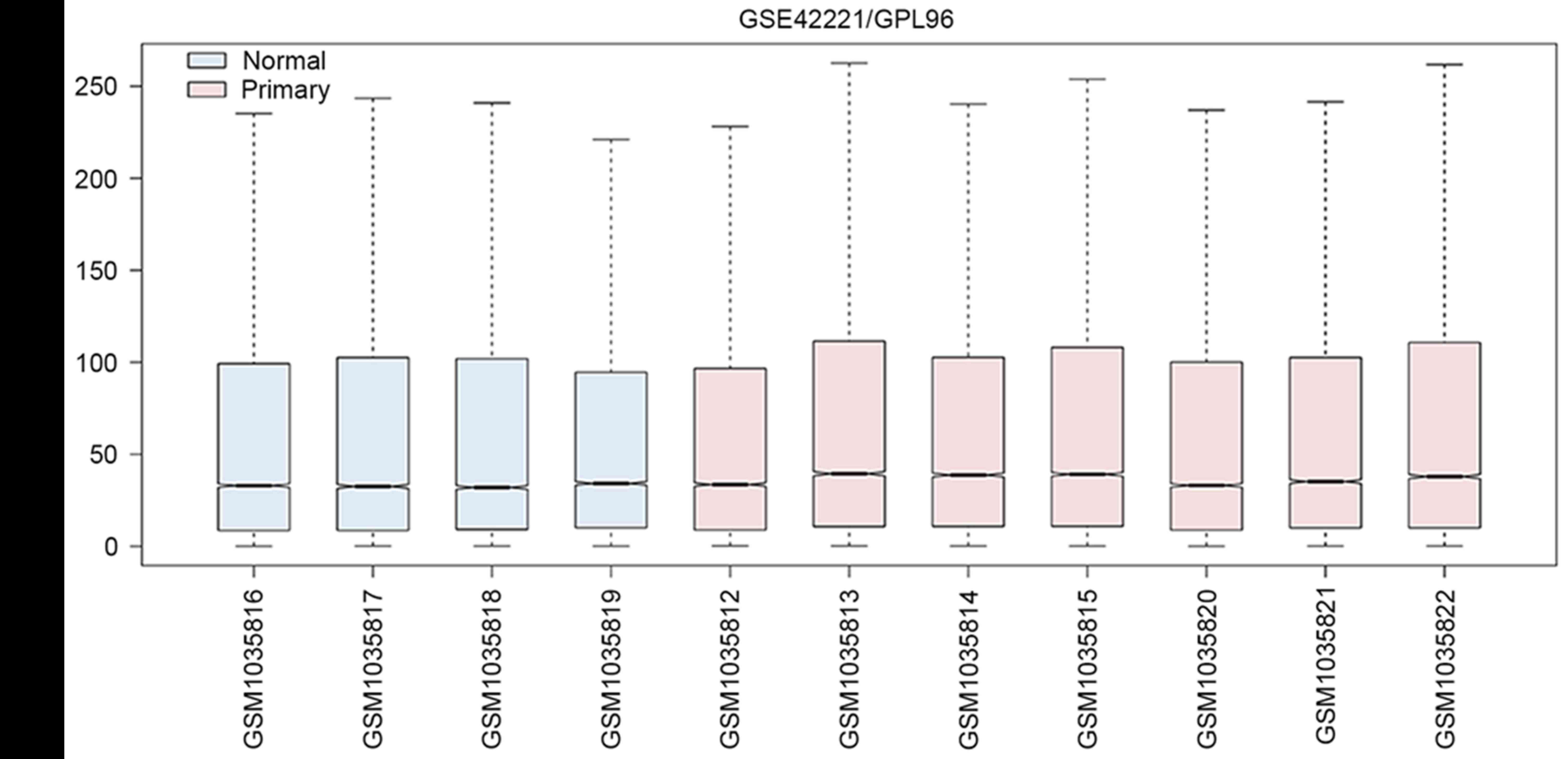
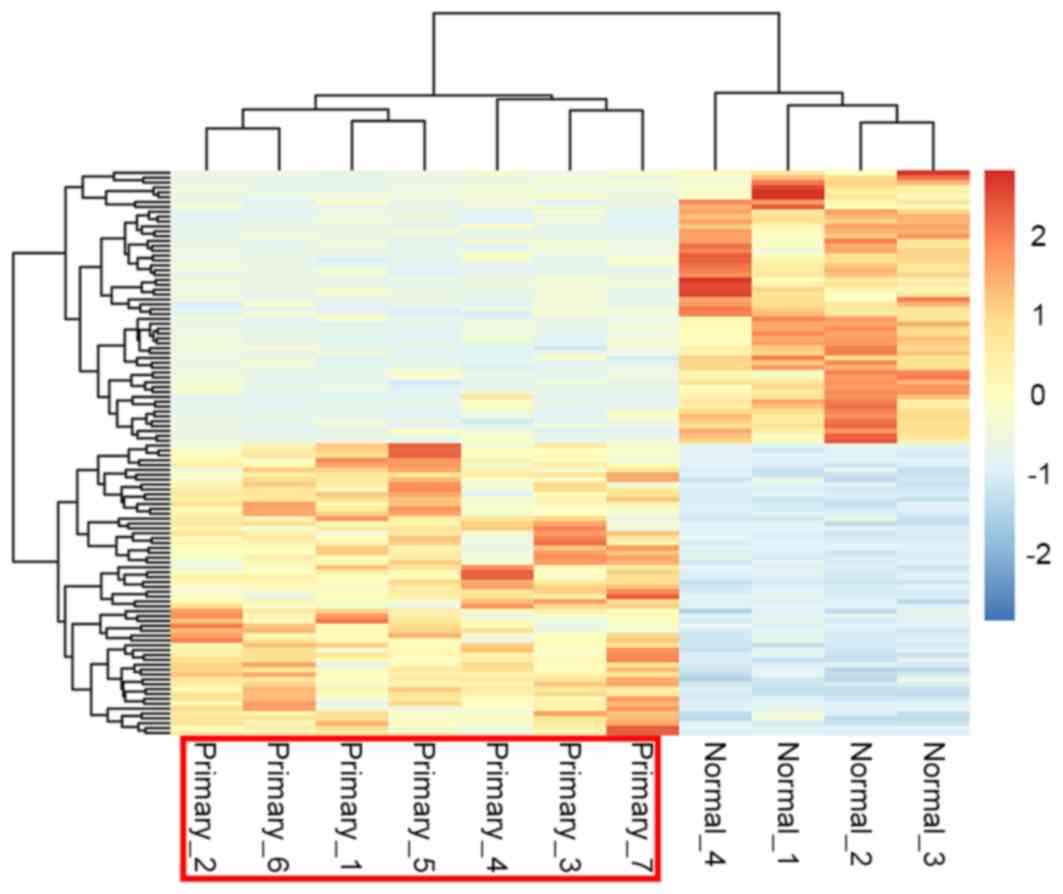
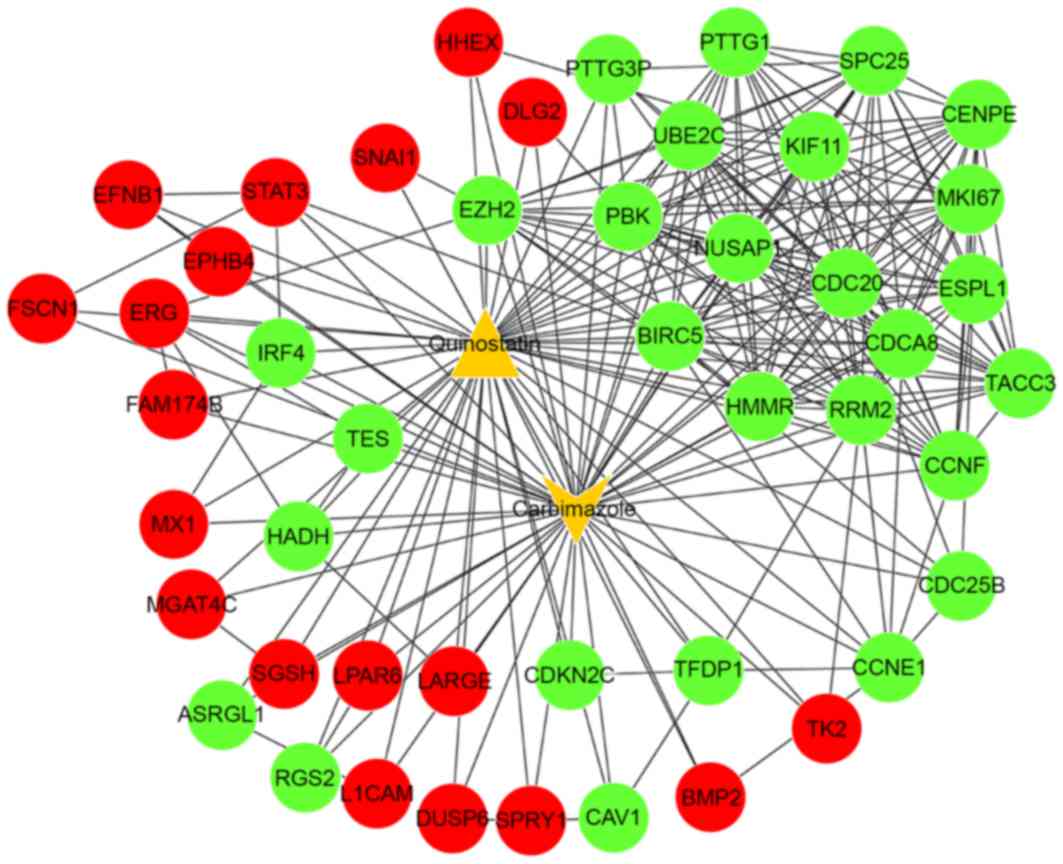
|
1
|
Krajinovic M, Lamothe S, Labuda D,
Lemieux-Blanchard E, Theoret Y, Moghrabi A and Sinnett D: Role of
MTHFR genetic polymorphisms in the susceptibility to childhood
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 103:252–257. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Howlader N, Noone A, Krapcho M, et al:
SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2011. Bethesda, MD: National
Cancer Institute. Journal; 2014
|
|
3
|
Barrington-Trimis JL, Cockburn M, Metayer
C, Gauderman WJ, Wiemels J and McKean-Cowdin R: Rising rates of
acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Hispanic children: Trends in
incidence from 1992 to 2011. Blood. 125:3033–3034. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martelli MF, Di Ianni M, Ruggeri L,
Falzetti F, Carotti A, Terenzi A, Pierini A, Massei MS, Amico L,
Urbani E, et al: HLA-haploidentical transplantation with regulatory
and conventional T-cell adoptive immunotherapy prevents acute
leukemia relapse. Blood. 124:638–644. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coustan-Smith E, Song G, Clark C, Key L,
Liu P, Mehrpooya M, Stow P, Su X, Shurtleff S, Pui CH, et al: New
