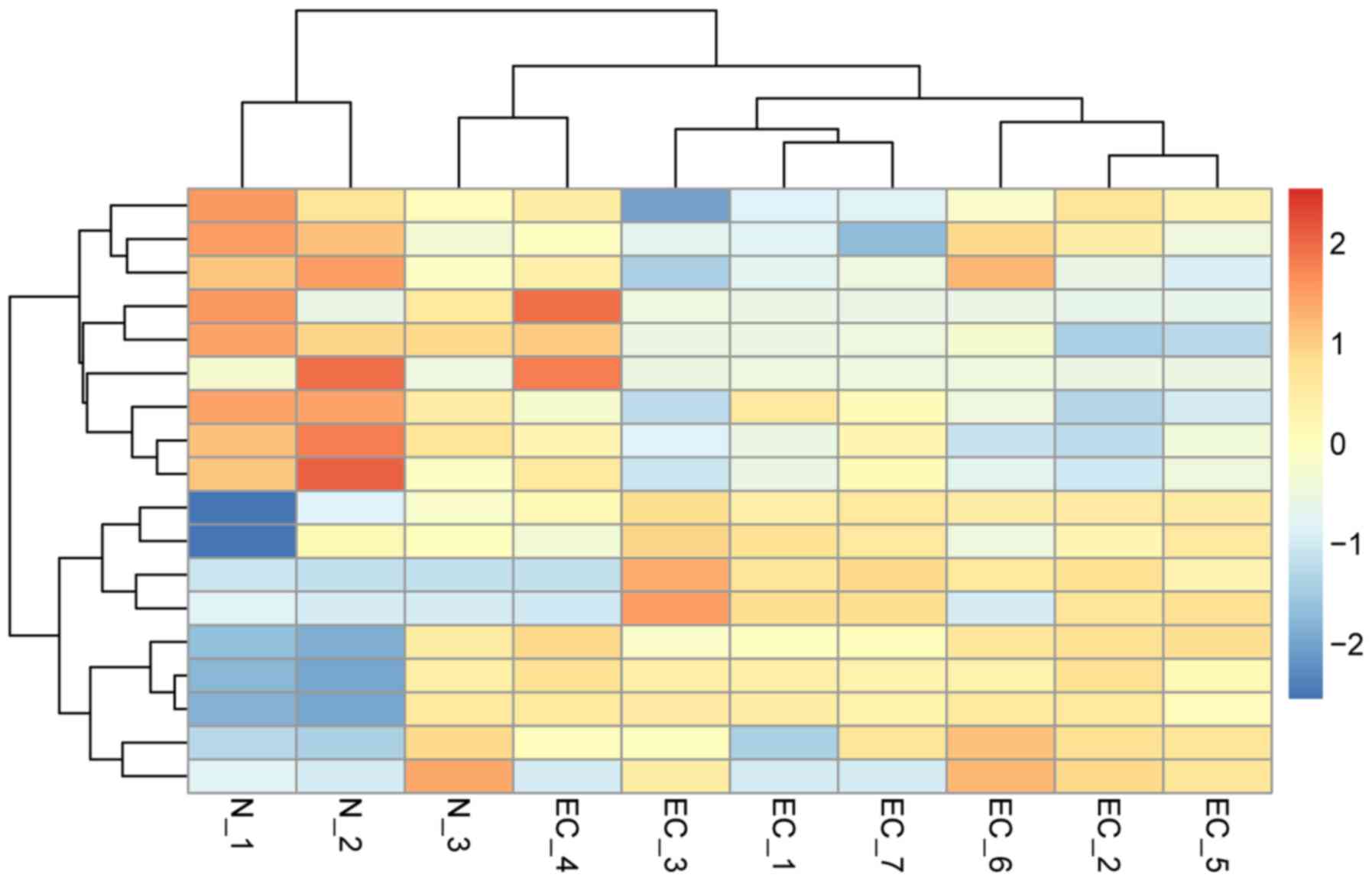
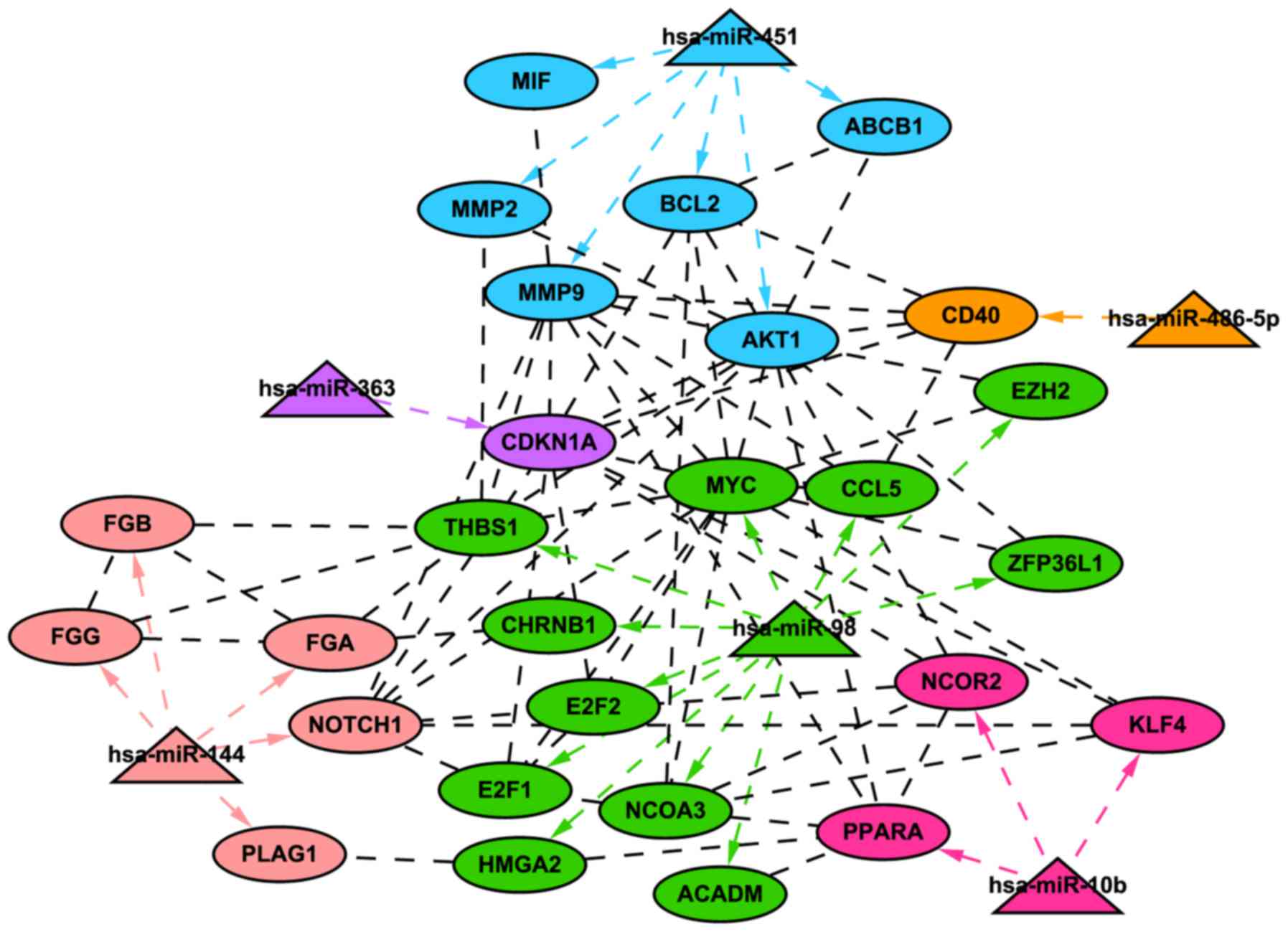
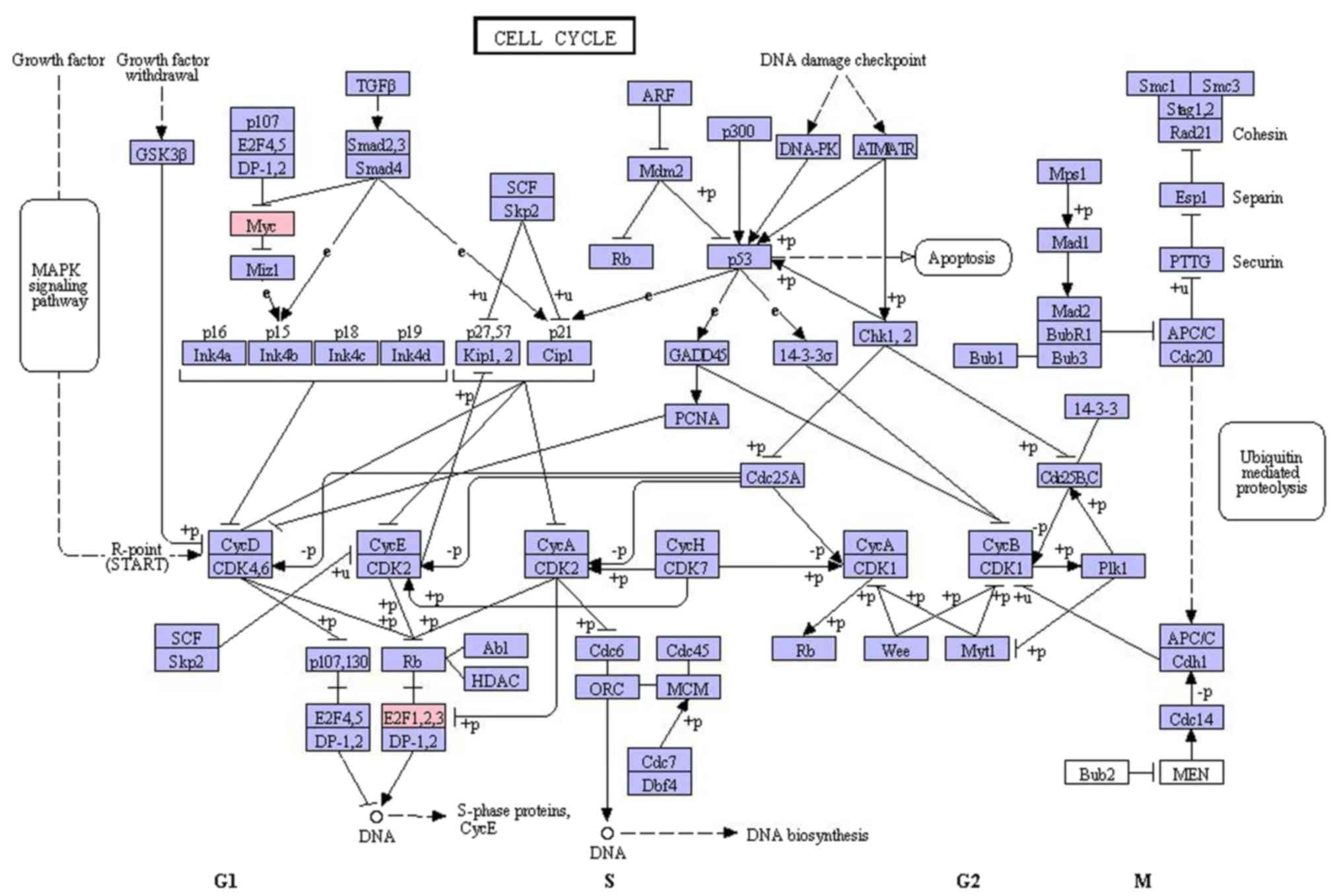
|
1
|
Whiteman DC: Esophageal cancer: Priorities
for prevention. Curr Epidemiol Rep. 1:138–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Fan Y,
Qiao Y and Zhou Q: Esophageal cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2010. Thorac Cancer. 5:343–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei WQ, Yang J, Zhang SW, Chen WQ and Qiao
YL: Esophageal cancer mortality trends during the last 30 years in
high risk areas in China: Comparison of results from national death
surveys conducted in the 1970's, 1990's and 2004–2005. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 12:1821–1826. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang M, Liu R, Sheng J, Liao J, Wang Y,
Pan E, Guo W, Pu Y and Yin L: Differential expression profiles of
microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:169–176.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gu J, Wang Y and Wu X: MicroRNA in the
pathogenesis and prognosis of esophageal cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
19:1292–1300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao WJ, Wang YL, Lu JG, Guo L, Qi B and
Chen ZJ: MicroRNA-506 inhibits esophageal cancer cell proliferation
via targeting CREB1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:10868–10874.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lucas K and Raikhel AS: Insect microRNAs:
