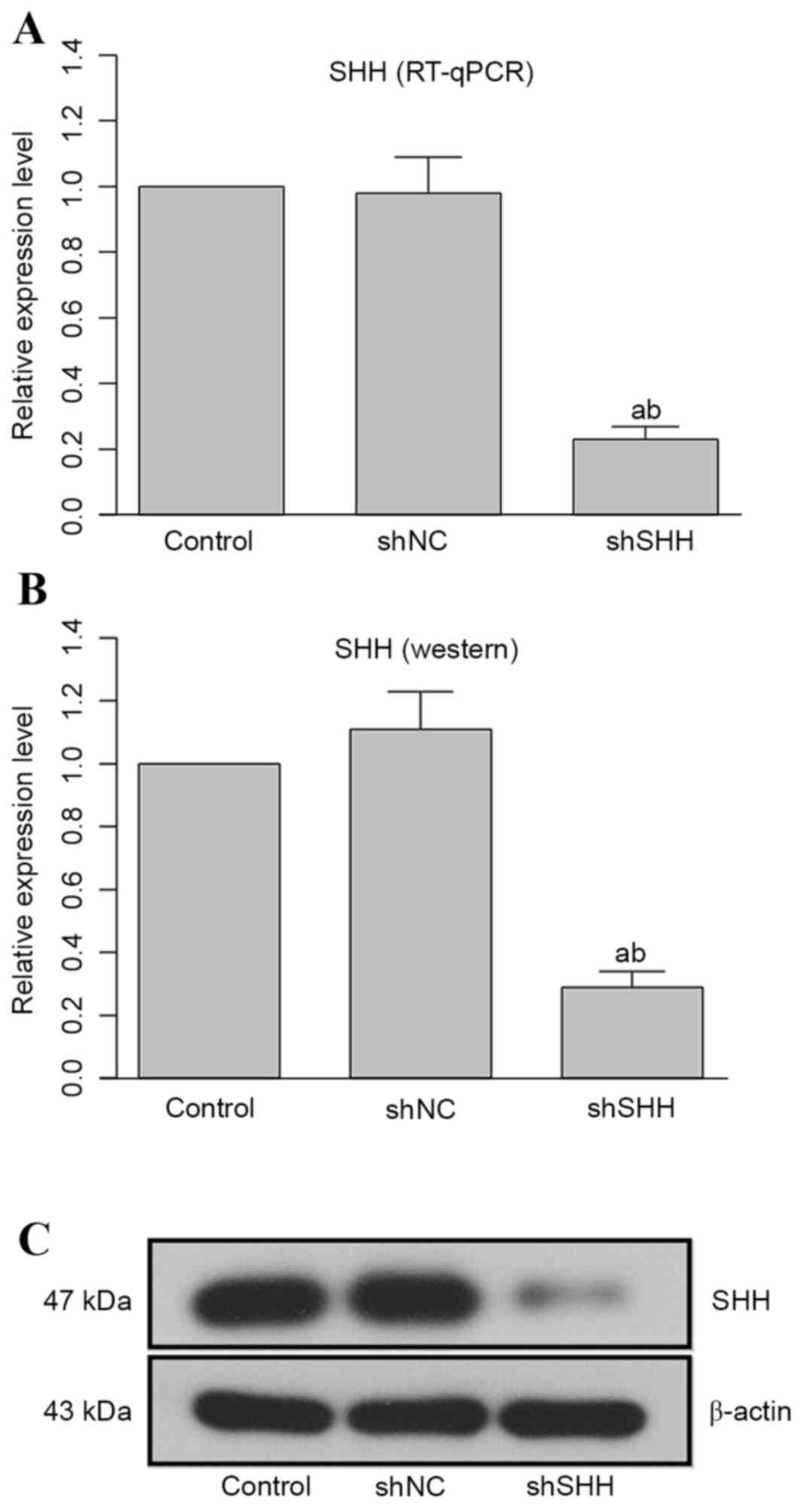
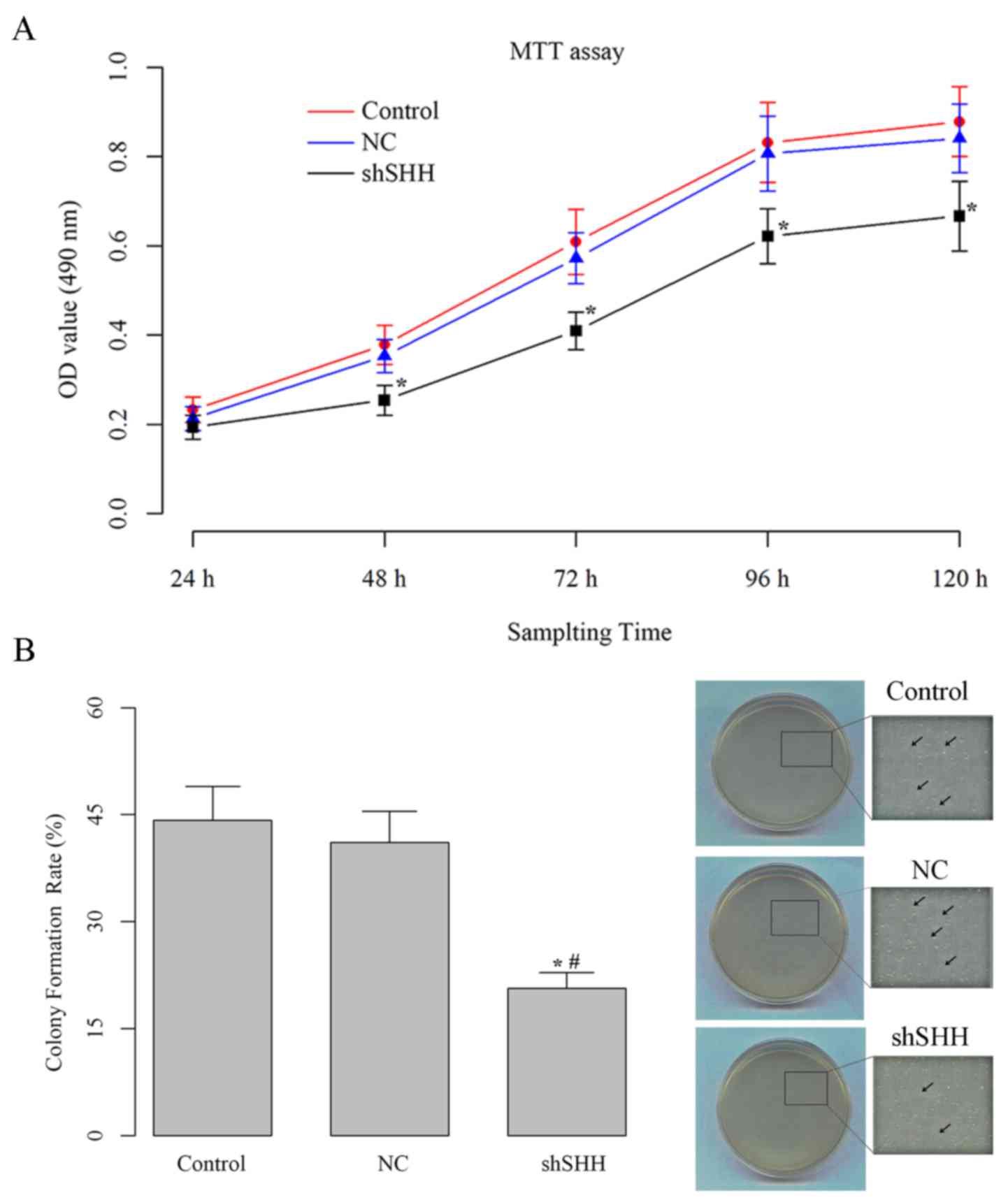
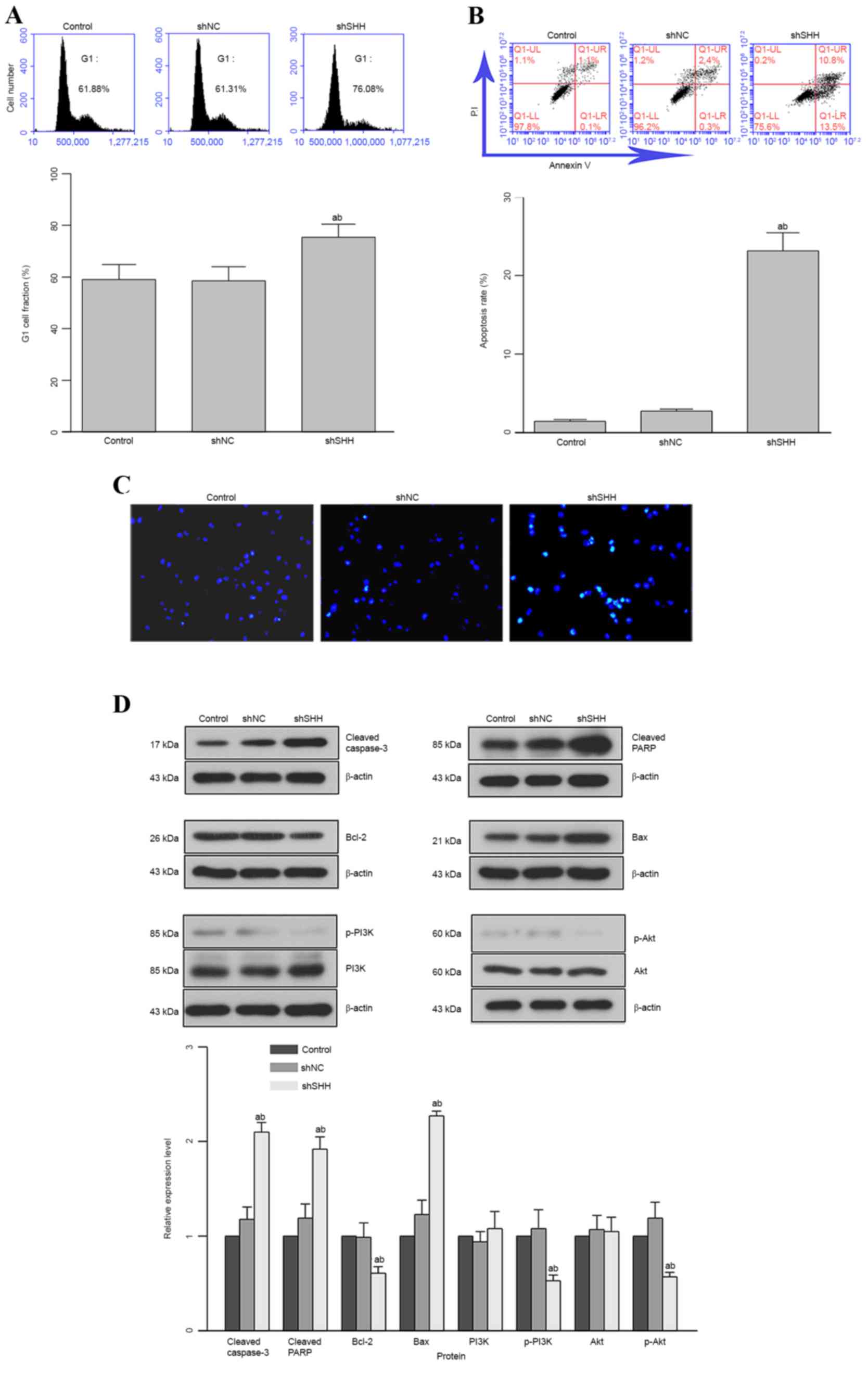
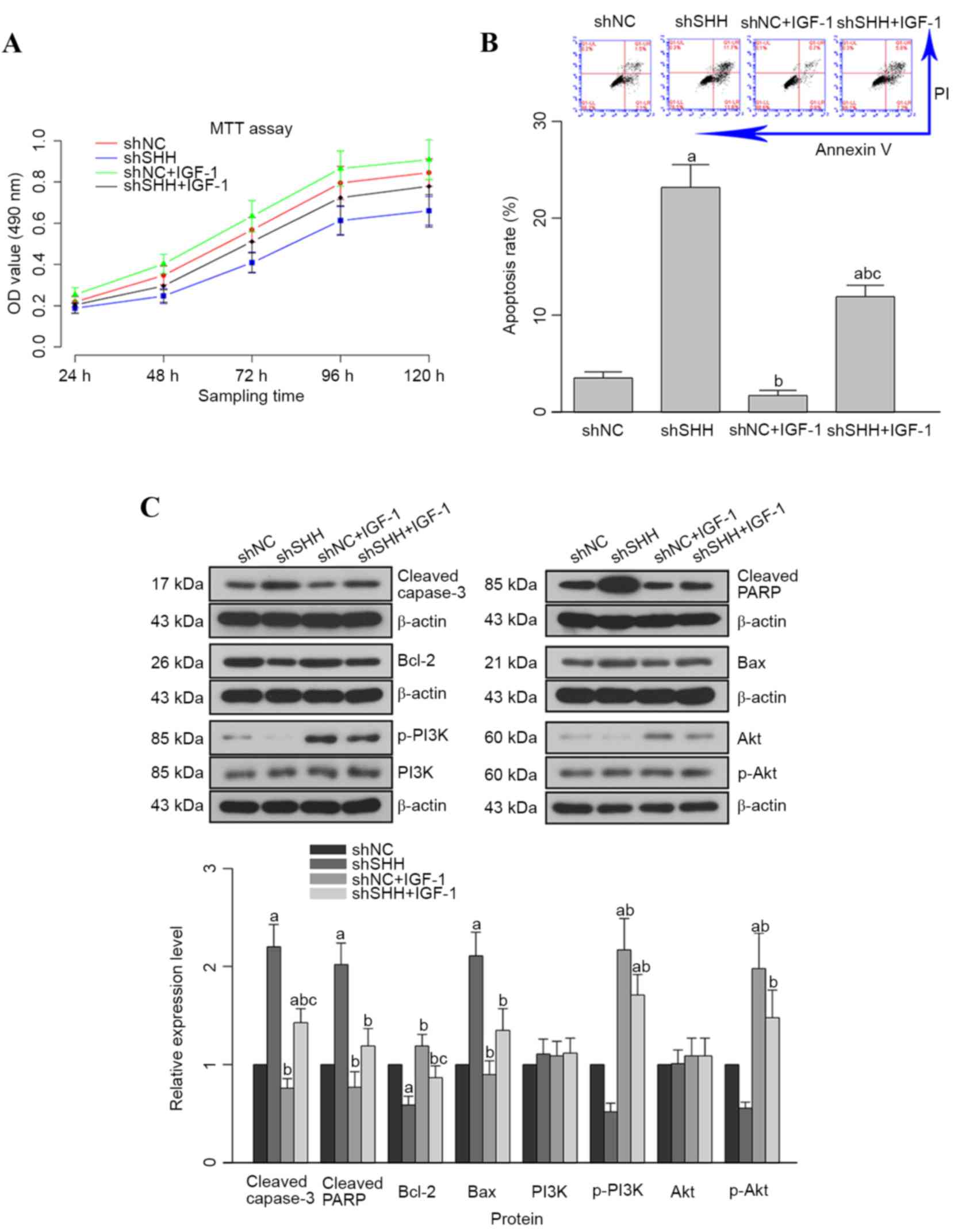
|
1
|
Devesa SS: The incidence of
retinoblastoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 80:263–265. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Q, Wang Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Liu T and
Kunda PE: Tandem therapy for retinoblastoma: Immunotherapy and
chemotherapy enhance cytotoxicity on retinoblastoma by increasing
apoptosis. J Cancer Res Clin. 139:1357–1372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Broaddus E, Topham A and Singh AD:
Survival with retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. Brit J
Ophthalmol. 93:24–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Milla LA, González-Ramírez CN and Palma V:
Sonic Hedgehog in cancer stem cells: A novel link with autophagy.
