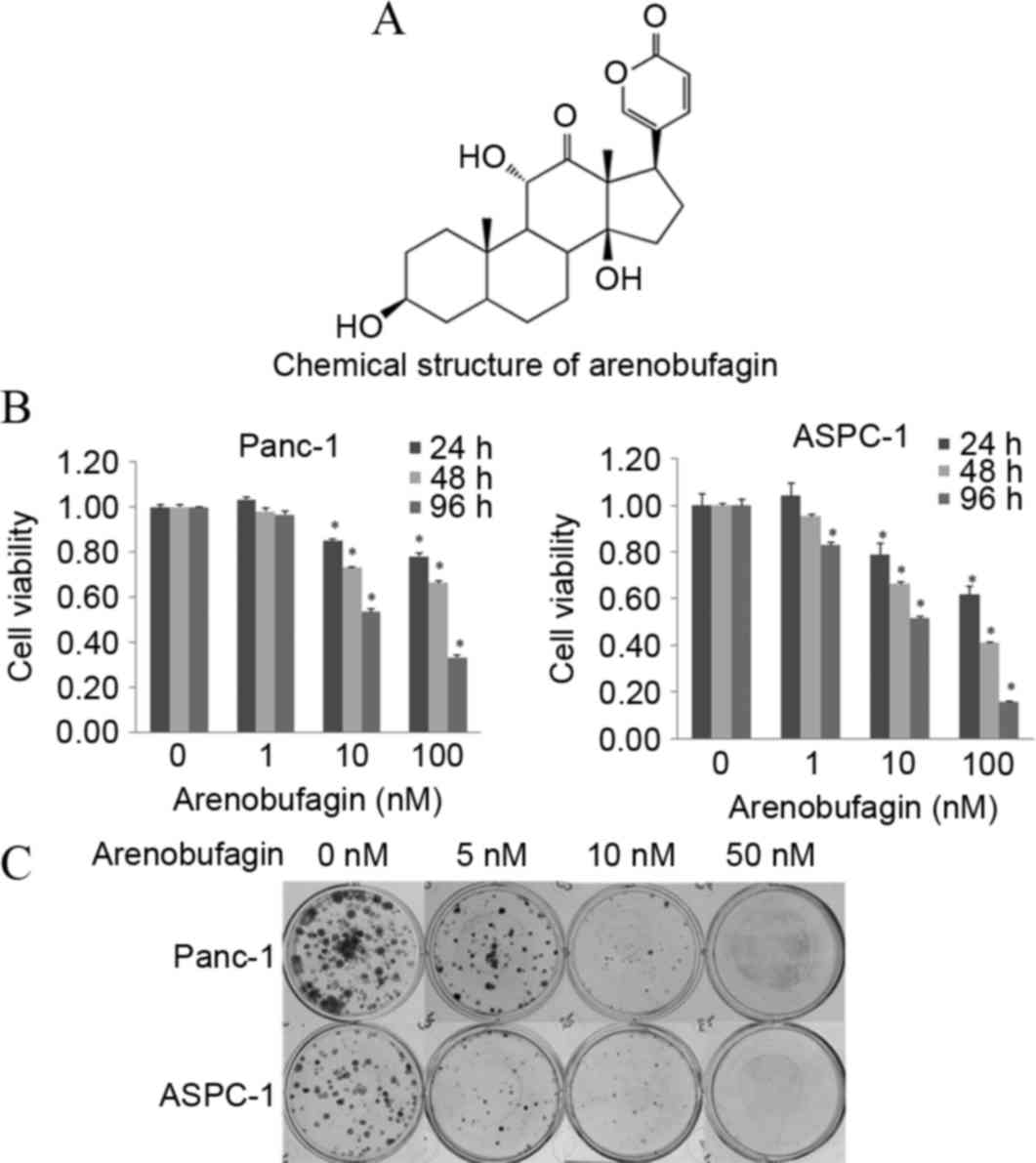
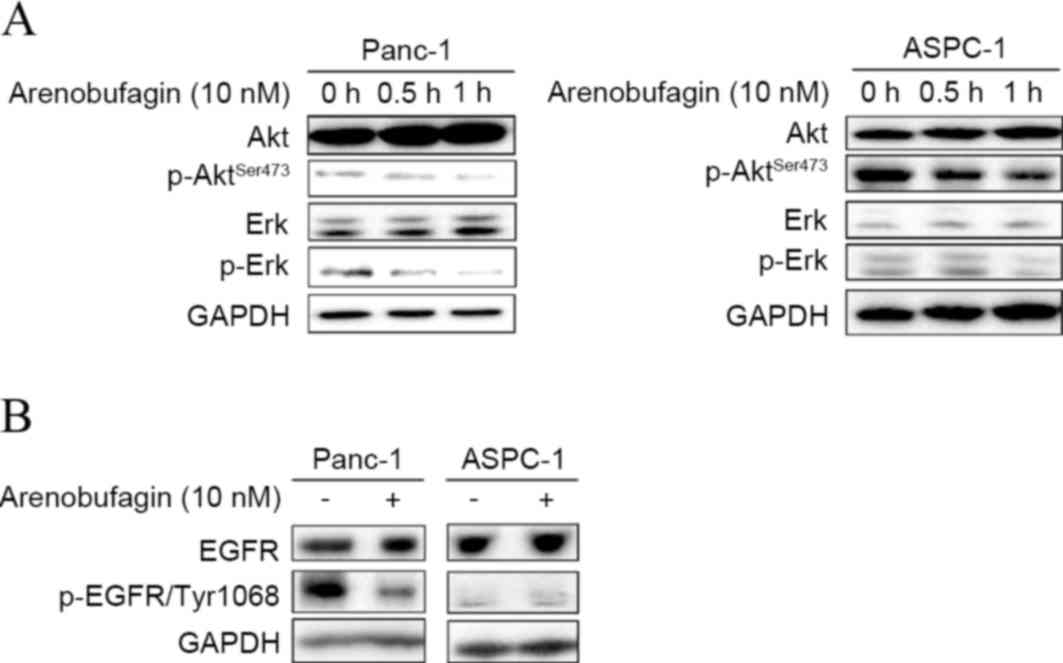
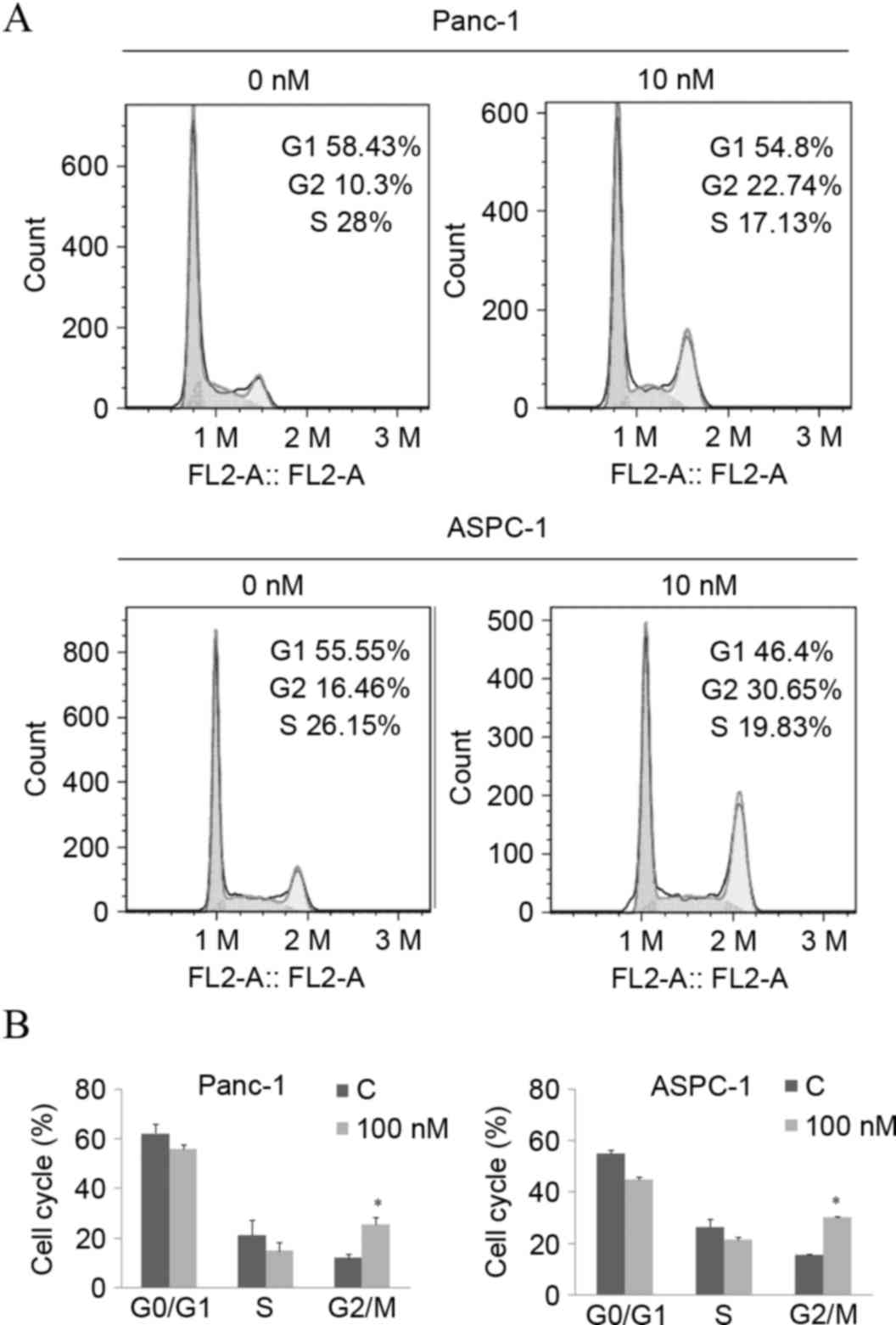
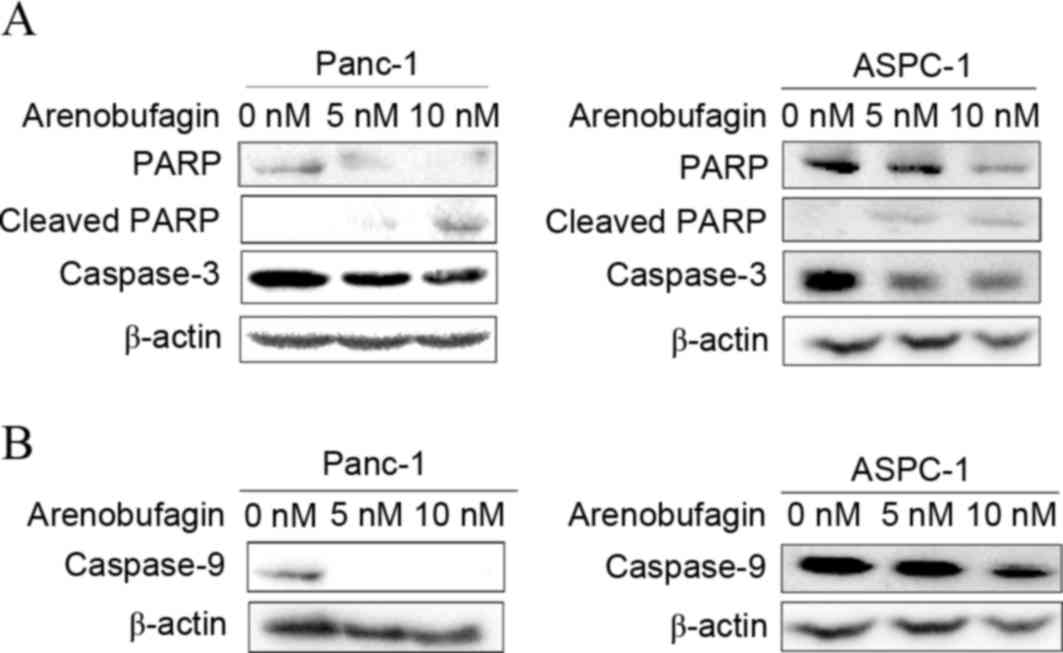
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH
and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 378:607–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Berlin J and Benson AB III: Chemotherapy:
Gemcitabine remains the standard of care for pancreatic cancer. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 7:135–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ducreux M, Boige V and Malka D: Treatment
of advanced pancreatic cancer. Semin Oncol. 34 (2 Suppl 1):S25–S30.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ying JE, Zhu LM and Liu BX: Developments
in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Is gemcitabine still the standard?
