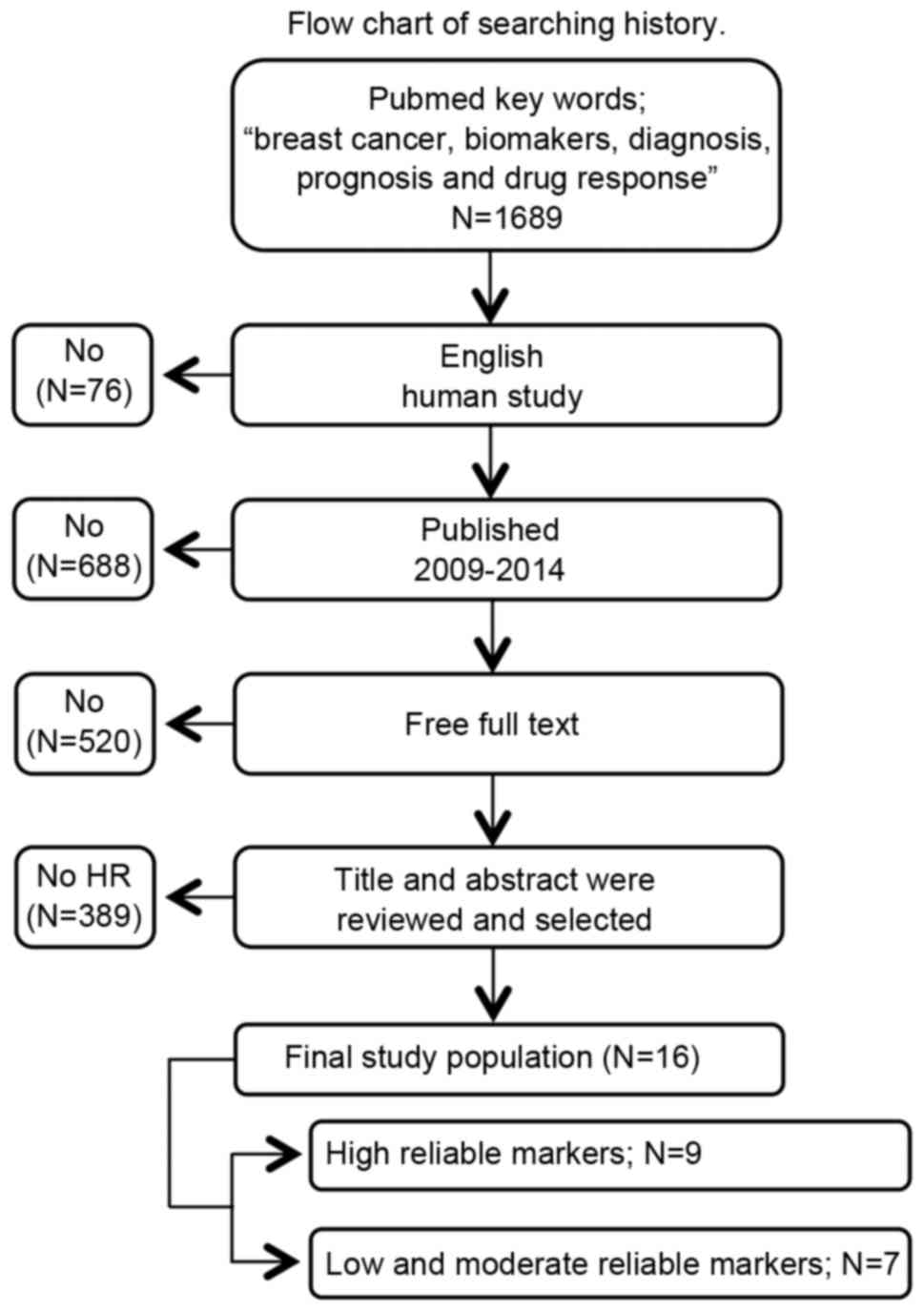
|
1
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel members:
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Henderson IC and Patek AJ: The
relationship between prognostic and predictive factors in the
management of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 52:261–288.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lang JE, Wecsler JS, Press MF and Tripathy
D: Molecular markers for breast cancer diagnosis, prognosis and
targeted therapy. J Surg Oncol. 111:81–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists'
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), . Effects of chemotherapy and
hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year
survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet.