Biol Res. 45:223–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Hedgehog target
genes: Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog
signaling activation. Curr Mol Med. 9:873–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Feldmann G, Dhara S, Fendrich V, Bedja D,
Beaty R, Mullendore M, Karikari C, Alvarez H, Iacobuzio-Donahue C,
Jimeno A, et al: Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic
cancer invasion and metastases: A new paradigm for combination
therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res. 67:2187–2196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kasperczyk H, Baumann B, Debatin KM and
Fulda S: Characterization of sonic hedgehog as a novel NF-kappaB
target gene that promotes NF-kappaB-mediated apoptosis resistance
and tumor growth in vivo. FASEB J. 23:21–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ke Z, Caiping S, Qing Z and Xiaojing W:
Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 signals promote epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in ovarian cancer by mediating PI3K/AKT pathway. Med
Oncol. 32:3682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choe JY, Yun JY, Jeon YK, Kim SH, Choung
HK, Oh S, Park M and Kim JE: Sonic hedgehog signalling proteins are
frequently expressed in retinoblastoma and are associated with
aggressive clinicopathological features. J Clin Pathol. 68:6–11.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng WH, Kar S, Doré S and Quirion R:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1): A neuroprotective trophic
factor acting via the Akt kinase pathway. J Neural Transm Suppl.
261–272. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hung HC, Hsiao YH and Gean PW: Sonic
hedgehog signaling regulates amygdalar neurogenesis and extinction
of fear memory. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 25:1723–1732. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR,
Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale
J, Olson JM and Beachy PA: Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by
hedgehog pathway blockade. Science. 297:1559–1561. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, De
Montes Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, Parker AR, Shimada Y,
Eshleman JR, Watkins DN and Beachy PA: Widespread requirement for
Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours.
Nature. 425:846–851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara
S, Gardner D, Maitra A, Isaacs JT, Berman DM and Beachy PA:
Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and
metastasis. Nature. 431:707–712. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW,
Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, Qi YP, Gysin S, Fernández-del
Castillo C, Yajnik V, et al: Hedgehog is an early and late mediator
of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature. 425:851–856. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang
B, Beachy PA and Baylin SB: Hedgehog signalling within airway
epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature.
422:313–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, Kim BH, Park JK,
Kim HK, Kim JS and Oh SC: Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes
metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and
MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mill P, Mo R, Hu MC, Dagnino L, Rosenblum
ND and Hui CC: Shh controls epithelial proliferation via
independent pathways that converge on N-Myc. Dev Cell. 9:293–303.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eilers M and Eisenman RN: Myc's broad
reach. Genes Dev. 22:2755–2766. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Javelaud D, Pierrat MJ and Mauviel A:
Crosstalk between TGF-β and hedgehog signaling in cancer. FEBS
Lett. 586:2016–2025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yanai K, Nakamura M, Akiyoshi T, Nagai S,
Wada J, Koga K, Noshiro H, Nagai E, Tsuneyoshi M, Tanaka M and
Katano M: Crosstalk of hedgehog and Wnt pathways in gastric cancer.
Cancer Lett. 263:145–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Riobo K, Lu X, Ai GM, Haines CP and
Emerson CP Jr: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase, Akt are essential for
Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:4505–4510.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|