World J Gastroenterol. 18:736–745. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davidson JD, Ma L, Flagella M, Geeganage
S, Gelbert LM and Slapak CA: An increase in the expression of
ribonucleotide reductase large subunit 1 is associated with
gemcitabine resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
Cancer Res. 64:3761–3766. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Itoi T, Sofuni A, Fukushima N, Itokawa F,
Tsuchiya T, Kurihara T, Moriyasu F, Tsuchida A and Kasuya K:
Ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 mRNA expression in pretreatment
biopsies obtained from unresectable pancreatic carcinomas. J
Gastroenterol. 42:389–394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakano Y, Tanno S, Koizumi K, Nishikawa T,
Nakamura K, Minoguchi M, Izawa T, Mizukami Y, Okumura T and Kohgo
Y: Gemcitabine chemoresistance and molecular markers associated
with gemcitabine transport and metabolism in human pancreatic
cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 96:457–463. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hagmann W, Jesnowski R and Löhr JM:
Interdependence of gemcitabine treatment, transporter expression,
and resistance in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Neoplasia.
12:740–747. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ng SS, Tsao MS, Nicklee T and Hedley DW:
Wortmannin inhibits pkb/akt phosphorylation and promotes
gemcitabine antitumor activity in orthotopic human pancreatic
cancer xenografts in immunodeficient mice. Clin Cancer Res.
7:3269–3275. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A,
Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, et al:
Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in
patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase III trial of the
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin
Oncol. 25:1960–1966. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fountzilas G, Bobos M, Kalogera-Fountzila
A, Xiros N, Murray S, Linardou H, Karayannopoulou G, Koutras AK,
Bafaloukos D, Samantas E, et al: Gemcitabine combined with
gefitinib in patients with inoperable or metastatic pancreatic
cancer: A phase II Study of the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group
with biomarker evaluation. Cancer Invest. 26:784–793. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Venkatasubbarao K, Peterson L, Zhao S,
Hill P, Cao L, Zhou Q, Nawrocki ST and Freeman JW: Inhibiting
signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 increases
response to gemcitabine and delays progression of pancreatic
cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:1042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang Y, Liu AH, Qin S, Sun JH, Yang M, Li
P and Guo DA: Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetics of
five bufadienolides in rat plasma after oral administration of
Chansu extract by SPE-HPLC method. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 46:442–448.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Lonard DM, Yu Y, Chow DC, Palzkill
TG, Wang J, Qi R, Matzuk AJ, Song X, Madoux F, et al: Bufalin is a
potent small-molecule inhibitor of the steroid receptor
coactivators SRC-3 and SRC-1. Cancer Res. 74:1506–1517. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cruz Jdos S and Matsuda H: Arenobufagin, a
compound in toad venom, blocks Na(+)-K+ pump current in cardiac
myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 239:223–226. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cruz Jdos S and Matsuda H: Depressive
effects of arenobufagin on the delayed rectifier K+ current of
guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 266:317–325. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cao HH, Zhang DM, Liu JS, Hou CY, Kurihara
H and Ye WC: Inhibitory effect of arenobufagin on the adhesion,
invasion and migration of human hepatoma carcinoma cells. Chinese
Pharmacol Bull. 27:19–23. 2011.
|
|
21
|
Zhang DM, Liu JS, Deng LJ, Chen MF, Yiu A,
Cao HH, Tian HY, Fung KP, Kurihara H, Pan JX and Ye WC:
Arenobufagin, a natural bufadienolide from toad venom, induces
apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Carcinogenesis.
34:1331–1342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li M, Wu S, Liu Z, Zhang W, Xu J, Wang Y,
Liu J, Zhang D, Tian H, Li Y and Ye W: Arenobufagin, a
bufadienolide compound from toad venom, inhibits VEGF-mediated
angiogenesis through suppression of VEGFR-2 signaling pathway.
Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Ma X, Li F, Wang J, Chen H, Wang G,
Lv X, Sun C and Jia J: Preparative separation and purification of
bufadienolides from Chinese traditional medicine of ChanSu using
high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Sep Sci. 33:1325–1330.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan Y, Qin L, Liu D, Wu RC, Mussi P, Zhou
S, Songyang Z and Xu J: Genetic Screening Reveals an Essential Role
of p27kip1 in Restriction of Breast Cancer Progression. Cancer Res.
67:8032–8042. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thomas RK, Baker AC, Debiasi RM, Winckler
W, Laframboise T, Lin WM, Wang M, Feng W, Zander T, MacConaill L,
et al: High-throughput oncogene mutation profiling in human cancer.