365:1687–1717. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Niederreither K and Dollé P: Retinoic acid
in development: Towards an integrated view. Nat Rev Genet.
9:541–553. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hua S, Kittler R and White KP: Genomic
antagonism between retinoic acid and estrogen signaling in breast
cancer. Cell. 137:1259–1271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johansson HJ, Sanchez BC, Mundt F, Forshed
J, Kovacs A, Panizza E, Hultin-Rosenberg L, Lundgren B, Martens U,
Máthé G, et al: Retinoic acid receptor alpha is associated with
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Nat Commun. 4:21752013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Esteban JM, Warsi Z, Haniu M, Hall P,
Shively JE and Chen S: Detection of intratumoral aromatase in
breast carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study with
clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Pathol. 140:337–343.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miki Y, Suzuki T and Sasano H:
Controversies of aromatase localization in human breast
cancer-stromal versus parenchymal cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 106:97–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ellis MJ, Coop A, Singh B, Mauriac L,
Llombert-Cussac A, Jänicke F, Miller WR, Evans DB, Dugan M, Brady
C, et al: Letrozole is more effective neoadjuvant endocrine therapy
than tamoxifen for ErbB-1- and/or ErbB-2-positive, estrogen
receptor-positive primary breast cancer: Evidence from a phase III
randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 19:3808–3816. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eiermann W, Paepke S, Appfelstaedt J,
Llombart-Cussac A, Eremin J, Vinholes J, Mauriac L, Ellis M, Lassus
M, Chaudri-Ross HA, et al: Preoperative treatment of postmenopausal
breast cancer patients with letrozole: A randomized double-blind
multicenter study. Ann Oncol. 12:1527–1532. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ellis MJ, Tao Y, Luo J, A'Hern R, Evans
DB, Bhatnagar AS, Ross HA Chaudri, von Kameke A, Miller WR, Smith
I, et al: Outcome prediction for estrogen receptor-positive breast
cancer based on postneoadjuvant endocrine therapy tumor
characteristics. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:1380–1388. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ellis MJ, Coop A, Singh B, Tao Y,
Llombart-Cussac A, Jänicke F, Mauriac L, Quebe-Fehling E,
Chaudri-Ross HA, Evans DB and Miller WR: Letrozole inhibits tumor
proliferation more effectively than tamoxifen independent of HER1/2
expression status. Cancer Res. 63:6523–6531. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M and Clark
GM: Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by
immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 11:155–168.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ellis MJ, Miller WR, Tao Y, Evans DB, Ross
HA Chaudri, Miki Y, Suzuki T and Sasano H: Aromatase expression and
outcomes in the P024 neoadjuvant endocrine therapy trial. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 116:371–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Senger DR, Wirth DF and Hynes RO:
Transformed mammalian cells secrete specific proteins and
phosphoproteins. Cell. 16:885–893. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brown LF, Papadopoulos-Sergiou A, Berse B,
Manseau EJ, Tognazzi K, Perruzzi CA, Dvorak HF and Senger DR:
Osteopontin expression and distribution in human carcinomas. Am J
Pathol. 145:610–623. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pang H, Lu H, Song H, Meng Q, Zhao Y, Liu
N, Lan F, Liu Y, Yan S, Dong X and Cai L: Prognostic values of
osteopontin-c, E-cadherin and β-catenin in breast cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol. 37:985–992. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ortiz-Martínez F, Perez-Balaguer A,
Ciprián D, Andrés L, Ponce J, Adrover E, Sánchez-Payá J, Aranda FI,
Lerma E and Peiró G: Association of increased osteopontin and
splice variant-c mRNA expression with HER2 and
triple-negative/basal-like breast carcinomas subtypes and
recurrence. Hum Pathol. 45:504–512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bramwell VH, Tuck AB, Chapman JA, Anborgh
PH, Postenka CO, Al-Katib W, Shepherd LE, Han L, Wilson CF,
Pritchard KI, et al: Assessment of osteopontin in early breast
cancer: Correlative study in a randomised clinical trial. Breast
Cancer Res. 16:R82014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohno S, Chow LW, Sato N, Masuda N, Sasano
H, Takahashi F, Bando H, Iwata H, Morimoto T, Kamigaki S, et al:
Randomized trial of preoperative docetaxel with or without
capecitabine after 4 cycles of
5-fluorouracil-epirubicin-cyclophosphamide (FEC) in early-stage
breast cancer: Exploratory analyses identify Ki67 as a predictive
biomarker for response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 142:69–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Denkert C, Loibl S, Muller BM, Eidtmann H,
Schmitt WD, Eiermann W, Gerber B, Tesch H, Hilfrich J, Huober J, et
al: Ki67 levels as predictive and prognostic parameters in
pretherapeutic breast cancer core biopsies: A translational
investigation in the neoadjuvant GeparTrio trial. Ann Oncol.
