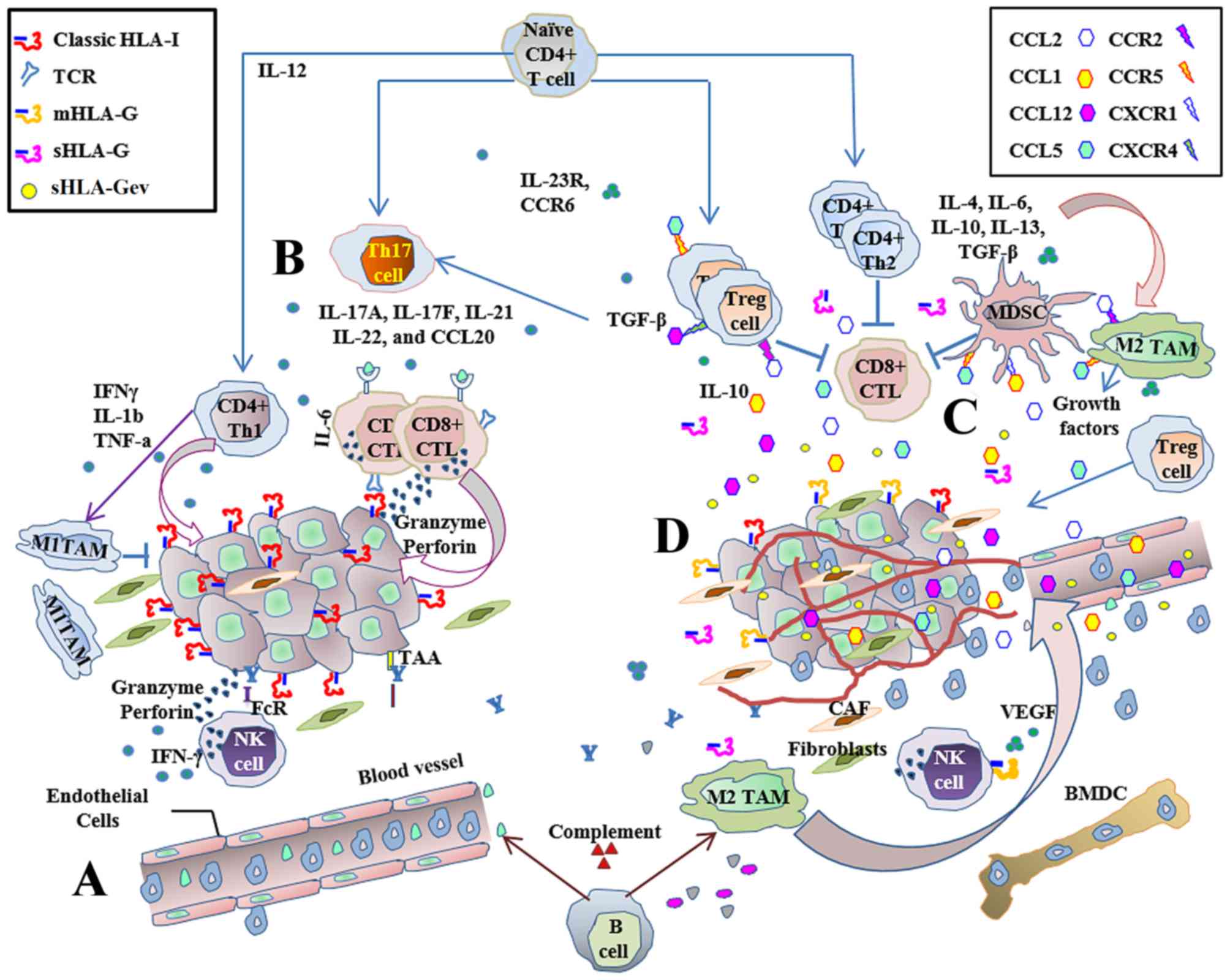
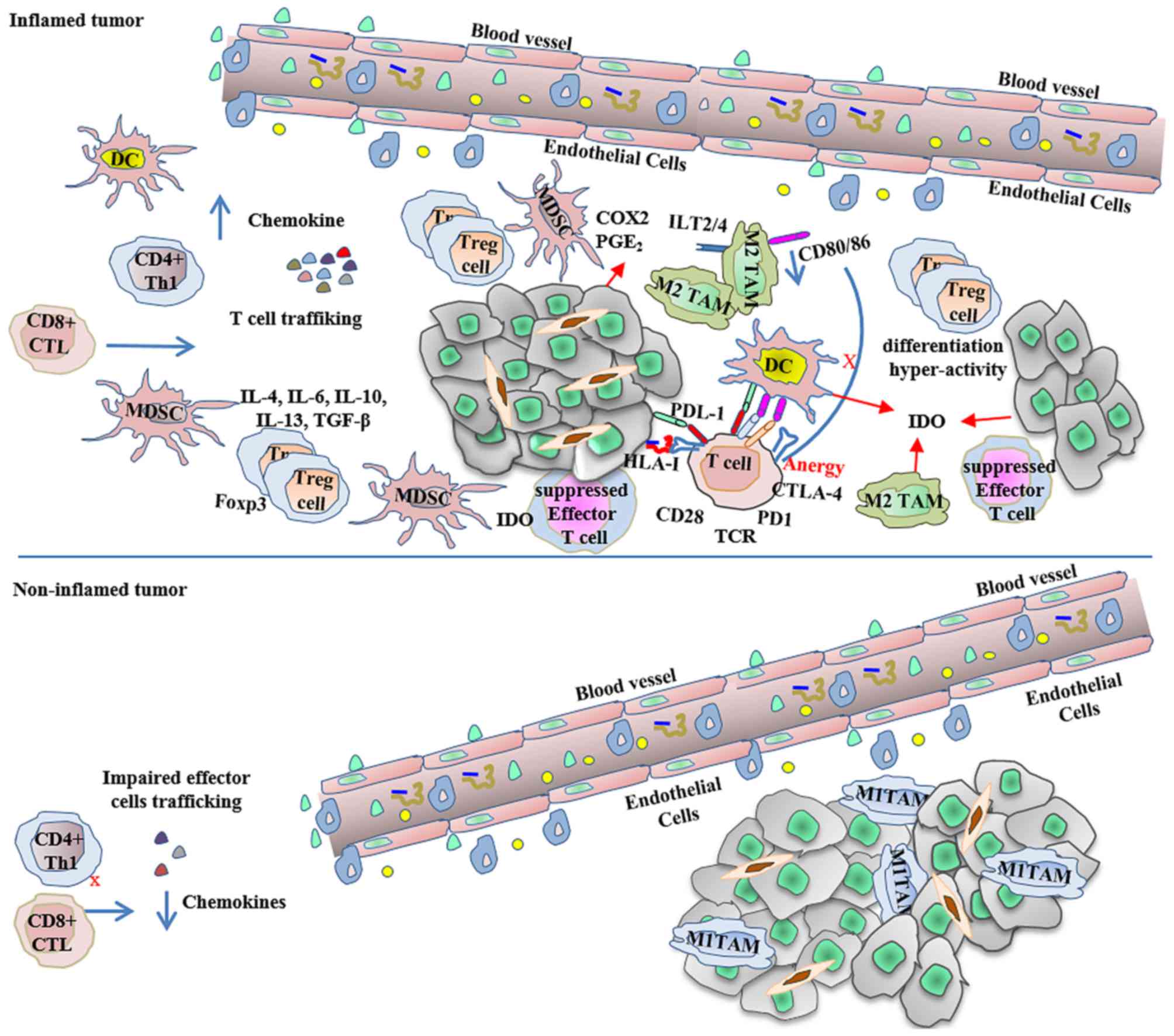
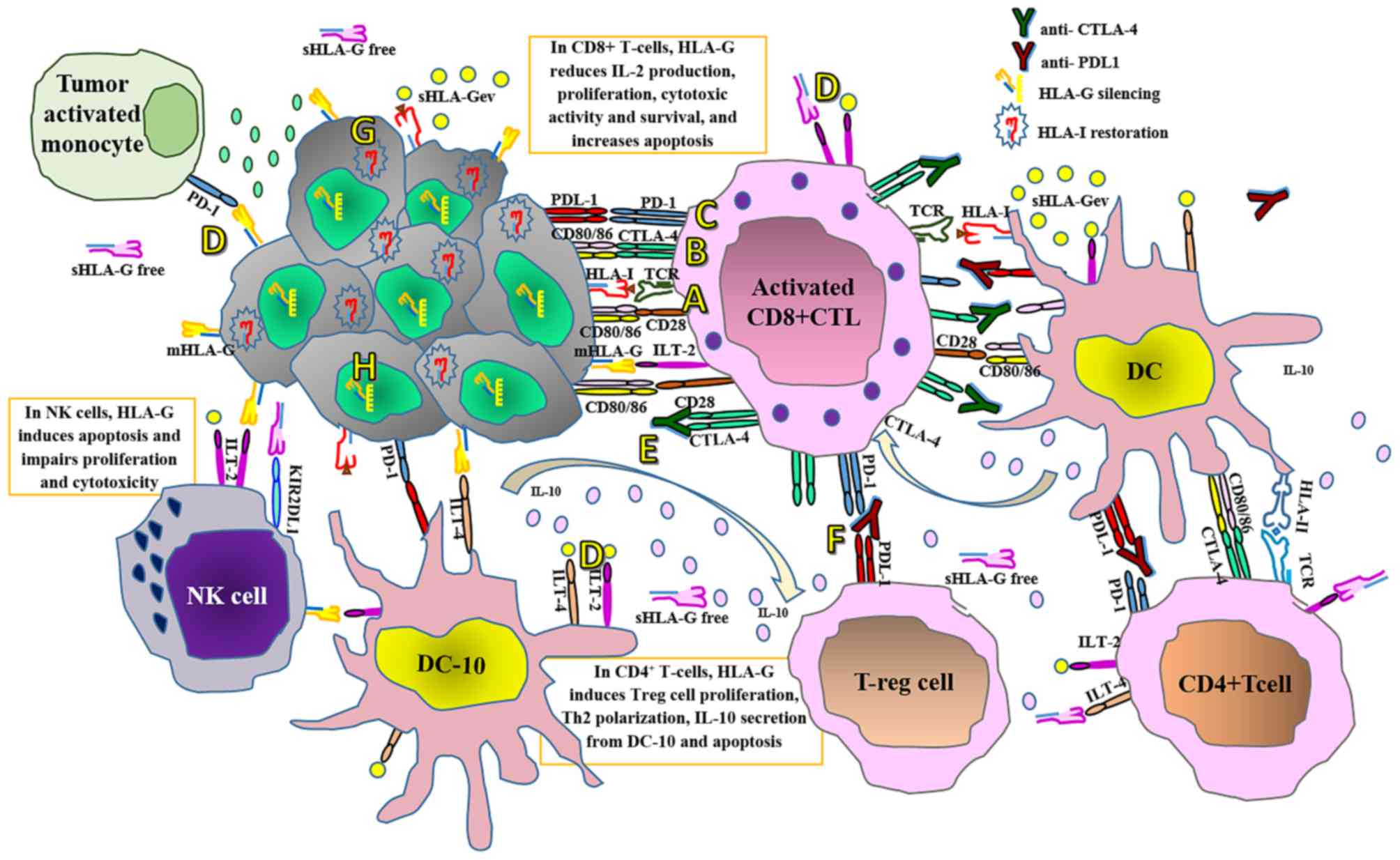
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, Inflammation and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van den Boorn JG and Hartmann G: Turning
tumors into vaccines: Co-opting the innate immune system. Immunity.