Biogenesis, expression profiling and biological functions. Insect
Biochem Mol Biol. 43:24–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, Fujimura L,
Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M and
Matsubara H: miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive
miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int
Cancer. 127:2804–2814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kong KL, Kwong DL, Chan TH, Law SY, Chen
L, Li Y, Qin YR and Guan XY: MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth
and metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through
repressing insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Gut. 61:33–42.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen ZL, Zhao XH, Wang JW, Li BZ, Wang Z,
Sun J, Tan FW, Ding DP, Xu XH, Zhou F, et al: microRNA-92a promotes
lymph node metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
via E-cadherin. J Biol Chem. 286:10725–10734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H,
Tsujiura M, Morimura R, Nagata H, Kosuga T, Iitaka D, Konishi H,
Shiozaki A, et al: Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with
oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:104–111.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee YH and Wong DT: Saliva: An emerging
biofluid for early detection of diseases. Am J Dent. 22:241–248.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pfaffe T, Cooper-White J, Beyerlein P,
Kostner K and Punyadeera C: Diagnostic potential of saliva: Current
state and future applications. Clin Chem. 57:675–687. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Elashoff D, Oh M, Sinha U, St John
MA, Zhou X, Abemayor E and Wong DT: Serum circulating human mRNA
profiling and its utility for oral cancer detection. J Clin Oncol.
24:1754–1760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mbulaiteye SM, Walters M, Engels EA,
Bakaki PM, Ndugwa CM, Owor AM, Goedert JJ, Whitby D and Biggar RJ:
High levels of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in saliva and peripheral
blood from Ugandan mother-child pairs. J Infect Dis. 193:422–426.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie Z, Chen G, Zhang X, Li D, Huang J,
Yang C, Zhang P, Qin Y, Duan Y, Gong B and Li Z: Salivary microRNAs
as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e575022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database issue):
D991–D995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fujita A, Sato JR, Lde O Rodrigues,
Ferreira CE and Sogayar MC: Evaluating different methods of
microarray data normalization. BMC Bioinformatics. 7:4692006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W, Irizarry
RA and Dudoit S: Springer; New York: pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Cao C, Ma Q, Zeng Q, Wang H, Cheng
Z, Zhu G, Qi J, Ma H, Nian H and Wang Y: RNA-seq analyses of
multiple meristems of soybean: Novel and alternative transcripts,
evolutionary and functional implications. BMC Plant Biol.
14:1692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue): D105–D110.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database issue): D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu J, Mao X, Cai T, Luo J and Wei L: KOBAS
server: A web-based platform for automated annotation and pathway
identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Web Server issue): W720–W724.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:1–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Subramaniam D, Ponnurangam S, Ramamoorthy
P, Standing D, Battafarano RJ, Anant S and Sharma P: Curcumin
induces cell death in esophageal cancer cells through modulating
Notch signaling. PLoS One. 7:e305902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peters JH and Avisar N: The molecular
pathogenesis of Barrett's esophagus: Common signaling pathways in
embryogenesis metaplasia and neoplasia. J Gastrointest Surg. 14
Suppl 1:81–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mendelson J, Song S, Li Y, Maru DM, Mishra
B, Davila M, Hofstetter WL and Mishra L: Dysfunctional transforming
growth factor-β signaling with constitutively active Notch
signaling in Barrett's esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer.
