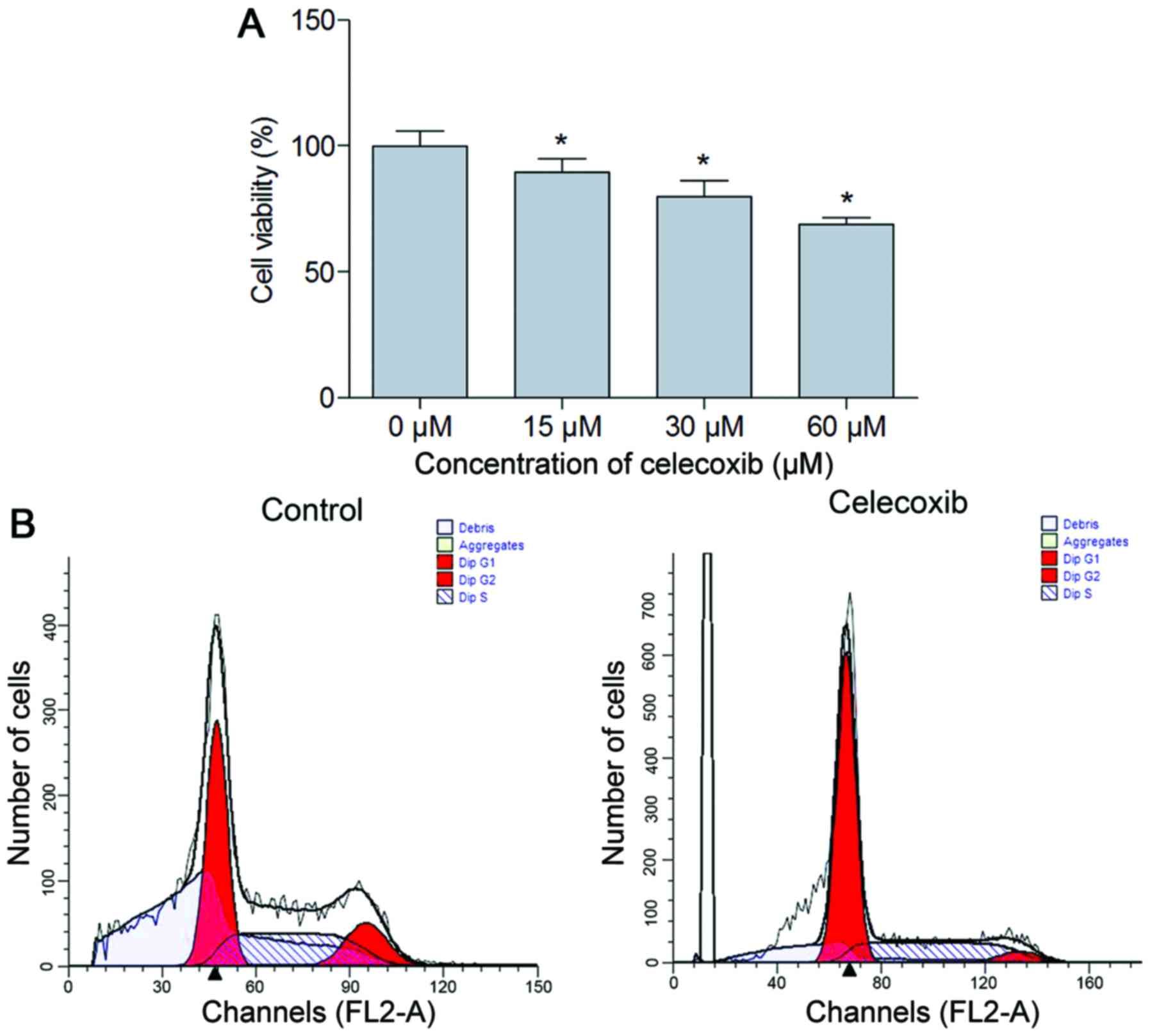
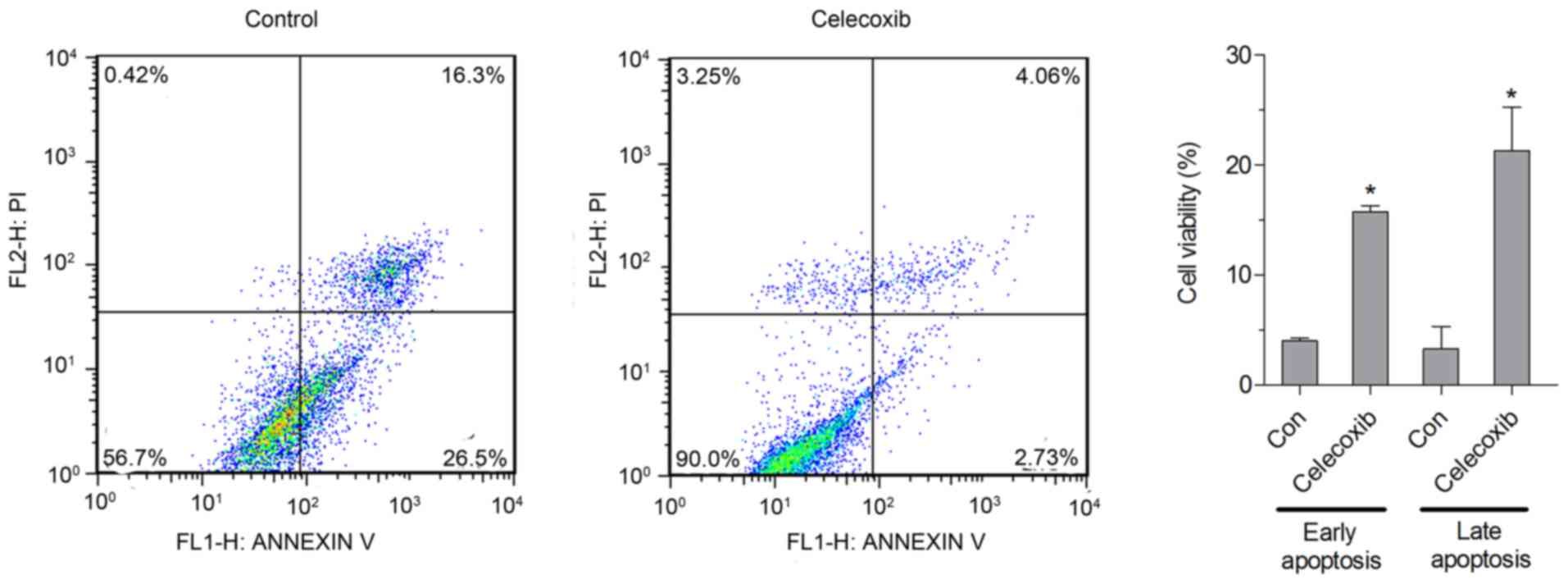
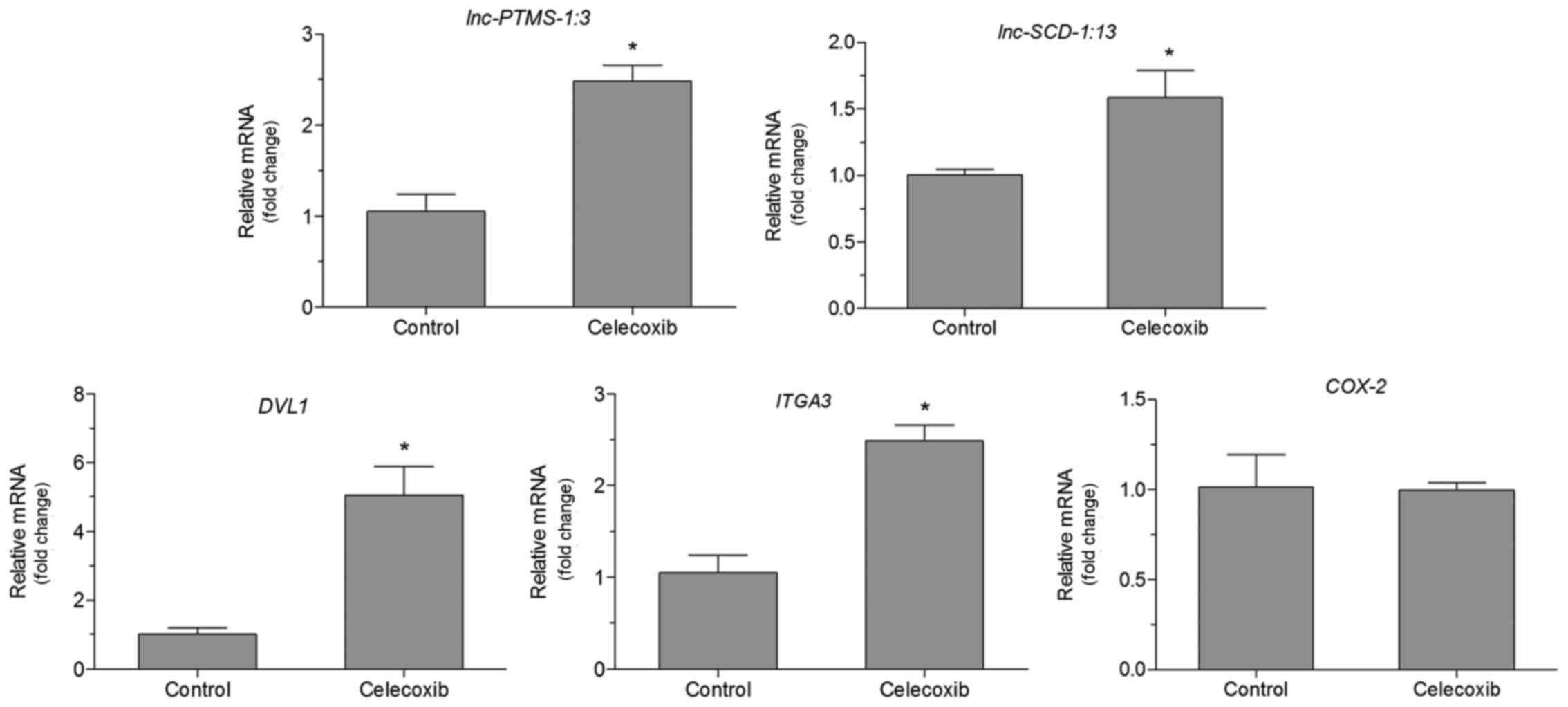
|
1
|
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E and Ferlay J:
Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult
population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 132:1133–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Akagi H, Higuchi H, Sumimoto H, Igarashi
T, Kabashima A, Mizuguchi H, Izumiya M, Sakai G, Adachi M,
Funakoshi S, et al: Suppression of myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1)
enhances chemotherapy-associated apoptosis in gastric cancer cells.
Gastric Cancer. 16:100–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harris RE, Namboodiri KK and Farrar WB:
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and breast cancer.
Epidemiology. 7:203–205. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Funkhouser EM and Sharp GB: Aspirin and
reduced risk of esophageal carcinoma. Cancer. 76:1116–1119. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Levy GN: Prostaglandin H synthases,
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and colon cancer. FASEB J.
11:234–247. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsu AL, Ching TT, Wang DS, Song X,
Rangnekar VM and Chen CS: The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib
induces apoptosis by blocking Akt activation in human prostate
cancer cells independently of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem. 275:11397–11403.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang WH, Huang JQ, Zheng GF, Lam SK,
Karlberg J and Wong BC: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use
and the risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:1784–1791. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pairet M and Engelhardt G: Distinct
isoforms (COX-1 and COX-2) of cyclooxygenase: Possible
physiological and therapeutic implications. Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
10:1–17. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Williams CS, Mann M and Dubois RN: The
role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development.
Oncogene. 18:7908–7916. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu M, Li CM, Chen ZF, Ji R, Guo QH, Li Q,
Zhang HL and Zhou YN: Celecoxib regulates apoptosis and autophagy
via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in SGC-7901 gastric cancer
cells. Int J Mol Med. 33:1451–1458. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lan C, Yang L, Fan L, Zhang Y, Wang J, Guo
