Introduction
Pancreatic cancer is the fourth leading cause of
cancer-related deaths, with a 5-year survival rate less than 7%
(1). The only curative treatment for
this malignancy is complete resection, which is possible in only
10–20% of patients (1–3). Pancreatic cancer rapidly metastasizes to
the liver, lungs, lymph nodes and peritoneum, and the majority of
patients eventually succumb with widespread metastatic lesions.
Metastasis to regional lymph nodes is one of the key indicators of
aggressive tumors. Lymph node status is a powerful predictor of
patient survival and one of the key parameters used for staging
tumors (4). These data suggest that
there are significant prognostic implications of lymph node
metastasis in pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic cancer is characterized by abundant
desmoplastic stroma with activated pancreatic stellate cells and an
excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (5). Interactions between cancer cells and
various stromal cells promote malignancy and inhibit drug
penetration into tumors and drug uptake by cancer cells (6). In previous studies, it has been reported
that for resectable pancreatic cancer, high α-smooth muscle actin
(αSMA) expression in the primary tumor was a poor prognostic
factor, while high stroma density was a favorable prognostic factor
(7–9).
Furthermore, a recent report showed that distant pancreatic cancer
metastases have highly fibrotic stroma, similar to the primary
tumors, and there was no significant difference in the degree of
desmoplasia between primary tumors and metastatic lesions (10). In papillary thyroid tumors, lymph node
metastasis with desmoplasia was correlated with reduced
disease-free survival times (11).
However, there are no reports investigating desmoplasia in
metastatic lymph nodes in pancreatic cancer patients. Therefore,
the precise contribution of desmoplasia to the malignant
progression of lymph node metastases in pancreatic cancer remains
unclear.
In this study, we evaluated the degree of
desmoplasia in metastatic lymph node lesions from pancreatic cancer
patients using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and
immunohistochemical staining for cytokeratin 19 (CK19) and αSMA. In
addition, we measured the size of lymph node metastases and
investigated potential correlations between the degree of
desmoplasia and the size of lymph node metastases as well as
evaluating its clinical significance based on clinicopathological
findings and prognoses.
Materials and methods
Case selection
We investigated 216 metastatic lymph nodes and 10
lymph nodes without cancer cells dissected from 65 patients with
invasive pancreatic ductal carcinomas, which were macroscopically
curatively resected at our institution between August 2007 and
February 2012. Pancreatectomy was performed in three broad
categories, standard pancreaticoduodenectomy, distal pancreatectomy
and total pancreatectomy. The lymph node dissection technique at
our institution has been standardized to D2 lymph node dissection,
according to the general rules for the study of pancreatic cancer
by Japan Pancreas Society (12,13).
Unusual differentiation variants of ductal carcinoma, such as
intraductal mucinous neoplasms with invasive carcinoma, were
excluded from the study.
Clinical and pathologic data were retrospectively
obtained from surgical and pathologic reports. The clinical data
included age, sex, neoadjuvant chemotherapy and postoperative
chemotherapy; the pathologic data included T, N and R status
according to the 7th AJCC/UICC TNM classification system,
histologic grade and invasion factors (vascular, lymphatic,
perineural, or extranodal) (14).
Overall survival was measured as the time from pancreatic resection
to death. Survival analyses were performed in August 2016. Overall
survival was analyzed based on the number of metastatic lymph nodes
and the degree of desmoplasia in the metastatic lesions.
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics
Committee of Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan (approval nos.
24–222 and 25–117) and conformed to the Ethical Guidelines for
Human Genome/Gene Research enacted by the Japanese Government and
the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided signed informed
consent, approving the use of their personal health information for
unspecified research purposes.
Immunohistochemical analysis
Metastatic lymph node tissues from primary
pancreatic cancer patients were evaluated by H&E, and CK19 and
αSMA immunohistochemistry. Tissues were sliced 4-µm thick and
incubated with mouse anti-CK19 antibody (1:500; #sc-376126; Santa
Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) or mouse anti-αSMA
antibody (1:500; #M0851; Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa
Clara, CA, USA) overnight at 4°C. Staining was performed on serial
sections. The percentage of fibrous components in the metastatic
lymph node lesions were classified into three categories, high
(≥70%), moderate (10–70%), and low (<10%). The optimal cut off
value in degree of desmoplasia was determined according to our
previous report (7). The sizes of the
lesions were also classified into three categories, 0–999,
1,000–1,999, and ≥2,000 µm. When the several status of the degree
of desmoplasia in lymph nodes was observed in one patient, the
status of the degree of desmoplasia was defined based on the
highest degree of desmoplasia in all lymph nodes from such patient.
Images were acquired using a confocal laser-scanning microscope
(BZ-X700; Keyence, Osaka, Japan).
Statistical analysis
Results are presented as means ± SD. Patient
characteristics were analyzed using the χ2 and Student's t-tests.