Nat Genet. 39:347–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aguirre AJ, Bardeesy N, Sinha M, Lopez L,
Tuveson DA, Horner J, Redston MS and DePinho RA: Activated Kras and
Ink4a/Arf deficiency cooperate to produce metastatic pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 17:3112–3126. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hingorani SR, Petricoin EF, Maitra A,
Rajapakse V, King C, Jacobetz MA, Ross S, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD,
Hitt BA, et al: Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer
and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell. 4:437–450. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hingorani SR, Wang L, Multani AS, Combs C,
Deramaudt TB, Hruban RH, Rustgi AK, Chang S and Tuveson DA:
Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal
instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
in mice. Cancer Cell. 7:469–483. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Collins MA, Bednar F, Zhang Y, Brisset JC,
Galbán S, Galbán CJ, Rakshit S, Flannagan KS, Adsay NV and di
Magliano Pasca M: Oncogenic Kras is required for both the
initiation and maintenance of pancreatic cancer in mice. J Clin
Invest. 122:639–653. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sweet RW, Yokoyama S, Kamata T, Feramisco
JR, Rosenberg M and Gross M: The product of ras is a GTPase and the
T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature.
311:273–275. 1984. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hofmann I, Weiss A, Elain G, Schwaederle
M, Sterker D, Romanet V, Schmelzle T, Lai A, Brachmann SM,
Bentires-Alj M, et al: K-RAS mutant pancreatic tumors show higher
sensitivity to MEK than to PI3K inhibition in vivo. PLoS One.
7:e441462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Navas C, Hernandez-Porras I, Schuhmacher
AJ, Sibilia M, Guerra C and Barbacid M: EGF receptor signaling is
essential for k-ras oncogene-driven pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 22:318–330. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pryczynicz A, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K,
Czyzewska J and Kemona A: Expression of epidermal growth factors
and apoptosis markers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Folia
Histochem Cytobiol. 47:667–671. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Weiss GA, Rossi MR, Khushalani NI, Lo K,
Gibbs JF, Bharthuar A, Cowell JK and Iyer R: Evaluation of
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase catalytic subunit (PIK3CA) and
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutations in
pancreaticobiliary adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:20–29.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barr S, Thomson S, Buck E, Russo S, Petti
F, Sujka-Kwok I, Eyzaguirre A, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Gibson NW,
Miglarese M, et al: Bypassing cellular EGF receptor dependence
through epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transitions. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:685–693. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Miyabayashi K, Ijichi H, Mohri D, Tada M,
Yamamoto K, Asaoka Y, Ikenoue T, Tateishi K, Nakai Y, Isayama H, et
al: Erlotinib prolongs survival in pancreatic cancer by blocking
gemcitabine-induced MAPK signals. Cancer Res. 73:2221–2234. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Walters DM, Lindberg JM, Adair SJ, Newhook
TE, Cowan CR, Stokes JB, Borgman CA, Stelow EB, Lowrey BT,
Chopivsky ME, et al: Inhibition of the growth of patient-derived
pancreatic cancer xenografts with the MEK inhibitor trametinib is
augmented by combined treatment with the epidermal growth factor
receptor/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib. Neoplasia. 15:143–155. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Nakaya K, Yoshida T and Kuroiwa
Y: Induction by bufalin of differentiation of human leukemia cells
HL60, U937, and ML1 toward macrophage/monocyte-like cells and its
potent synergistic effect on the differentiation of human leukemia
cells in combination with other inducers. Cancer Res. 52:4634–4641.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Masuda Y, Kawazoe N, Nakajo S, Yoshida T,
Kuroiwa Y and Nakaya K: Bufalin induces apoptosis and influences
the expression of apoptosis-related genes in human leukemia cells.
Leuk Res. 19:549–556. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yu CH, Kan SF, Pu HF, Chien Jea E and Wang
PS: Apoptotic signaling in bufalin- and cinobufagin-treated
androgen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 99:2467–2476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zalatnai A and Molnár J: Review. Molecular
background of chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. In Vivo.
21:339–347. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mimeault M, Hauke R and Batra SK: Recent
advances on the molecular mechanisms involved in the drug
resistance of cancer cells and novel targeting therapies. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 83:673–691. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|