24:2786–2793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Budczies J, Klauschen F, Sinn BV, Győrffy
B, Schmitt WD, Darb-Esfahani S and Denkert C: Cutoff finder: A
comprehensive and straightforward web application enabling rapid
biomarker cutoff optimization. PLoS One. 7:e518622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
DeCensi A, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Gandini S,
Serrano D, Cazzaniga M, Mora S, Johansson H, Lien EA, Pruneri G,
Viale G and Bonanni B: Prognostic significance of Ki-67 labeling
index after short-term presurgical tamoxifen in women with
ER-positive breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 22:582–587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kuroki M, Matsuo Y, Kinugasa T and
Matsuoka Y: Three different NCA species, CGM6/CD67, NCA-95 and
NCA-90, are comprised in the major 90 to 100-kDa band of
granulocyte NCA detectable upon SDS-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 182:501–506. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blumenthal RD, Leon E, Hansen HJ and
Goldenberg DM: Expression patterns of CEACAM5 and CEACAM6 in
primary and metastatic cancers. BMC cancer. 7:22007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Poola I, Shokrani B, Bhatnagar R, DeWitty
RL, Yue Q and Bonney G: Expression of carcinoembryonic antigen cell
adhesion molecule 6 oncoprotein in atypical ductal hyperplastic
tissues is associated with the development of invasive breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4773–4783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsang JY, Kwok YK, Chan KW, Ni YB, Chow
WN, Lau KF, Shao MM, Chan SK, Tan PH and Tse GM: Expression and
clinical significance of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell
adhesion molecule 6 in breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
142:311–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
German S, Aslam HM, Saleem S, Raees A,
Anum T, Alvi AA and Haseeb A: Carcinogenesis of PIK3CA. Hered
Cancer Clin Pract. 11:52013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hanker AB, Pfefferle AD, Balko JM, Kuba
MG, Young CD, Sánchez V, Sutton CR, Cheng H, Perou CM, Zhao JJ, et
al: Mutant PIK3CA accelerates HER2-driven transgenic mammary tumors
and induces resistance to combinations of anti-HER2 therapies. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:14372–14377. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cizkova M, Dujaric ME, Lehmann-Che J,
Scott V, Tembo O, Asselain B, Pierga JY, Marty M, de Cremoux P,
Spyratos F and Bieche I: Outcome impact of PIK3CA mutations in
HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab. Br J
Cancer. 108:1807–1809. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hortobagyi GN and Holmes FA: Single-agent
paclitaxel for the treatment of breast cancer: An overview. Semin
Oncol. 23(1): Suppl 1. S4–S9. 1996.
