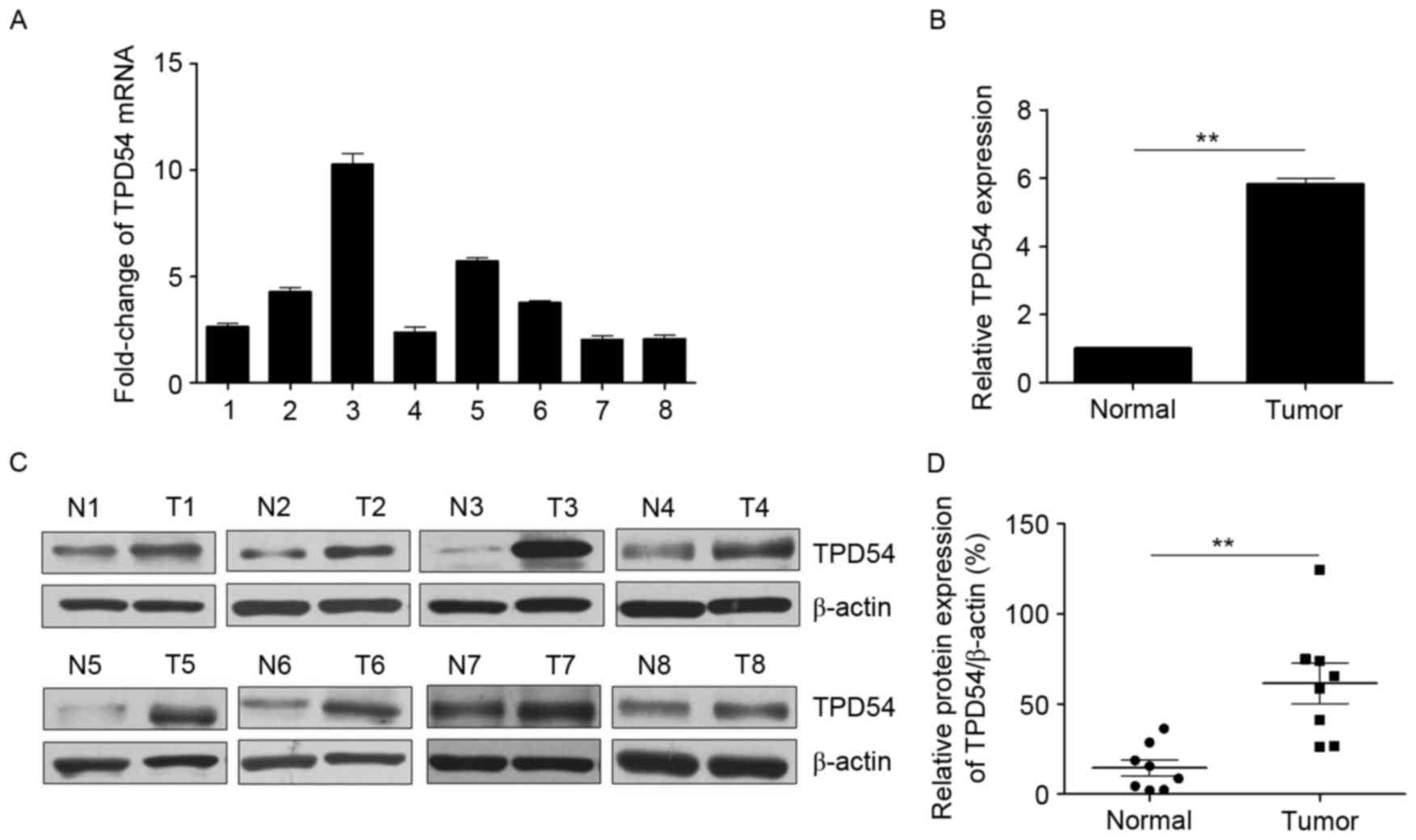
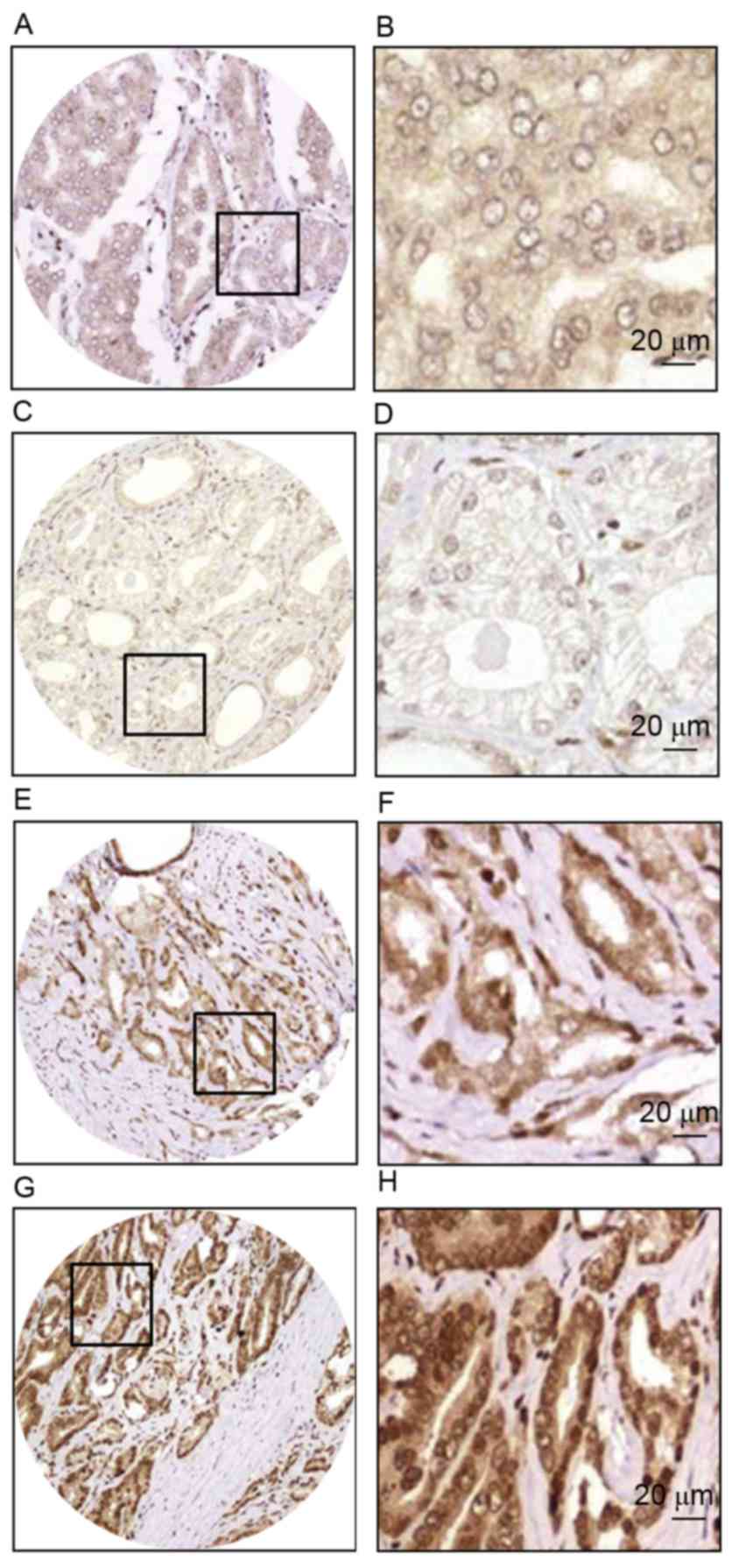
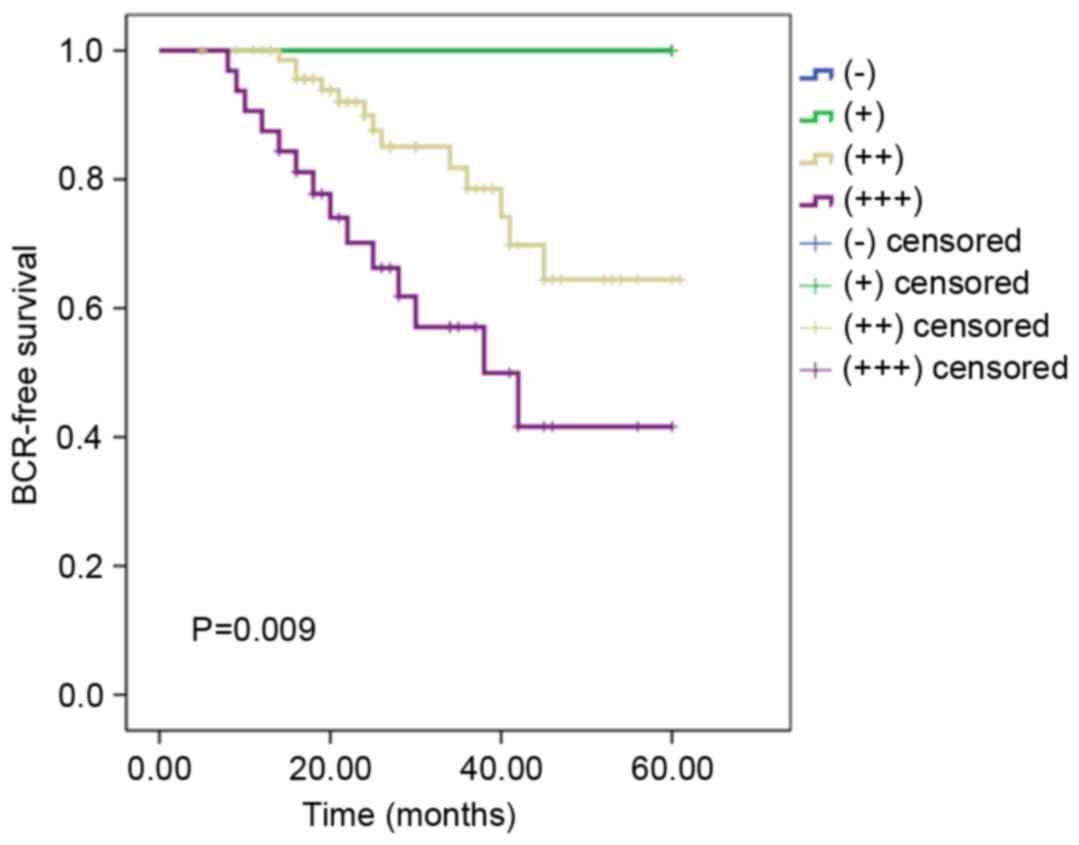
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parnes HL, House MG and Tangrea JA:
Prostate cancer prevention: Strategies for agent development. Curr
Opin Oncol. 25:242–251. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walz J, Joniau S, Chun FK, Isbarn H,
Jeldres C, Yossepowitch O, Chao-Yu H, Klein EA, Scardino PT,
Reuther A, et al: Pathological results and rates of treatment
failure in high-risk prostate cancer patients after radical
prostatectomy. BJU Int. 107:765–770. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Andriole GL, Crawford ED, Grubb RL III,
Buys SS, Chia D, Church TR, Fouad MN, Gelmann EP, Kvale PA, Reding
DJ, et al: Mortality results from a randomized prostate-cancer
screening trial. N Engl J Med. 360:1310–1319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shariat SF, Semjonow A, Lilja H, Savage C,
Vickers AJ and Bjartell A: Tumor markers in prostate cancer I:
Blood-based markers. Acta Oncol. 50 Suppl 1:S61–S75. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Byrne JA, Nourse CR, Basset P and Gunning
P: Identification of homo- and heteromeric interactions between
members of the breast carcinoma-associated D52 protein family using
the yeast two-hybrid system. Oncogene. 16:873–881. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boutros R, Fanayan S, Shehata M and Byrne