Statistical significance was defined as P<0.05. Survival
analyses were conducted using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the
curves were compared using the log-rank test. All statistical
analyses were performed using JMP 12 software (SAS Institute, Cary,
NC, USA).
Results
We investigated 226 lymph nodes from 65 patients
with invasive pancreatic ductal carcinomas; 216 had metastatic
involvement and 10 were cancer-free. The mean age of the patients
was 66 years (range, 36–85 years), and 35% were females (n=23). The
median tumor size was 37 mm (range, 13–80 mm). The median number of
examined lymph nodes was 32 (range, 7–75), and the median number of
metastatic lymph nodes was 5 (range, 1–25). At the last follow-up
assessment, 56 patients (86%) had died and 9 (14%) were alive;
median survival was 22 months. No patients underwent neoadjuvant
chemotherapy prior to resection, but postoperative chemotherapy was
given to 58 patients (89%). The clinicopathological characteristics
of the study cohort are summarized in Table I.
 | Table I.Clinicopathological features of the
institutional cohort. |
Table I.
Clinicopathological features of the
institutional cohort.
| Characteristic | Institutional cohort
n=65 (%) |
|---|
| Sex |
|
|
Female | 23 (35) |
| Male | 42 (65) |
| Age |
|
|
Years | 66.1 (36–85) |
| Tumor size (median,
mm) | 37 (13–80) |
| T stage |
|
| T1 | 1 (1.5) |
| T2 | 2 (3.1) |
| T3 | 59 (90.8) |
| T4 | 3 (4.6) |
| Median number of LNs
examined (range) | 32 (7–75) |
| Median number of LNs
with metastasis (range) | 5 (1–25) |
| Outcome |
|
| Dead | 56 (86) |
|
Alive | 9 (14) |
| Median survival
(months) | 22 |
To investigate desmoplasia in lymph node metastases,
we assessed the extent of fibrotic components in the 216 lymph
nodes with a variety of sizes of metastatic lesions and the ten
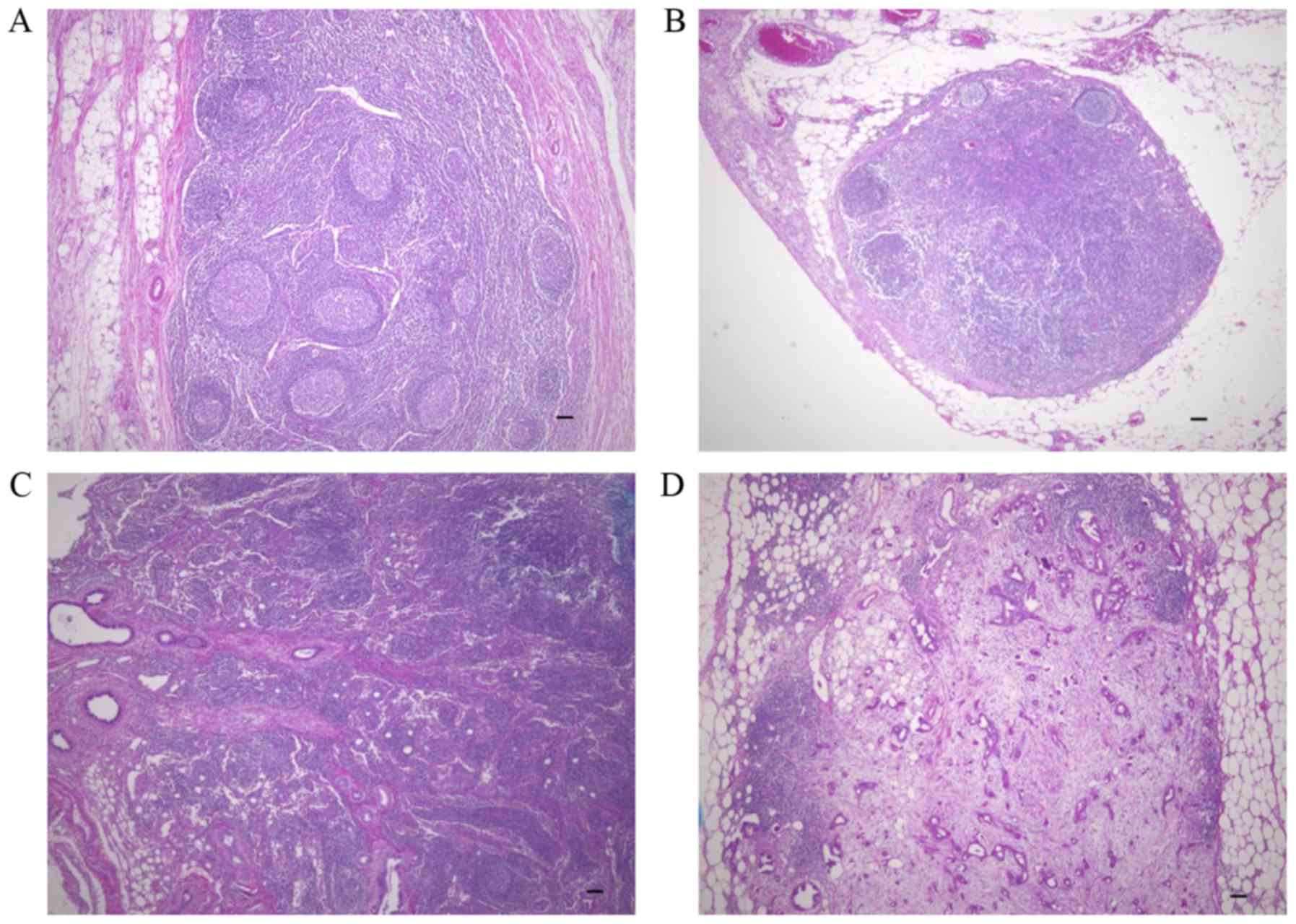
cancer-free lymph nodes (Fig. 1). No
desmoplasia was observed in lymph nodes without metastases
(Fig. 1A) or in lymph nodes with
small metastatic lesions (<100 µm) composed of few cancer cells
(Fig. 1B). In lymph nodes with
>100 µm metastatic lesions, desmoplasia was observed in some,
but not all cases (Fig. 1C). In the
lymph nodes with >2,000 µm metastatic lesions, desmoplasia was
frequently observed (Fig. 1D).
