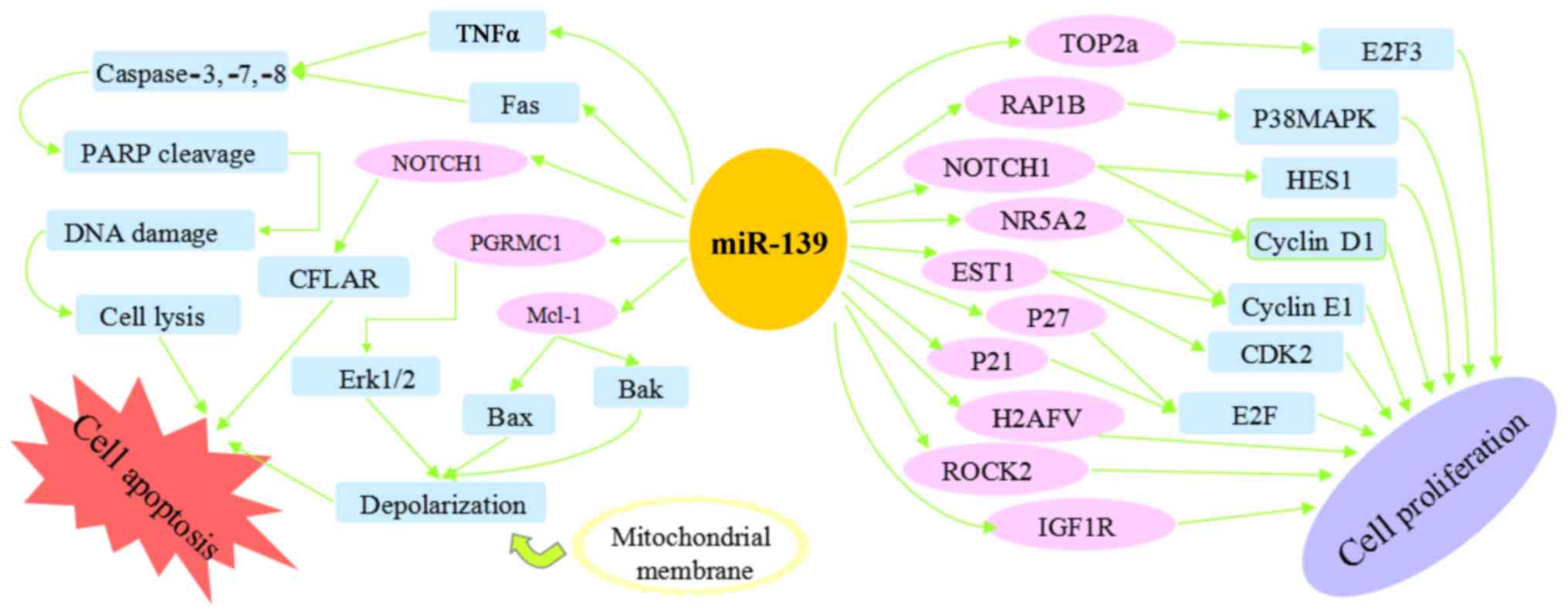
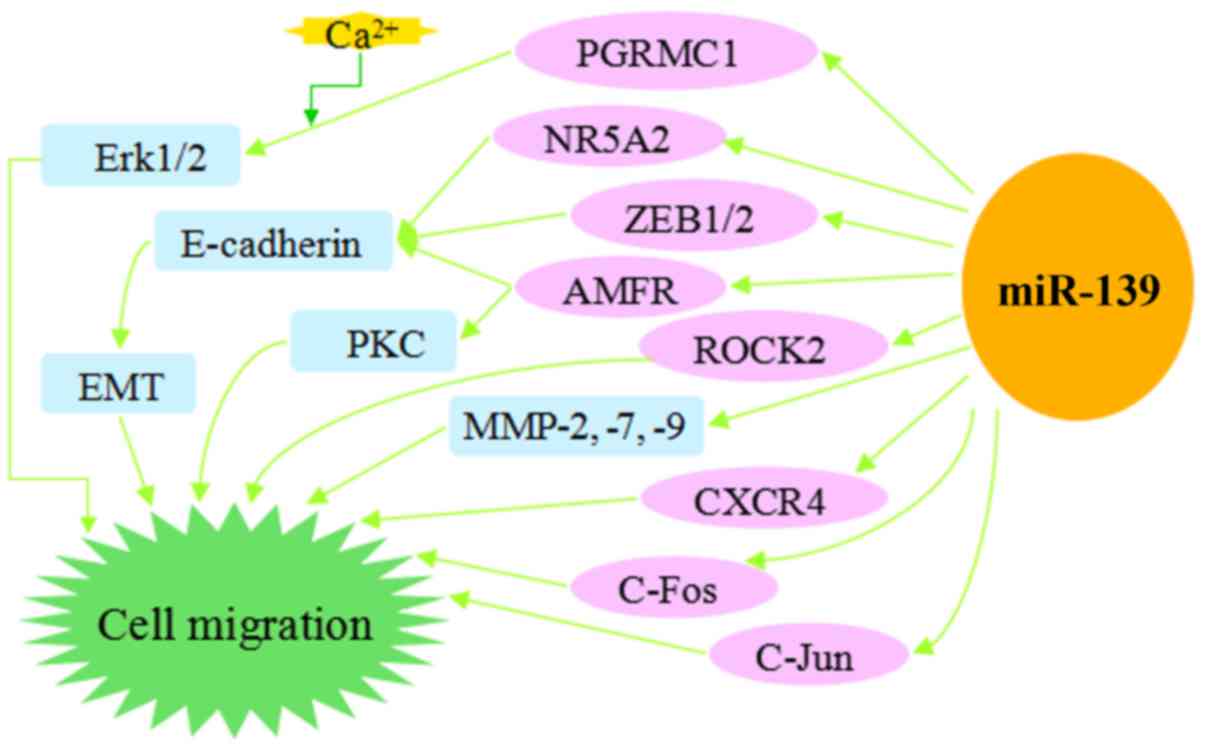
|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
Elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:pp. 15524–15529. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saba R, Goodman CD, Huzarewich RL,
Robertson C and Booth SA: A miRNA signature of prion induced
neurodegeneration. PLoS One. 3:e36522008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Chen Z, Yu J, Xia J and Zhou X:
MicroRNA profiling and head and neck cancer. Comp Funct Genomics.
8375142009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, Evans BR, Medina DJ,
Liu CG and Yang JM: Role of MicroRNA miR-27a and miR-451 in the
regulation of MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression in human cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 76:582–588. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li T, Leong MH, Harms B, Kennedy G and
Chen L: MicroRNA-21 as a potential colon and rectal cancer
biomarker. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5615–5621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen K, Liang Q, Xu K, Cui D, Jiang L, Yin
P, Lu Y, Li Q and Liu J: MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis
of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth
factor receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:320–330. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu W, Li X and Wang J: miR-139 regulates
the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma through
the WNT/TCF-4 pathway. Oncol Rep. 31:397–404. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bar M, Wyman SK, Fritz BR, Qi J, Garg KS,
Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Bendoraite A, Mitchell PS, Nelson AM, et al:
MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by
deep sequencing of small RNA libraries. Stem Cells. 26:2496–2505.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z,
Meng D and Wang Y: Differential expression of microRNA species in
human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:652–657. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mascaux C, Laes JF, Anthoine G, Haller A,
Ninane V, Burny A and Sculier JP: Evolution of microRNA expression
during human bronchial squamous carcinogenesis. Eur Respir J.
33:352–359. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hiroki E, Akahira J, Suzuki F, Nagase S,
Ito K, Suzuki T, Sasano H and Yaegashi N: Changes in microRNA
expression levels correlate with clinicopathological features and
prognoses in endometrial serous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Sci.
