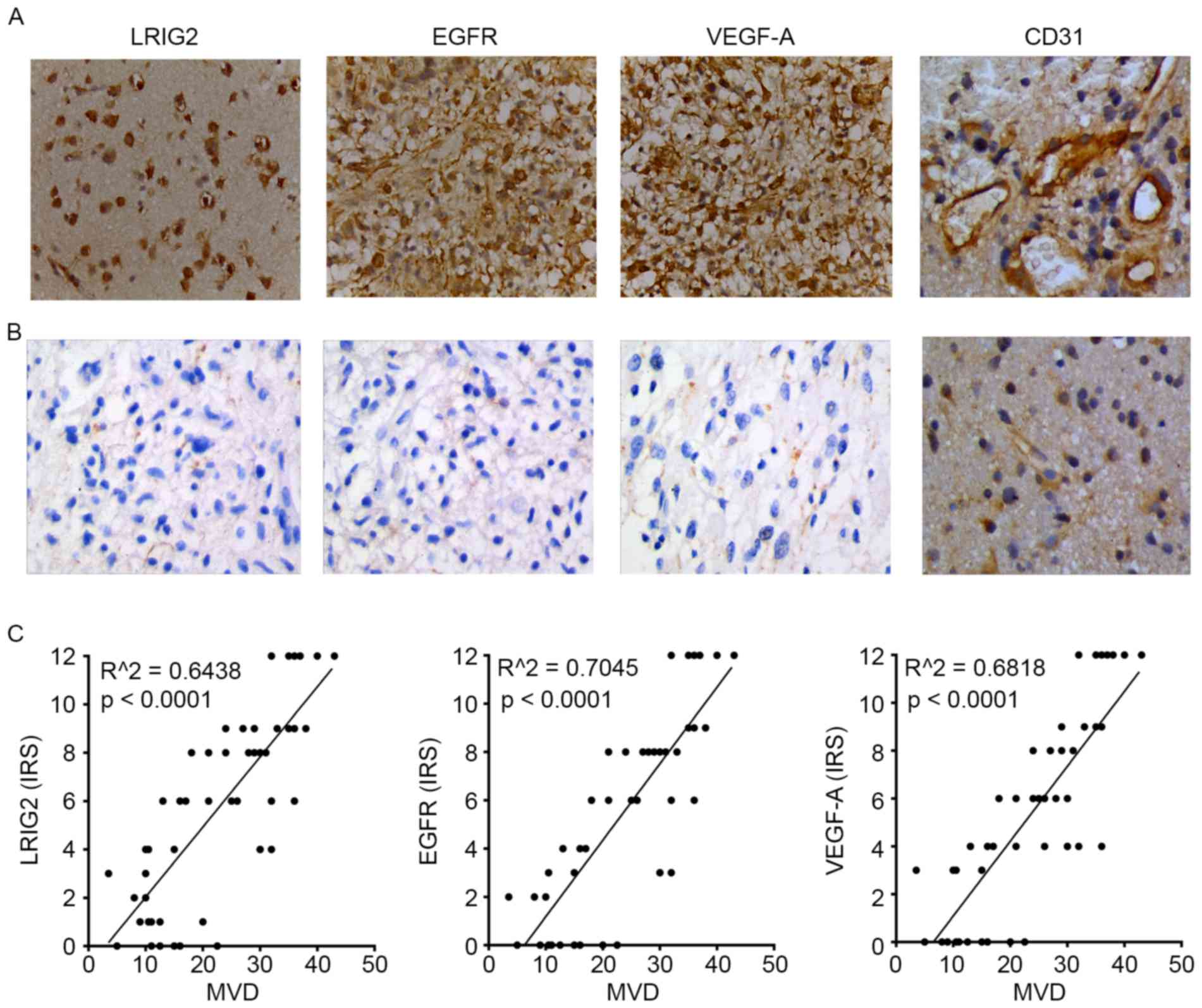
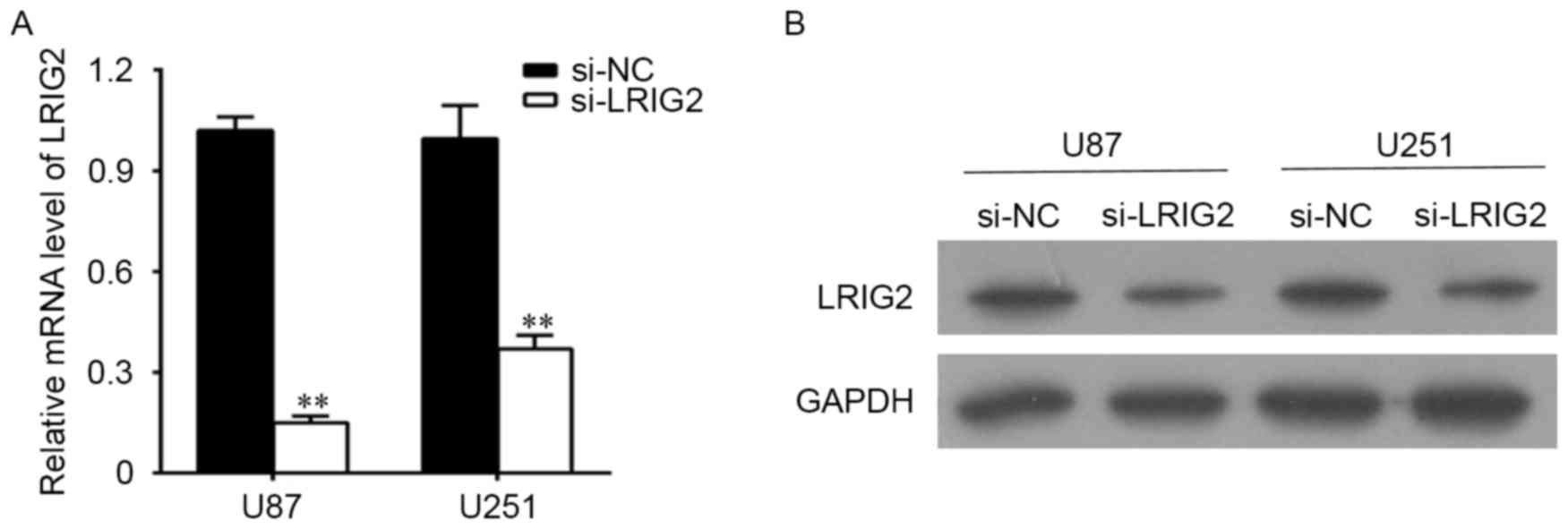
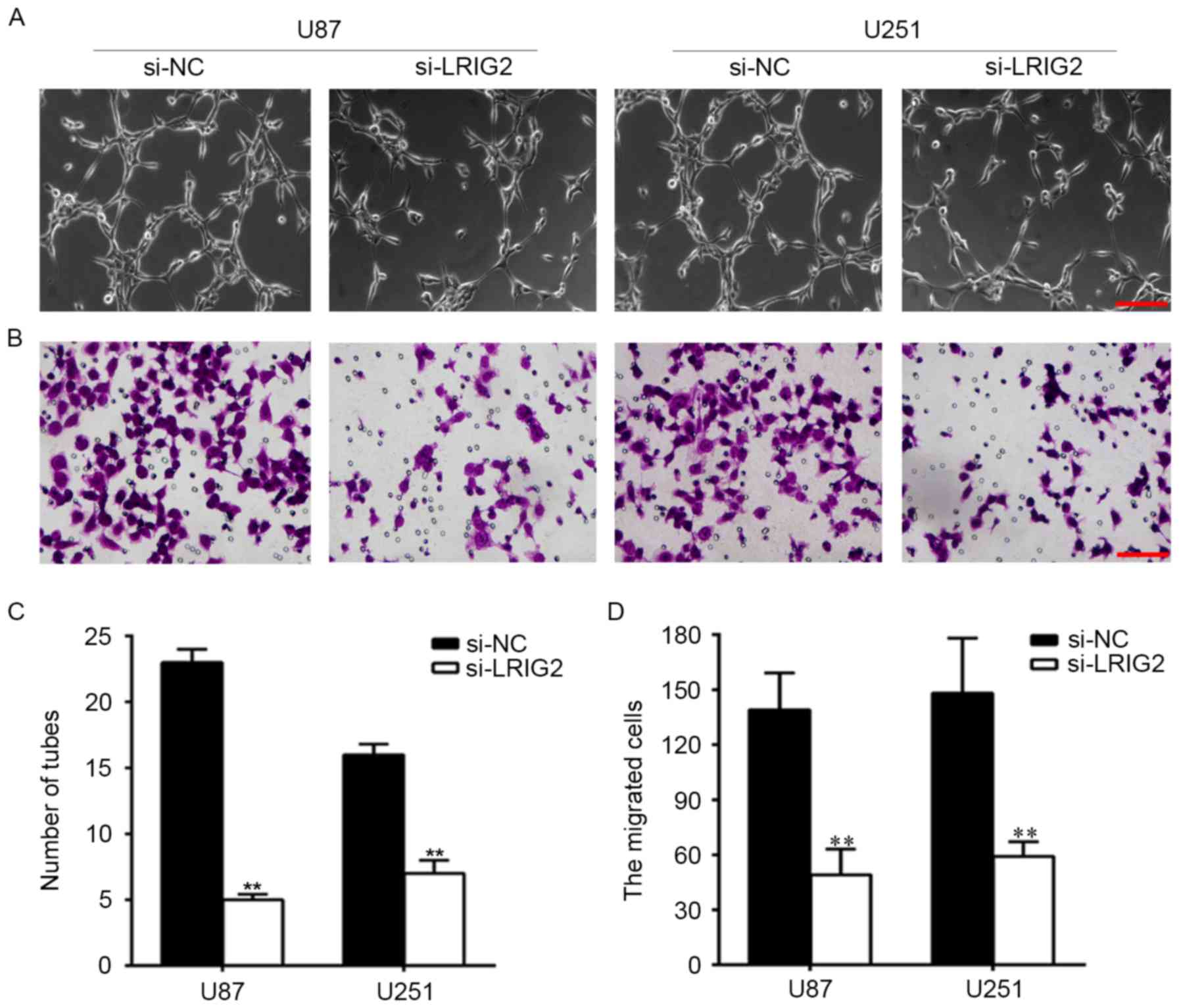
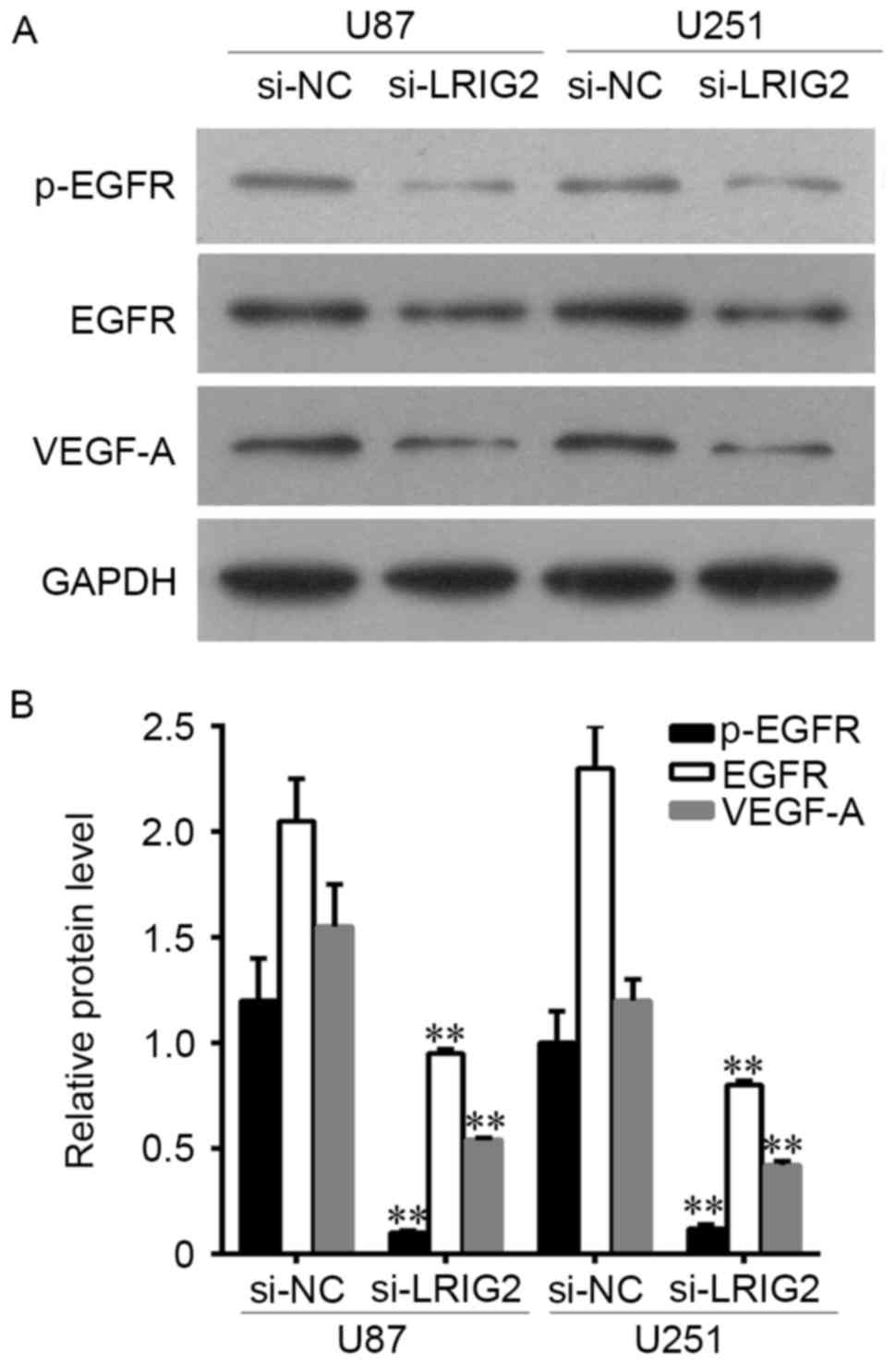
|
1
|
Wen PY and Reardon DA: Neuro-oncology in
2015: Progress in glioma diagnosis, classification and treatment.
Nat Rev Neurol. 12:69–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malla RR, Gopinath S, Gondi CS, Alapati K,
Dinh DH, Gujrati M and Rao JS: Cathepsin B and uPAR knockdown
inhibits tumor-induced angiogenesis by modulating VEGF expression
in glioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 18:419–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babykutty S SPPJNR, Kumar MA, Nair MS,