39:27–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Campoli M and Ferrone S: HLA antigen
changes in malignant cells: Epigenetic mechanisms and biologic
significance. Oncogene. 27:5869–5885. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang CC, Campoli M and Ferrone S:
Classical and nonclassical HLA class I antigen and NK
Cell-activating ligand changes in malignant cells: Current
challenges and future directions. Adv Cancer Res. 93:189–234. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garrido F, Cabrera T, Concha A, Glew S,
Ruiz-Cabello F and Stern PL: Natural history of HLA expression
during tumour development. Immunol Today. 14:491–499. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garrido F, Ruiz-Cabello F, Cabrera T,
Pérez-Villar JJ, López-Botet M, Duggan-Keen M and Stern PL:
Implications for immunosurveillance of altered HLA class I
phenotypes in human tumours. Immunol Today. 18:89–95. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koopman LA, Corver WE, van der Slik AR,
Giphart MJ and Fleuren GJ: Multiple genetic alterations cause
frequent and heterogeneous human histocompatibility leukocyte
antigen class I loss in cervical cancer. J Exp Med. 191:961–976.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moreau P, Rousseau P, Rouas-Freiss N, Le
Discorde M, Dausset J and Carosella ED: HLA-G protein processing
and transport to the cell surface. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1460–1466.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adams JL, Smothers J, Srinivasan R and
Hoos A: Big opportunities for small molecules in immuno-oncology.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:603–622. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Srinivasan R and Wolchok JD: Tumor
antigens for cancer immunotherapy: Therapeutic potential of
xenogeneic DNA vaccines. J Transl Med. 2:122004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Waldhauer I and Steinle A: NK cells and
cancer immunosurveillance. Oncogene. 27:5932–5943. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaeger BN and Vivier E: Natural killer
cell tolerance: Control by self or self-control? Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 4:pii: a007229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pegram HJ, Andrews DM, Smyth MJ, Darcy PK
and Kershaw MH: Activating and inhibitory receptors of natural
killer cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 89:216–224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yokoyama WM and Kim S: Licensing of
natural killer cells by self-major histocompatibility complex class
I. Immunol Rev. 214:143–154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG and
Ravetch JV: Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytotoxicity
against tumor targets. Nat Med. 6:443–496. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayakawa Y and Smyth MJ: Innate immune
recognition and suppression of tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 95:293–322.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lennerz V, Fatho M, Gentilini C, Frye RA,
Lifke A, Ferel D, Wölfel C, Huber C and Wölfel T: The response of
autologous T cells to a human melanoma is dominated by mutated
neoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:16013–16018. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perez-Diez A, Joncker NT, Choi K, Chan WF,
Anderson CC, Lantz O and Matzinger P: CD4 cells can be more
efficient at tumor rejection than CD8 cells. Blood. 109:5346–5354.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gotter J, Brors B, Hergenhahn M and
Kyewski B: Medullary epithelial cells of the human thymus express a
highly diverse selection of tissue-specific genes colocalized in
chromosomal clusters. J Exp Med. 199:155–166. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gerloni M and Zanetti M: CD4 T cells in
tumor immunity. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 27:37–48. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Palm NW and Medzhitov R: Pattern
recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity. Immunol
Rev. 227:221–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smith-Garvin JE, Koretzky GA and Jordan
MS: T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:591–619. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Coaña Pico Y, Choudhury A and Kiessling
R: Checkpoint blockade for cancer therapy: Revitalizing a
suppressed immune system. Trends Mol Med. 21:482–491. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Carreno BM and Collins M: The B7 family of
ligands and its receptors: New pathways for costimulation and
inhibition of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 20:29–53. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Nakatani
K, Hara M, Matsumori A, Sasayama S, Mizoguchi A, Hiai H, Minato N
and Honjo T: Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1
receptor-deficient mice. Science. 291:319–322. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Waterhouse P, Penninger JM, Timms E,
Wakeham A, Shahinian A, Lee KP, Thompson CB, Griesser H and Mak TW:
Lymphoproliferative disorders with early lethality in mice
deficient in Ctla-4. Science. 270:985–988. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chemnitz JM, Parry RV, Nichols KE, June CH
and Riley JL: SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor
tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary
human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T
cell activation. J Immunol. 173:945–954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kirchhof MG, Chau LA, Lemke CD, Vardhana
S, Darlington PJ, Márquez ME, Taylor R, Rizkalla K, Blanca I,
Dustin ML and Madrenas J: Modulation of T cell activation by
stomatin-like protein 2. J Immunol. 181:1927–1936. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Teft WA, Kirchhof MG and Madrenas J: A
molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol.
24:65–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Contini P, Ghio M, Poggi A, Filaci G,
Indiveri F, Ferrone S and Puppo F: Soluble HLA-A,-B,-C and -G
molecules induce apoptosis in T and NK CD8+ cells and inhibit
cytotoxic T cell activity through CD8 ligation. Eur J Immunol.