GJ, Wan S, Yang S, Wang R and Fang D: Celecoxib inhibits
helicobacter pylori-induced invasion of gastric cancer cells
through an adenine nucleotide translocator-dependent mechanism.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:1267–1272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu P, Yu J, Zeng Z, Leung WK, Lin HL, Tang
BD, Bai AH and Sung JJ: Chemoprevention of gastric cancer by
celecoxib in rats. Gut. 53:195–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du Z, Fei T, Verhaak RG, Su Z, Zhang Y,
Brown M, Chen Y and Liu XS: Integrative genomic analyses reveal
clinically relevant long noncoding RNAs in human cancer. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 20:908–913. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Passon DM, Lee M, Rackham O, Stanley WA,
Sadowska A, Filipovska A, Fox AH and Bond CS: Structure of the
heterodimer of human NONO and paraspeckle protein component 1 and
analysis of its role in subnuclear body formation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:pp. 4846–4850. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song B, Du J, Feng Y, Gao YJ and Zhao JS:
Co-expressed differentially expressed genes and long non-coding
RNAs involved in the celecoxib treatment of gastric cancer: An RNA
sequencing analysis. Exp Ther Med. 12:2455–2468. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yeh TS, Wu CW, Hsu KW, Liao WJ, Yang MC,
Li AF, Wang AM, Kuo ML and Chi CW: The activated Notch1 signal
pathways is associated with gastric cancer progression through
cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 69:5039–5048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thiel A, Mrena J and Ristimäki A:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastric cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
30:387–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cho SJ, Kim N, Kim JS, Jung HC and Song
IS: The anti-cancer effect of COX-2 inhibitors on gastric cancer
cells. Dig Dis Sci. 52:1713–1721. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu SL, Wu YL, Zhang YP, Qiao MM and Chen
Y: Anti-cancer effects of COX-2 inhibitors and they correlation
with angiogenesis and invasion in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:1971–1974. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts
HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C and Kaidi A: The COX-2/PGE2 pathways:
Key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour
microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 30:377–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ristimäki A, Honkanen N, Jänkälä H,
Sipponen P and Härkönen M: Expressions of cyclooxygenase-2 in human
gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 57:1276–1280. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Uefuji K, Ichikura T and Mochizuki H:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expressions is relate to prostaglandin
biosynthesis and angiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 6:135–138. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsuji S, Kawano S, Sawaoka H, Takei Y,
Kobayashi I, Nagano K, Fusamoto H and Kamada T: Evidences for
involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 in proliferation of two
gastrointestinal cancer cell lines. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent
Fatty Acids. 55:179–183. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim N, Kim CH, Ahn DW, Lee KS, Cho SJ,
Park JH, Lee MK, Kim JS, Jung HC and Song IS: Anti-gastric cancer
effects of celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, through
inhibition of Akt signaling. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:480–487.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Charalambous D and O'brien PE: Inhibition
of colon cancer precursors in the rat by sulindac sulphone is not
dependent on inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 11:307–310. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Elder D, Halton DE, Hague A and Paraskeva
C: Induction of apoptotic cell death in human colorectal carcinoma
cell lines by a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-selective nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drug: Independence from COX-2 protein
expressions. Clin Cancer Res. 3:1679–1683. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hanif R, Pittas A, Feng Y, Koutsos MI,
Qiao L, Staiano-Coico L, Shiff SI and Rigas B: Effects of
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on proliferation and on
induction of apoptosis in colon cancer cells by a
prostaglandin-independent pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 52:237–245.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song X, Zhong H, Zhou J, Hu X, Zhou Y, Ye
Y, Lu X, Wang J, Ying B and Wang L: Association between
polymorphisms of microRNA-binding sites in integrin genes and
gastric cancer in Chinese Han population. Tumor Biol. 36:2785–2792.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang Y: Wnt/Planar cell polarity
