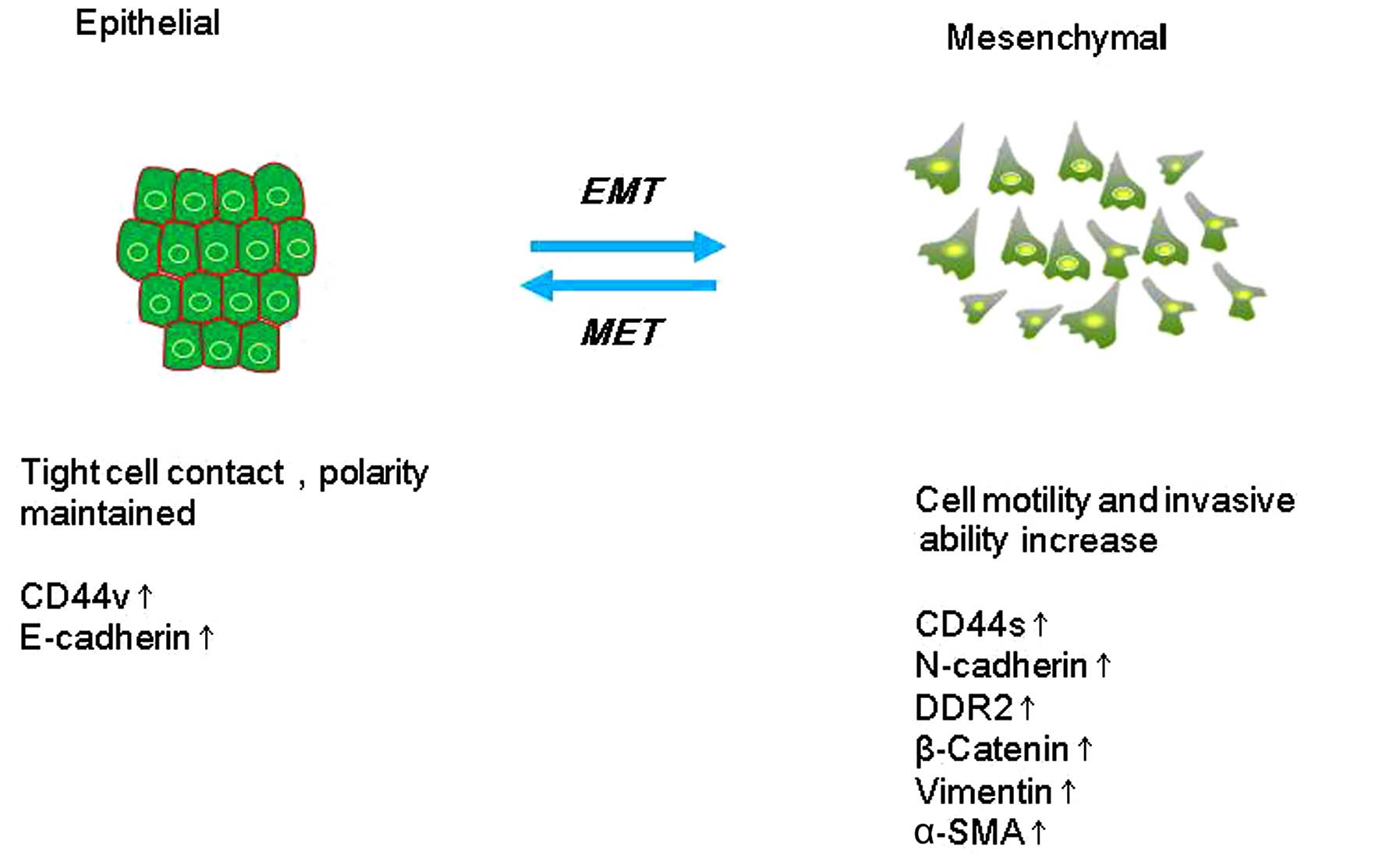
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Cli. 61:409–418. 2011.
|
|
3
|
O'Shaughnessy J: Extending survival with
chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 10:(Suppl 3).