33:125–134. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Le Bouteiller P, Fons P, Herault JP, Bono
F, Chabot S, Cartwright JE and Bensussan A: Soluble HLA-G and
control of angiogenesis. J Reprod Immunol. 76:17–22. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Colonna M, Samaridis J, Cella M, Angman L,
Allen RL, O'Callaghan CA, Dunbar R, Ogg GS, Cerundolo V and Rolink
A: Human myelomonocytic cells express an inhibitory receptor for
classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules. J Immunol.
160:3096–3100. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rajagopalan S and Long EO: A human
histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G-specific receptor
expressed on all natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 189:1093–1100.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pankratz S, Ruck T, Meuth SG and Wiendl H:
CD4(+)HLA-G(+) regulatory T cells: Molecular signature and
pathophysiological relevance. Hum Immunol. 77:727–733. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim R, Emi M and Tanabe K: Cancer
immunoediting from immune surveillance to immune escape.
Immunology. 121:1–14. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vesely MD, Kershaw MH, Schreiber RD and
Smyth MJ: Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu Rev
Immunol. 29:235–271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Monjazeb AM, Zamora AE, Grossenbacher SK,
Mirsoian A, Sckisel GD and Murphy WJ: Immunoediting and antigen
loss: Overcoming the achilles heel of immunotherapy with antigen
non-specific therapies. Front Oncol. 3:1972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Khong HT and Restifo NP: Natural selection
of tumor variants in the generation of ‘tumor escape’ phenotypes.
Nat Immunol. 3:999–1005. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koebel CM, Vermi W, Swann JB, Zerafa N,
Rodig SJ, Old LJ, Smyth MJ and Schreiber RD: Adaptive immunity
maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature.
450:903–907. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gunderson AJ and Coussens LM: B cells and
their mediators as targets for therapy in solid tumors. Exp Cell
Res. 319:1644–1649. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Esquivel-Velázquez M, Ostoa-Saloma P,
Palacios-Arreola MI, Nava-Castro KE, Castro JI and Morales-Montor
J: The role of cytokines in breast cancer development and
progression. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 35:1–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lippitz BE: Cytokine patterns in patients
with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 14:e218–e228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gajewski TF, Meng Y, Blank C, Brown I,
Kacha A, Kline J and Harlin H: Immune resistance orchestrated by
the tumor microenvironment. Immunol Rev. 213:131–145. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gajewski TF, Fuertes M, Spaapen R, Zheng Y
and Kline J: Molecular profiling to identify relevant immune
resistance mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin
Immunol. 23:286–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mahoney KM and Atkins MB: Prognostic and
predictive markers for the new immunotherapies. Oncology (Williston
Park). 28 Suppl 3:S39–S48. 2014.
|
|
48
|
Wong SC, Puaux AL, Chittezhath M, Shalova
I, Kajiji TS, Wang X, Abastado JP, Lam KP and Biswas SK: Macrophage
polarization to a unique phenotype driven by B cells. Eur J
Immunol. 40:2296–2307. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R,
Viale G, Van Eenoo F, Rouas G, Francis P, Crown JP, Hitre E, et al:
Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in
node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to
doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02–98. J Clin
Oncol. 31:860–867. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tanchot C, Terme M, Pere H, Tran T,
Benhamouda N, Strioga M, Banissi C, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G and
Tartour E: Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells: Phenotype, role,
mechanism of expansion in situ and clinical significance. Cancer
Microenviron. 6:147–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Petersson M, Charo J, Salazar-Onfray F,
Noffz G, Mohaupt M, Qin Z, Klein G, Blankenstein T and Kiessling R:
Constitutive IL-10 production accounts for the high NK sensitivity,
low MHC class I expression, and poor transporter associated with
antigen processing (TAP)-1/2 function in the prototype NK target
YAC-1. J Immunol. 161:2099–2105. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Salazar-Onfray F, Charo J, Petersson M,