markers for minimal residual disease detection in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 117:6267–6276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ross ME, Zhou X, Song G, Shurtleff SA,
Girtman K, Williams WK, Liu HC, Mahfouz R, Raimondi SC, Lenny N, et
al: Classification of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia by
gene expression profiling. Blood. 102:2951–2959. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cario G, Stanulla M, Fine BM, Teuffel O,
Neuhoff NV, Schrauder A, Flohr T, Schäfer BW, Bartram CR, Welte K,
et al: Distinct gene expression profiles determine molecular
treatment response in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Blood. 105:821–826. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen JS, Coustan-Smith E, Suzuki T, Neale
GA, Mihara K, Pui CH and Campana D: Identification of novel markers
for monitoring minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Blood. 97:2115–2120. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei MC and Cleary ML: Novel methods and
approaches to acute lymphoblastic leukemia drug discovery. Expert
Opin Drug Discov. 9:1435–1446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Habibi D, Ogloff N, Jalili RB, Yost A,
Weng AP, Ghahary A and Ong CJ: Borrelidin, a small molecule
nitrile-containing macrolide inhibitor of threonyl-tRNA synthetase,
is a potent inducer of apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Invest New Drugs. 30:1361–1370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harder L, Eschenburg G, Zech A,
Kriebitzsch N, Otto B, Streichert T, Behlich AS, Dierck K, Klingler
B, Hansen A, et al: Aberrant ZNF423 impedes B cell differentiation
and is linked to adverse outcome of ETV6-RUNX1 negative B precursor
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 210:2289–2304. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harder L, Otto B and Horstmann MA:
Transcriptional dysregulation of the multifunctional zinc finger
factor 423 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood. Genomics
Data. 2:96–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujita A, Sato JR, Lde O Rodrigues,
Ferreira CE and Sogayar MC: Evaluating different methods of
microarray data normalization. BMC Bioinformatics. 7:4692006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Springer; pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Statistical Soc Series B
(Methodological). 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
16
|
Szekely GJ and Rizzo ML: Hierarchical
clustering via joint between-within distances: Extending Ward's
minimum variance method. J Classification. 22:151–183. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT and
Flannery BP: Hierarchical Clustering by Phylogenetic Trees. Section
16.4Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing. 3rd.