JA: The tumor protein D52 family: Many pieces, many puzzles.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 325:1115–1121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thomas DD, Frey CL, Messenger SW, August
BK and Groblewski GE: A role for tumor protein TPD52
phosphorylation in endo-membrane trafficking during cytokinesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:583–587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tennstedt P, Bölch C, Strobel G, Minner S,
Burkhardt L, Grob T, Masser S, Sauter G, Schlomm T and Simon R:
Patterns of TPD52 overexpression in multiple human solid tumor
types analyzed by quantitative PCR. Int J Oncol. 44:609–615. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mukudai Y, Kondo S, Fujita A, Yoshihama Y,
Shirota T and Shintani S: Tumor protein D54 is a negative regulator
of extracellular matrix-dependent migration and attachment in oral
squamous cell carcinoma-derived cell lines. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
36:233–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Sun J, Zhao Y, Guo W, Lv K and
Zhang Q: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of tumor protein D52-like 2
inhibits glioma cell proliferation. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
60:39–44. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He Y, Chen F, Cai Y and Chen S: Knockdown
of tumor protein D52-like 2 induces cell growth inhibition and
apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Biol Int.
39:264–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu J, Wang W, Zhu Z, Wei Z, Yang D and Cai
Q: Tumor protein D52-like 2 accelerates gastric cancer cell
proliferation in vitro. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 30:111–116.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang M, Wang X, Jia J, Gao H, Chen P, Sha
X and Wu S: Tumor protein D52-like 2 contributes to proliferation
of breast cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 30:1–7. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pan ZY, Yang Y, Pan H, Zhang J, Liu H,
Yang Y, Huang G, Yin L, Huang J and Zhou WP: Lentivirus-mediated
TPD52L2 depletion inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells
in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:2334–2341. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao H, Logothetis CJ and Gorlov IP:
Usefulness of the top-scoring pairs of genes for prediction of
prostate cancer progression. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
13:252–259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barbaric D, Byth K, Dalla-Pozza L and
Byrne JA: Expression of tumor protein D52-like genes in childhood
leukemia at diagnosis: Clinical and sample considerations. Leuk
Res. 30:1355–1363. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|