Freland S, Noffz G, Qin Z, Blankenstein T, Ljunggren HG and
Kiessling R: Down-regulation of the expression and function of the
transporter associated with antigen processing in murine tumor cell
lines expressing IL-10. J Immunol. 159:3195–3202. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen CJ, Sung WW, Su TC, Chen MK, Wu PR,
Yeh KT, Ko JL and Lee H: High expression of interleukin 10 might
predict poor prognosis in early stage oral squamous cell carcinoma
patients. Clin Chim Acta. 415:25–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Goncalves AS, Wastowski IJ, Capeletti LR,
Sacono NT, Cortez AP, Valadares MC, Silva TA and Batista AC: The
clinicopathologic significance of the expression of HLA-G in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol. 117:361–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Levy EM, Bianchini M, Von Euw EM, Barrio
MM, Bravo AI, Furman D, Domenichini E, Macagno C, Pinsky V,
Zucchini C, et al: Human leukocyte antigen-E protein is
overexpressed in primary human colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
32:633–641. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gasparoto TH, de Souza Malaspina TS,
Damante JH, de Mello EF Jr, Ikoma MR, Garlet GP, Costa MR,
Cavassani KA, da Silva JS and Campanelli AP: Regulatory T cells in
the actinic cheilitis. J Oral Pathol Med. 43:754–760. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mendez R, Aptsiauri N, Del Campo A, Maleno
I, Cabrera T, Ruiz-Cabello F, Garrido F and Garcia-Lora A: HLA and
melanoma: Multiple alterations in HLA class I and II expression in
human melanoma cell lines from ESTDAB cell bank. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 58:1507–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ferns DM, Heeren AM, Samuels S, Bleeker
MC, de Gruijl TD, Kenter GG and Jordanova ES: Classical and
non-classical HLA class I aberrations in primary cervical squamous-
and adenocarcinomas and paired lymph node metastases. J Immunother
Cancer. 4:782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Campoli M and Ferrone S: HLA antigen and
NK cell activating ligand expression in malignant cells: A story of
loss or acquisition. Semin Immunopathol. 33:321–334. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Nilsson Lynge L, Djurisic S and Hviid TV:
Controlling the immunological crosstalk during conception and
pregnancy: HLA-G in reproduction. Front Immunol.
5:1982014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cabrera T, López-Nevot MA, Gaforio JJ,
Ruiz-Cabello F and Garrido F: Analysis of HLA expression in human
tumor tissues. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 52:1–9. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Goncalves AS, Oliveira JP, Oliveira CF,
Silva TA, Mendonca EF, Wastowski IJ and Batista AC: Relevance of
HLA-G, HLA-E and IL-10 expression in lip carcinogenesis. Hum
Immunol. 77:785–790. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Reimers MS, Engels CC, Putter H, Morreau
H, Liefers GJ, van de Velde CJ and Kuppen PJ: Prognostic value of
HLA class I, HLA-E, HLA-G and Tregs in rectal cancer: A
retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer. 14:4862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rouas-Freiss N, Moreau P, Ferrone S and
Carosella ED: HLA-G proteins in cancer: Do they provide tumor cells
with an escape mechanism? Cancer Res. 65:10139–10144. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Carosella ED, Moreau P, Le Maoult J, Le
Discorde M, Dausset J and Rouas-Freiss N: HLA-G molecules: From
maternal-fetal tolerance to tissue acceptance. Adv Immunol.
81:199–252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
LeMaoult J, Zafaranloo K, Le Danff C and
Carosella ED: HLA-G up-regulates ILT2, ILT3, ILT4, and KIR2DL4 in
antigen presenting cells, NK cells, and T cells. FASEB J.
19:662–664. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Braud VM, Allan DS, O'Callaghan CA,
Söderström K, D'Andrea A, Ogg GS, Lazetic S, Young NT, Bell JI,
Phillips JH, et al: HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors
CD94/NKG2A, B and C. Nature. 391:795–799. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Braud VM, Aldemir H, Breart B and Ferlin
WG: Expression of CD94-NKG2A inhibitory receptor is restricted to a
subset of CD8+ T cells. Trends Immunol. 24:162–164. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Garrido F, Cabrera T and Aptsiauri N:
“Hard” and “soft” lesions underlying the HLA class I alterations in
cancer cells: Implications for immunotherapy. Int J Cancer.