S20–S29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Creighton CJ, Chang JC and Rosen JM:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in tumor-initiating cells
and its clinical implications in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 15:253–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF and Liotta LA:
General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer 80 (Suppl). 1529–1537.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua
P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S and Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis:
A new significant and independent prognostic indicator in
early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Ins. 84:1875–1887.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J
Biol chem. 267:10931–10934. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Folkman J: The role of angiogenesis in
tumor growth. S Cancer Biol. 3:65–71. 1992.
|
|
11
|
Chao YL, Shepard CR and Wells A: Breast
carcinoma cells re-express E-cadherin during mesenchymal to
epithelial reverting transition. Mol Cancer. 9:1792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaffer CL, Brennan JP, Slavin JL, Blick
T, Thompson EW and Williams ED: Mesenchymal-to-epithelial
transition facilitates bladder cancer metastasis: Role of
fibroblast growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res. 66:11271–11278.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chaffer CL, Thompson EW and Williams ED:
Mesenchymal to epithelial transition in development and disease.
Cells Tissues Organs. 185:7–19. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hyafil F, Babinet C and Jacob F: Cell-cell
interactions in early embryogenesis: A molecular approach to the
role of calcium. Cell. 26:447–454. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cavallaro U and Christofori G: Cell
adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:118–132. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hay ED and Zuk A: Transformations between
epithelium and mesenchyme: Normal, pathological, and experimentally
induced. Am J Kidney Dis. 26:678–690. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vleminckx K, Vakaet L Jr, Mareel M, Fiers
W and van Roy F: Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by
epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell.
66:107–119. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perl AK, Wilgenbus P, Dahl U, Semb H and
Christofori G: A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from
adenoma to carcinoma. Nature. 392:190–193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Canel M, Serrels A, Frame MC and Brunton
VG: E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and
metastasis. J Cell Sci. 126:393–401. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heimann R, Lan F, McBride R and Hellman S:
Separating favorable from unfavorable prognostic markers in breast
cancer: The role of E-cadherin. Cancer Res. 60:298–304.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hunt NC, Douglas-Jones AG, Jasani B,
Morgan JM and Pignatelli M: Loss of E-cadherin expression
associated with lymph node metastases in small breast carcinomas.
Virchows Arch. 430:285–289. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oka H, Shiozaki H, Kobayashi K, Inoue M,
Tahara H, Kobayashi T, Takatsuka Y, Matsuyoshi N, Hirano S and
Takeichi M: Expression of E-cadherin cell adhesion molecules in
human breast cancer tissues and its relationship to metastasis.
Cancer Res. 53:1696–1701. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Siitonen SM, Kononen JT, Helin HJ, Rantala
IS, Holli KA and Isola JJ: Reduced E-cadherin expression is
associated with invasiveness and unfavorable prognosis in breast
cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 105:394–402. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mahler-Araujo B, Savage K, Parry S and
Reis-Filho JS: Reduction of E-cadherin expression is associated
with non-lobular breast carcinomas of basal-like and triple
negative phenotype. J Clin Pathol. 61:615–620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lopes N, Carvalho J, Durães C, Sousa B,
Gomes M, Costa JL, Oliveira C, Paredes J and Schmitt F: 1Alpha,
25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces de novo E-cadherin expression in
triple-negative breast cancer cells by CDH1-promoter demethylation.
Anticancer Res. 32:249–257. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi Y, Lee HJ, Jang MH, Gwak JM, Lee KS,
Kim EJ, Kim HJ, Lee HE and Park SY: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition increases during the progression of in situ to invasive
basal-like breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 44:2581–2589. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gravdal K, Halvorsen OJ, Haukaas SA and
Akslen LA: A switch from E-cadherin to N-cadherin expression
indicates epithelial to mesenchymal transition and is of strong and
independent importance for the progress of prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:7003–7011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chao Y, Wu Q, Acquafondata M, Dhir R and
Wells A: Partial mesenchymal to epithelial reverting transition in
breast and prostate cancer metastases. Cancer Microenviron:.
5:19–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brown RL, Reinke LM, Damerow MS, Perez D,
Chodosh LA, Yang J and Cheng C: CD44 splice isoform switching in
human and mouse epithelium is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest.
121:1064–1074. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leth-Larsen R, Lund R, Hansen HV,
Laenkholm AV, Tarin D, Jensen ON and Ditzel HJ: Metastasis-related
plasma membrane proteins of human breast cancer cells identified by
comparative quantitative mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics.
8:1436–1449. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vogel W, Gish GD, Alves F and Pawson T:
The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by
collagen. Mol Cell. 1:13–23. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M,
Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT,
Roberts AB, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Goldsmith EC, Hoffman A, Morales MO, Potts
JD, Price RL, McFadden A, Rice M and Borg TK: Organization of
fibroblasts in the heart. Dev Dyn. 230:787–794. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yan Z, Jin S, Wei Z, Huilian H, Zhanhai Y,
Yue T, Juan L, Jing L, Libo Y and Xu L: Discoidin domain receptor 2
facilitates prostate cancer bone metastasis via regulating
parathyroid hormone-related protein. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1842:1350–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Evtimova V, Zeillinger R and Weidle UH:
Identification of genes associated with the invasive status of
human mammary carcinoma cell lines by transcriptional profiling.