101:241–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang KH, Miller N, Kheirelseid EA,
Lemetre C, Ball GR, Smith MJ, Regan M, McAnena OJ and Kerin MJ:
MicroRNA signature analysis in colorectal cancer: Identification of
expression profiles in stage II tumors associated with aggressive
disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 26:1415–1422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H,
Kawakami K, Tatarano S, Nishiyama K, Nohata N, Seki N and Nakagawa
M: The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting
TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:808–818. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang Y, Chen HC, Chiang CW, Yeh CT, Chen
SJ and Chou CK: Identification of a two-layer regulatory network of
proliferation-related microRNAs in hepatoma cells. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:10478–10493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miles GD, Seiler M, Rodriguez L, Rajagopal
G and Bhanot G: Identifying microRNA/mRNA dysregulations in ovarian
cancer. BMC Res Notes. 5:1642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu R, Yang M, Meng Y, Liao J, Sheng J, Pu
Y, Yin L and Kim SJ: Tumor-suppressive function of miR-139-5p in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e770682013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang M, Liu R, Sheng J, Liao J, Wang Y,
Pan E, Guo W, Pu Y and Yin L: Differential expression profiles of
microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:169–176.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dettmer MS, Perren A, Moch H, Komminoth P,
Nikiforov YE and Nikiforova MN: MicroRNA profile of poorly
differentiated thyroid carcinomas: New diagnostic and prognostic
insights. J Mol Endocrinol. 52:181–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li RY, Chen LC, Zhang HY, Du WZ, Feng Y,
Wang HB, Wen JQ, Liu X, Li XF, Sun Y, et al: MiR-139 inhibits Mcl-1
expression and potentiates TMZ-induced apoptosis in glioma. CNS
Neurosci Ther. 19:477–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Sand D, Georgas D, Hahn
SA, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P and Bechara FG: Expression of
microRNAs in basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 167:847–855.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu X, Weng L, Li X, Guo C, Pal SK, Jin JM,
Li Y, Nelson RA, Mu B, Onami SH, et al: Identification of a
4-microRNA signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis
and prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e356612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo HN, Wang ZH, Sheng Y, Zhang Q, Yan J,
Hou J, Zhu K, Cheng Y, Xu YL, Zhang XH, et al: MiR-139 targets
CXCR4 and inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of laryngeal
squamous carcinoma cells. Med Oncol. 31:7892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu W, Hang M, Yuan CY, Wu FL, Chen SB and
Xue K: MicroRNA-139-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in human non-small
cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3864–3870.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li L, Li B, Chen D, Liu L, Huang C, Lu Z,
Lun L and Wan X: miR-139 and miR-200c regulate pancreatic cancer
endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Oncol Rep. 34:51–58.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mi L, Chen Y, Zheng X, Li Y, Zhang Q, Mo D
and Yang G: MicroRNA-139-5p suppresses 3T3-L1 preadipocyte
differentiation through notch and IRS1/PI3K/Akt insulin signaling
pathways. J Cell Biochem. 116:1195–1204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mi L, Li Y, Zhang Q, Zhao C, Peng Y, Yang
G and Zheng X: MicroRNA-139-5p regulates C2C12 cell myogenesis
through blocking Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Cell
Biol. 93:8–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao G, Zhou X, Fang T, Hou Y and Hu Y:
Hyaluronic acid promotes the expression of progesterone receptor
membrane component 1 via epigenetic silencing of miR-139-5p in
human and rat granulosa cells. Biol Reprod. 91:1162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
MacLellan SA, MacAulay C, Lam S and Garnis
C: Pre-profiling factors influencing serum microRNA levels. BMC
Clin Pathol. 14:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp.
10513–10518. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cava C, Bertoli G, Ripamonti M, Mauri G,
Zoppis I, Rosa PA Della, Gilardi MC and Castiglioni I: Integration
of mRNA expression profile, copy number alterations, and microRNA
expression levels in breast cancer to improve grade definition.
PLoS One. 9:e976812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Li J and Tang
JH: MiR-139-5p: Promising biomarker for cancer. Tumour Biol.
36:1355–1365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Corbetta S, Vaira V, Guarnieri V,
Scillitani A, Eller-Vainicher C, Ferrero S, Vicentini L, Chiodini
I, Bisceglia M, Beck-Peccoz P, et al: Differential expression of
microRNAs in human parathyroid carcinomas compared with normal
parathyroid tissue. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:135–146. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shen K, Mao R, Ma L, Li Y, Qiu Y, Cui D,
Le V, Yin P, Ni L and Liu J: Post-transcriptional regulation of the
tumor suppressor miR-139-5p and a network of miR-139-5p-mediated
mRNA interactions in colorectal cancer. FEBS J. 281:3609–3624.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tombol Z, Eder K, Kovács A, Szabó PM,
Kulka J, Likó I, Zalatnai A, Rácz G, Tóth M, Patócs A, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiling in benign (sporadic and hereditary)
and recurring adrenal pheochromocytomas. Mod Pathol. 23:1583–1595.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qin C, Huang RY and Wang ZX: Potential
role of miR-100 in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Tumour
Biol. 36:1403–1409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu DN, Huang Q and Tian L: The molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microRNA-7 in cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:415–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, Au SL, Lee JM,
Poon RT, Man K and Ng IO: The microRNA miR-139 suppresses
metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by
down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology. 140:322–331. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Aghagolzadeh P and Radpour R: New trends
in molecular and cellular biomarker discovery for colorectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:5678–5693. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kodahl AR, Lyng MB, Binder H, Cold S,
Gravgaard K, Knoop AS and Ditzel HJ: Novel circulating microRNA
signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in
ER-positive early-stage breast cancer: A case control study. Mol
Oncol. 8:874–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rask L, Balslev E, Søkilde R, Høgdall E,
Flyger H, Eriksen J and Litman T: Differential expression of
miR-139, miR-486 and miR-21 in breast cancer patients
sub-classified according to lymph node status. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
37:215–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M, Lioudmer P,
Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Miller K, Kilic E, Erbersdobler A, Weikert
S and Jung K: miRNA profiling identifies candidate mirnas for
bladder cancer diagnosis and clinical outcome. J Mol Diagn.
