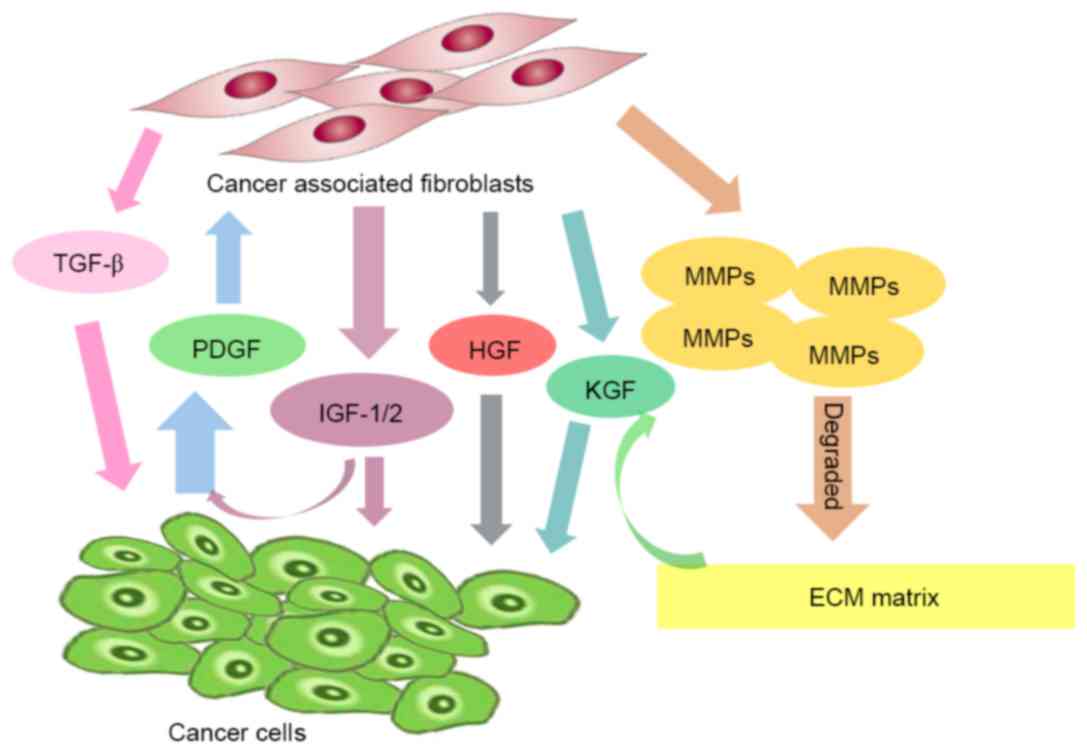
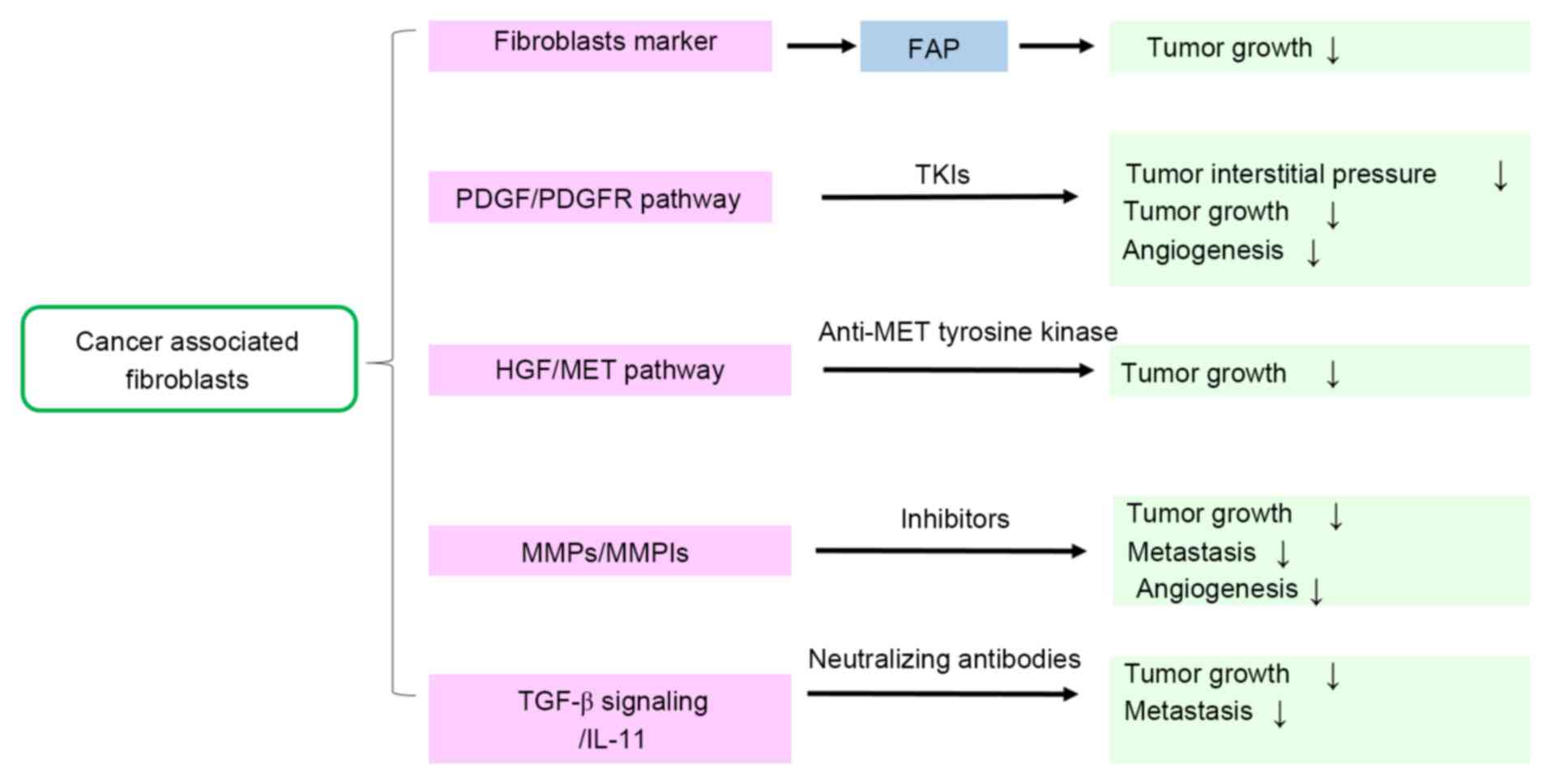
|
1
|
Balkwill FR, Capasso M and Hagemann T: The
tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci. 125:5591–5596.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Spano D and Zollo M: Tumor
microenvironment: A main actor in the metastasis process. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 29:381–395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swartz MA, Iida N, Roberts EW, Sangaletti
S, Wong MH, Yull FE, Coussens LM and DeClerck YA: Tumor
microenvironment complexity: Emerging roles in cancer therapy.
Cancer Res. 72:2473–2480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quail DF and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.
19:1423–1437. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P:
Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: A diabolic liaison
driving cancer progression. Cancer Metast Rev. 31:195–208. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Marsh T, Pietras K and McAllister SS:
Fibroblasts as architects of cancer pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1832:1070–1078. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun Y: Translational horizons in the tumor
microenvironment: Harnessing breakthroughs and targeting cures. Med
Res Rev. 35:408–436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Slany A, Bileck A, Muqaku B and Gerner C:
Targeting breast cancer-associated fibroblasts to improve
anti-cancer therapy. Breast. 24:532–538. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Anderberg C and Pietras K: On the origin
of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 8:1461–1462. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Hu T, Shen J, Li SF, Lin JW, Zheng
XH, Gao QH and Zhou HM: Separation, cultivation and biological
characteristics of oral carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Oral Dis.
