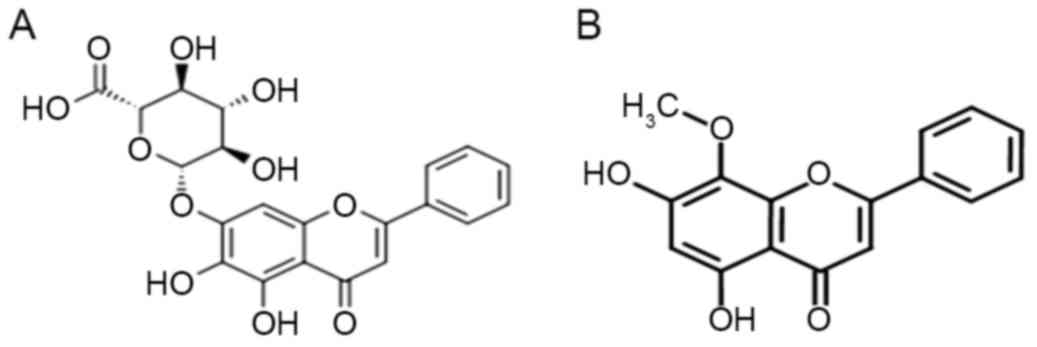
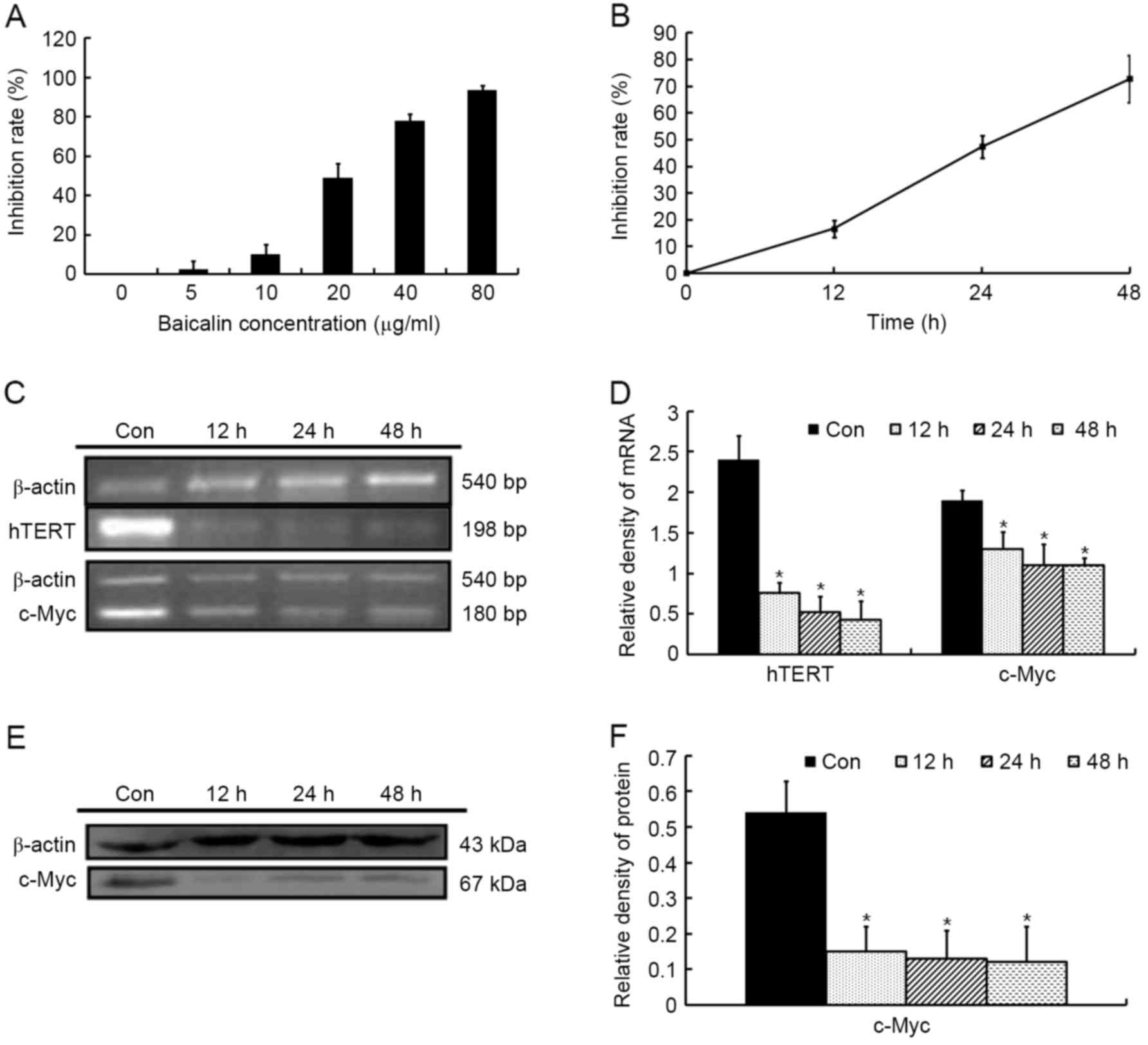
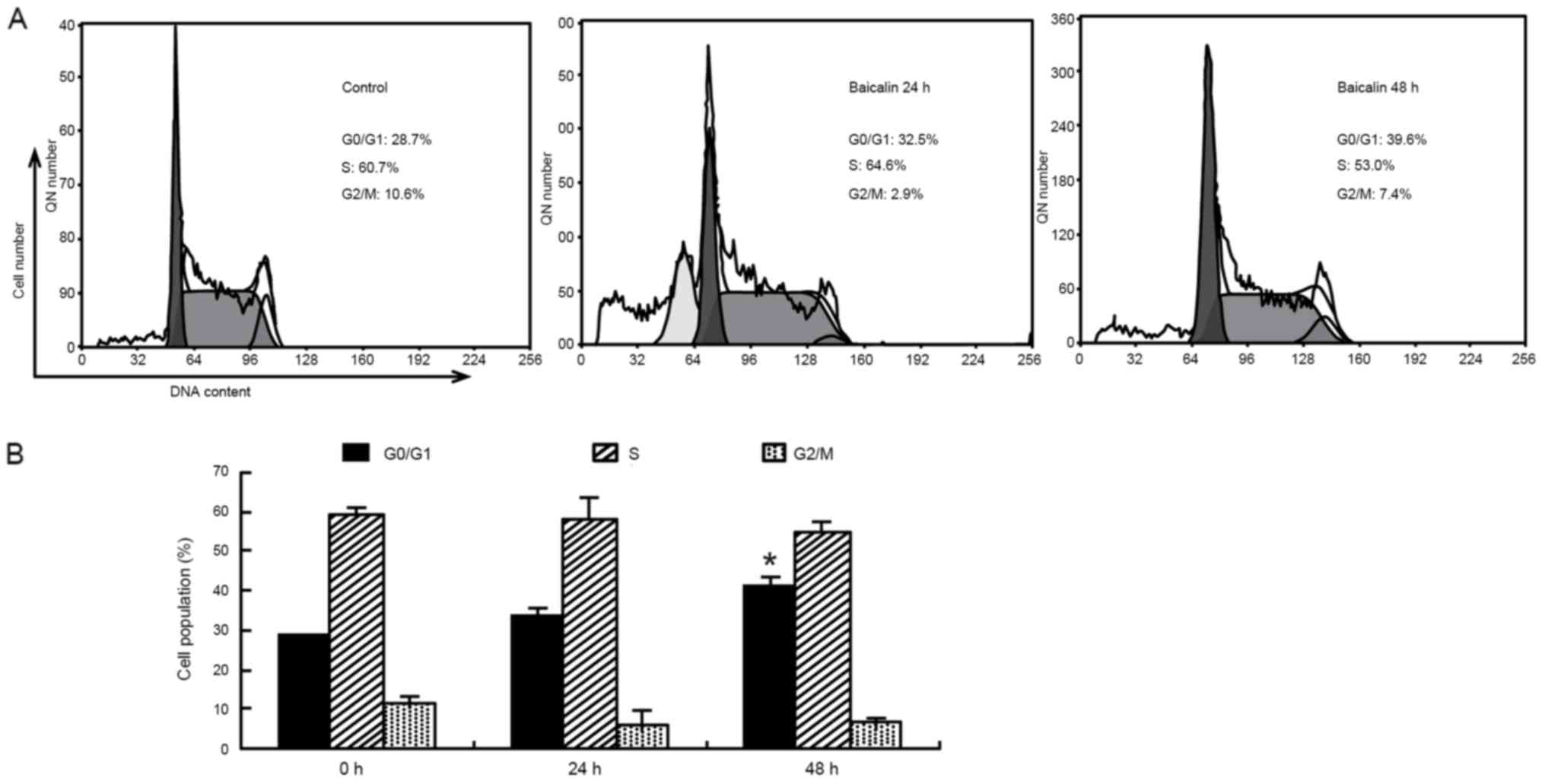
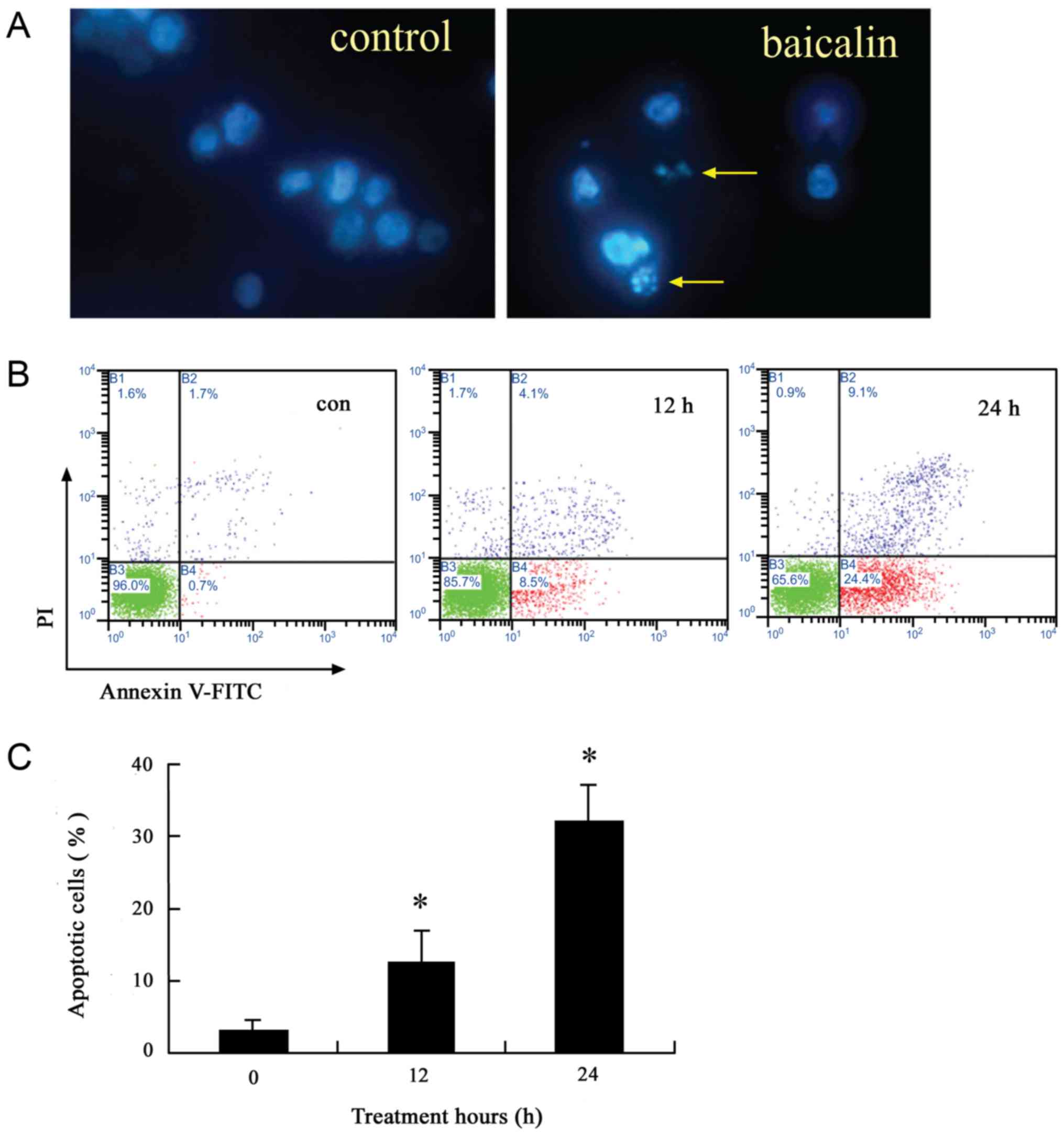
|
1
|
Huang WH, Lee AR and Yang CH:
Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities of
polyhydroxyflavonoids of Scutellaria baicalensis GEORGI. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 70:2371–2380. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shang X, He X, He X, Li M, Zhang R, Fan P,
Zhang Q and Jia Z: The genus Scutellaria an ethnopharmacological
and phytochemical review. J Ethnopharmacol. 128:279–313. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ikezoe T, Chen SS, Heber D, Taguchi H and
Koeffler HP: Baicalin is a major component of PC-SPES which
inhibits the proliferation of human cancer cells via apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest. Prostate. 49:285–292. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zheng J, Hu JD, Chen YY, Chen BY, Huang Y,
Zheng ZH and Liu TB: Baicalin induces apoptosis in leukemia
HL-60/ADR cells via possible down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:1119–1124. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parajuli P, Joshee N, Rimando AM, Mittal S
and Yadav AK: In vitro antitumor mechanisms of various Scutellaria
extracts and constituent flavonoids. Planta Med. 275:41–48. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ueda S, Nakamura H, Masutani H, Sasada T,
Takabayashi A, Yamaoka Y and Yodoi J: Baicalin induces apoptosis
via mitochondrial pathway as prooxidant. Mol Immunol. 38:781–791.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shieh DE, Cheng HY, Yen MH, Chiang LC and