Cambridge University Press; New York, NY: 2007
|
|
18
|
Deza MM and Deza E: Encyclopedia of
distances. Springer; Heidelberg: pp. 1–583. 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database issue): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networksData Mining in Proteomics. Springer; pp. 291–303. 2011
|
|
23
|
Iwamoto S, Mihara K, Downing JR, Pui CH
and Campana D: Mesenchymal cells regulate the response of acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells to asparaginase. J Clin Invest.
117:1049–1057. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Figueroa ME, Wouters BJ, Skrabanek L,
Glass J, Li Y, Erpelinck-Verschueren CA, Langerak AW, Löwenberg B,
Fazzari M, Greally JM, et al: Genome wide epigenetic analysis
delineates a biologically distinct immature acute leukemia with
myeloid/T-lymphoid features. Blood. 113:2795–27804. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma L, Lu MF, Schwartz RJ and Martin JF:
Bmp2 is essential for cardiac cushion epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and myocardial patterning. Development. 132:5601–5611.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schmitt B, Ringe J, Häupl T, Notter M,
Manz R, Burmester GR, Sittinger M and Kaps C: BMP2 initiates
chondrogenic lineage development of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells in high-density culture. Differentiation. 71:567–577. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiaramonte R, Basile A, Tassi E,
Calzavara E, Cecchinato V, Rossi V, Biondi A and Comi P: A wide
role for NOTCH1 signaling in acute leukemia. Cancer Lett.
219:113–120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mendes-da-Cruz DA, Brignier AC, Asnafi V,
Baleydier F, Messias CV, Lepelletier Y, Bedjaoui N, Renand A,
Smaniotto S, Canioni D, et al: Semaphorin 3F and Neuropilin-2
control the migration of human T-cell precursors. PLoS One.
9:e1034052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang G, Freywald T, Webster J, Kozan D,
Geyer R, DeCoteau J, Narendran A and Freywald A: In human leukemia
cells ephrin-B-induced invasive activity is supported by lck and is
associated with reassembling of lipid raft signaling complexes. Mol
Cancer Res. 6:291–305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
O'Brien MM, Lee-Kim Y, George TI, McClain
KL, Twist CJ and Jeng M: Precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia presenting with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 50:381–383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Medyouf H, Alcalde H, Berthier C,
Guillemin MC, dos Santos NR, Janin A, Decaudin D, de Thé H and
Ghysdael J: Targeting calcineurin activation as a therapeutic
strategy for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Med.
13:736–741. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Morris JP
III, Silverman LB, Sanchez-Irizarry C, Blacklow SC, Look AT and
Aster JC: Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Science. 306:269–271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barata JT, Cardoso AA, Nadler LM and
Boussiotis VA: Interleukin-7 promotes survival and cell cycle
progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by
down-regulating the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(kip1).