12:375–380. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sugimoto H, Mundel TM, Kieran MW and
Kalluri R: Identification of fibroblast heterogeneity in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1640–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park JE, Lenter MC, Zimmermann RN,
Garin-Chesa P, Old LJ and Rettig WJ: Fibroblast activation protein,
a dual specificity serine protease expressed in reactive human
tumor stromal fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 274:36505–36512. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim HM, Jung WH and Koo JS: Expression of
cancer-associated fibroblast related proteins in metastatic breast
cancer: An immunohistochemical analysis. J Transl Med. 13:2222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rupp C, Scherzer M, Rudisch A, Unger C,
Haslinger C, Schweifer N, Artaker M, Nivarthi H, Moriggl R,
Hengstschläger M, et al: IGFBP7, a novel tumor stroma marker, with
growth-promoting effects in colon cancer through a paracrine
tumor-stroma interaction. Oncogene. 34:815–825. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Navab R, Strumpf D, Bandarchi B, Zhu CQ,
Pintilie M, Ramnarine VR, Ibrahimov E, Radulovich N, Leung L,
Barczyk M, et al: Prognostic gene-expression signature of
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts in non-small cell lung cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:pp. 7160–7165. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu CQ, Popova SN, Brown ER,
Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Navab R, Shih W, Li M, Lu M, Jurisica I, Penn
LZ, et al: Integrin alpha11 regulates IGF2 expression in
fibroblasts to enhance tumorigenicity of human non-small-cell lung
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 11754–11759. 2007;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakagawa H, Liyanarachchi S, Davuluri RV,
Auer H, Martin EW Jr, de la Chapelle A and Frankel WL: Role of
cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts in metastatic colon cancer to
the liver and their expression profiles. Oncogene. 23:7366–7377.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Walter K, Omura N, Hong SM, Griffith M,
Vincent A, Borges M and Goggins M: Overexpression of smoothened
activates the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1781–1789. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rozenchan PB, Carraro DM, Brentani H, de
Carvalho Mota LD, Bastos EP, e Ferreira EN, Torres CH, Katayama ML,
Roela RA, Lyra EC, et al: Reciprocal changes in gene expression
profiles of cocultured breast epithelial cells and primary
fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 125:2767–2777. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kalluri R and Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:392–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Räsänen K and Vaheri A: Activation of
fibroblasts in cancer stroma. Exp Cell Res. 316:2713–2722. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Clayton A, Evans RA, Pettit E, Hallett M,
Williams JD and Steadman R: Cellular activation through the
ligation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Cell Sci.
111:443–453. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mitra AK, Zillhardt M, Hua Y, Tiwari P,
Murmann AE, Peter ME and Lengyel E: MicroRNAs reprogram normal
fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer.
Cancer Discov. 2:1100–1108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao L, Sun Y, Hou Y, Peng Q, Wang L, Luo
H, Tang X, Zeng Z and Liu M: MiRNA expression analysis of
cancer-associated fibroblasts and normal fibroblasts in breast
cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2051–2059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Enkelmann A, Heinzelmann J, von Eggeling
F, Walter M, Berndt A, Wunderlich H and Junker K: Specific protein
and miRNA patterns characterise tumour-associated fibroblasts in
bladder cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:751–759. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu Z, Willmarth NE, Zhou J, Katiyar S,
Wang M, Liu Y, McCue PA, Quong AA, Lisanti MP and Pestell RG:
microRNA 17/20 inhibits cellular invasion and tumor metastasis in
breast cancer by heterotypic signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:pp. 8231–8236. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aprelikova O, Yu X, Palla J, Wei BR, John
S, Yi M, Stephens R, Simpson RM, Risinger JI, Jazaeri A and
Niederhuber J: The role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 9:4387–4398. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang S, Wang Z, Xu K, Ruan Z and Chen L:
miRNA expression analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts and
normal fibroblasts in colorectal cancer. J Mod Oncol. 09:1918–1922.
2013.
|
|
31
|
Bhowmick NA, Neilson E G and Moses HL:
Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature.
432:332–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gonda TA, Varro A, Wang TC and Tycko B:
Molecular biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts: Can these cells
be targeted in anti-cancer therapy? Seminars Cell Dev Biol. 21:pp.