Lin CC: Baicalin-induced apoptosis is mediated by Bcl-2-dependent,
but not p53-dependent, pathway in human leukemia cell lines. Am J
Chin Med. 34:245–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu HF, Hsueh SC, Ho YT, Kao MC, Yang JS,
Chiu TH, Huamg SY, Lin CC and Chung JG: ROS mediates
baicalin-induced apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60
cells through the expression of the Gadd153 and
mitochondrial-depedent pathway. Anticancer Res. 27:117–125.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grandori C, Cowley SM, James LP and
Eisenman RN: The Myc/Max/Mad network and the transcriptional
control of cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 16:653–699. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Felsher DW: MYC inactivation elicits
oncogene addiction through both tumor cell-intrinsic and
host-dependent mechanisms. Genes Cancer. 1:597–604. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sirinian MI, Pisegna S, Paroli M, Militi
S, Testa U and Peschle C: Zinc modulates c-Myc/Mad1 balance in
human leukemia cells. Leukemia. 17:272–274. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang ST, Wang CY, Yang RC, Chu CJ, Wu HT
and Pang JH: Wogonin, an active compound in Scutellaria
baicalensis, induces apoptosis and reduces telomerase activity in
the HL-60 leukemia cells. Phytomedicine. 17:47–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ren X, Zhang Y, Li C, Wang H, Jiang Z,
Zhang Z, Guo Q, Song G, Bi K and Jiang G: Enhancement of baicalin