Tumor Biol. 24:189–198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang K, Corsa CA, Ponik SM, Prior JL,
Piwnica-Worms D, Eliceiri KW, Keely PJ and Longmore GD: The
collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor 2 stabilizes SNAIL1 to
facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 15:677–687.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ren T, Zhang W, Liu X, Zhao H, Zhang J,
Zhang J, Li X, Zhang Y, Bu X, Shi M, et al: Discoidin domain
receptor 2 (DDR2) promotes breast cancer cell metastasis and the
mechanism implicates epithelial-mesenchymal transition programme
under hypoxia. J Pathol. 234:526–537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bienz M: beta-Catenin: A pivot between
cell adhesion and Wnt signalling. Curr Biol. 15:R64–R67. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brabletz T, Jung A, Hermann K, Günther K,
Hohenberger W and Kirchner T: Nuclear overexpression of the
oncoprotein beta-catenin in colorectal cancer is localized
predominantly at the invasion front. Pathol Res Pract. 194:701–704.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Prasad CP, Rath G, Mathur S, Bhatnagar D,
Parshad R and Ralhan R: Expression analysis of E-cadherin, Slug and
GSK3beta in invasive ductal carcinoma of breast. BMC Cancer.
9:3252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li L, Liu C, Amato RJ, Chang JT, Du G and
Li W: CDKL2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast
cancer progression. Oncotarget. 5:10840–10853. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scanlon CS, Van Tubergen EA, Inglehart RC
and D'Silva NJ: Biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res. 92:114–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Raymond WA and Leong AS: Vimentin - a new
prognostic parameter in breast carcinoma? J Pathol. 158:107–114.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bindels S, Mestdagt M, Vandewalle C,
Jacobs N, Volders L, Noël A, van Roy F, Berx G, Foidart JM and
Gilles C: Regulation of vimentin by SIP1 in human epithelial breast
tumor cells. Oncogene. 25:4975–4985. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Patel NA, Patel PS and Vora HH: Role of
PRL-3, Snail, Cytokeratin and Vimentin expression in epithelial
mesenchymal transition in breast carcinoma. Breast Dis. 35:113–127.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gabbiani G, Kapanci Y, Barazzone P and
Franke WW: Immunochemical identification of intermediate-sized
filaments in human neoplastic cells. A diagnostic aid for the
surgical pathologist. Am J Pathol. 104:206–216. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Damonte P, Gregg JP, Borowsky AD, Keister
BA and Cardiff RD: EMT tumorigenesis in the mouse mammary gland.
Lab Invest. 87:1218–1226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sarrió D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson
D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G and Palacios J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype.
Cancer Res. 68:989–997. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yamashita M, Ogawa T, Zhang X, Hanamura N,
Kashikura Y, Takamura M, Yoneda M and Shiraishi T: Role of stromal
myofibroblasts in invasive breast cancer: Stromal expression of
alpha-smooth muscle actin correlates with worse clinical outcome.
Breast Cancer. 19:170–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Barrallo-Gimeno A and Nieto MA: The Snail
genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: Implications in
development and cancer. Development. 132:3151–3161. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
McGrail DJ, Mezencev R, Kieu QM, McDonald
JF and Dawson MR: SNAIL-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition produces concerted biophysical changes from altered
cytoskeletal gene expression. FASEB. 29:1280–1289. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Smith BN, Burton LJ, Henderson V, Randle
DD, Morton DJ, Smith BA, Taliaferro-Smith L, Nagappan P, Yates C,
Zayzafoon M, et al: Snail promotes epithelial mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer cells in part via activation of nuclear
ERK2. PloS One. 9:e1049872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ferrari-Amorotti G, Chiodoni C, Shen F,
Cattelani S, Soliera AR, Manzotti G, Grisendi G, Dominici M, Rivasi
F, Colombo MP, et al: Suppression of invasion and metastasis of
triple-negative breast cancer lines by pharmacological or genetic
inhibition of slug activity. Neoplasia. 16:1047–1058. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier
B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H and Foisner R:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shirakihara T, Saitoh M and Miyazono K:
Differential regulation of epithelial and mesenchymal markers by
deltaEF1 proteins in epithelial mesenchymal transition induced by
TGF-beta. Mol Biol Cell. 18:3533–3544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gamba CO, Campos LC, Negreiros-Lima GL,
Maciel-Lima K, Sousa LP, Estrela-Lima A, Ferreira E and Cassali GD:
ZEB2 and ZEB1 expression in a spontaneous canine model of invasive
micropapillary carcinoma of the mammary gland. Res Vet Sci.