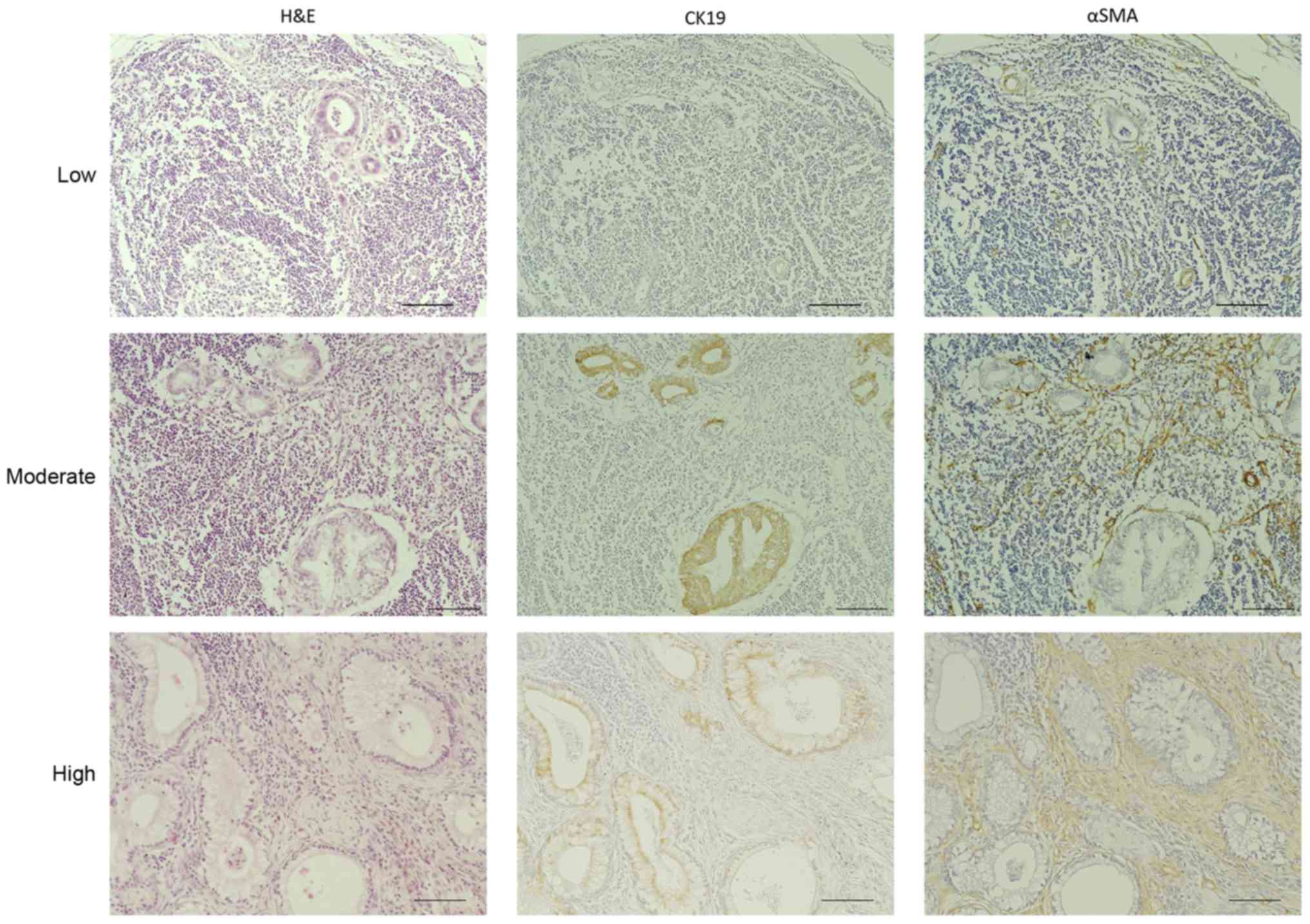
To investigate the clinical significance of
desmoplasia in pancreatic cancer lymph node metastases, we stained
the 216 metastatic lymph nodes with H&E, anti-CK19, which is a
marker for cancer cells, and anti-αSMA, which is a marker for
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Then, we evaluated the area covered
by the fibrotic components in the samples. We classified these
metastatic lesions into three categories according to the
percentage of the total area of the metastatic lesions that were
histologically fibrotic, high (≥70%), moderate (10–70%), and low
(<10%) (Fig. 2). Based on this
classification, 37 (56.9%), 16 (24.6%) and 12 (18.5%) of the 65
evaluable cases fell into the high, moderate and low degree of
desmoplasia categories, respectively. Furthermore, 107 lymph nodes
(49.54%) of the 216 evaluable samples had a high degree of
desmoplasia, 64 (29.63%) had a moderate degree and 45 (20.83%) had