Blood. 98:1524–1531. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trageser D, Iacobucci I, Nahar R, Duy C,
von Levetzow G, Klemm L, Park E, Schuh W, Gruber T, Herzog S, et
al: Pre-B cell receptor-mediated cell cycle arrest in Philadelphia
chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia requires IKAROS
function. J Exp Med. 206:1739–1753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Russell LJ, Capasso M, Vater I, Akasaka T,
Bernard OA, Calasanz MJ, Chandrasekaran T, Chapiro E, Gesk S,
Griffiths M, et al: Deregulated expression of cytokine receptor
gene, CRLF2, is involved in lymphoid transformation in B-cell
precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 114:2688–2698. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chiron D, Di Liberto M, Martin P, Huang X,
Sharman J, Blecua P, Mathew S, Vijay P, Eng K, Ali S, et al:
Cell-cycle reprogramming for PI3K inhibition overrides a
relapse-specific C481S BTK mutation revealed by longitudinal
functional genomics in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov.
4:1022–1035. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hou YY, Cao WW, Li L, Li SP, Liu T, Wan
HY, Liu M, Li X and Tang H: MicroRNA-519d targets MKi67 and
suppresses cell growth in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line
QGY-7703. Cancer Lett. 307:182–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bosch A Vanden, Raemaekers T, Denayer S,
Torrekens S, Smets N, Moermans K, Dewerchin M, Carmeliet P and
Carmeliet G: NuSAP is essential for chromatin-induced spindle
formation during early embryogenesis. J Cell Sci. 123:3244–3255.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Borowitz MJ, Devidas M, Hunger SP, Bowman
WP, Carroll AJ, Carroll WL, Linda S, Martin PL, Pullen DJ,
Viswanatha D, et al: Clinical significance of minimal residual
disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its
relationship to other prognostic factors: A Children's Oncology
Group study. Blood. 111:5477–5485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Campana D: Molecular determinants of
treatment response in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology Am
Soc Hematol Educ Program. 1–373. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tetzlaff MT, Bai C, Finegold M, Wilson J,
Harper JW, Mahon KA and Elledge SJ: Cyclin F disruption compromises
placental development and affects normal cell cycle execution. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:2487–2498. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bhadri VA, Cowley MJ, Kaplan W, Trahair TN
and Lock RB: Evaluation of the NOD/SCID xenograft model for
glucocorticoid-regulated gene expression in childhood B-cell
precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Genomics. 12:5652011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hatfield KJ, Reikvam H and Bruserud Ø:
Identification of a subset of patients with acute myeloid leukemia
characterized by long-term in vitro proliferation and altered cell
cycle regulation of the leukemic cells. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
18:1237–1251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Paganin M and Ferrando A: Molecular
pathogenesis and targeted therapies for NOTCH1-induced T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Rev. 25:83–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schnell SA, Ambesi-Impiombato A,
Sanchez-Martin M, Belver L, Xu L, Qin Y, Kageyama R and Ferrando
AA: Therapeutic targeting of HES1 transcriptional programs in
T-ALL. Blood. 125:2806–2814. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang J, Shamji A, Matchacheep S and
Schreiber SL: Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of class
Ia PI3Ks with cell-based screening. Chem Biol. 14:371–377. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Au W, Lie A, Kung A, Liang R, Hawkins B
and Kwong Y: Autoimmune thyroid dysfunction after hematopoietic
stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 35:383–388.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tatevossian R, Blair JC, Plowman PN,
Savage MO and Shankar AG: Thyrotoxicosis after matched unrelated
bone marrow transplantation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 26:529–531.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mangolini M, de Boer J,
Walf-Vorderwülbecke V, Pieters R, den Boer ML and Williams O: STAT3
mediates oncogenic addiction to TEL-AML1 in t(12; 21) acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 122:542–549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Iyer J, Moghe S, Furukawa M and Tsai MY:
What's Nu(SAP) in mitosis and cancer? Cell Signal. 23:991–998.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tian W, Li B, Warrington R, Tomchick DR,
Yu H and Luo X: Structural analysis of human Cdc20 supports
multisite degron recognition by APC/C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:pp. 18419–18424. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Battula VL, Chen Y, Mda G Cabreira, Ruvolo
V, Wang Z, Ma W, Konoplev S, Shpall E, Lyons K, Strunk D, et al:
Connective tissue growth factor regulates adipocyte differentiation
of mesenchymal stromal cells and facilitates leukemia bone marrow
engraftment. Blood. 122:357–366. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|