97:554–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Aigner K, Dampier B, Descovich L, Mikula
M, Sultan A, Schreiber M, Mikulits W, Brabletz T, Strand D, Obrist
P, et al: The transcription factor ZEB1 (deltaEF1) promotes tumor
cell dedifferentiation by repressing master regulators of
epithelial polarity. Oncogene. 26:6979–6988. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Aigner K, Descovich L, Mikula M, Sultan A,
Dampier B, Bonné S, van Roy F, Mikulits W, Schreiber M, Brabletz T,
et al: The transcription factor ZEB1 (deltaEF1) represses
Plakophilin 3 during human cancer progression. FEBS Lett.
581:1617–1624. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vandewalle C, Comijn J, De Craene B,
Vermassen P, Bruyneel E, Andersen H, Tulchinsky E, Van Roy F and
Berx G: SIP1/ZEB2 induces EMT by repressing genes of different
epithelial cell-cell junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:6566–6578.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang P, Sun Y and Ma L: ZEB1: At the
crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and
therapy resistance. Cell Cycle. 14:481–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Moyret-Lalle C, Ruiz E and Puisieux A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factors and miRNAs:
‘Plastic surgeons’ of breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:311–322.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yu W, Kamara H and Svoboda KK: The role of
twist during palate development. Dev Dyn. 237:2716–2725. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kida Y, Asahina K, Teraoka H, Gitelman I
and Sato T: Twist relates to tubular epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and interstitial fibrogenesis in the obstructed kidney.
J Histochem Cytochem. 55:661–673. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang
SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC and Wu KJ: Direct regulation of TWIST by
HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:295–305. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mironchik Y, Winnard PT Jr, Vesuna F, Kato
Y, Wildes F, Pathak AP, Kominsky S, Artemov D, Bhujwalla Z, Van
Diest P, et al: Twist overexpression induces in vivo angiogenesis
and correlates with chromosomal instability in breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:10801–10809. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wushou A, Hou J, Zhao YJ and Shao ZM:
Twist-1 up-regulation in carcinoma correlates to poor survival. Int
J Mol Sci. 15:21621–21630. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mani SA, Yang J, Brooks M, Schwaninger G,
Zhou A, Miura N, Kutok JL, Hartwell K, Richardson AL and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchyme Forkhead 1 (FOXC2) plays a key role in metastasis
and is associated with aggressive basal-like breast cancers. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10069–10074. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Taube JH, Herschkowitz JI, Komurov K, et
al: Core epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition interactome
gene-expression signature is associated with claudin-low and
metaplastic breast cancer subtypes. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
107:15449–15454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ravindranath A, Yuen HF, Chan KK, Grills
C, Fennell DA, Lappin TR and El-Tanani M: Wnt-β-catenin-Tcf-4
signalling-modulated invasiveness is dependent on osteopontin
expression in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 105:542–551. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li H, Chen X, Gao Y, Wu J, Zeng F and Song
F: XBP1 induces snail expression to promote epithelial-
to-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer cells. Cell
Signal. 27:82–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li Y, Yang W, Yang Q and Zhou S: Nuclear
localization of GLI1 and elevated expression of FOXC2 in breast
cancer is associated with the basal-like phenotype. Histol
Histopathol. 27:475–484. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lim JC, Koh VC, Tan JS, Tan WJ, Thike AA
and Tan PH: Prognostic significance of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition proteins Twist and Foxc2 in phyllodes tumors of the
breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 150:19–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hartwell KA, Muir B, Reinhardt F,
Carpenter AE, Sgroi DC and Weinberg RA: The Spemann organizer gene,
Goosecoid, promotes tumor metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:18969–18974. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F and Mo YY:
miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 26:2799–2803. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, Chen X, Xu J, Sun Y,
Zhao L, Qu H, Fan Y and Wu C: Antagonism of miR-21 reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype
through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PloS One.
