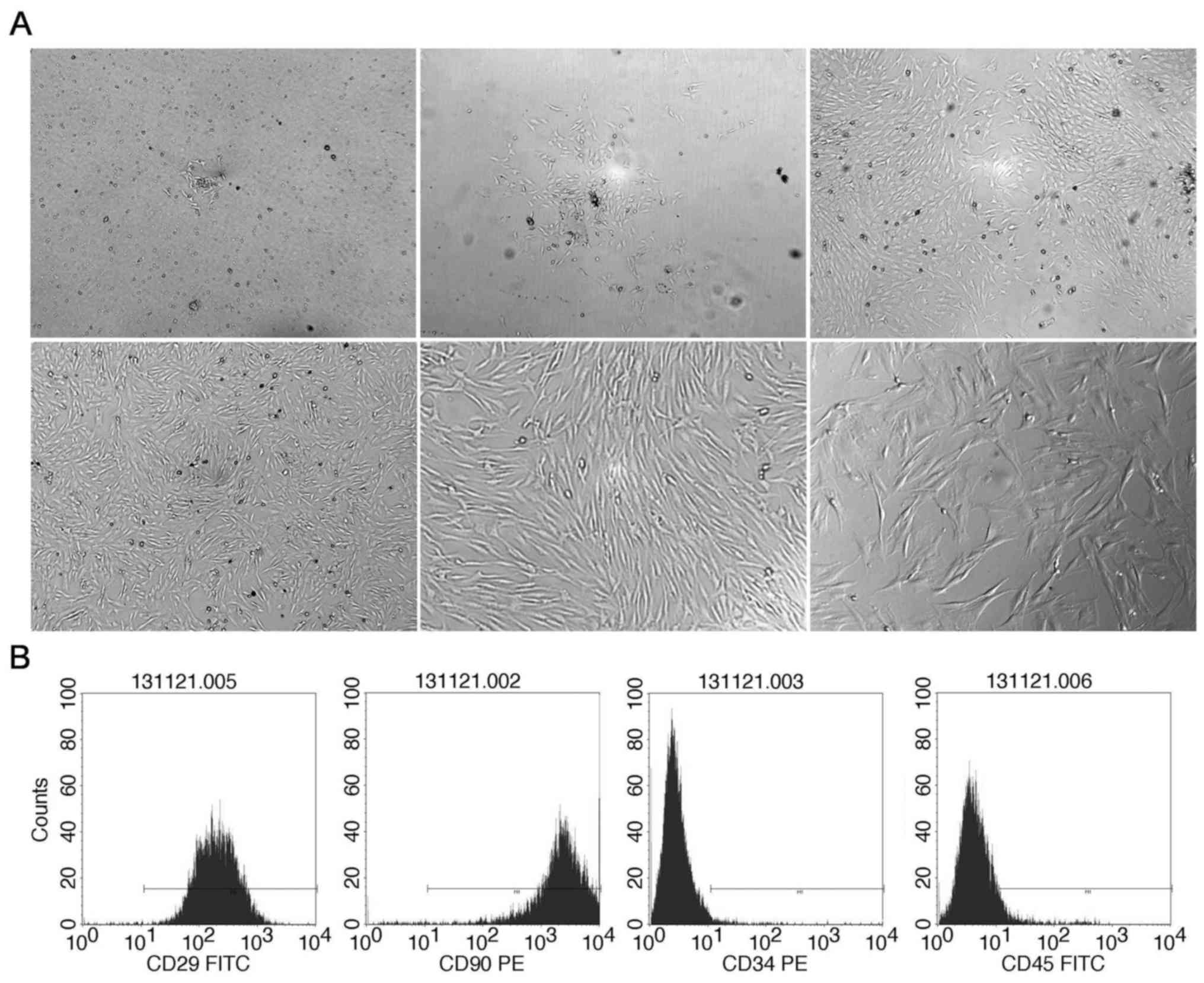
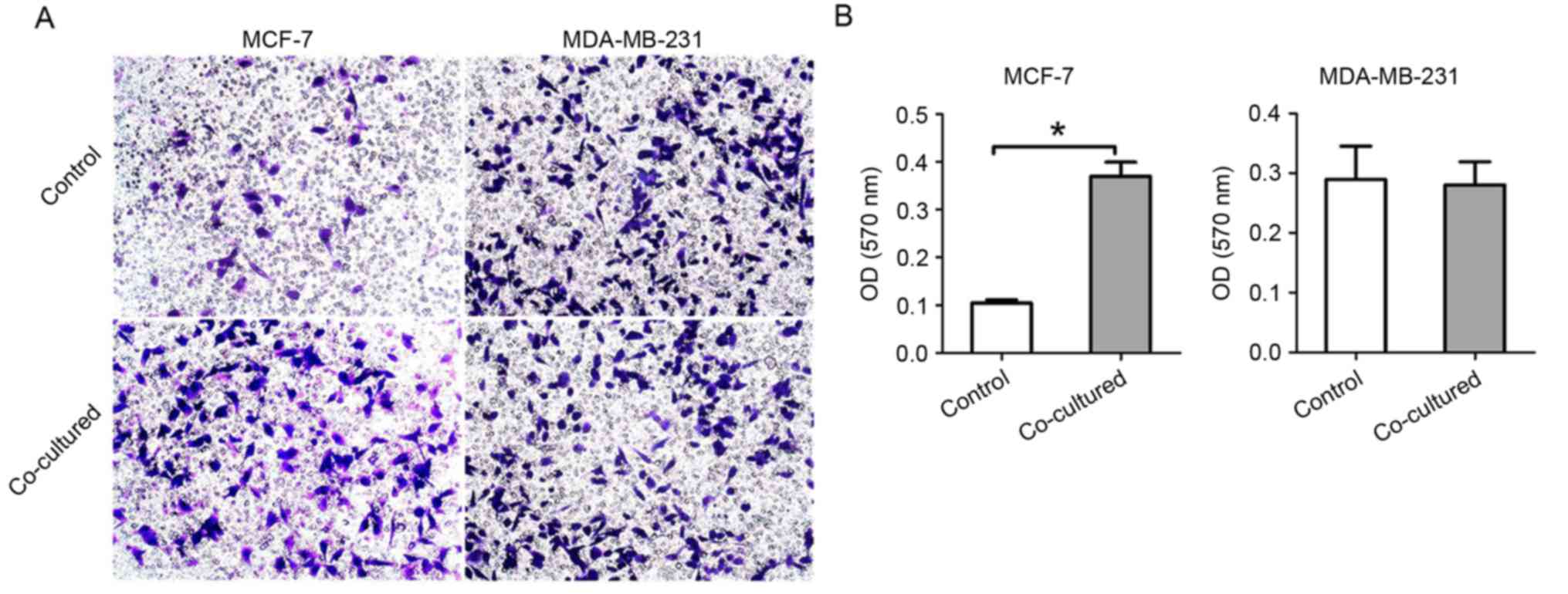
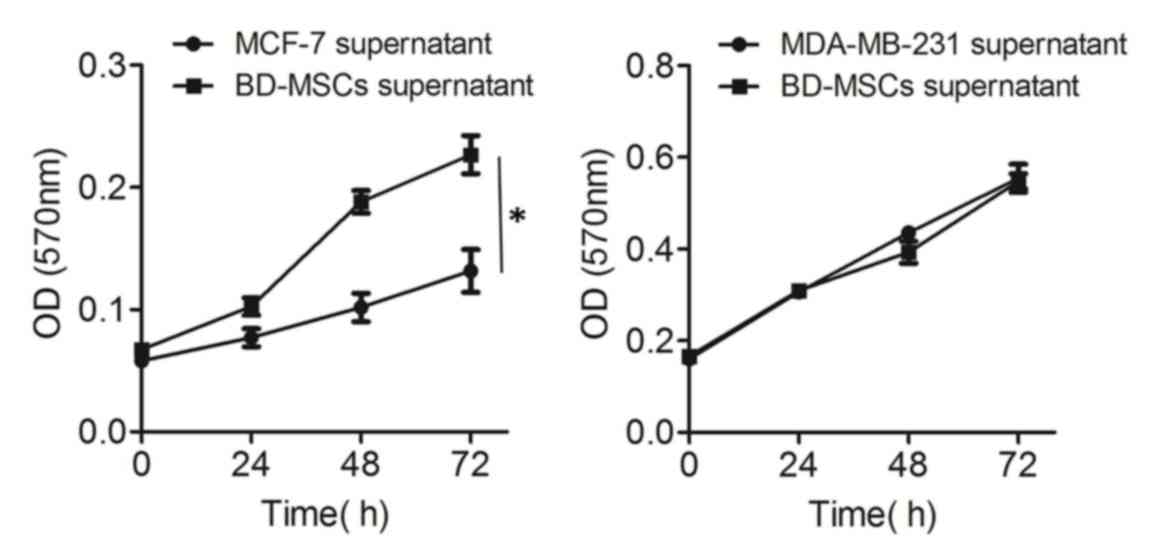
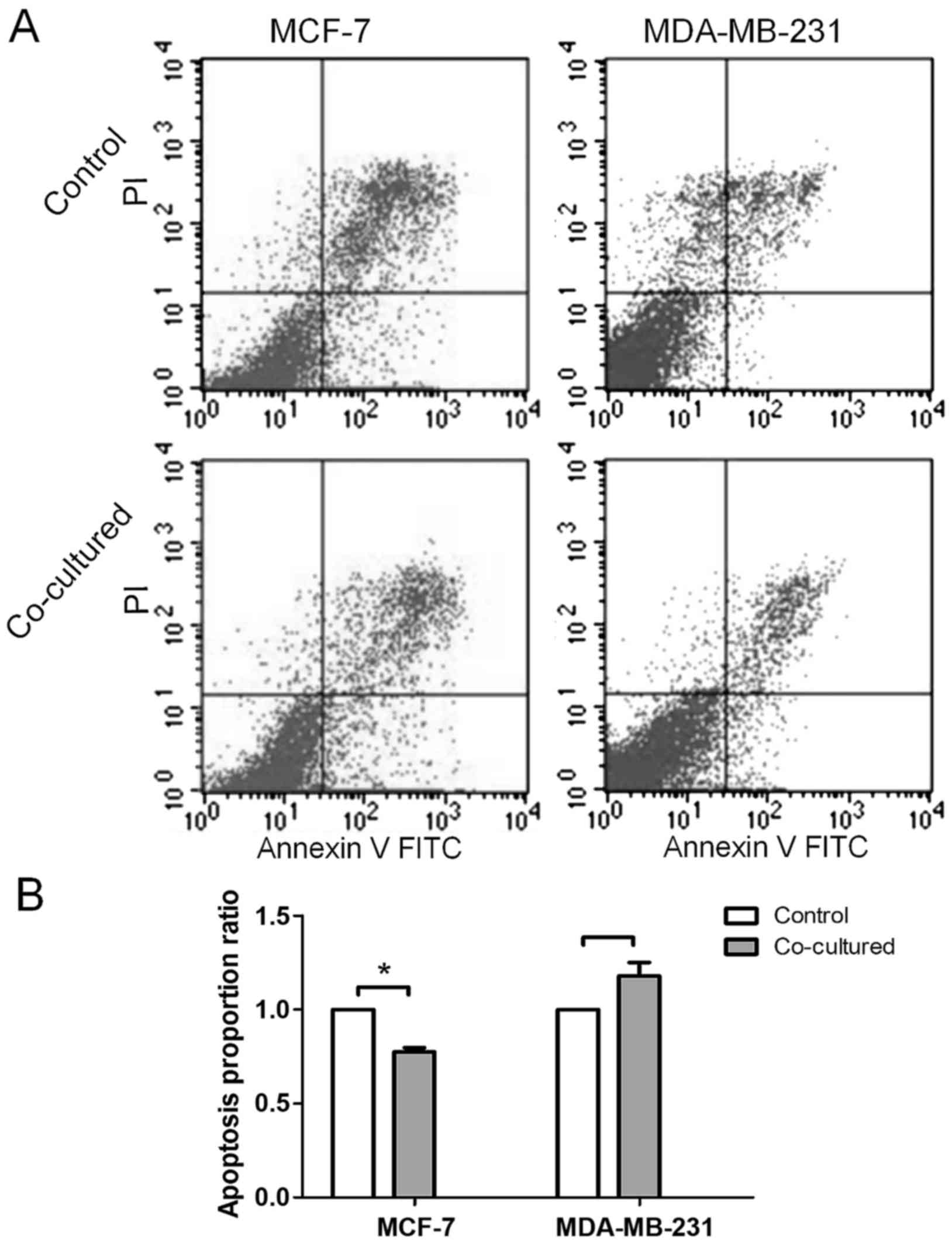
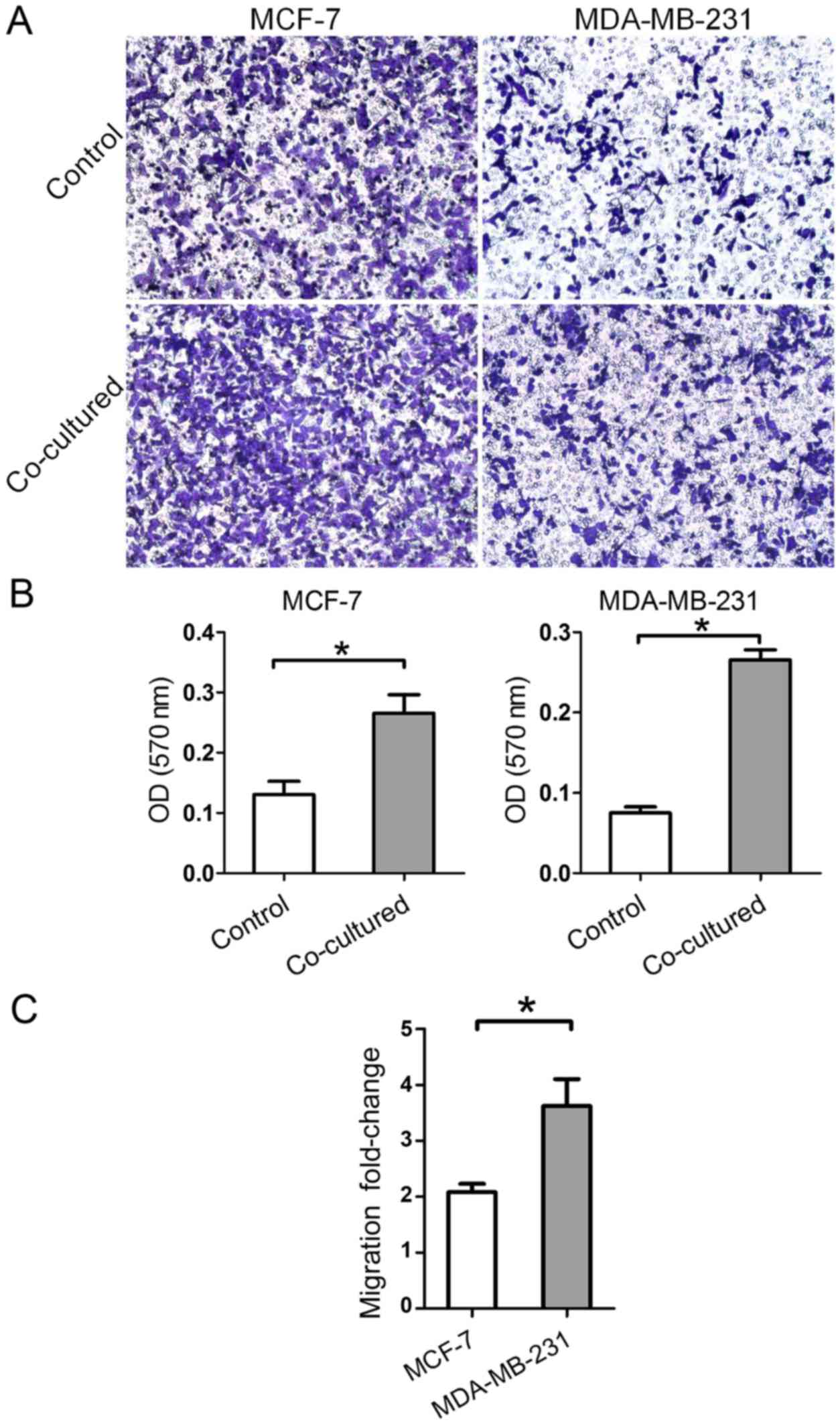
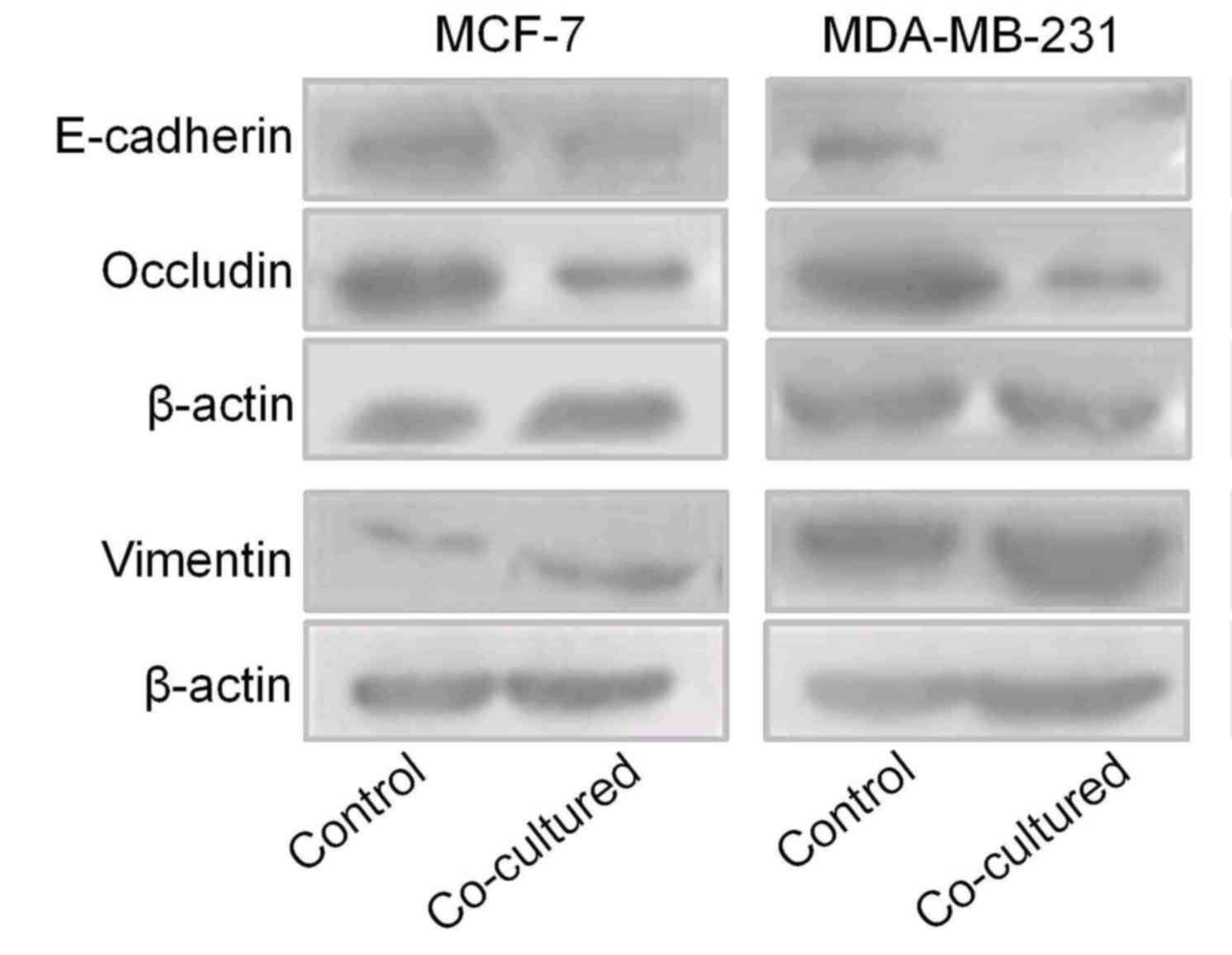
|
1
|
Savci-Heijink CD, Halfwerk H, Hooijer GK,
Horlings HM, Wesseling J and van de Vijver MJ: Retrospective
analysis of metastatic behaviour of breast cancer subtypes. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 150:547–557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel members:
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang XR, Sherman ME, Rimm DL, Lissowska J,
Brinton LA, Peplonska B, Hewitt SM, Anderson WF,
Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Bardin-Mikolajczak A, et al: Differences in
risk factors for breast cancer molecular subtypes in a
population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:439–443. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Spitale A, Mazzola P, Soldini D,
Mazzucchelli L and Bordoni A: Breast cancer classification
according to immunohistochemical markers: Clinicopathologic
features and short-term survival analysis in a population-based
study from the South of Switzerland. Ann Oncol. 20:628–635. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamimi RM, Colditz GA, Hazra A, Baer HJ,
Hankinson SE, Rosner B, Marotti J, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ and
Collins LC: Traditional breast cancer risk factors in relation to
molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
131:159–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wirapati P, Sotiriou C, Kunkel S, Farmer
P, Pradervand S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Ignatiadis M, Sengstag
T, Schutz F, et al: Meta-analysis of gene expression profiles in
breast cancer: Toward a unified understanding of breast cancer
subtyping and prognosis signatures. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R652008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang
MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO and Gelmon K: Metastatic
behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 28:3271–3277.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smid M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM, Yu
J, Klijn JG, Foekens JA and Martens JW: Subtypes of breast cancer
show preferential site of relapse. Cancer Res. 68:3108–3114. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Andre F, Mardis E, Salm M, Soria JC, Siu
LL and Swanton C: Prioritizing targets for precision cancer
medicine. Ann Oncol. 25:2295–2303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parker JS and Perou CM: Tumor
heterogeneity: Focus on the leaves, the trees, or the forest?
Cancer Cell. 28:149–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sihto H, Lundin J, Lundin M, Lehtimaki T,
Ristimaki A, Holli K, Sailas L, Kataja V, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T,
Isola J, et al: Breast cancer biological subtypes and protein
expression predict for the preferential distant metastasis sites: A
nationwide cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R872011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA and McCauley LK:
Cancer to bone: A fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:411–425.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Janni W, Vogl FD, Wiedswang G, Synnestvedt
M, Fehm T, Jückstock J, Borgen E, Rack B, Braun S, Sommer H, et al:
Persistence of disseminated tumor cells in the bone marrow of
breast cancer patients predicts increased risk for relapse--a
European pooled analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2967–2976. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Corcoran KE, Trzaska KA, Fernandes H,
Bryan M, Taborga M, Srinivas V, Packman K, Patel PS and Rameshwar
P: Mesenchymal stem cells in early entry of breast cancer into bone
marrow. PLoS One. 3:e25632008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spaeth E, Klopp A, Dembinski J, Andreeff M
and Marini F: Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: Defining
the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther.