|
|
33
|
Bergh J, Jönsson PE, Glimelius B and
Nygren P: SBU-group. Swedish Council of Technology Assessment in
Health Care. A systematic overview of chemotherapy effects in
breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 40:253–281. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chromek M, Tullus K, Lundahl J and Brauner
A: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 activates normal human
granulocytes, protects them from apoptosis, and blocks their
transmigration during inflammation. Infect Immun. 72:82–88. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schrohl AS, Meijer-van Gelder ME,
Holten-Andersen MN, Christensen IJ, Look MP, Mouridsen HT, Brünner
N and Foekens JA: Primary tumor levels of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases-1 are predictive of resistance to chemotherapy
in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
12:7054–7058. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu D, Zha X, Hu M, Tao A, Zhou H, Zhou X
and Sun Y: High expression of TIMP-1 in human breast cancer tissues
is a predictive of resistance to paclitaxel-based chemotherapy. Med
Oncol. 29:3207–3215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arosio P, Yokota M and Drysdale JW:
Structural and immunological relationships of isoferritins in
normal and malignant cells. Cancer Res. 36:1735–1739.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Levi S, Yewdall SJ, Harrison PM,
Santambrogio P, Cozzi A, Rovida E, Albertini A and Arosio P:
Evidence of H- and L-chains have co-operative roles in the
iron-uptake mechanism of human ferritin. Biochem J. 288:591–596.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ricolleau G, Charbonnel C, Lodé L,
Loussouarn D, Joalland MP, Bogumil R, Jourdain S, Minvielle S,
Campone M, Déporte-Fety R, et al: Surface-enhanced laser
desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry protein
profiling identifies ubiquitin and ferritin light chain as
prognostic biomarkers in node-negative breast cancer tumors.
Proteomics. 6:1963–1975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jézéquel P, Campion L, Spyratos F,
Loussouarn D, Campone M, Guérin-Charbonnel C, Joalland MP, André J,
Descotes F, Grenot C, et al: Validation of tumor-associated
macrophage ferritin light chain as a prognostic biomarker in
node-negative breast cancer tumors: A multicentric 2004 national
PHRC study. Int J Cancer. 131:426–437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duffy MJ: Urokinase plasminogen activator
and its inhibitor, PAI-1, as prognostic markers in breast cancer:
From pilot to level 1 evidence studies. Clin Chem. 48:1194–1197.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mengele K, Napieralski R, Magdolen V,
Reuning U, Gkazepis A, Sweep F, Brünner N, Foekens J, Harbeck N and
Schmitt M: Characteristics of the level-of-evedence-1 disease
forcast cancer biomarkers uPA and its inhibitor PAI-1. Expert Rev
Mol Diagn. 10:947–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Harbeck N, Schmitt M, Meisner C, Friedel
C, Untch M, Schmidt M, Sweep CG, Lisboa BW, Lux MP, Beck T, et al:
Ten-year analysis of the prospective multicentre Chemo-N0 trial
validates American society of clinical oncology (ASCO)-recommended
biomarkers uPA and PAI-1 for therapy decision making in
node-negative breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 49:1825–1835.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Favaro E, Amadori A and Indraccolo S:
Cellular interactions in the vascular niche: Implications in the
regulation of tumor dormancy. APMIS. 116:648–659. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Allin KH and Nordestgaard BG: Elevated
C-reactive protein in the diagnosis, prognosis, and cause of
cancer. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 48:155–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Villaseñor A, Flatt SW, Marinac C,
Natarajan L, Pierce JP and Patterson RE: Postdiagnosis C-reactive
protein and breast cancer survivorship: Findings from the WHEL
study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:189–199. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zody MC, Garber M, Adams DJ, Sharpe T,
Harrow J, Lupski JR, Nicholson C, Searle SM, Wilming L, Young SK,
et al: DNA sequence of human chromosome 17 and analysis of
rearrangement in the human lineage. Nature. 440:1045–1049. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Watters AD, Going JJ, Cooke TG and
Bartlett JM: Chromosome 17 aneusomy is associated with poor
prognostic factors in invasive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 77:109–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Corzo C, Bellosillo B, Corominas JM,
Salido M, Coll MD, Serrano S, Albanell J, Solé F and Tusquets I:
Does polysomy of chromosome 17 have a role in ERBB2 and
topoisomerase IIalpha expression? Gene, mRNA and protein
expression: A comprehensive analysis. Tumor Biol. 28:221–228. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Earl HM, Hiller L, Dunn JA, Vallier AL,