a low degree (Table II). Next, we
measured the lesion size of these 216 metastatic lymph nodes to
investigate possible correlations between the degree of desmoplasia
and lesion size. These results showed that 95.7% of the metastases
smaller than 1,000 µm (69/216, 32.0%) were in the low desmoplasia
group. Among the metastases larger than 1,000 µm (52/216, 24.1%),
44.2% showed moderate or high degrees of desmoplasia, and among the
metastases larger than 2,000 µm (95/216, 44.0 %), 87.3% showed
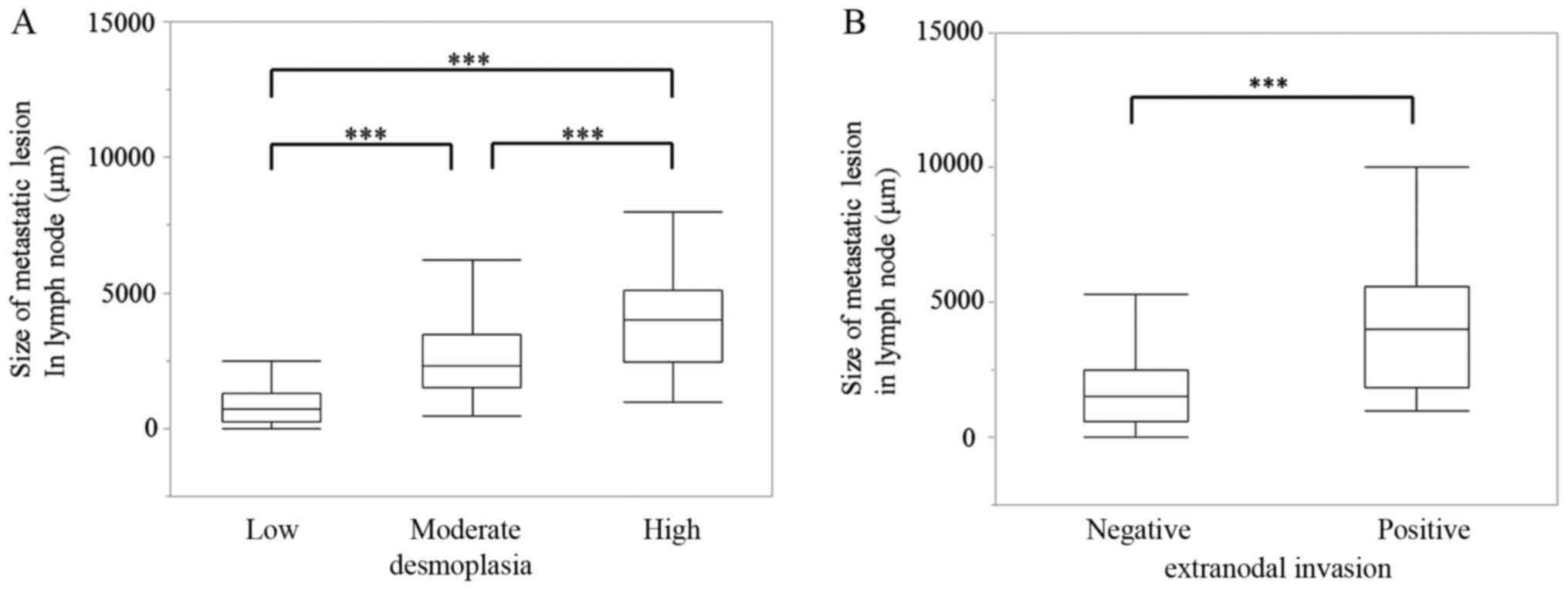
moderate or high degrees of desmoplasia (Table II). There was a significant
correlation between metastatic lesion size and the degree of
desmoplasia in these patient-derived samples (P<0.001; Fig. 3A). Additionally, there was a
significant correlation between metastatic lesion size and locally
extranodal invasion in these samples (P<0.001; Fig. 3B).
 | Table II.Relationship between desmoplasia and
metastatic lesion size. |
Table II.
