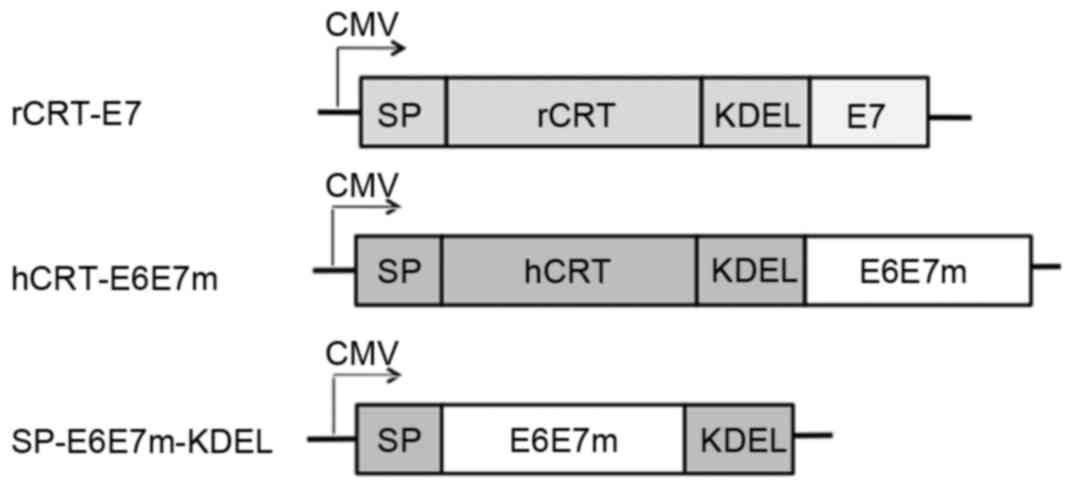
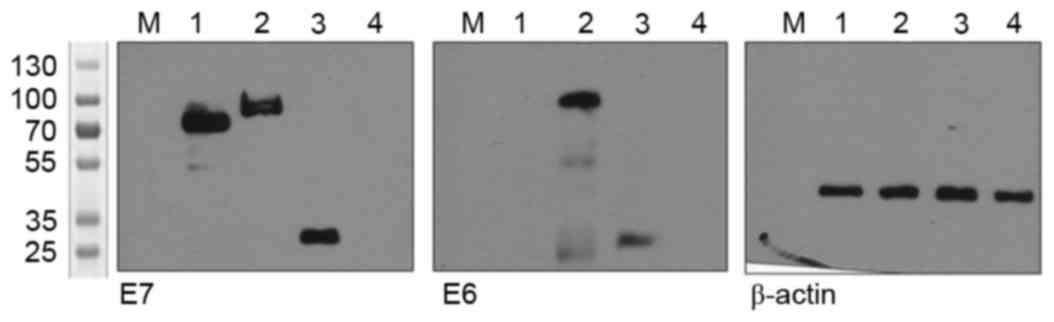
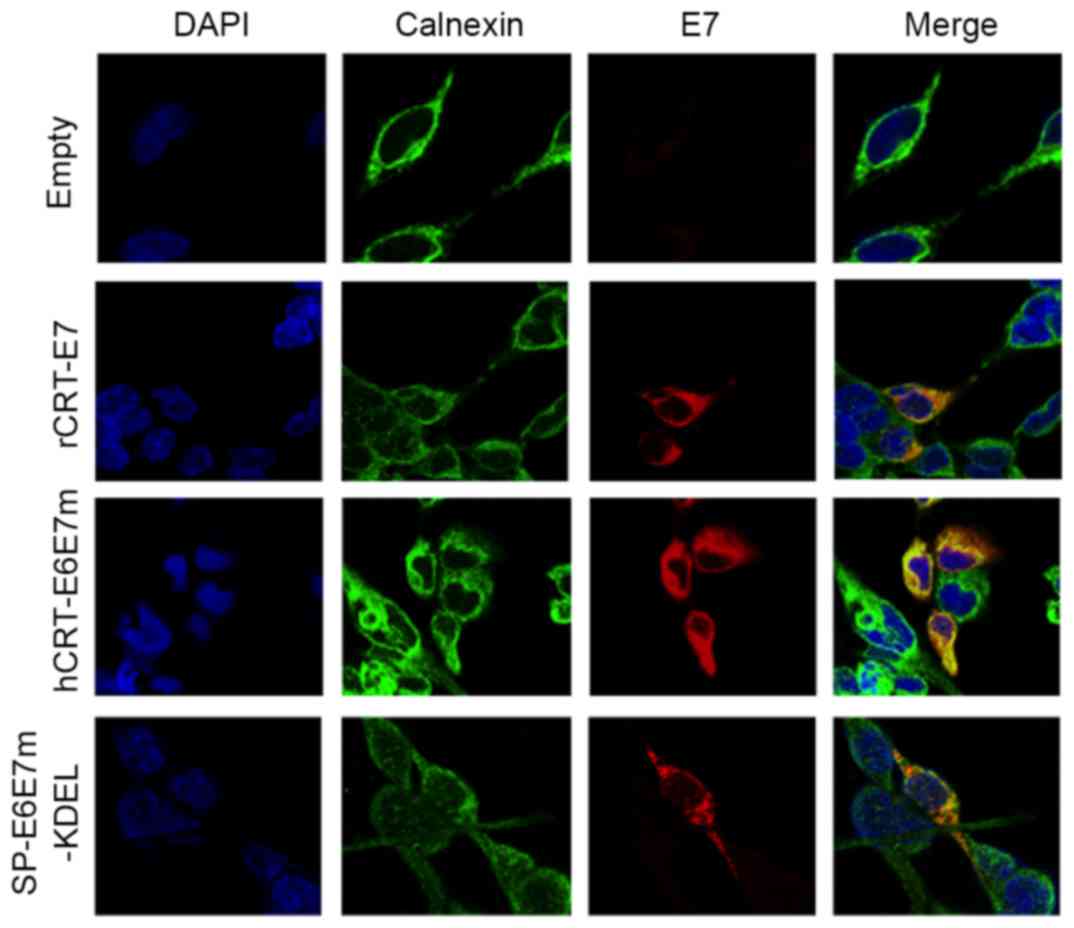
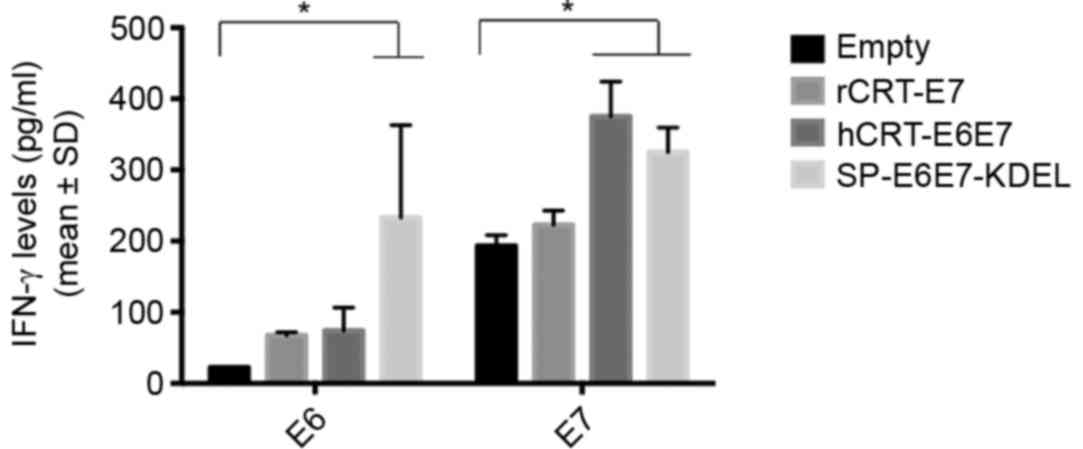
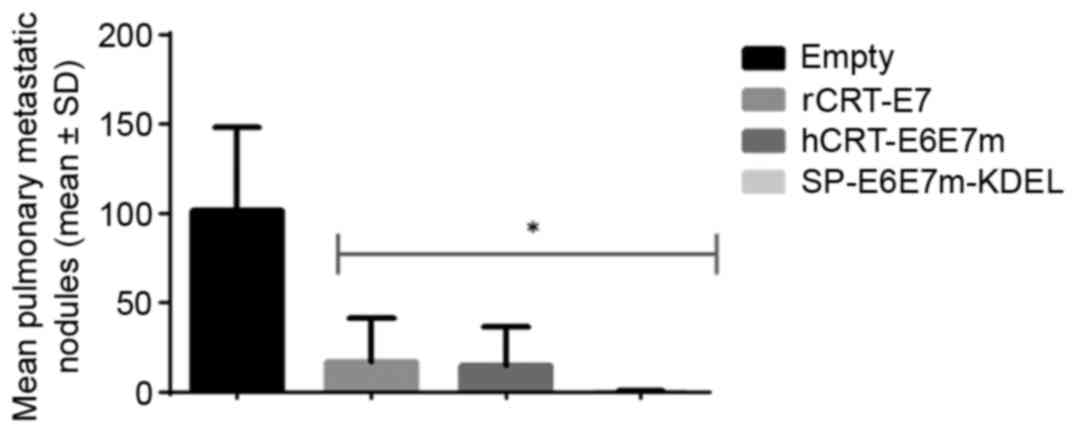
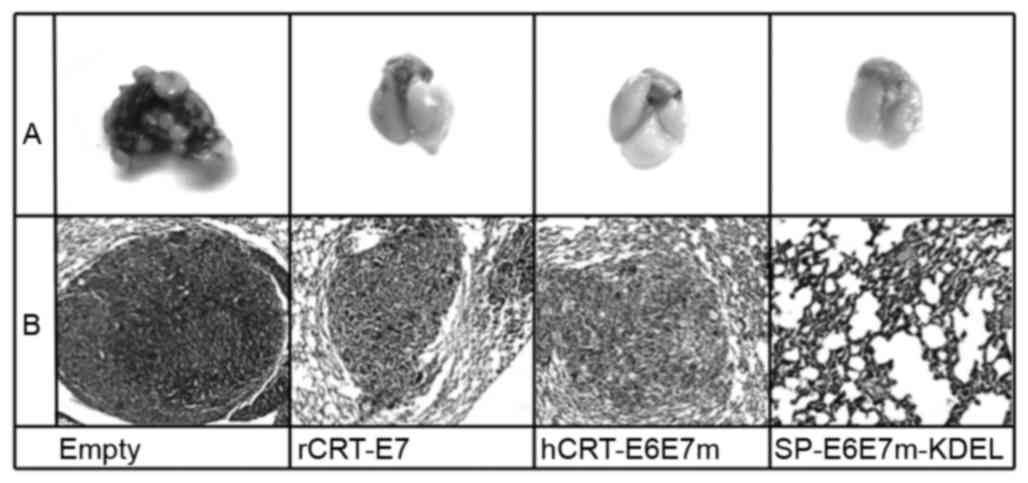
|
1
|
Tan S, de Vries EG, van der Zee AG and de
Jong S: Anticancer drugs aimed at E6 and E7 activity in
HPV-positive cervical cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 12:170–184.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Boer MA, Jordanova ES, van Poelgeest
MI, van den Akker BE, van der Burg SH, Kenter GG and Fleuren GJ:
Circulating human papillomavirus type 16 specific T-cells are
associated with HLA Class I expression on tumor cells, but not
related to the amount of viral oncogene transcripts. Int J Cancer.