2–10. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ostman A and Augsten M: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts and tumor growth-bystanders turning into key players.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 19:67–73. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Servais C and Erez N: From sentinel cells
to inflammatory culprits: Cancer-associated fibroblasts in
tumour-related inflammation. J Pathol. 229:198–207. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luker KE, Lewin SA, Mihalko LA, Schmidt
BT, Winkler JS, Coggins NL, Thomas DG and Luker GD: Scavenging of
CXCL12 by CXCR7 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of
CXCR4-positive breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 31:4750–4758. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Augsten M, Sjöberg E, Frings O, Vorrink
SU, Frijhoff J, Olsson E, Borg Å and Östman A: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts expressing CXCL14 rely upon NOS1-derived nitric oxide
signaling for their tumor-supporting properties. Cancer Res.
74:2999–3010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mi Z, Bhattacharya SD, Kim VM, Guo H,
Talbot LJ and Kuo PC: Osteopontin promotes CCL5-mesenchymal stromal
cell-mediated breast cancer metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 32:477–487.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Quante M, Tu SP, Tomita H, Gonda T, Wang
SS, Takashi S, Baik GH, Shibata W, Diprete B, Betz KS, et al: Bone
marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the mesenchymal stem
cell niche and promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 19:257–272. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li X, Xu Q, Wu Y, Li J, Tang D, Han L and
Fan Q: A CCL2/ROS autoregulation loop is critical for
cancer-associated fibroblasts-enhanced tumor growth of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 35:1362–1370. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shibuya M and Claesson-Welsh L: Signal
transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and
lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 312:549–560. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gomes FG, Nedel F, Alves AM, Nör JE and
Tarquinio SB: Tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis:
Tumor/endothelial crosstalk and cellular/microenvironmental
signaling mechanisms. Life Sci. 92:101–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ferrara N: Pathways mediating
VEGF-independent tumor angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
21:21–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang J and Liu J: Tumor stroma as targets
for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 137:200–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nagasaki T, Hara M, Nakanishi H, Takahashi
H, Sato M and Takeyama H: Interleukin-6 released by colon
cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis:
Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and
inhibited tumour-stroma interaction. Br J Cancer. 110:469–478.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karagiannis GS, Poutahidis T, Erdman SE,
Kirsch R, Riddell RH and Diamandis EP: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts drive the progression of metastasis through both
paracrine and mechanical pressure on cancer tissue. Mol Cancer Res.
10:1403–1418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vpavlides S, Vera I, Gandara R, Sneddon S,
Pestell RG, Mercier I, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Howell A, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Warburg meets autophagy:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts accelerate tumor growth and
metastasis via oxidative stress, mitophagy, and aerobic glycolysis.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1264–1284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
De Wever O, Van Bockstal M, Mareel M,
Hendrix A and Bracke M: Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts provide
operational flexibility in metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 25:33–46.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dumont N, Liu B, DeFilippis RA, Chang H,
Rabban JT, Karnezis AN, Tjoe JA, Marx J, Parvin B and Tlsty TD:
Breast fibroblasts modulate early dissemination, tumorigenesis, and
metastasis through alteration of extracellular matrix
characteristics. Neoplasia. 15:249–262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Olumi AF, Grossfeld GD, Hayward SW,
Carroll PR, Tlsty TD and Cunha GR: Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
direct tumor progression of initiated human prostatic epithelium.
Cancer Res. 59:5002–5011. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Calvo F, Ege N, Grande-Garcia A, Hooper S,
Jenkins RP, Chaudhry SI, Harrington K, Williamson P, Moeendarbary
E, Charras G and Sahai E: Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent
matrix remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance
of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol. 15:637–646. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and
Hanahan D: Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient
neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an
NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cancer cell. 17:135–147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang XH, Jin X, Malladi S, Zou Y, Wen YH,
Brogi E, Smid M, Foekens JA and Massagué J: Selection of bone
metastasis seeds by mesenchymal signals in the primary tumor
stroma. Cell. 154:1060–1073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Aprelikova O, Palla J, Hibler B, Yu X,
Greer YE, Yi M, Stephens R, Maxwell GL, Jazaeri A, Risinger JI, et
al: Silencing of miR-148a in cancer-associated fibroblasts results
in WNT10B-mediated stimulation of tumor cell motility. Oncogene.
