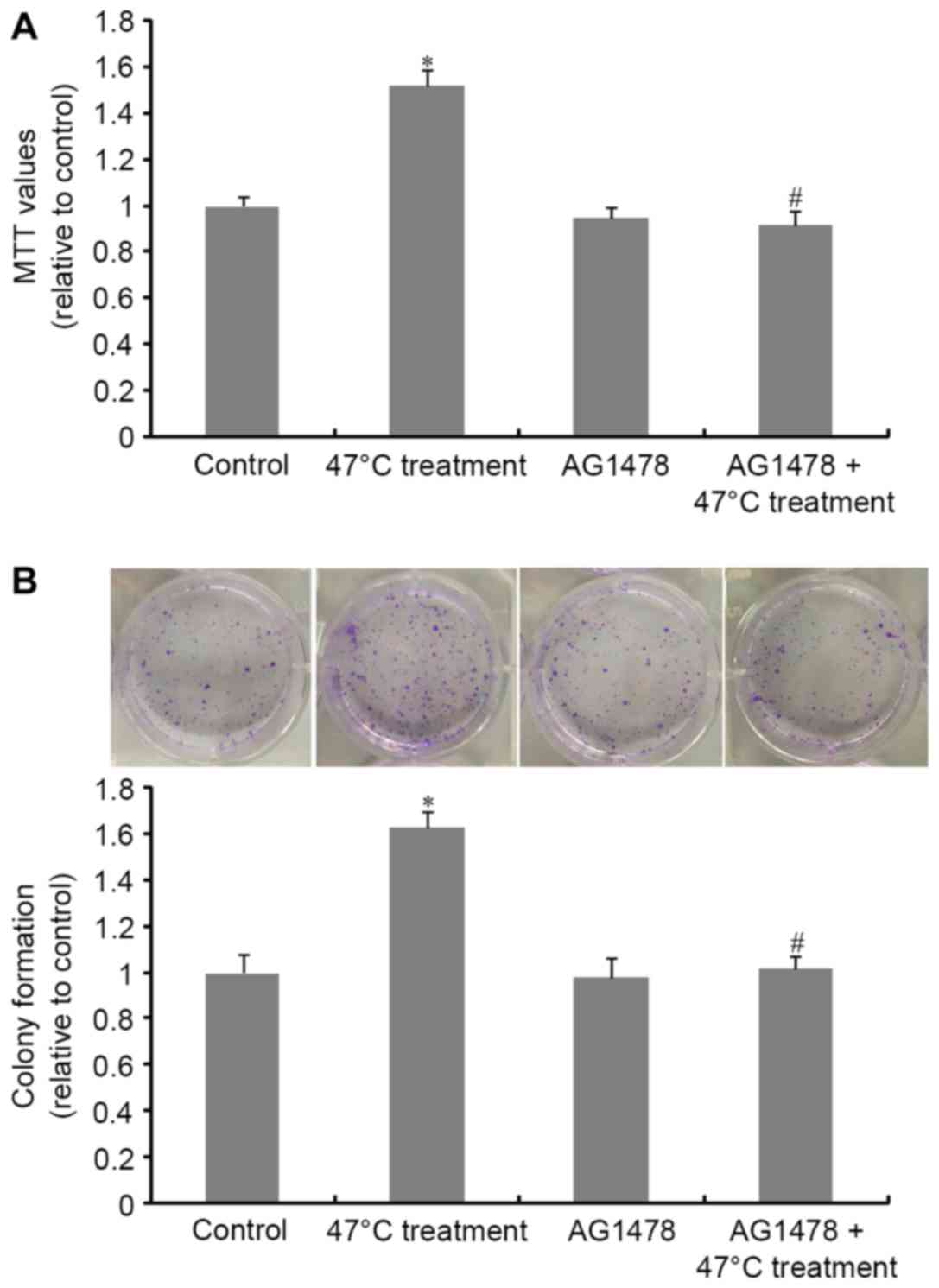
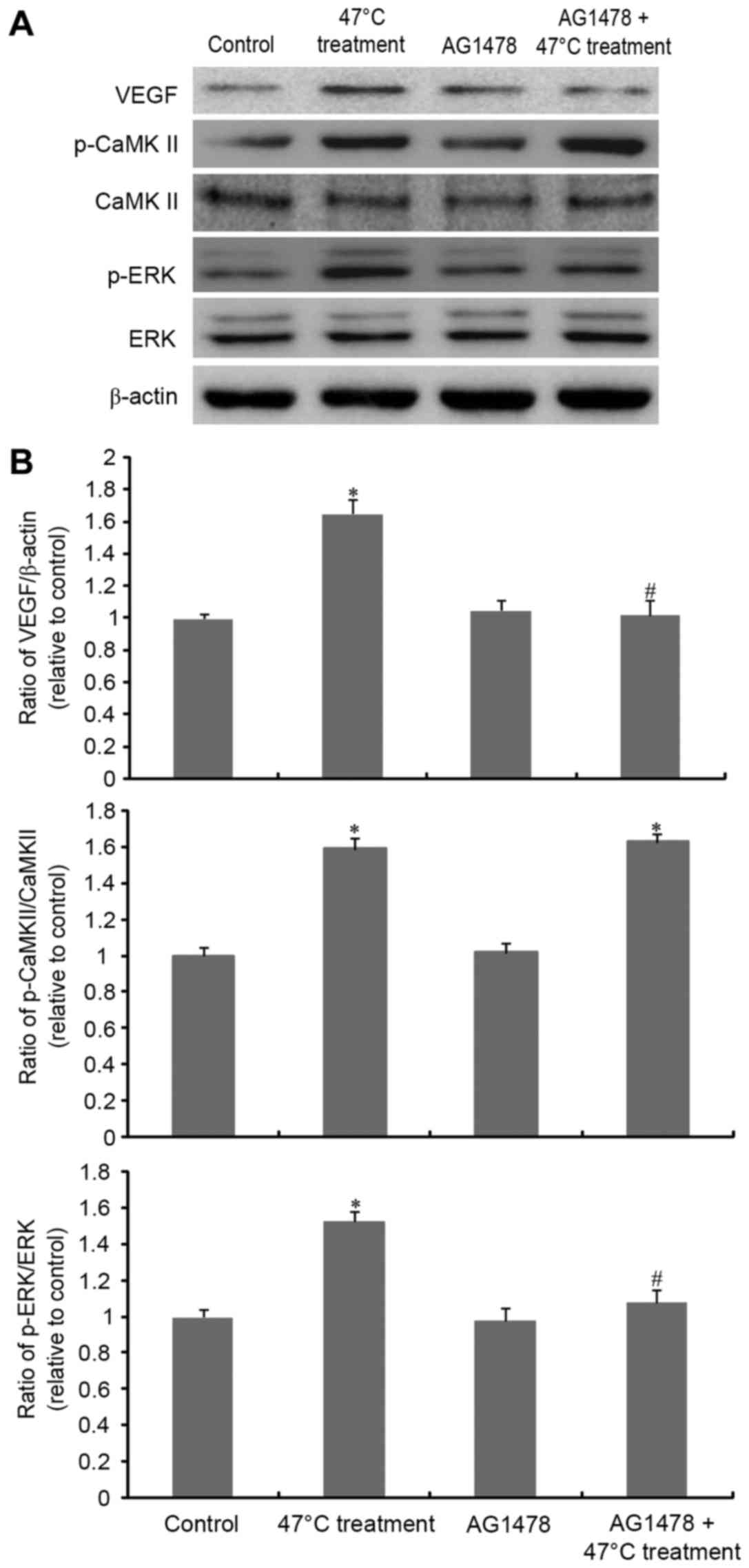
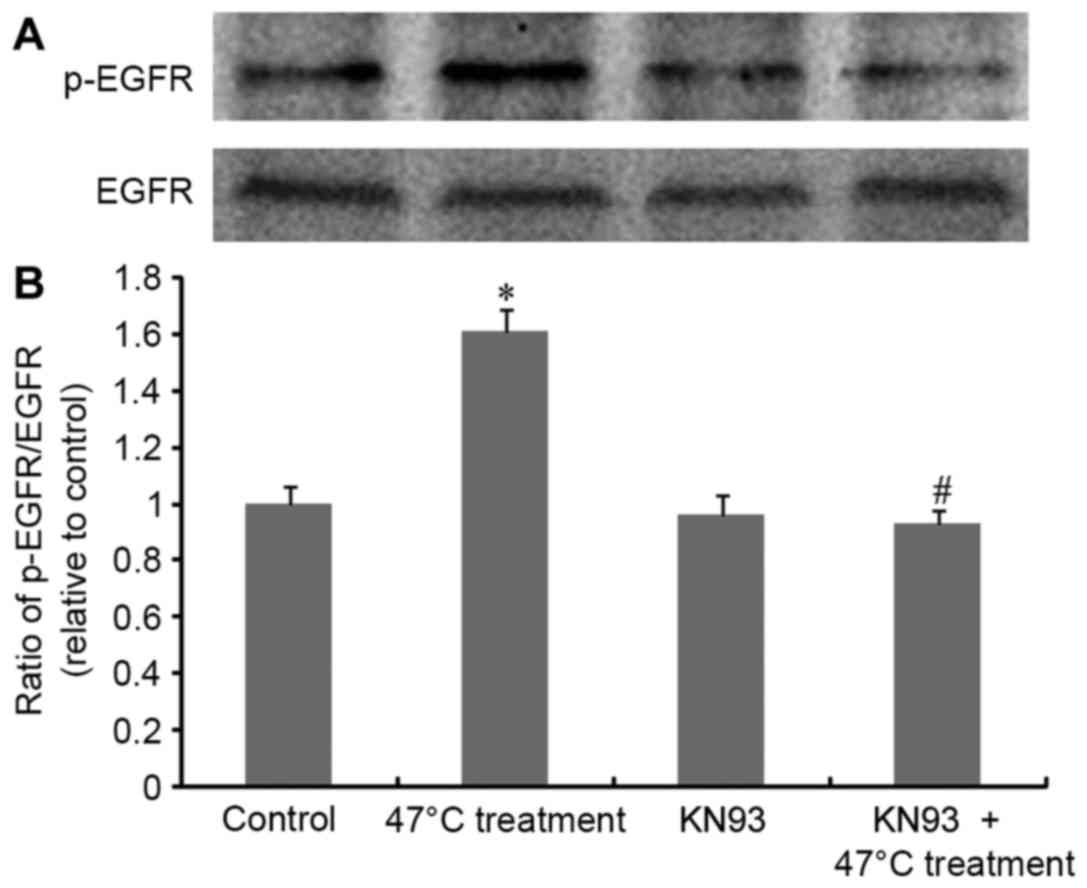
|
1
|
Che YH, Chongsuvivatwong V, Li L, Sriplung
H, Wang YY, You J, Ma SJ, Yan Y, Zhang RY, Shen T, et al: Financial
burden on the families of patients with hepatitis B virus-related
liver diseases and the role of public health insurance in Yunnan
province of China. Public Health. 130:13–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fouad AA, Al-Mulhim AS and Jresat I:
Therapeutic effect of coenzyme Q10 against experimentally-induced
hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
35:100–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J and de
Guevara LL: The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 15 Suppl
4:S5–S13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lau WY and Lai EC: The current role of
radiofrequency ablation in the management of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A systematic review. Ann Surg. 249:20–25. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang N, Wang L, Chai ZT, Zhu ZM, Zhu XD,
Ma DN, Zhang QB, Zhao YM, Wang M, Ao JY, et al: Incomplete
radiofrequency ablation enhances invasiveness and metastasis of
residual cancer of hepatocellular carcinoma cell HCCLM3 via
activating β-catenin signaling. PLoS One. 9:e1159492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Z, Dai H, Jia G, Li Y, Liu X and Ren
W: Insufficient radiofrequency ablation promotes human hepatoma
SMMC7721 cell proliferation by stimulating vascular endothelial
growth factor overexpression. Oncol Lett. 9:1893–1896.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ouyang Y, Liu K, Hao M, Zheng R, Zhang C,
Wu Y, Zhang X, Li N, Zheng J and Chen D: Radiofrequency
ablation-increased CXCL10 is associated with earlier recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting stemness. Tumour Biol.