121:2711–2715. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bukur J, Jasinski S and Seliger B: The
role of classical and non-classical HLA class I antigens in human
tumors. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:350–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yewdell JW: Not such a dismal science: The
economics of protein synthesis, folding, degradation and antigen
processing. Trends Cell Biol. 11:294–297. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ashrafi GH, Brown DR, Fife KH and Campo
MS: Down-regulation of MHC class I is a property common to
papillomavirus E5 proteins. Virus Res. 120:208–211. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hicklin DJ, Marincola FM and Ferrone S:
HLA class I antigen downregulation in human cancers: T-cell
immunotherapy revives an old story. Mol Med Today. 5:178–186. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tatsis N and Ertl HC: Adenoviruses as
vaccine vectors. Mol Ther. 10:616–629. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neefjes J, Jongsma ML, Paul P and Bakke O:
Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II
antigen presentation. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:823–836. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang B, Jeang J, Yang A, Wu TC and Hung
CF: DNA vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
10:3153–3164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsieh CJ, Kim TW, Hung CF, Juang J, Moniz
M, Boyd DA, He L, Chen PJ, Chen CH and Wu TC: Enhancement of
vaccinia vaccine potency by linkage of tumor antigen gene to gene
encoding calreticulin. Vaccine. 22:3993–4001. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gomez-Gutierrez JG, Elpek KG, de Oca-Luna
R Montes, Shirwan H, Sam Zhou H and McMasters KM: Vaccination with
an adenoviral vector expressing calreticulin-human papillomavirus
16 E7 fusion protein eradicates E7 expressing established tumors in
mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 56:997–1007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheng W, Chen C, Dong M, Zhou J, Liu Q,
Dong Q and Li F: Overexpression of calreticulin contributes to the
development and progression of pancreatic cancer. J Cell Physiol.
229:887–897. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Erić-Nikolić A, Milovanović Z, Sánchez D,
Pekáriková A, Džodić R, Matić IZ, Tučková L, Jevrić M, Buta M,
Rašković S and Juranić Z: Overexpression of calreticulin in
malignant and benign breast tumors: Relationship with humoral
immunity. Oncology. 82:48–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Loera-Arias MJ, Martínez-Pérez AG,
Barrera-Hernández A, Ibarra-Obregón ER, González-Saldívar G,
Martínez-Ortega JI, Rosas-Taraco A, Villanueva-Olivo A,
Esparza-González SC, Villatoro-Hernandez J, et al: Targeting and
retention of HPV16 E7 to the endoplasmic reticulum enhances immune
tumour protection. J Cell Mol Med. 14:890–894. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng S, Tomson TT, Trimble C, He L, Hung
CF and Wu TC: A combination of DNA vaccines targeting human
papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 generates potent antitumor
effects. Gene Ther. 13:257–265. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan J, Reichenbach DK, Corbitt N, Hokey
DA, Ramanathan MP, McKinney KA, Weiner DB and Sewell D: Induction
of antitumor immunity in vivo following delivery of a novel HPV-16
DNA vaccine encoding an E6/E7 fusion antigen. Vaccine. 27:431–440.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou X, Qian X, Zhao Q, Lu Y and Xiong M:
Efficient expression of modified human papillomavirus 16 e6/e7
fusion protein and the antitumor efficacy in a mouse model. Biol
Pharm Bull. 27:303–307. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi W, Bu P, Liu J, Polack A, Fisher S and
Qiao L: Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 DNA vaccine: Mutation in
the open reading frame of E7 enhances specific cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte induction and antitumor activity. J Virol.