Relationship between desmoplasia and
metastatic lesion size.
|
| Size of metastatic
lesion in lymph node |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Desmoplasia | 0-999 µm | 1,000–1,999 µm | 2,000 µm | Total (%) |
|---|
| High | 0 | 7 | 38 | 45 (21) |
| Moderate | 3 | 16 | 45 | 64 (30) |
| Low | 66 | 29 | 12 | 107 (49) |
| Total | 69 (32%) | 52 (24%) | 95 (44%) | 216 |
We also investigated possible correlations between
clinicopathological factors and the degree of desmoplasia. As shown
in Table III, the degree of
desmoplasia in metastatic lesions was not correlated with most
clinicopathological factors, such as pT category and lymphatic
invasion. Number of metastatic lymph node and locally extranodal
invasion were significantly correlated with the degree of
desmoplasia in the metastatic lesions.
 | Table III.Association between the degree of
desmoplasia and clinicopathological factors. |
Table III.
Association between the degree of
desmoplasia and clinicopathological factors.
|
| Desmoplasia |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Characteristics | High n=37 (%) | Moderate n=16
(%) | Low n=12 (%) | P-value |
|---|
| Age (years) |
|
|
|
|
| ≥65 | 21 (57) | 11 (69) | 6
(50) | 0.5732 |
|
<65 | 16 (43) | 5
(31) | 6
(50) |
|
| pT category |
|
|
|
|
|
pT1-3 | 37 (100) | 14 (87.5) | 11 (92) | 0.0681 |
|
pT4 | 0 (0) | 2 (12.5) | 1 (8) |
|
| Histologic
grade |
|
|
|
|
|
G1/G2 | 15 (41) | 5
(31) | 6
(50) | 0.6003 |
| G3 | 22 (59) | 11 (69) | 6
(50) |
|
| Pathologic
margin |
|
|
|
|
|
Negative | 25 (68) | 12 (75) | 8
(67) | 0.8420 |
|
Positive | 12 (32) | 4
(25) | 4
(33) |
|
| Lymphatic
invasion |
|
|
|
|
| No | 5
(14) | 2
(12) | 3
(25) | 0.6210 |
|
Yes | 32 (86) | 14 (88) | 9
(70) |
|
| Vascular
invasion |
|
|
|
|
| No | 9
(24) | 5
(31) | 7
(58) | 0.1022 |
|
Yes | 28 (76) | 11 (69) | 5
(42) |
|
| Perineural
invasion |
|
|
|
|
| No | 3 (8) | 0 (0) | 1 (8) | 0.3095 |
|
Yes | 34 (92) | 16 (100) | 11 (92) |
|
| Extranodal
invasion |
|
|
|
|
| No | 18 (48.65) | 15 (93.75) | 12 (100) |
<0.0001a |
|
Yes | 19 (51.35) | 1 (6.25) | 0 (0) |
|