7:e395202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Harquail J, Benzina S and Robichaud GA:
MicroRNAs and breast cancer malignancy: An overview of
miRNA-regulated cancer processes leading to metastasis. Cancer
Biomark. 11:269–280. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J,
Bhat B, Marcusson EG, Teruya-Feldstein J, Bell GW and Weinberg RA:
Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse
mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol. 28:341–347. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh
P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S,
et al: miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin
and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 12:247–256. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gwak JM, Kim HJ, Kim EJ, Chung YR, Yun S,
Seo AN, Lee HJ and Park SY: MicroRNA-9 is associated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, breast cancer stem cell
phenotype and tumor progression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 147:39–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Martello G, Rosato A, Ferrari F, Manfrin
A, Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Enzo E, Guzzardo V, Rondina M, Spruce T,
et al: A MicroRNA targeting dicer for metastasis control. Cell.
141:1195–1207. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer
O, Vincan E, Spaderna S and Brabletz T: A reciprocal repression
between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and
invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 9:582–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Korpal M, Ell BJ, Buffa FM, Ibrahim T,
Blanco MA, Celià-Terrassa T, Mercatali L, Khan Z, Goodarzi H, Hua
Y, et al: Direct targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer
cell secretome and promotes metastatic colonization. Nat Med.
17:1101–1108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jang K, Ahn H, Sim J, Han H, Abdul R, Paik
SS, Chung MS and Jang SJ: Loss of microRNA-200a expression
correlates with tumor progression in breast cancer. Transl Res.
163:242–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N,
Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF and Goodall GJ: A double-negative
feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
68:7846–7854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hong S, Noh H, Teng Y, Shao J, Rehmani H,
Ding HF, Dong Z, Su SB, Shi H, Kim J and Huang S: SHOX2 is a direct
miR-375 target and a novel epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
inducer in breast cancer cells. Neoplasia. 16:279–290.e1-5. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Arora H, Qureshi R and Park WY: Mir-506
regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cell
lines. PloS One. 8:e642732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Moes M, Le Bechec A, Crespo I, Laurini C,
Halavatyi A, Vetter G, Del Sol A and Friederich E: A novel network
integrating a miRNA-203/SNAI1 feedback loop which regulates
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PloS One. 7:e354402012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ding X, Park SI, McCauley LK and Wang CY:
Signaling between transforming growth factor β(TGF-β) and
transcription factor SNAI2 represses expression of microRNA miR-203
to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis.
J Biol Chem. 288:10241–10253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Hünten S, Kaller
M, Menssen A, Götz U and Hermeking H: miR-34 and SNAIL form a
double-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions. Cell Cycle. 10:4256–4271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Saito YD, Jensen AR, Salgia R and Posadas
EM: Fyn: A novel molecular target in cancer. Cancer. 116:1629–1637.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jechlinger M, Sommer A, Moriggl R, Seither
P, Kraut N, Capodiecci P, Donovan M, Cordon-Cardo C, Beug H and
Grünert S: Autocrine PDGFR signaling promotes mammary cancer
metastasis. J Clin Invest. 116:1561–1570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Choi YL, Bocanegra M, Kwon MJ, Shin YK,
Nam SJ, Yang JH, Kao J, Godwin AK and Pollack JR: LYN is a mediator
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and a target of dasatinib in
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 70:2296–2306. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hutterer M, Knyazev P, Abate A, Reschke M,
Maier H, Stefanova N, Knyazeva T, Barbieri V, Reindl M, Muigg A, et
al: Axl and growth arrest-specific gene 6 are frequently
overexpressed in human gliomas and predict poor prognosis in
patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res. 14:130–138.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Li Y, Ye X, Tan C, Hongo JA, Zha J, Liu J,
Kallop D, Ludlam MJ and Pei L: Axl as a potential therapeutic
target in cancer: Role of Axl in tumor growth, metastasis and
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 28:3442–3455. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhang YX, Knyazev PG, Cheburkin YV, Sharma
K, Knyazev YP, Orfi L, Szabadkai I, Daub H, Kéri G and Ullrich A:
AXL is a potential target for therapeutic intervention in breast
cancer progression. Cancer Res. 68:1905–1915. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Asiedu MK, Beauchamp-Perez FD, Ingle JN,
Behrens MD, Radisky DC and Knutson KL: AXL induces
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and regulates the function of
breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 33:1316–1324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wu X, Liu X, Koul S, Lee CY, Zhang Z and
Halmos B: AXL kinase as a novel target for cancer therapy.
Oncotarget. 5:9546–9563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Taglienti CA, Wysk M and Davis RJ:
Molecular cloning of the epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein
kinase p56 KKIAMRE. Oncogene. 13:2563–2574. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Gomi H, Sun W, Finch CE, Itohara S,
Yoshimi K and Thompson RF: Learning induces a CDC2-related protein
kinase, KKIAMRE. J Neurosci. 19:9530–9537. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|