73:7877–7881. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bahrami AA, Ghaemi A, Tabarraei A,
Sajadian A, Gorji A and Soleimanjahi H: DNA vaccine encoding HPV-16
E7 with mutation in L-Y-C-Y-E pRb-binding motif induces potent
anti-tumor responses in mice. J Virol Methods. 206:12–18. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheung YK, Cheng SC, Sin FW and Xie Y:
Plasmid encoding papillomavirus Type 16 (HPV16) DNA constructed
with codon optimization improved the immunogenicity against HPV
infection. Vaccine. 23:629–638. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amine A, Rivera S, Opolon P, Dekkal M,
Biard DS, Bouamar H, Louache F, McKay MJ, Bourhis J, Deutsch E and
Vozenin-Brotons MC: Novel anti-metastatic action of cidofovir
mediated by inhibition of E6/E7, CXCR4 and Rho/ROCK signaling in
HPV+ tumor cells. PLoS One. 4:e50182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Del Cid N, Jeffery E, Rizvi SM, Stamper E,
Peters LR, Brown WC, Provoda C and Raghavan M: Modes of
calreticulin recruitment to the major histocompatibility complex
class I assembly pathway. J Biol Chem. 285:4520–4535. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gelebart P, Opas M and Michalak M:
Calreticulin, a Ca2+-binding chaperone of the endoplasmic
reticulum. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:260–266. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murphy-Ullrich JE: The de-adhesive
activity of matricellular proteins: Is intermediate cell adhesion
an adaptive state? J Clin Invest. 107:785–790. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goicoechea S, Orr AW, Pallero MA, Eggleton
P and Murphy-Ullrich JE: Thrombospondin mediates focal adhesion
disassembly through interactions with cell surface calreticulin. J
Biol Chem. 275:36358–36368. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim JW, Hung CF, Juang J, He L, Kim TW,
Armstrong DK, Pai SI, Chen PJ, Lin CT, Boyd DA and Wu TC:
Comparison of HPV DNA vaccines employing intracellular targeting
strategies. Gene Ther. 11:1011–1018. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peng S, Ji H, Trimble C, He L, Tsai YC,
Yeatermeyer J, Boyd DA, Hung CF and Wu TC: Development of a DNA
vaccine targeting human papillomavirus type 16 oncoprotein E6. J
Virol. 78:8468–8476. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kang TH, Chung JY, Monie A, Pai SI, Hung
CF and Wu TC: Enhancing DNA vaccine potency by co-administration of
xenogenic MHC class-I DNA. Gene Ther. 17:531–540. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng WF, Hung CF, Chai CY, Hsu KF, He L,
Ling M and Wu TC: Tumor-specific immunity and antiangiogenesis
generated by a DNA vaccine encoding calreticulin linked to a tumor
antigen. J Clin Invest. 108:669–678. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zamanian M, Veerakumarasivam A, Abdullah S
and Rosli R: Calreticulin and cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:149–154.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chiang WF, Hwang TZ, Hour TC, Wang LH,
Chiu CC, Chen HR, Wu YJ, Wang CC, Wang LF, Chien CY, et al:
Calreticulin, an endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein, is highly
expressed and essential for cell proliferation and migration in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 49:534–541. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi F, Shang L, Pan BQ, Wang XM, Jiang YY,
Hao JJ, Zhang Y, Cai Y, Xu X, Zhan QM and Wang MR: Calreticulin
promotes migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by
upregulating neuropilin-1 expression via STAT5A. Clin Cancer Res.
20:6153–6162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peachman KK, Rao M and Alving CR:
Immunization with DNA through the skin. Methods. 31:232–242. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ji H, Chang EY, Lin KY, Kurman RJ, Pardoll
DM and Wu TC: Antigen-specific immunotherapy for murine lung
metastatic tumors expressing human papillomavirus type 16 E7
oncoprotein. Int J Cancer. 78:41–45. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee SY, Kang TH, Knoff J, Huang Z, Soong
RS, Alvarez RD, Hung CF and Wu TC: Intratumoral injection of
therapeutic HPV vaccinia vaccine following cisplatin enhances
HPV-specific antitumor effects. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
62:1175–1185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen S, Liao C, Lai Y, Fan Y, Lu G, Wang
H, Zhang X, Lin MC, Leng S and Kung HF: De-oncogenic HPV E6/E7
vaccine gets enhanced antigenicity and promotes tumoricidal synergy
with cisplatin. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:6–14. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|