| Number of
metastatic lymph node |
|
|
|
|
| 1 | 1 (3) | 2 (12.5) | 5
(42) | 0.0042a |
| ≥2 | 36 (97) | 14 (87.5) | 7
(58) |
|
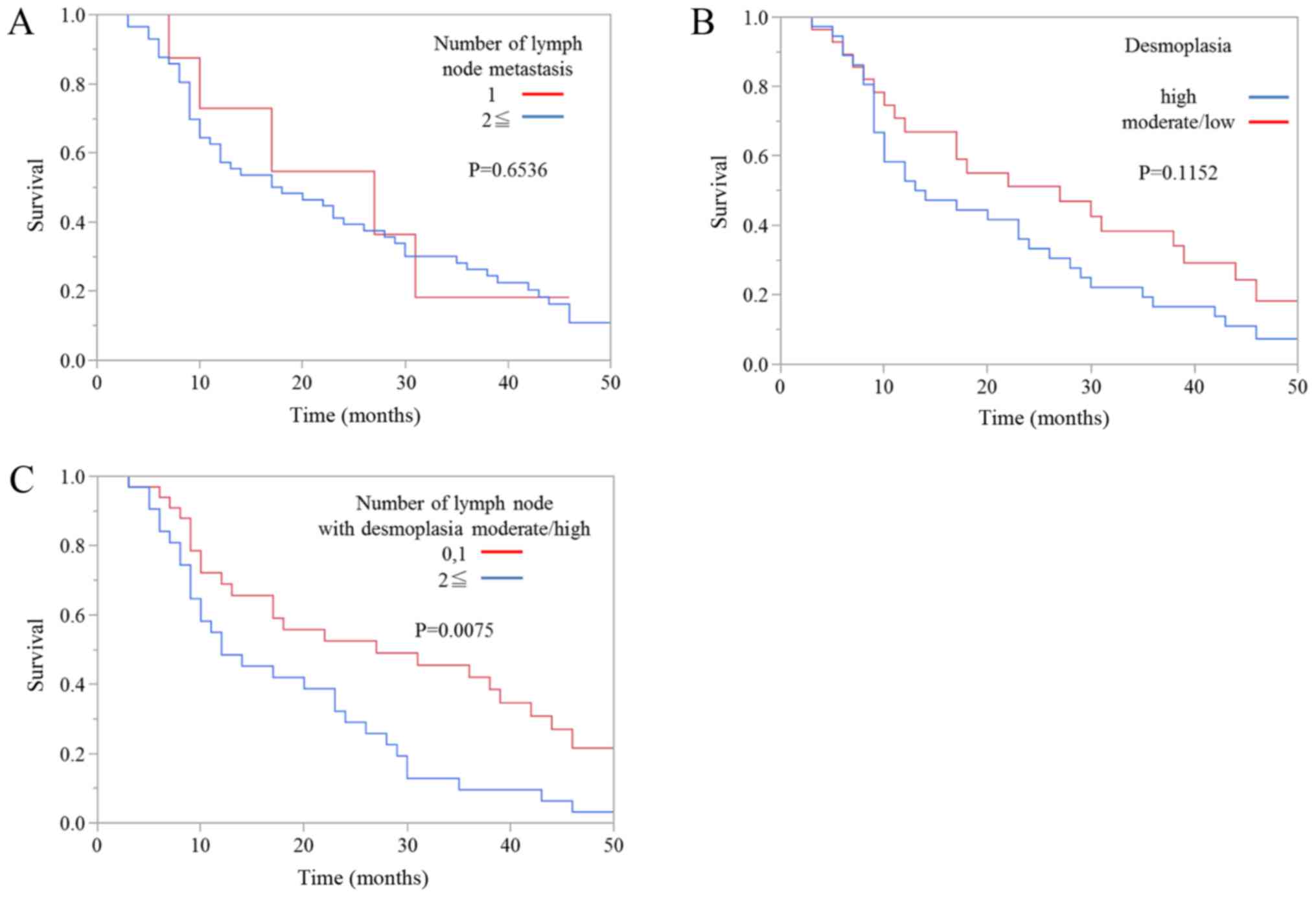
Next, we evaluated the association between prognosis
and the degree of desmoplasia in metastatic lymph node lesions.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that there was no significant
difference in overall survival between patients with one metastatic
lymph node and patients with more than one metastatic lymph node
(Fig. 4A). Moreover, there was no
significant difference in overall survival between patients with a
high degree of metastatic lymph node desmoplasia and patients with
moderate or low degrees of desmoplasia (Fig. 4B). However, the prognosis of patients
with one or zero metastatic lymph nodes with high or moderate
degrees of desmoplasia was also significantly better than patients
with two or more metastatic lymph nodes with high or moderate
degrees of desmoplasia (Fig. 4C).
Finally, we evaluated the clinicopathological
findings, including the degree of desmoplasia in metastatic lymph
node lesions, to identify prognostic factors for overall survival
in pancreatic cancer patients with lymph node metastasis using
univariate and multivariate analyses (Table IV). In the univariate analysis, we
found sex (P=0.0203), locally extranodal invasion (P=0.0051) and
multiple metastatic lymph nodes with high or moderate desmoplasia
(P=0.0098) to be prognostic factors. In multivariate analysis, the
presence of multiple metastatic lymph nodes with high or moderate
desmoplasia was also a prognostic factor (P=0.0466). Because we
analyzed only patients with lymph node metastases who underwent
surgical resection for pancreatic cancer in this study, patients
with pT4 were exactly the same group as the patients with UICC
Stage III or IV. Therefore, we did not include UICC stage in
Tables III and IV.
 | Table IV.Prognostic factors for overall
survival in univariate and multivariate analyses. |
Table IV.
Prognostic factors for overall
survival in univariate and multivariate analyses.