Srinivas P and Gopala S: Nimbolide retards tumor cell migration,
invasion, and angiogenesis by downregulating MMP-2/9 expression via
inhibiting ERK1/2 and reducing DNA-binding activity of NF-κB in
colon cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 51:475–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Petrillo M, Borriello M, Fuoco G, Legge F,
Iannone V and Ferrandina G: Novel VEGF-independent strategies
targeting tumor vasculature: Clinical aspects. Curr Pharm Des.
18:2702–2712. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reardon DA, Turner S, Peters KB,
Desjardins A, Gururangan S, Sampson JH, McLendon RE, Herndon JE II,
Jones LW, Kirkpatrick JP, et al: A review of VEGF/VEGFR-targeted
therapeutics for recurrent glioblastoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
9:414–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cea V, Sala C and Verpelli C:
Antiangiogenic therapy for glioma. J Signal Transduct.
2012:4830402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Casaletto JB and McClatchey AI: Spatial
regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in development and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 12:387–400. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Larsen AK, Ouaret D, El Ouadrani K and
Petitprez A: Targeting EGFR and VEGF(R) pathway cross-talk in tumor
survival and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Ther. 131:80–90. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malik U and Javed A: LRIGs: A
prognostically significant family with emerging therapeutic
competence against cancers. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 17:3–16.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Erp S, van den Heuvel DM, Fujita Y,
Robinson RA, Hellemons AJ, Adolfs Y, Van Battum EY, Blokhuis AM,
Kuijpers M, Demmers JA, et al: Lrig2 negatively regulates
ectodomain shedding of Axon guidance receptors by ADAM proteases.