15:695–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Di Nicola M,
Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN and Pass HI: microRNAs derived
from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening
and diagnosing. J Thorac Oncol. 8:1156–1162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu X, Xiong F, Wei X, Yang H and Zhou R:
LAPTM4B-35, a novel tetratransmembrane protein and its PPRP motif
play critical roles in proliferation and metastatic potential of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 100:2335–2340. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ather MH and Nazim SM: New and
contemporary markers of prognosis in nonmuscle invasive urothelial
cancer. Korean J Urol. 56:553–564. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Guo H, Hu X, Ge S, Qian G and Zhang J:
Regulation of RAP1B by miR-139 suppresses human colorectal
carcinoma cell proliferation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1465–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Stork PJ: Does rap1 deserve a bad rap?
Trends Biochem Sci. 28:267–275. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang L, Dong Y, Zhu N, Tsoi H, Zhao Z, Wu
CW, Wang K, Zheng S, Ng SS, Chan FK, et al: microRNA-139-5p exerts
tumor suppressor function by targeting NOTCH1 in colorectal cancer.
Mol Cancer. 13:1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mitrea DM, Yoon MK, Ou L and Kriwacki RW:
Disorder-function relationships for the cell cycle regulatory
proteins p21 and p27. Biol Chem. 393:259–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z,
Quan C, Zhou L, Hu Y, Wang Q, Ni S, et al: MiR-139-5p inhibits
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR
and NOTCH1. Protein Cell. 5:851–861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fang S, Ferrone M, Yang C, Jensen JP,
Tiwari S and Weissman AM: The tumor autocrine motility factor
receptor, gp78, is a ubiquitin protein ligase implicated in
degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:pp. 14422–14427. 2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang L, Hou G, Xue L, Li J, Wei P and Xu
P: Autocrine motility factor receptor signaling pathway promotes
cell invasion via activation of ROCK-2 in esophageal squamous cell
cancer cells. Cancer Invest. 28:993–1003. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chiu CG, St-Pierre P, Nabi IR and Wiseman
SM: Autocrine motility factor receptor: A clinical review. Expert
Rev Anticancer Ther. 8:207–217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gu J, Chen Y, Huang H, Yin L, Xie Z and
Zhang MQ: Gene module based regulator inference identifying miR-139
as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Mol Biosyst.
10:3249–3254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Tsang FH,
Ng IO and Wong CM: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically
silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver
cancer metastasis. Hepatology. 56:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, Man K and Ng
IO: Rho-kinase 2 is frequently overexpressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma and involved in tumor invasion. Hepatology. 49:1583–1594.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Qiu G, Lin Y, Zhang H and Wu D: miR-139-5p
inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:315–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Vandewalle C, Van Roy F and Berx G: The
role of the ZEB family of transcription factors in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:773–787. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gheldof A, Hulpiau P, van Roy F, De Craene
B and Berx G: Evolutionary functional analysis and molecular
regulation of the ZEB transcription factors. Cell Mol Life Sci.
69:2527–2541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang Y, Shen WL, Shi ML, Zhang LZ, Zhang
Z, Li P, Xing LY, Luo FY, Sun Q, Zheng XF, et al: Involvement of
aberrant miR-139/Jun feedback loop in human gastric cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1853:481–488. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Guo L, Guo Y and Xiao S: Expression of
tyrosine kinase Etk/Bmx and its relationship with AP-1- and
NF-kappaB-associated proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncology. 72:410–416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yoon JH, Choi YJ and Lee SG: Ginsenoside
Rh1 suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression through
inhibition of activator protein-1 and mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 679:24–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Fan Q, He M, Deng X, Wu WK, Zhao L, Tang
J, Wen G, Sun X and Liu Y: Derepression of c-Fos caused by
microRNA-139 down-regulation contributes to the metastasis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem Funct. 31:319–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Humbert PO, Verona R, Trimarchi JM, Rogers
C, Dandapani S and Lees JA: E2f3 is critical for normal cellular
proliferation. Gene Dev. 14:690–703. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Krishnan K, Steptoe AL, Martin HC,
Pattabiraman DR, Nones K, Waddell N, Mariasegaram M, Simpson PT,
Lakhani SR, Vlassov A, et al: miR-139-5p is a regulator of
metastatic pathways in breast cancer. RNA. 19:1767–1780. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wagner RT, Xu X, Yi F, Merrill BJ and
Cooney AJ: Canonical Wnt/β-catenin regulation of liver receptor
homolog-1 mediates pluripotency gene expression. Stem Cells.