|
|
| Univariate |
| Multivariate |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
|
Characteristics | N | HR (95%) CI | P-value | HR (95%) CI | P-value |
|---|
| Age,
≥65/<65 | 38/27 | 1.11
(0.64–1.93) | 0.7110 |
|
|
| Sex,
male/female | 42/23 | 0.51
(0.27–0.90) | 0.0203a | 0.66
(0.34–1.21) | 0.1855 |
| pT category,
pT1-3/T4 | 62/3 | 2.36
(0.57–6.57) | 0.2048 |
|
|
| Histologic grade,
G1-G2/G3 | 26/39 | 1.25
(0.73–2.20) | 0.4224 |
|
|
| Pathologic margin,
−/+ | 45/20 | 1.60
(0.86–2.84) | 0.1305 | 1.93
(1.02–3.52) | 0.0437a |
| Lymphatic invasion,
−/+ | 10/45 | 1.04
(0.53–2.27) | 0.9235 |
|
|
| Vascular invasion,
−/+ | 21/44 | 1.58
(0.89–2.93) | 0.1173 | 1.45
(0.79–2.78) | 0.2312 |
| Perineural
invasion, −/+ | 4/61 | 0.44
(0.18–1.46) | 0.1586 | 0.39
(0.15–1.37) | 0.1302 |
| Extranodal
invasion, −/+ | 45/20 | 2.39
(1.31–4.31) | 0.0051a | 1.63
(0.82–3.22) | 0.1632 |
| Number of lymph
node with desmoplasia high or moderate, 0,1/≥2 | 33/32 | 2.07
(1.19–3.63) | 0.0098a | 1.90
(1.01–3.61) | 0.0466a |
Discussion
The main findings of this study were: i) the degree
of desmoplasia in metastatic lymph node lesions from pancreatic
cancer patients was significantly correlated with lesion size; ii)
the degree of desmoplasia in metastatic lymph nodes was
significantly correlated with locally extranodal invasion; and iii)
the presence of multiple lymph nodes with high or moderate
desmoplasia was correlated with poor prognosis.
In this study, the median number of regional lymph
nodes examined per case was 32, and the median number of lymph
nodes with metastases was 5. These median values are higher than
most values reported in the literature (4,15–17). Also, the percentage of T4 cases in our
institutional cohort was higher, possibly due to the fact that this
study only included cases with lymph node metastases. The male to
female ratio was also higher in our study, but this is a recognized
tendency in previous Japanese studies (18). The median age and tumor size were
similar to previous reports. These data suggested that our cohort
was representative of the general group of patients with resectable
pancreatic cancer, except for there being more advanced cancers and
a greater number of metastatic lymph nodes, which was due to our
study including only lymph node metastasis cases.
A recent report showed that there were significant
prognostic implications of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic
cancer (4). In this study, we focused
on desmoplasia, a characteristic pathological finding in primary
pancreatic cancer lesions, in metastatic lymph node lesions. Our
data showed that there were significant correlations between the
size of metastatic lesions and the degree of desmoplasia in the
lesions. We also found no increase in the fibrotic component of
cancer-free lymph nodes in patients with other metastatic lymph
nodes, suggesting that there was no induction of stromal cells as a
pre-metastatic niche in lymph nodes without metastases.
Furthermore, these findings also suggested that desmoplasia in
lymph node lesions was not present in the early stages of
metastasis, but was induced and/or increased with the growth of the
lesions. Also, we found that the number of metastatic lymph node
was significantly correlated with the degree of desmoplasia. In
cases with multiple lymph node metastases, a high degree of
desmoplasia was frequently observed. These findings also suggest
that desmoplasia in lymph node lesions was induced and/or increased
with the progression of lymph node metastasis.
Finally, we also investigated correlations between
clinicopathological factors and the degree of desmoplasia in
metastatic lymph nodes, finding that locally extranodal invasion
was significantly correlated with the degree of desmoplasia. In
addition, locally extranodal invasion was significantly correlated
with metastatic lesion size. These results suggest the possibility
that locally extranodal invasion in lymph nodes can be controlled
by suppressing desmoplasia, and treatment for desmoplasia may
improve the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients with lymph node
metastasis accompanied by desmoplasia or locally extranodal
invasion. The locally extranodal invasion of lymph nodes is a
histological feature that has been considered a prognostic factor
in several cancers (19–21), and recent reports have shown that
locally extranodal invasion of lymph node metastases in pancreatic
cancer and cancer of the papilla of Vater was common in these
tumors, leading to a significantly increased risk for all-cause
mortality (22). Although the
nonrandomized nature and small number of patients in this study
limit generalizable conclusions, the results regarding locally
extranodal invasion raise important issues that should be
investigated in future studies.
In conclusion, these data demonstrated that the
presence of multiple metastatic lymph nodes with high or moderate
degrees of desmoplasia was correlated with overall survival in
univariate and multivariate analyses. We performed multivariate
analysis with six factors (10% of sample size) as shown in Table IV because the number of samples in
the present study was small. We also confirmed that the results
obtained in multivariate analysis including all factors showed the
similar results (number of lymph node with desmoplasia high or
moderate, 0, 1/≥2; P=0.0087) and didn't alter the interpretation of
our findings and the conclusions of the present study. Locally
extranodal invasion and metastatic lesion size were also correlated
with the degree of desmoplasia in metastatic lymph nodes. To
further determine the contribution of desmoplasia to lymph node
metastases, we should clarify the functional role of desmoplasia in
the establishment and/or growth of lymph node metastases in the
future.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E. Manabe, S. Sadatomi and M.
Ohmori (Department of Surgery and Oncology, Kyushu University
Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan). The present study was supported in part
by a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid for
Scientific Research (B) and (C) and Scientific Research on
Innovative Areas (grant nos. 26293305, 25713050, 16K15621,
16K10601, 16K10600, 16H05417, 15H04933, 15K15498 and 16H05418).