by hexamethylene bisacetamide on the induction of apoptosis
contributes to simultaneous activation of the intrinsic and
extrinsic apoptotic pathways in human leukemia cells. Oncol Rep.
30:2071–2080. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kyo S, Takakura M, Taira T, Kanaya T, Itoh
H, Yutsudo M, Ariga H and Inoue M: Sp1 cooperates with c-Myc to
activate transcription of the human telomerase reverse
transcriptase gene (hTERT). Nucleic Acids Res. 28:669–677. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH and
Thompson CB: Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix
configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 10:709–717. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B,
Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ and
Los M: Apoptosis and cancer: Mutations within caspase genes. J Med
Genet. 46:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Steinman RA: Cell cycle regulators and
hematopoiesis. Oncogene. 21:3403–3413. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lavrik IN, Golks A and Krammer PH:
Caspases: Pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin
Invest. 115:2665–2672. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fulda S: Caspase 8 in cancer biology and
therapy. Cancer Lett. 281:128–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Arnoult D: Mitochondrial fragmentation in
apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 17:6–11. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peng Y, Fu ZZ, Guo CS, Zhang YX, Di Y,
Jiang B and Li QW: Effects and mechanism of baicalin on apoptosis
of cervical cancer HeLa cells In-vitro. Iran J Pharm Res.
14:251–261. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen WC, Kuo TH, Tzeng YS and Tsai YC:
Baicalin induces apoptosis in SW620 human colorectal carcinoma
cells in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Molecule.
17:3844–3857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chang WH, Chen CH and Lu FJ: Different
effects of baicalein, baicalin and wogonin on mitochondrial
function, glutathione content and cell cycle progression in human
hepatoma cell lines. Planta Med. 68:128–132. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thorburn A: Death receptor-induced cell
killing. Cell Signal. 16:139–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kolenko VM, Uzzo RG, Bukowski R and Finke
JH: Caspase-dependent and -independent death pathways in cancer
therapy. Apoptosis. 5:17–20. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meyer N and Penn LZ: Reflecting on 25
years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:976–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nie Z, Hu G, Wei G, Cui K, Yamane A, Resch
W, Wang R, Green DR, Tessarollo L, Casellas R, et al: c-Myc is a
universal amplifier of expressed genes in lymphocytes and embryonic
stem cells. Cell. 151:68–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Biroccio A, Amodei S, Benassi B, Scarsella
M, Cianciulli A, Mottolese M, Del Bufalo D, Leonetti C and Zupi G:
Reconstitution of hTERT restores tumorigenicity in melanoma-derived
c-Myc low-expressing clones. Oncogene. 21:3011–3019. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|