127:249–256. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Vermeulen CF, Jordanova ES,
Zomerdijk-Nooijen YA, ter Haar NT, Peters AA and Fleuren GJ:
Frequent HLA class I loss is an early event in cervical
carcinogenesis. Hum Immunol. 66:1167–1173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Brady CS, Bartholomew JS, Burt DJ,
Duggan-Keen MF, Glenville S, Telford N, Little AM, Davidson JA,
Jimenez P, Ruiz-Cabello F, et al: Multiple mechanisms underlie HLA
dysregulation in cervical cancer. Tissue Antigens. 55:401–411.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Maleno I, Aptsiauri N, Cabrera T, Gallego
A, Paschen A, López-Nevot MA and Garrido F: Frequent loss of
heterozygosity in the β2-microglobulin region of chromosome 15 in
primary human tumors. Immunogenetics. 63:65–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Rodriguez JA, Galeano L, Palacios DM,
Gómez C, Serrano ML, Bravo MM and Combita AL: Altered HLA class I
and HLA-G expression is associated with IL-10 expression in
patients with cervical cancer. Pathobiology. 79:72–83. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Carosella ED, Rouas-Freiss N, Tronik-Le
Roux D, Moreau P and LeMaoult J: HLA-G: An immune checkpoint
molecule. Adv Immunol. 127:33–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Seliger B, Ritz U and Ferrone S: Molecular
mechanisms of HLA class I antigen abnormalities following viral
infection and transformation. Int J Cancer. 118:129–138. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ristich V, Liang S, Zhang W, Wu J and
Horuzsko A: Tolerization of dendritic cells by HLA-G. Eur J
Immunol. 35:1133–1142. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Caumartin J, Favier B, Daouya M, Guillard
C, Moreau P, Carosella ED and LeMaoult J: Trogocytosis-based
generation of suppressive NK cells. EMBO J. 26:1423–1433. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
König L, Kasimir-Bauer S, Hoffmann O,
Bittner AK, Wagner B, Manvailer LF, Schramm S, Bankfalvi A, Giebel
B, Kimmig R, et al: The prognostic impact of soluble and vesicular
HLA-G and its relationship to circulating tumor cells in
neoadjuvant treated breast cancer patients. Hum Immunol.
77:791–799. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bainbridge DR, Ellis SA and Sargent IL:
The short forms of HLA-G are unlikely to play a role in pregnancy
because they are not expressed at the cell surface. J Reprod
Immunol. 47:1–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gong FL, Feng XW and Grosse-Wilde H:
Impaired antigen-presenting capability of monocytes correlated with
their decreased expression of HLA-II antigens in patients with
myeloid leukemia. J Tongji Med Univ. 13:65–70. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yang XX, Pan HZ, Li PY, Li FX, Xu WW, Wu
YS, Yao GY and Li M: HLA class II variants in Chinese breast cancer
patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:3075–3079. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hu JM, Li L, Chen YZ, Liu C, Cui X, Yin L,
Yang L, Zou H, Pang L, Zhao J, et al: HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1
methylation changes promote the occurrence and progression of
Kazakh ESCC. Epigenetics. 9:1366–1373. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liang J, Xu A, Xie Y, Awonuga AO and Lin
Z: Some but not all of HLA-II alleles are associated with cervical
cancer in Chinese women. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 187:95–100. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
National Cancer Institute. Chemotherapy
and you U.S. Department of health and human services national
institutes of health. 2011.
|
|
85
|
Taylor A and Powell ME:
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy-what is it? Cancer Imaging.
4:68–73. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Galluzzi L, Vacchelli E, Bravo-San Pedro
JM, Buqué A, Senovilla L, Baracco EE, Bloy N, Castoldi F, Abastado
JP, Agostinis P, et al: Classification of current anticancer
immunotherapies. Oncotarget. 5:12472–12508. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Copier J, Dalgleish AG, Britten CM, Finke
LH, Gaudernack G, Gnjatic S, Kallen K, Kiessling R, Schuessler-Lenz
M, Singh H, et al: Improving the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
Eur J Cancer. 45:1424–1431. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Young PA, Morrison SL and Timmerman JM:
Antibody-cytokine fusion proteins for treatment of cancer:
Engineering cytokines for improved efficacy and safety. Semin
Oncol. 41:623–636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I, O'Day S,
Weber J, Garbe C, Lebbe C, Baurain JF, Testori A, Grob JJ, et al:
Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 364:2517–2526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Attia P, Phan GQ, Maker AV, Robinson MR,
Quezado MM, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Topalian SL, Kammula US, Royal RE,
et al: Autoimmunity correlates with tumor regression in patients
with metastatic melanoma treated with anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte
antigen-4. J Clin Oncol. 23:6043–6053. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Fong L and Small EJ: Anti-cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte antigen-4 antibody: The first in an emerging class of
immunomodulatory antibodies for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol.