37:3697–3704. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dong S, Kong J, Kong F, Kong J, Gao J, Ke
S, Wang S, Ding X, Sun W and Zheng L: Insufficient radiofrequency
ablation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through Akt and ERK signaling
pathways. J Transl Med. 11:2732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moreno-Càceres J, Caja L, Mainez J,
Mayoral R, Martín-Sanz P, Moreno-Vicente R, Del Pozo MÁ, Dooley S,
Egea G and Fabregat I: Caveolin-1 is required for TGF-β-induced
transactivation of the EGF receptor pathway in hepatocytes through
the activation of the metalloprotease TACE/ADAM17. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai H, Song D, Xu J, Li B, Hertz L and
Peng L: Ammonia-induced Na,K-ATPase/ouabain-mediated EGF receptor
transactivation, MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling and ROS formation
cause astrocyte swelling. Neurochem Int. 63:610–625. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhuang S and Schnellmann RG: H2O2-induced
transactivation of EGF receptor requires Src and mediates ERK1/2,
but not Akt, activation in renal cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
286:F858–F865. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Forrester SJ, Kawai T, O'Brien S, Thomas
W, Harris RC and Eguchi S: Epidermal growth factor receptor
transactivation: Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and potential
therapies in the cardiovascular system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
56:627–653. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Michailov Y, Ickowicz D and Breitbart H:
Zn2+-stimulation of sperm capacitation and of the acrosome reaction
is mediated by EGFR activation. Dev Biol. 396:246–255. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu M, Xie XH, Xie XY, Xu ZF, Liu GJ, Zheng
YL, Huang GL, Wang W, Zheng SG and Lü MD: Sorafenib suppresses the
rapid progress of hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient
radiofrequency ablation therapy: An experiment in vivo. Acta
Radiol. 54:199–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng LM, Jiang JG, Sun ZY, Chen C, Dackor
RT, Zeldin DC and Wang DW: The epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-stimulated
phosphorylation of EGF-R involves the activation of
metalloproteinases and the release of HB-EGF in cancer cells. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 31:211–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Niederlechner S, Baird C, Petrie B,
Wischmeyer E and Wischmeyer PE: Epidermal growth factor receptor
expression and signaling are essential in glutamine's
cytoprotective mechanism in heat-stressed intestinal epithelial-6
cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 304:G543–G552.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li L, Qi L, Liang Z, Song W, Liu Y, Wang
Y, Sun B, Zhang B and Cao W: Transforming growth factor-β1 induces
EMT by the transactivation of epidermal growth factor signaling
through HA/CD44 in lung and breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Med.
36:113–122. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao M, Zhan YQ, Yu M, Ge CH, Li CY, Zhang
JH, Wang XH, Ge ZQ and Yang XM: Hepassocin activates the EGFR/ERK
cascade and induces proliferation of L02 cells through the
Src-dependent pathway. Cell Signal. 26:2161–2166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai B, Zhan Y, Qi J and Zhang Y:
Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker inhibits human chronic myeloid leukemia
cell K562 growth by inducing G2-M phase cell cycle arrest and
targeting EGFR signaling pathway and in S180 tumor-bearing mice.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 37:1177–1185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Midgley AC, Rogers M, Hallett MB, Clayton
A, Bowen T, Phillips AO and Steadman R: Transforming growth
factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-stimulated fibroblast to myofibroblast
differentiation is mediated by hyaluronan (HA)-facilitated
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and CD44 co-localization in
lipid rafts. J Biol Chem. 288:14824–14838. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishi H, Maeda N, Izumi S, Higa-Nakamine
S, Toku S, Kakinohana M, Sugahara K and Yamamoto H: Differential
regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor by hydrogen peroxide
and flagellin in cultured lung alveolar epithelial cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 748:133–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ulu N, Henning RH, Guner S, Zoto T,
Duman-Dalkilic B, Duin M and Gurdal H: Intracellular
transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor by
α1A-adrenoceptor is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
independently of activation of extracellular signal regulated
kinases 1/2 and serine-threonine kinases in Chinese hamster ovary
cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 347:47–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ginnan R, Pfleiderer PJ, Pumiglia K and
Singer HA: PKC-delta and CaMKII-delta 2 mediate ATP-dependent
activation of ERK1/2 in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 286:C1281–C1289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|