32:3246–3253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Verghese ET, Drury R, Green CA, Holliday
DL, Lu X, Nash C, Speirs V, Thorne JL, Thygesen HH, Zougman A, et
al: MiR-26b is down-regulated in carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
from ER-positive breast cancers leading to enhanced cell migration
and invasion. J Pathol. 231:388–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA,
Merchant AS, Nowicki MO, Mathsyaraja H, Srinivasan R, Trimboli AJ,
Martin CK, Li F, et al: Reprogramming of the tumour
microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320. Nat Cell Biol.
14:159–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Mongiat M, Marastoni S, Ligresti G,
Lorenzon E, Schiappacassi M, Perris R, Frustaci S and Colombatti A:
The extracellular matrix glycoprotein elastin microfibril interface
located protein 2: A dual role in the tumor microenvironment.
Neoplasia. 12:294–304. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Correia AL and Bissell MJ: The tumor
microenvironment is a dominant force in multidrug resistance. Drug
Resist Updat. 15:39–49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kerbel RS: A cancer therapy resistant to
resistance. Nature. 390:335–336. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Swartz MA and Lund AW: Lymphatic and
interstitial flow in the tumour microenvironment: Linking
mechanobiology with immunity. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:210–219. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Khawar IA, Kim JH and Kuh HJ: Improving
drug delivery to solid tumors: Priming the tumor microenvironment.
J Control Release. 201:78–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Pietras K, Östman A, Sjöquist M,
Buchdunger E, Reed RK, Heldin CH and Rubin K: Inhibition of
Platelet-derived growth factor receptors reduces interstitial
hypertension and increases transcapillary transport in tumors.
Cancer Res. 61:2929–2934. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pietras K, Rubin K, Sjöblom T, Buchdunger
E, Sjöquist M, Heldin CH and Ostman A: Inhibition of PDGF receptor
signaling in tumor stroma enhances antitumor effect of
chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 62:5476–5484. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wilson TR, Fridlyand J, Yan Y, Penuel E,
Burton L, Chan E, Peng J, Lin E, Wang Y, Sosman J, et al:
Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to
anticancer kinase inhibitors. Nature. 487:505–509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Straussman R, Morikawa T, Shee K,
Barzily-Rokni M, Qian ZR, Du J, Davis A, Mongare MM, Gould J,
Frederick DT, et al: Tumour micro-environment elicits innate
resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature.
487:500–504. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yano S, Wang W, Li Q, Yamada T, Takeuchi
S, Matsumoto K, Nishioka Y and Sone S: HGF-MET in resistance to
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Curr Signal Trans
Ther. 6:228–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Liska D, Chen CT, Bachleitner-Hofmann T,
Christensen JG and Weiser MR: HGF rescues colorectal cancer cells
from EGFR inhibition via MET activation. Clin Cancer Res.
17:472–482. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yamatodani T, Ekblad L, Kjellén E,
Johnsson A, Mineta H and Wennerberg J: Epidermal growth factor
receptor status and persistent activation of Akt and p44/42 MAPK
pathways correlate with the effect of cetuximab in head and neck
and colon cancer cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
135:3954022009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Liska D, Chen CT, Bachleitner-Hofmann T,
Christensen JG and Weiser MR: HGF rescues colorectal cancer cells
from EGFR inhibition via MET activation. Clin Cancer Res.