Dev Cell. 35:537–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo D, Nilsson J, Haapasalo H, Raheem O,
Bergenheim T, Hedman H and Henriksson R: Perinuclear leucine-rich
repeats and immunoglobulin-like domain proteins (LRIG1-3) as
prognostic indicators in astrocytic tumors. Acta Neuropathol.
111:238–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lindström AK, Asplund A and Hellberg D:
Correlation between LRIG1 and LRIG2 expressions and expression of
11 tumor markers, with special reference to tumor suppressors, in
CIN and normal cervical epithelium. Gynecol Oncol. 122:372–376.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Powell AE, Wang Y, Li Y, Poulin EJ, Means
AL, Washington MK, Higginbotham JN, Juchheim A, Prasad N, Levy SE,
et al: The pan-ErbB negative regulator Lrig1 is an intestinal stem
cell marker that functions as a tumor suppressor. Cell.
149:146–158. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wong VW, Stange DE, Page ME, Buczacki S,
Wabik A, Itami S, van de Wetering M, Poulsom R, Wright NA, Trotter
MW, et al: Lrig1 controls intestinal stem-cell homeostasis by
negative regulation of ErbB signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 14:401–408.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu L, Teixeira VH, Yuan Z, Graham TA,
Endesfelder D, Kolluri K, Al-Juffali N, Hamilton N, Nicholson AG,
Falzon M, et al: LRIG1 regulates cadherin-dependent contact
inhibition directing epithelial homeostasis and pre-invasive
squamous cell carcinoma development. J Pathol. 229:608–620. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai L, McEachern D, Yang CY, Lu J, Sun H
and Wang S: LRIG1 modulates cancer cell sensitivity to Smac
mimetics by regulating TNFα expression and receptor tyrosine kinase
signaling. Cancer Res. 72:1229–1238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hedman H, Lindström AK, Tot T, Stendahl U,
Henriksson R and Hellberg D: LRIG2 in contrast to LRIG1 predicts
poor survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine
cervix. Acta Oncol. 49:812–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Holmlund C, Haapasalo H, Yi W, Raheem O,
Brännström T, Bragge H, Henriksson R and Hedman H: Cytoplasmic
LRIG2 expression is associated with poor oligodendroglioma patient
survival. Neuropathology. 29:242–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang B, Han L, Chen R, Cai M, Han F, Lei T
and Guo D: Downregulation of LRIG2 expression by RNA interference
inhibits glioblastoma cell (GL15) growth, causes cell cycle
redistribution, increases cell apoptosis and enhances cell adhesion
and invasion in vitro. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1018–1023. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tai YT, Acharya C, An G, Moschetta M,
Zhong MY, Feng X, Cea M, Cagnetta A, Wen K, van Eenennaam H, et al:
APRIL and BCMA promote human multiple myeloma growth and
immunosuppression in the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood.
127:3225–3236. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang G, Wu J and Song H: LRIG2 expression
and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 8:667–672.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cui L, Xu S, Song Z, Zhao G, Liu X and
Song Y: Pituitary tumor transforming gene: A novel therapeutic
target for glioma treatment. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
47:414–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang T, Qiao M, Zhou F, Ren S, Su C and
Zhou C: Effect of combined therapy inhibiting EGFR and VEGFR
pathways in non-small-cell lung cancer on progression-free and
overall survival. Clin Lung Cancer. Dec 29–2016.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
25
|
Yu X, Li W, Deng Q, You S, Liu H, Peng S,
Liu X, Lu J, Luo X, Yang L, et al: Neoalbaconol inhibits
angiogenesis and tumor growth by suppressing EGFR-mediated VEGF
production. Mol Carcinog. 56:1414–1426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|