Bowden SJ, Jordan SD, Blows F, Munro A, Bathers S, Grieve R, et al:
Adjuvant epirubicin followed by cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and
fluorouracil (CMF) vs CMF in early breast cancer: Results with over
7 years median follow-up from the randomised phase III NEAT/BR9601
trials. Br J Cancer. 107:1257–1267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sias PE, Kotts CE, Vetterlein D, Shepard M
and Wong WL: ELISA for quantitation of the extracellular domain of
p185HER2 in biological fluids. J Immunol Methods. 132:73–80. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Codony-Servat J, Albanell J,
Lopez-Talavera JC, Arribas J and Baselga J: Cleavage of the HER2
ectodomain is a pervanadate-activable process that is inhibited by
the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases-1 in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 59:1196–1201. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tse C, Gauchez AS, Jacot W and Lamy PJ:
HER2 shedding and serum HER2 extracellular domain: Biology and
clinical utility in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:133–142.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ,
Geyer CE Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman
PA, et al: Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable
HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:1673–1684. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Moreno-Aspitia A, Hillman DW, Dyar SH,
Tenner KS, Gralow J, Kaufman PA, Davidson NE, Lafky JM, Reinholz
MM, Lingle WL, et al: Soluble human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2 (HER2) levels in patients with HER2-positive breast
cancer receiving chemotherapy with or without trastuzumab: Results
from north central cancer treatment group adjuvant trial N9831.
Cancer. 119:2675–2682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tsukasaki K, Miller CW, Greenspun E,
Eshaghian S, Kawabata H, Fujimoto T, Tomonaga M, Sawyers C, Said JW
and Koeffler HP: Mutations in the mitotic check point gene, MAD1L1,
in human cancers. Oncogene. 20:3301–3305. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sun Q, Zhang X, Liu T, Liu X, Geng J, He
X, Liu Y and Pang D: Increased expression of mitotic arrest
deficient-like 1 (MAD1L1) is associated with poor prognosis and
insensitive to Taxol treatment in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 140:323–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Baylin SB and Herman JG: DNA
hypermethylation in tumorigenesis: Epigenetics joins genetics.
Trends Genet. 16:168–174. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jones PA: DNA methylation errors and
cancer. Cancer Res. 56:2463–2467. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Herman JG and Baylin SB: Gene silencing in
cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med.
349:2042–2054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Frühwald MC: DNA methylation patterns in
cancer: Novel prognostic indicators? Am J Pharmacogenomics.
3:245–260. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Laird PW: The power and the promise of DNA
methylation markers. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:253–266. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Maier S, Nimmrich I, Koenig T,
Eppenberger-Castori S, Bohlmann I, Paradiso A, Spyratos F, Thomssen
C, Mueller V, Nährig J, et al: DNA-methylation of the homeodomain
transcription factor PITX2 reliably predicts risk of distant
disease recurrence in tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast
cancer patients-Technical and clinical validation in a multi-centre
setting in collaboration with the European Organisation for
Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) PathoBiology group. Eur J
Cancer. 43:1679–1686. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Martens JW, Nimmrich I, Koenig T, Look MP,
Harbeck N, Model F, Kluth A, Bolt-de Vries J, Sieuwerts AM,
Portengen H, et al: Association of DNA methylation of phosphoserine
aminotransferase with response to endocrine therapy in patients
with recurrent breast cancer. Cancer Res. 65:4101–4117. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Widschwendter M, Siegmund KD, Müller HM,
Fiegl H, Marth C, Müller-Holzner E, Jones PA and Laird PW:
Association of breast cancer DNA methylation profiles with hormone
receptor status and response to tamoxifen. Cancer Res.
64:3807–3813. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hartmann O, Spyratos F, Harbeck N,
Dietrich D, Fassbender A, Schmitt M, Eppenberger-Castori S,
Vuaroqueaux V, Lerebours F, Welzel K, et al: DNA methylation
markers predict outcome in node-positive, estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer with adjuvant anthracycline-based
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:315–323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|