17:472–482. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Luraghi P, Reato G, Cipriano E, Sassi F,
Orzan F, Bigatto V, De Bacco F, Menietti E, Han M, Rideout WM III,
et al: MET signaling in colon cancer stem-like cells blunts the
therapeutic response to EGFR inhibitors. Cancer Res. 74:1857–1869.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Qian DZ, Rademacher BL, Pittsenbarger J,
Huang CY, Myrthue A, Higano CS, Garzotto M, Nelson PS and Beer TM:
CCL2 is induced by chemotherapy and protects prostate cancer cells
from docetaxel-induced cytotoxicity. Prostate. 70:433–442.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Moisan F, Francisco EB, Brozovic A, Duran
GE, Wang YC, Chaturvedi S, Seetharam S, Snyder LA, Doshi P and
Sikic BI: Enhancement of paclitaxel and carboplatin therapies by
CCL2 blockade in ovarian cancers. Mol Oncol. 8:1231–1239. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tsuyada A, Chow A, Wu J, Somlo G, Chu P,
Loera S, Luu T, Li AX, Wu X, Ye W, et al: CCL2 mediates cross-talk
between cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts that regulates breast
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 72:2768–2779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Weekes CD, Song D, Arcaroli J, Wilson LA,
Rubio-Viqueira B, Cusatis G, Garrett-Mayer E, Messersmith WA, Winn
RA and Hidalgo M: Stromal cell-derived factor 1α mediates
resistance to mTOR-directed therapy in pancreatic cancer.
Neoplasia. 14:690–701. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Singh S, Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Owen
LB and Singh AP: CXCL12-CXCR4 signalling axis confers gemcitabine
resistance to pancreatic cancer cells: A novel target for therapy.
Br J Cancer. 103:1671–1679. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Domanska UM, Timmer-Bosscha H, Nagengast
WB, Munnink TH Oude, Kruizinga RC, Ananias HJ, Kliphuis NM, Huls G,
De Vries EG, de Jong IJ and Walenkamp AM: CXCR4 inhibition with
AMD3100 sensitizes prostate cancer to docetaxel chemotherapy.
Neoplasia. 14:709–718. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Heckmann D, Maier P, Laufs S, Wenz F,
Zeller WJ, Fruehauf S and Allgayer H: CXCR4 expression and
treatment with SDF-1α or plerixafor modulate proliferation and
chemosensitivity of colon cancer cells. Transl Oncol. 6:124–132.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Burger JA, Stewart DJ, Wald O and Peled A:
Potential of CXCR4 antagonists for the treatment of metastatic lung
cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 11:621–630. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lotti F, Jarrar AM, Pai RK, Hitomi M,
Lathia J, Mace A, Gantt GA Jr, Sukhdeo K, DeVecchio J, Vasanji A,
et al: Chemotherapy activates cancer-associated fibroblasts to
maintain colorectal cancer-initiating cells by IL-17A. J Exp Med.
210:2851–2872. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Cochaud S, Giustiniani J, Thomas C,
Laprevotte E, Garbar C, Savoye AM, Curé H, Mascaux C, Alberici G,
Bonnefoy N, et al: IL-17A is produced by breast cancer TILs and
promotes chemoresistance and proliferation through ERK1/2. Sci Rep.
3:34562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Studebaker AW, Storci G, Werbeck JL,
Sansone P, Sasser AK, Tavolari S, Huang T, Chan MW, Marini FC,
Rosol TJ, et al: Fibroblasts isolated from common sites of breast
cancer metastasis enhance cancer cell growth rates and invasiveness
in an interleukin-6-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 68:9087–9095.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gao SP, Mark KG, Leslie K, Pao W, Motoi N,
Gerald WL, Travis WD, Bornmann W, Veach D, Clarkson B and Bromberg
JF: Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation
via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas. J Clin Invest.
117:3846–3856. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Yao Z, Fenoglio S, Gao DC, Camiolo M,
Stiles B, Lindsted T, Schlederer M, Johns C, Altorki N, Mittal V,
et al: TGF-beta IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive
mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 15535–15540. 2010;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sun X, Mao Y, Wang J, Zu L, Hao M, Cheng
G, Qu Q, Cui D, Keller ET, Chen X, et al: IL-6 secreted by
cancer-associated fibroblasts induces tamoxifen resistance in
luminal breast cancer. Oncogene. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.158.
|
|
85
|
Sun Y, Campisi J, Higano C, Beer TM,
Porter P, Coleman I, True L and Nelson PS: Treatment-induced damage
to the tumor microenvironment promotes prostate cancer therapy
resistance through WNT16B. Nat Med. 18:1359–1368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Amornsupuk K, Insawang T, Thuwajit P,
O-Charoenrat P, Eccles SA and Thuwajit C: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts induce high mobility group box 1 and contribute to
resistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
14:9552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cullen KJ, Smith HS, Hill S, Rosen N and
Lippman ME: Growth factor messenger RNA expression by human breast
fibroblasts from benign and malignant lesions. Cancer Res.