26:5275–5283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Aerts M, Benteyn D, Van Vlierberghe H,
Thielemans K and Reynaert H: Current status and perspectives of
immune-based therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:253–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Boasberg P, Hamid O and O'Day S:
Ipilimumab: Unleashing the power of the immune system through
CTLA-4 blockade. Semin Oncol. 37:440–449. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ugurel S, Röhmel J, Ascierto PA, Flaherty
KT, Grob JJ, Hauschild A, Larkin J, Long GV, Lorigan P, McArthur
GA, et al: Survival of patients with advanced metastatic melanoma:
The impact of novel therapies. Eur J Cancer. 53:125–134. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Thor Straten P and Garrido F: Targetless T
cells in cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 4:232016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Vavrova K, Vrabcova P, Filipp D,
Bartunkova J and Horvath R: Generation of T cell effectors using
tumor cell-loaded dendritic cells for adoptive T cell therapy. Med
Oncol. 33:1362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Fesnak AD, June CH and Levine BL:
Engineered T cells: The promise and challenges of cancer
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:566–581. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Redeker A and Arens R: Improving adoptive
T cell therapy: The particular role of t cell costimulation,
cytokines, and post-transfer vaccination. Front Immunol. 7:3452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Del Campo AB, Aptsiauri N, Méndez R,
Zinchenko S, Vales A, Paschen A, Ward S, Ruiz-Cabello F,
González-Aseguinolaza G and Garrido F: Efficient recovery of HLA
class I expression in human tumor cells after beta2-microglobulin
gene transfer using adenoviral vector: Implications for cancer
immunotherapy. Scand J Immunol. 70:125–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Del Campo AB, Carretero J, Muñoz JA,
Zinchenko S, Ruiz-Cabello F, González-Aseguinolaza G, Garrido F and
Aptsiauri N: Adenovirus expressing β2-microglobulin recovers HLA
class I expression and antitumor immunity by increasing T-cell
recognition. Cancer Gene Ther. 21:317–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Penaloza-MacMaster P, Kamphorst AO,
Wieland A, Araki K, Iyer SS, West EE, O'Mara L, Yang S, Konieczny
BT, Sharpe AH, et al: Interplay between regulatory T cells and PD-1
in modulating T cell exhaustion and viral control during chronic
LCMV infection. J Exp Med. 211:1905–1918. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Wherry EJ: T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol.
12:492–499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Pauken KE and Wherry EJ: Overcoming T cell
exhaustion in infection and cancer. Trends Immunol. 36:265–276.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Page DB, Postow MA, Callahan MK, Allison
JP and Wolchok JD: Immune modulation in cancer with antibodies.
Annu Rev Med. 65:185–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Mellman I, Coukos G and Dranoff G: Cancer
immunotherapy comes of age. Nature. 480:480–489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Okamoto M, Kobayashi M, Yonemitsu Y, Koido
S and Homma S: Dendritic cell-based vaccine for pancreatic cancer
in Japan. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 7:133–138. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wang Z, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Shang Y and Gao Q:
MDSC-decreasing chemotherapy increases the efficacy of
cytokine-induced killer cell immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma and pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 7:4760–4769. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhao X, Ji CY, Liu GQ, Ma DX, Ding HF, Xu
M and Xing J: Immunomodulatory effect of DC/CIK combined with
chemotherapy in multiple myeloma and the clinical efficacy. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13146–13155. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Amiot L, Ferrone S, Grosse-Wilde H and
Seliger B: Biology of HLA-G in cancer: A candidate molecule for
therapeutic intervention? Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:417–431. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|