117:3691–3702. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weisel JW: Fibrinogen and fibrin. Adv
Protein Chem. 70:247–299. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takeuchi H, Ikeuchi S, Kitagawa Y, Shimada
A, Oishi T, Isobe Y, Kubochi K, Kitajima M and Matsumoto S:
Pretreatment plasma fibrinogen level correlates with tumor
progression and metastasis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma
of the esophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:2222–2227. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matsuda S, Takeuchi H, Fukuda K, Nakamura
R, Takahashi T, Wada N, Kawakubo H, Saikawa Y, Omori T and Kitagawa
Y: Clinical significance of plasma fibrinogen level as a predictive
marker for postoperative recurrence of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma in patients receiving neoadjuvant treatment. Dis
Esophagus. 27:654–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Freeman-Cook KD, Autry C, Borzillo G,
Gordon D, Barbacci-Tobin E, Bernardo V, Briere D, Clark T, Corbett
M, Jakubczak J, et al: Design of selective, ATP-competitive
inhibitors of Akt. J Med Chem. 53:4615–4622. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eide PW, Cekaite L, Danielsen SA,
Eilertsen IA, Kjenseth A, Fykerud TA, Ågesen TH, Bruun J, Rivedal
E, Lothe RA and Leithe E: NEDD4 is overexpressed in colorectal
cancer and promotes colonic cell growth independently of the
PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway. Cell Signal. 25:12–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lahtz C and Pfeifer GP: Epigenetic changes
of DNA repair genes in cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:51–58. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weber SM, Bornstein S, Li Y, Malkoski SP,
Wang D, Rustgi AK, Kulesz-Martin MF, Wang XJ and Lu SL:
Tobacco-specific carcinogen nitrosamine
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone induces AKT
activation in head and neck epithelia. Int J Oncol. 39:1193–1198.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
West KA, Brognard J, Clark AS, Linnoila
IR, Yang X, Swain SM, Harris C, Belinsky S and Dennis PA: Rapid Akt
activation by nicotine and a tobacco carcinogen modulates the
phenotype of normal human airway epithelial cells. J Clin Invest.
111:81–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Samantaray S, Sharma R, Chattopadhyaya TK,
Gupta SD and Ralhan R: Increased expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
130:37–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B and
Szmitkowski M: The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and
their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pazienza V, Vinciguerra M and Mazzoccoli
G: PPARs signaling and cancer in the gastrointestinal system. PPAR
Res. 2012:5608462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dang DT, Pevsner J and Yang VW: The
biology of the mammalian Krüppel-like family of transcription
factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 32:1103–1121. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tian Y, Luo A, Cai Y, Su Q, Ding F, Chen H
and Liu Z: MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through
KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem.
285:7986–7994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Peter ME: Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs:
Guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression. Cell Cycle.
8:843–852. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sugimura K, Miyata H, Tanaka K, Hamano R,
Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Yamasaki M, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori
M and Doki Y: Let-7 expression is a significant determinant of
response to chemotherapy through the regulation of IL-6/STAT3
pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:5144–5153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bretones G, Delgado MD and León J: Myc and
cell cycle control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:506–516. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamazaki K, Hasegawa M, Ohoka I, Hanami K,
Asoh A, Nagao T, Sugano I and Ishida Y: Increased E2F-1 expression
via tumour cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis are
correlated with adverse prognosis in patients with squamous cell
carcinoma of the oesophagus. J Clin Pathol. 58:904–910. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Laresgoiti U, Apraiz A, Olea M, Mitxelena
J, Osinalde N, Rodriguez JA, Fullaondo A and Zubiaga AM: E2F2 and
CREB cooperatively regulate transcriptional activity of cell cycle
genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:10185–10198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xanthoulis A and Tiniakos DG: E2F
transcription factors and digestive system malignancies: How much
do we know? World J Gastroenterol. 19:3189–3198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sun Q, Zhang J, Cao W, Wang X, Xu Q, Yan
M, Wu X and Chen W: Dysregulated miR-363 affects head and neck
cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting podoplanin. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:513–520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hsu KW, Wang AM, Ping YH, Huang KH, Huang
TT, Lee HC, Lo SS, Chi CW and Yeh TS: Downregulation of tumor
suppressor MBP-1 by microRNA-363 in gastric carcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 35:208–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gartel AL and Radhakrishnan SK: Lost in
transcription: p21 repression, mechanisms, and consequences. Cancer
Res. 65:3980–3985. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kehry MR: CD40-mediated signaling in B
cells. Balancing cell survival, growth, and death. J Immunol.
156:2345–2348. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Posner MR, Cavacini LA, Upton MP, Tillman
KC, Gornstein ER and Norris CM Jr: Surface membrane-expressed CD40
is present on tumor cells from squamous cell cancer of the head and
neck in vitro and in vivo and regulates cell growth in tumor cell
lines. Clin Cancer Res. 5:2261–2270. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cao W, Cavacini LA, Tillman KC and Posner
MR: CD40 function in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck.
Oral Oncol. 41:462–469. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|