28:1794–1804. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang S, Lan F, Huang L, Dong L, Zhu Z, Li
Z, Xie Y and Fu J: Suppression of hLRH-1 mediated by a DNA
vector-based RNA interference results in cell cycle arrest and
induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell BEL-7402.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 333:917–924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chand AL, Herridge KA, Thompson EW and
Clyne CD: The orphan nuclear receptor LRH-1 promotes breast cancer
motility and invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:965–975. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kothapalli D, Zhao L, Hawthorne EA, Cheng
Y, Lee E, Pure E and Assoian RK: Hyaluronan and CD44 antagonize
mitogen-dependent cyclin D1 expression in mesenchymal cells. J Cell
Biol. 176:535–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kaneko T, Saito H, Toya M, Satio T,
Nakahara K and Hiroi M: Hyaluronic acid inhibits apoptosis in
granulosa cells via CD44. J Assist Reprod Genet. 17:162–167. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Peluso JJ, Liu X, Gawkowska A, Lodde V and
Wu CA: Progesterone inhibits apoptosis in part by PGRMC1-regulated
gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 320:153–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Szczesna-Skorupa E and Kemper B:
Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 inhibits the activity of
drug-metabolizing cytochromes P450 and binds to cytochrome p450
reductase. Mol Pharmacol. 79:340–350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Abe R: Angiogenesis in tumor growth and
metastasis. Curr Pharm Des. 14:37792008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Maehara Y, Kabashima A, Koga T, Tokunaga
E, Takeuchi H, Kakeji Y and Sugimachi K: Vascular invasion and
potential for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in gastric
carcinoma. Surgery. 128:408–416. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bao W, Fu HJ, Xie QS, Wang L, Zhang R, Guo
ZY, Zhao J, Meng YL, Ren XL, Wang T, et al: HER2 interacts with
CD44 to up-regulate CXCR4 via epigenetic silencing of microRNA-139
in gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 141:2076–2087.e6. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Carlson RW, Anderson BO, Burstein HJ,
Carter WB, Edge SB, Farrar WB, Goldstein LJ, Gradishar WJ, Hayes
DF, Hudis CA, et al: Invasive breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 5:246–312. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hua W, Sa KD, Zhang X, Jia LT, Zhao J,
Yang AG, Zhang R, Fan J and Bian K: MicroRNA-139 suppresses
proliferation in luminal type breast cancer cells by targeting
Topoisomerase II alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:1077–1083.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shimizu S, Narita M and Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2
family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by
the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature. 399:483–487. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bannerji R, Kitada S, Flinn IW, Pearson M,
Young D, Reed JC and Byrd JC: Apoptotic-regulatory and
complement-protecting protein expression in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia: Relationship to in vivo rituximab resistance. J Clin
Oncol. 21:1466–1471. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Hussain SR, Cheney CM, Johnson AJ, Lin TS,
Grever MR, Caligiuri MA, Lucas DM and Byrd JC: Mcl-1 is a relevant
therapeutic target in acute and chronic lymphoid malignancies:
Down-regulation enhances rituximab-mediated apoptosis and
complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2144–2150.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kaji D, Miura Y and Takano T: Adjuvant
trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:663–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chen X, Shi K, Wang Y, Song M, Zhou W, Tu
H and Lin Z: Clinical value of integrated-signature miRNAs in
colorectal cancer: miRNA expression profiling analysis and
experimental validation. Oncotarget. 6:37544–37556. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Singh AK, Swarnalatha M and Kumar V:
c-ETS1 facilitates G1/S-phase transition by up-regulating cyclin E
and CDK2 genes and cooperates with hepatitis B virus X protein for
their deregulation. J Biol Chem. 286:21961–21970. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|