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
H&E
|
hematoxylin and eosin
|
|
CK19
|
cytokeratin 19
|
|
αSMA
|
α-smooth muscle actin
|
References
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH
and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 378:607–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malvezzi M, Carioli G, Bertuccio P, Rosso
T, Boffetta P, Levi F, La Vecchia C and Negri E: European cancer
mortality predictions for the year 2016 with focus on leukaemias.
Ann Oncol. 27:725–731. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Basturk O, Saka B, Balci S, Postlewait LM,
Knight J, Goodman M, Kooby D, Sarmiento JM, El-Rayes B, Choi H, et
al: Substaging of lymph node status in resected pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma has strong prognostic correlations: Proposal for a
revised N classification for TNM staging. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:(Suppl
3). 1187–1195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mahadevan D and Von Hoff DD: Tumor-stroma
interactions in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:1186–1197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nielsen MF, Mortensen MB and Detlefsen S:
Key players in pancreatic cancer-stroma interaction:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts, endothelial and inflammatory cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:2678–2700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujita H, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Nakata
K, Yu J, Kayashima T, Cui L, Manabe T, Ohtsuka T and Tanaka M:
Alpha-smooth muscle actin expressing stroma promotes an aggressive
tumor biology in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas.
39:1254–1262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sinn M, Denkert C, Striefler JK, Pelzer U,
Stieler JM, Bahra M, Lohneis P, Dörken B, Oettle H, Riess H and
Sinn BV: α-Smooth muscle actin expression and desmoplastic stromal
reaction in pancreatic cancer: Results from the CONKO-001 study. Br
J Cancer. 111:1917–1923. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang LM, Silva MA, D'Costa Z, Bockelmann
R, Soonawalla Z, Liu S, O'Neill E, Mukherjee S, McKenna WG, Muschel
R and Fokas E: The prognostic role of desmoplastic stroma in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:4183–4194. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Whatcott CJ, Diep CH, Jiang P, Watanabe A,
LoBello J, Sima C, Hostetter G, Shepard HM, Von Hoff DD and Han H:
Desmoplasia in primary tumors and metastatic lesions of pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:3561–3568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cho SY, Lee TH, Ku YH, Kim HI, Lee GH and
Kim MJ: Central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid
microcarcinoma can be stratified according to the number, the size
of metastatic foci, and the presence of desmoplasia. Surgery.
157:111–118. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Japan Pancreas Society, . Classification
of Pancreatic Carcinoma. 2nd English. Kanehara & Co.; Tokyo,
Japan: 2003
|
|
13
|
Japan Pancreas Society, . Classification
of Pancreatic Carcinoma. 1st English. Kanehara & Co.; Tokyo,
Japan: 2009
|
|
14
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1419. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brennan MF, Kattan MW, Klimstra D and
Conlon K: Prognostic nomogram for patients undergoing resection for
adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 240:293–298. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huebner M, Kendrick M, Reid-Lombardo KM,
Que F, Therneau T, Qin R, Donohue J, Nagorney D, Farnell M and Sarr
M: Number of lymph nodes evaluated: Prognostic value in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:920–926. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Strobel O, Hinz U, Gluth A, Hank T,
Hackert T, Bergmann F, Werner J and Büchler MW: Pancreatic
Adenocarcinoma: Number of positive nodes allows to distinguish
several N categories. Ann Surg. 261:961–969. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nimura Y, Nagino M, Takao S, Takada T,
Miyazaki K, Kawarada Y, Miyagawa S, Yamaguchi A, Ishiyama S, Takeda
Y, et al: Standard versus extended lymphadenectomy in radical
pancreatoduodenectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma of the head of the
pancreas: Long-term results of a Japanese multicenter randomized
controlled trial. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 19:230–241. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Veronese N, Nottegar A, Pea A, Solmi M,
Stubbs B, Capelli P, Sergi G, Manzato E, Fassan M, Wood LD, et al:
Prognostic impact and implications of extra-capsular lymph node
involvement in colorectal cancer: A systematic review with
meta-analysis. Ann Oncol. 27:42–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luchini C, Nottegar A, Solmi M, Sergi G,
Manzato E, Capelli P, Scarpa A and Veronese N: Prognostic
implications of extranodal extension in node-positive squamous cell
carcinoma of the vulva: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg
Oncol. 25:60–65. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Veronese N, Luchini C, Nottegar A, Kaneko
T, Sergi G, Manzato E, Solmi M and Scarpa A: Prognostic impact of
extra-nodal extension in thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. J Surg
Oncol. 112:828–833. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luchini C, Veronese N, Pea A, Sergi G,
Manzato E, Nottegar A, Solmi M, Capelli P and Scarpa A: Extranodal
extension in N1-adenocarcinoma of the pancreas and papilla of
Vater: A systematic review and meta-analysis of its prognostic
significance. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:205–209.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|