signaling: A new paradigm for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:2103–2109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hemler ME: Integrin associated proteins.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10:578–585. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dedhar S, Saulnier R, Nagle R and Overall
CM: Specific alterations in the expressions of α3β1 and α6β4
integrins in highly invasive and metastatic variants of human
prostate carcinoma cells selected by in vitro invasion through
reconstituted basement membrane. Clin Exper Met. 11:391–400. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sampson-Johannes A, Wang W and Shtivelman
E: Colonization of human lung grafts in SCID-hu mice by human colon
carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 65:864–869. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang MY, Yen LC, Liu HC, Liu PP, Chung
FY, Wang TN, Wang JY and Lin SR: Significant overexpression of DVL1
in taiwanese colorectal cancer patients with liver metastasis. Int
J Mol Sci. 14:20492–20507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Katoh M: WNT/PCP signaling pathways and
human cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 14:1583–1588. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tang H, Kong Y, Guo J, Tang Y and Xie X,
Yang L, Su Q and Xie X: Diallyl disulfide suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through Wnt-1
signaling pathways by up-regulation of miR-200b and miR-22. Cancer
Lett. 340:72–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin XC, Zhu Y, Chen WB, Lin LW, Chen DH,
Huang JR, Pan K, Lin Y, Wu BT, Dai Y and Tu ZG: Integrated analysis
of long non-coding RNAs and mRNA expressions profiles reveals the
potential role of lncRNAs in gastric cancer pathogenesis. Int J
Oncol. 45:619–628. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen S, Li P, Xiao B and Guo J: Long
noncoding RNA HMlincRNA717 and AC130710 have been officially name
as gastric cancer associated transcript 2 (GACAT2) and GACAT3,
respectively. Tumor Biol. 35:8351–8352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Hur K, Toden S,
Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Mohri Y, Kusunoki M, Boland CR and
Goel A: The expressions of metastasis-associated long non-coding
RNA, HOTAIR, is involved in cancer development and peritoneal
metastasis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 74:3553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|