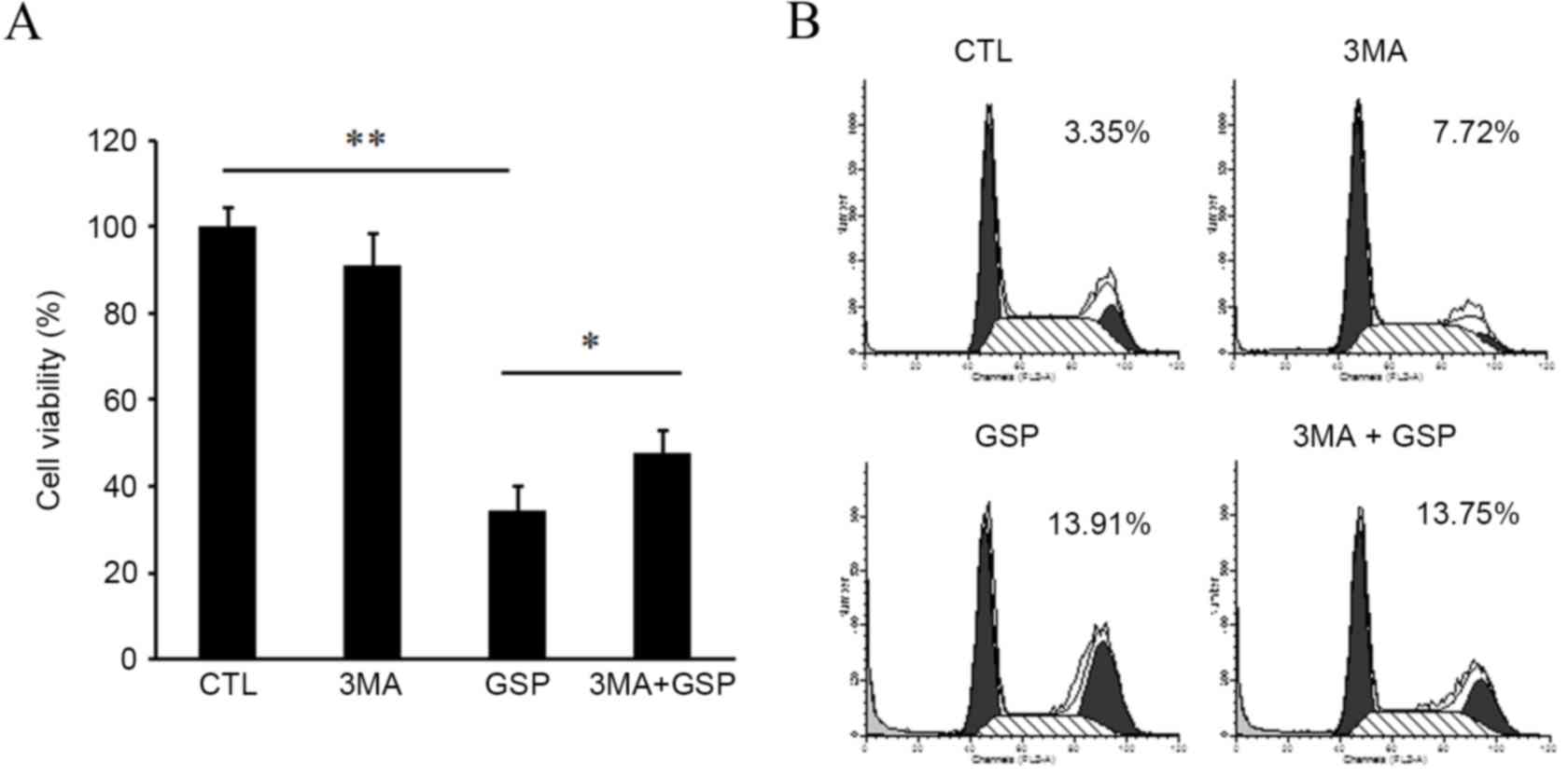
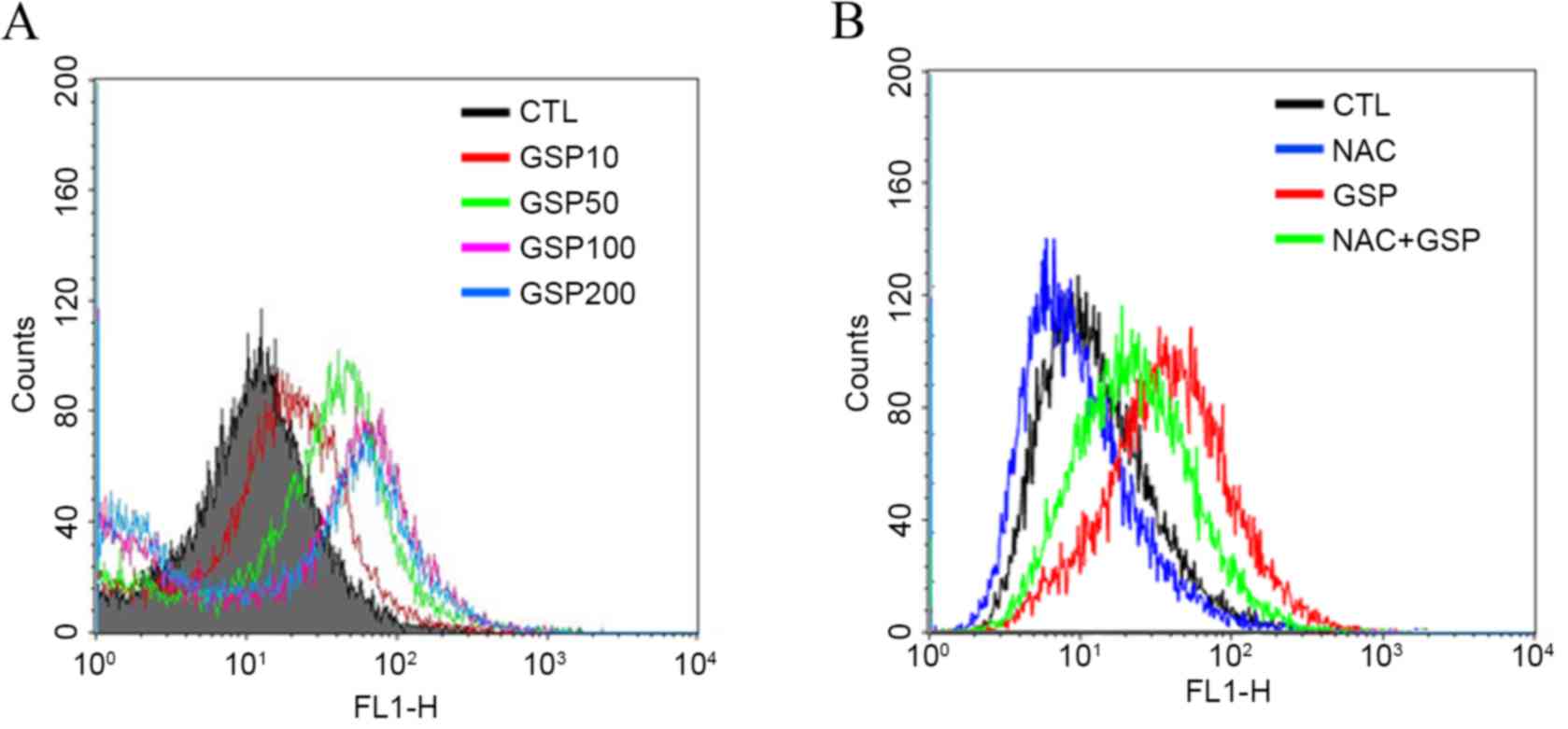
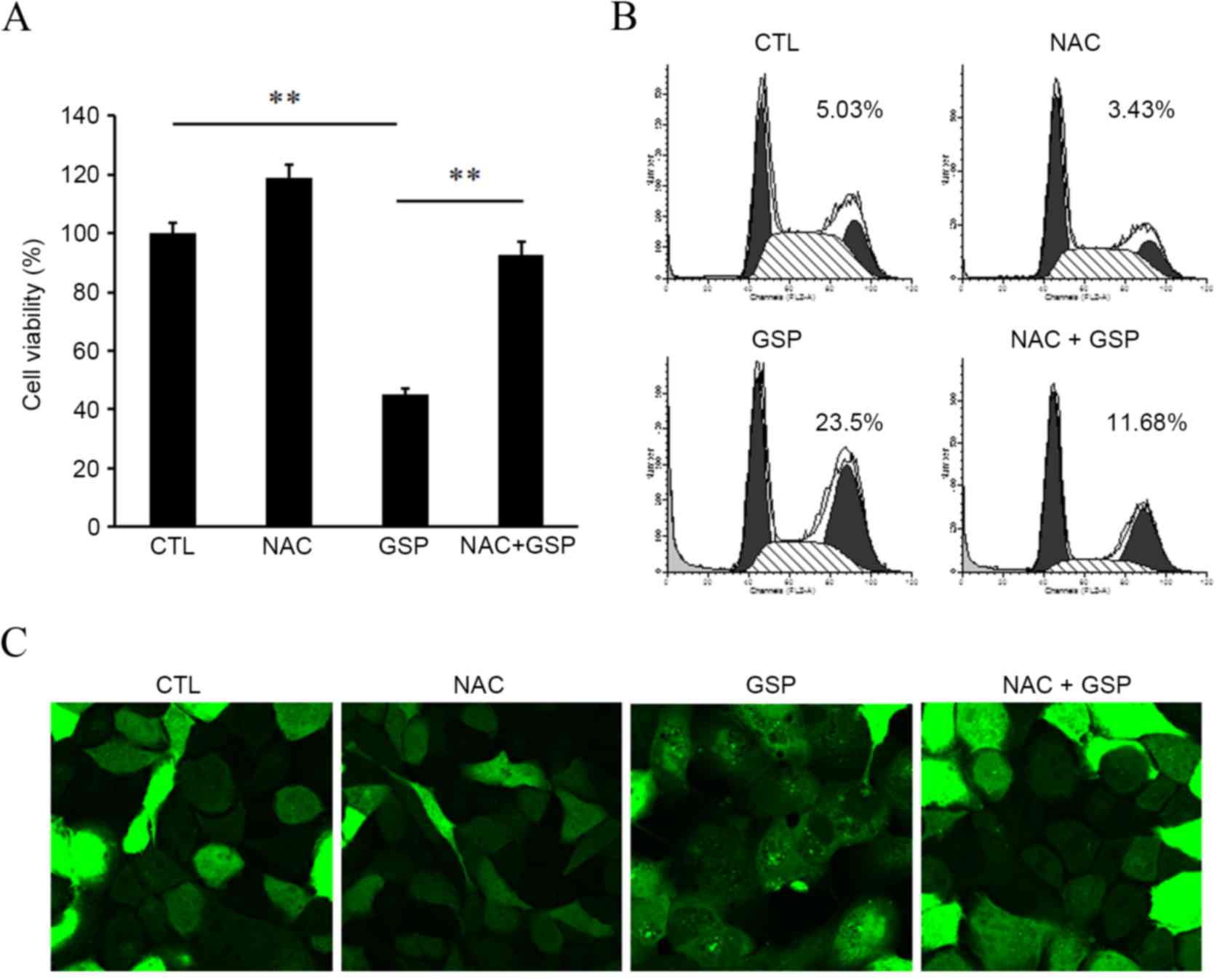
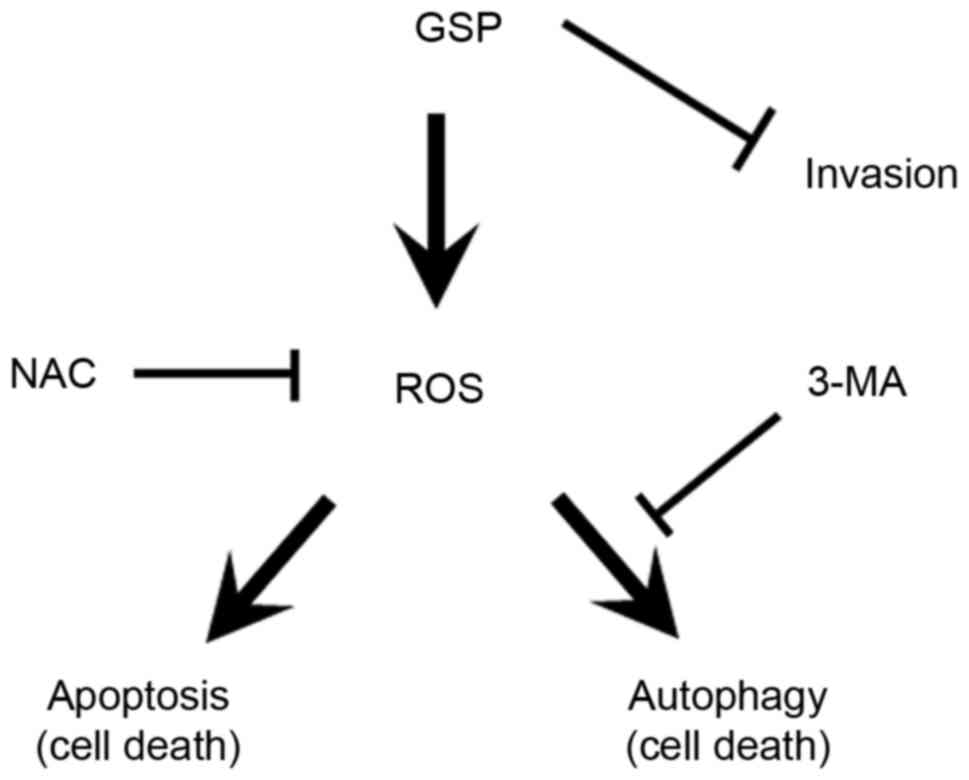
|
1
|
Hassan HM: Protective effects of red grape
seed extracts on DNA, brain and erythrocytes against oxidative
damage. Glob J Pharmacol. 7:241–248. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Fine AM: Oligomeric proanthocyanidin
complexes: History, structure, and phytopharmaceutical
applications. Altern Med Rev. 5:144–151. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ariga T: The antioxidative function,
preventive action on disease and utilization of proanthocyanidins.