15:730–738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Spaeth EL, Dembinski JL, Sasser AK, Watson
K, Klopp A, Hall B, Andreeff M and Marini F: Mesenchymal stem cell
transition to tumor-associated fibroblasts contributes to
fibrovascular network expansion and tumor progression. PLoS One.
4:e49922009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gunn WG, Conley A, Deininger L, Olson SD,
Prockop DJ and Gregory CA: A crosstalk between myeloma cells and
marrow stromal cells stimulates production of DKK1 and
interleukin-6: A potential role in the development of lytic bone
disease and tumor progression in multiple myeloma. Stem Cells.
24:986–991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kucerova L, Matuskova M, Hlubinova K,
Altanerova V and Altaner C: Tumor cell behaviour modulation by
mesenchymal stromal cells. Mol Cancer. 9:1292010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu YR, Yuan Y, Wang XJ, Wei LL, Chen YN,
Cong C, Li SF, Long D, Tan WD, Mao YQ, et al: The growth inhibitory
effect of mesenchymal stem cells on tumor cells in vitro and in
vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:245–251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Motaln H, Gruden K, Hren M, Schichor C,
Primon M, Rotter A and Lah TT: Human mesenchymal stem cells exploit
the immune response mediating chemokines to impact the phenotype of
glioblastoma. Cell Transplant. 21:1529–1545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Albarenque SM, Zwacka RM and Mohr A: Both
human and mouse mesenchymal stem cells promote breast cancer
metastasis. Stem Cell Res. 7:163–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Scquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Soleimani M and Nadri S: A protocol for
isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone
marrow. Nat Protoc. 4:102–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop D and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. the international society for cellular
therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Janni W, Rack B, Schindlbeck C, Strobl B,
Rjosk D, Braun S, Sommer H, Pantel K, Gerber B and Friese K: The
persistence of isolated tumor cells in bone marrow from patients
with breast carcinoma predicts an increased risk for recurrence.
Cancer. 103:884–891. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Janni W, Fehm T, Rack B, Muller V,
Solomayer E, Stickeler E, Sommer H, Schindlbeck C, Juckstock J and
Friese K: Clinical importance of the detection of isolated tumor
cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood in patients with primary
breast cancer. Geburtshilfe Und Frauenheilkunde. 67:653–660. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hall C, Krishnamurthy S, Lodhi A,
Mosalpuria K, Kuerer HM, Meric-Bernstam F, Bedrosian I, Hunt KK and
Lucci A: Disseminated tumor cells in biologic subtypes of stage
I–III breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:3252–3258. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Beca F, Santos R, Vieira D, Zeferino L,
Dufloth R and Schmitt F: Primary relapse site pattern in women with
triple-negative breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 210:571–575. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S,
Voduc D, Vickery T, Davies S, Fauron C, He X, Hu Z, et al:
Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic
subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 27:1160–1167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pantel K and Alix-Panabieres C: Bone
marrow as a reservoir for disseminated tumor cells: A special
source for liquid biopsy in cancer patients. Bonekey Rep.
3:5842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Braun S, Vogl FD, Naume B, Janni W,
Osborne MP, Coombes RC, Schlimok G, Diel IJ, Gerber B, Gebauer G,
et al: A pooled analysis of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast
cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:793–802. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hartkopf AD, Banys M, Meier-Stiegen F,
Hahn M, Rohm C, Hoffmann J, Helms G, Taran FA, Wallwiener M, Walter
C, et al: The HER2 status of disseminated tumor cells in the bone
marrow of early breast cancer patients is independent from primary
tumor and predicts higher risk of relapse. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
138:509–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|