51:4978–4985. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Shay G, Lynch CC and Fingleton B: Moving
targets: Emerging roles for MMPs in cancer progression and
metastasis. Matrix Biol 44–46. 1–206. 2015.
|
|
89
|
Jia CC, Wang TT, Liu W, Fu BS, Hua X, Wang
GY, Li TJ, Li X, Wu XY, Tai Y, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
from hepatocellular carcinoma promote malignant cell proliferation
by HGF secretion. PLoS One. 8:e632432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lin J, Liu C, Ge L, Gao Q, He X, Liu Y, Li
S, Zhou M, Chen Q and Zhou H: Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
promotes the proliferation of a lingual carcinoma cell line by
secreting keratinocyte growth factor. Tumor Biol. 32:597–602. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Weroha SJ and Haluska P: The insulin-like
growth factor system in cancer. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
41:335–350.vi. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hawinkels LJ, Paauwe M, Verspaget HW,
Wiercinska E, van der Zon JM, van der Ploeg K, Koelink PJ, Lindeman
JH, Mesker W, ten Dijke P and Sier CF: Interaction with colon
cancer cells hyperactivates TGF-β signaling in cancer-associated
fibroblasts. Oncogene. 33:97–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Mueller MM and Fusenig NE: Friends or
foes-bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:839–849. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Liu R, Li H, Liu L, Yu J and Ren X:
Fibroblast activation protein: A potential therapeutic target in
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:123–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
LeBeau AM, Brennen WN, Aggarwal S and
Denmeade SR: Targeting the cancer stroma with a fibroblast
activation protein-activated promelittin protoxin. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:1378–1386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ostermann E, Garin-Chesa P, Heider KH,
Kalat M, Lamche H, Puri C, Kerjaschki D, Rettig WJ and Adolf GR:
Effective immunoconjugate therapy in cancer models targeting a
serine protease of tumor fibroblasts. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4584–4592. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Adams S, Miller GT, Jesson MI, Watanabe T,
Jones B and Wallner BP: PT-100, a small molecule dipeptidyl
peptidase inhibitor, has potent antitumor effects and augments
antibody-mediated cytotoxicity via a novel immune mechanism. Cancer
Res. 64:5471–5480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Santos AM, Jung J, Aziz N, Kissil JL and
Puré E: Targeting fibroblast activation protein inhibits tumor
stromagenesis and growth in mice. J Clin Invest. 119:3613–3625.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Heldin CH: Targeting the PDGF signaling
pathway in tumor treatment. Cell Commun Signal. 11:972013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Steeghs N, Nortier JW and Gelderblom H:
Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of solid
tumors: An update of recent developments. Ann Surg Oncol.