Biofactors. 21:197–201. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jang JK and Han JY: The antioxidant
ability of grape seed extracts. Korean J Food Sci Technol.
34:524–528. 2002.
|
|
5
|
Pataki T, Bak I, Kovacs P, Bagchi D, Das
DK and Tosaki A: Grape seed proanthocyanidins improved cardiac
recovery during reperfusion after ischemia in isolated rat hearts.
Am J Clin Nutr. 75:894–899. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li WG, Zhang XY, Wu YJ and Tian X:
Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of proanthocyanidins from
grape seeds. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 22:1117–1120. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eng ET, Ye J, Williams D, Phung S, Moore
RE, Young MK, Gruntmanis U, Braunstein G and Chen S: Suppression of
estrogen biosynthesis by procyanidin dimers in red wine and grape
seeds. Cancer Res. 63:8516–8522. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tyagi A, Agarwal R and Agarwal C: Grape
seed extract inhibits EGF-induced and constitutively active
mitogenic signaling but activates JNK in human prostate carcinoma
DU145 cells: Possible role in antiproliferation and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 22:1302–1316. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meeran SM and Katiyar SK: Grape seed
proanthocyanidins promote apoptosis in human epidermoid carcinoma
A431 cells through alterations in Cdki-Cdk-cyclin cascade, and
caspase-3 activation via loss of mitochondrial membrane potential.
Exp Dermatol. 16:405–415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaur M, Singh RP, Gu M, Agarwal R and
Agarwal C: Grape seed extract inhibits in vitro and in vivo growth
of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6194–6202.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: A double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Classification of cell death:
Recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2009.
Cell Death Differ. 16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A,
Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y, Tokuhisa T and Mizushima N: The
role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period.
Nature. 432:1032–1036. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mills KR, Reginato M, Debnath J, Queenan B
and Brugge JS: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL) is required for induction of autophagy during lumen
formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:pp. 3438–3443.
2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lemasters JJ, Qian T, He L, Kim JS, Elmore
SP, Cascio WE and Brenner DA: Role of mitochondrial inner membrane
permeabilization in necrotic cell death, apoptosis, and autophagy.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 4:769–781. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Keston AS and Brandt R: The fluorometric
analysis of ultramicro quantities of hydrogen peroxide. Anal
Biochem. 11:1–5. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mantena SK, Baliga MS and Katiyar SK:
Grape seed proanthocyanidins induce apoptosis and inhibit
metastasis of highly metastatic breast carcinoma cells.
Carcinogenesis. 27:1682–1691. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schwartz GK and Shah MA: Targeting the
cell cycle: A new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
23:9408–9421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lakin ND and Jackson SP: Regulation of p53
in response to DNA damage. Oncogene. 18:7644–7655. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi HJ, Lim DY and Park JH: Induction of
G1 and G2/M cell cycle arrests by the dietary compound
3,3′-diindolylmethane in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. BMC
Gastroenterol. 9:392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Sensitization for
anticancer drug-induced apoptosis by the chemopreventive agent
resveratrol. Oncogene. 23:6702–6711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao Y and Klionsky DJ: Physiological
functions of Atg6/Beclin 1: A unique autophagy-related protein.
Cell Res. 17:839–849. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang KH, Yan MD, Yao CJ, Lin PC and Lai
GM: Honokiol-induced apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma
multiforme cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1435–1438. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu B, Cheng Y, Zhang B, Bian HJ and Bao
JK: Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy in
human melanoma A375 cells through a mitochondria-mediated
ROS-p38-p53 pathway. Cancer Lett. 275:54–60. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ooi KL, Muhammad TS and Sulaiman SF:
Growth arrest and induction of apoptotic and non-apoptotic
programmed cell death by, Physalis minima L. chloroform extract in
human ovarian carcinoma Caov-3 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 128:92–99.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sharma SD, Meeran SM and Katiyar SK:
Dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit UVB-induced oxidative
stress and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and
nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in in vivo SKH-1 hairless mice. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:995–1005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer
H, Gil L and Elazar Z: Reactive oxygen species are essential for
autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J.
26:1749–1760. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao M, Yeh PY, Lu YS, Hsu CH, Chen KF, Lee
WC, Feng WC, Chen CS, Kuo ML and Cheng AL: OSU-03012, a novel
celecoxib derivative, induces reactive oxygen species-related
autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:9348–9357.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|