14:942–953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Pietras K, Pahler J, Bergers G and Hanahan
D: Functions of paracrine PDGF signaling in the proangiogenic tumor
stroma revealed by pharmacological targeting. PLos Med. 5:e192008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Hilberg F, Roth GJ, Krssak M, Kautschitsch
S, Sommergruber W, Tontsch-Grunt U, Garin-Chesa P, Bader G, Zoephel
A, Quant J, et al: BIBF 1120: Triple angiokinase inhibitor with
sustained receptor blockade and good antitumor efficacy. Cancer
Res. 68:4774–4782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Cecchi F, Rabe DC and Bottaro DP:
Targeting the HGF/Met signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 16:553–572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Gherardi E, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C and
Woude G Vande: Targeting MET in cancer: Rationale and progress. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:89–103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Sadiq AA and Salgia R: MET as a possible
target for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:1089–1096.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Oliner KS, Tang R, Anderson A, et al:
Evaluation of MET pathway biomarkers in a phase II study of
rilotumumab (R, AMG 102) or placebo (P) in combination with
epirubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine (ECX) in patients (pts) with
locally advanced or metastatic gastric (G) or esophagogastric
junction (EGJ) cancerJ Clin Oncol Amer Soc Clin Oncol. 2318 Mill
Road, Ste 800, Alexandria, Va 22314 USA: 2012
|
|
107
|
Tan E, Park K, Lim WT, et al: Phase 1b
study of ficlatuzumab (AV-299), an anti-hepatocyte growth factor
monoclonal antibody, in combination with gefitinib in Asian
patients with NSCLC. J Clin Oncol. 29 Suppl:493S2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Katayama R, Aoyama A, Yamori T, Qi J,
Oh-hara T, Song Y, Engelman JA and Fujita N: Cytotoxic activity of
tivantinib (ARQ 197) is not due solely to c-MET inhibition. Cancer
Res. 73:3087–3096. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wakelee H, Gettinger S, Engelman J, et al:
A phase Ib/II study of XL184 (BMS 907351) with and without
erlotinib (E) in patients (pts) with non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings. pp. 30172010;
|
|
110
|
Tanizaki J, Okamoto I, Okamoto K, Takezawa
K, Kuwata K, Yamaguchi H and Nakagawa K: MET tyrosine kinase
inhibitor crizotinib (PF-02341066) shows differential antitumor
effects in non-small cell lung cancer according to MET alterations.
J Thorac Oncol. 6:1624–1631. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Feng Y, Thiagarajan PS and Ma PC: MET
signaling: Novel targeted inhibition and its clinical development
in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:459–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Blumenschein GR Jr, Mills GB and
Gonzalez-Angulo AM: Targeting the hepatocyte growth factor-cMET
axis in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 30:3287–3296. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Rundhaug JE: Matrix metalloproteinases and
angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 9:267–285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Pavlaki M and Zucker S: Matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitors (MMPIs): The beginning of phase I or
the termination of phase III clinical trials. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 22:177–203. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Shepherd FA, Giaccone G, Seymour L,
Debruyne C, Bezjak A, Hirsh V, Smylie M, Rubin S, Martins H, Lamont
A, et al: Prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
trial of marimastat after response to first-line chemotherapy in
patients with small-cell lung cancer: A trial of the national
cancer institute of Canada-clinical trials group and the European
organization for research and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol.
20:4434–4439. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV,
Papatsoris AG and Papavassiliou AG: Matrix metalloproteinase
inhibitors as anticancer agents. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
40:1156–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: TGF-β and cancer.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:29–40. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Lonning S, Mannick J and McPherson J:
Antibody targeting of TGF-β in cancer patients. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 12:2176–2189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Hawinkels LJ and Ten Dijke P: Exploring
anti-TGF-β therapies in cancer and fibrosis. Growth Factors.
29:140–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Rodon J, Carducci MA, Sepulveda-Sánchez
JM, Azaro A, Calvo E, Seoane J, Braña I, Sicart E, Gueorguieva I,
Cleverly AL, et al: First-in-human dose study of the novel
transforming growth factor-β receptor I kinase inhibitor LY2157299
monohydrate in patients with advanced cancer and glioma. Clin
Cancer Res. 21:553–560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Rani B, Dituri F, Cao Y, Engström U, Lupo
L, Dooley S, Moustakas A and Giannelli G: P0320: Targeting TGF-beta
I with the transforming growth factor receptor type I kinase
inhibitor, LY2157299, modulates stemness-related biomarkers in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 62:S4292015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Whatcott CJ, Dumas SN, Watanabe A, LoBello
J, Von Hoff DD and Han H: Abstract 2135: TGFβRI inhibition results
in reduced collagen expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Res. DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.
|
|
124
|
Johnstone CN, Chand A, Putoczki TL and
Ernst M: Emerging roles for IL-11 signaling in cancer development
and progression: Focus on breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 26:489–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S,
Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung
P, Zhang XH, et al: Dependency of colorectal cancer on a
TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation.
Cancer Cell. 22:571–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|