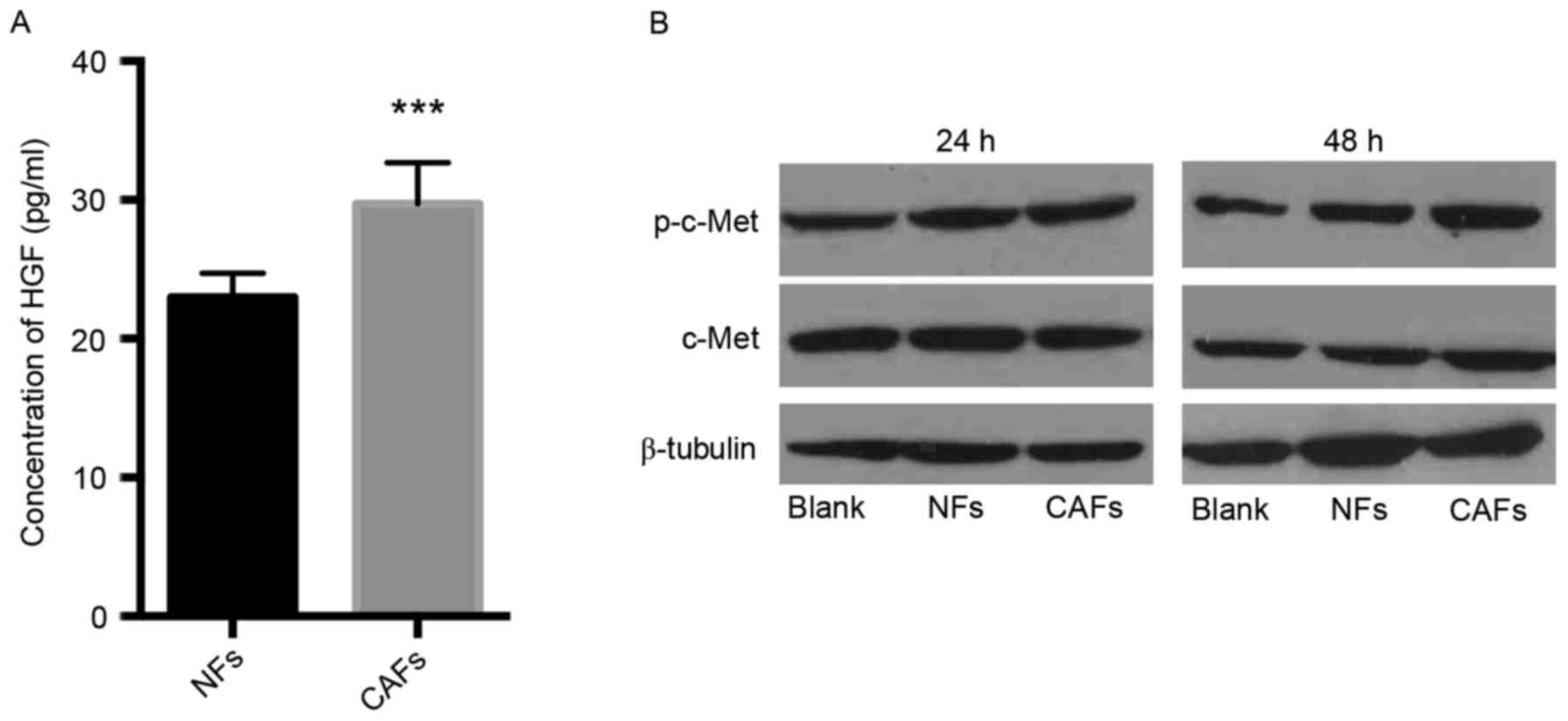
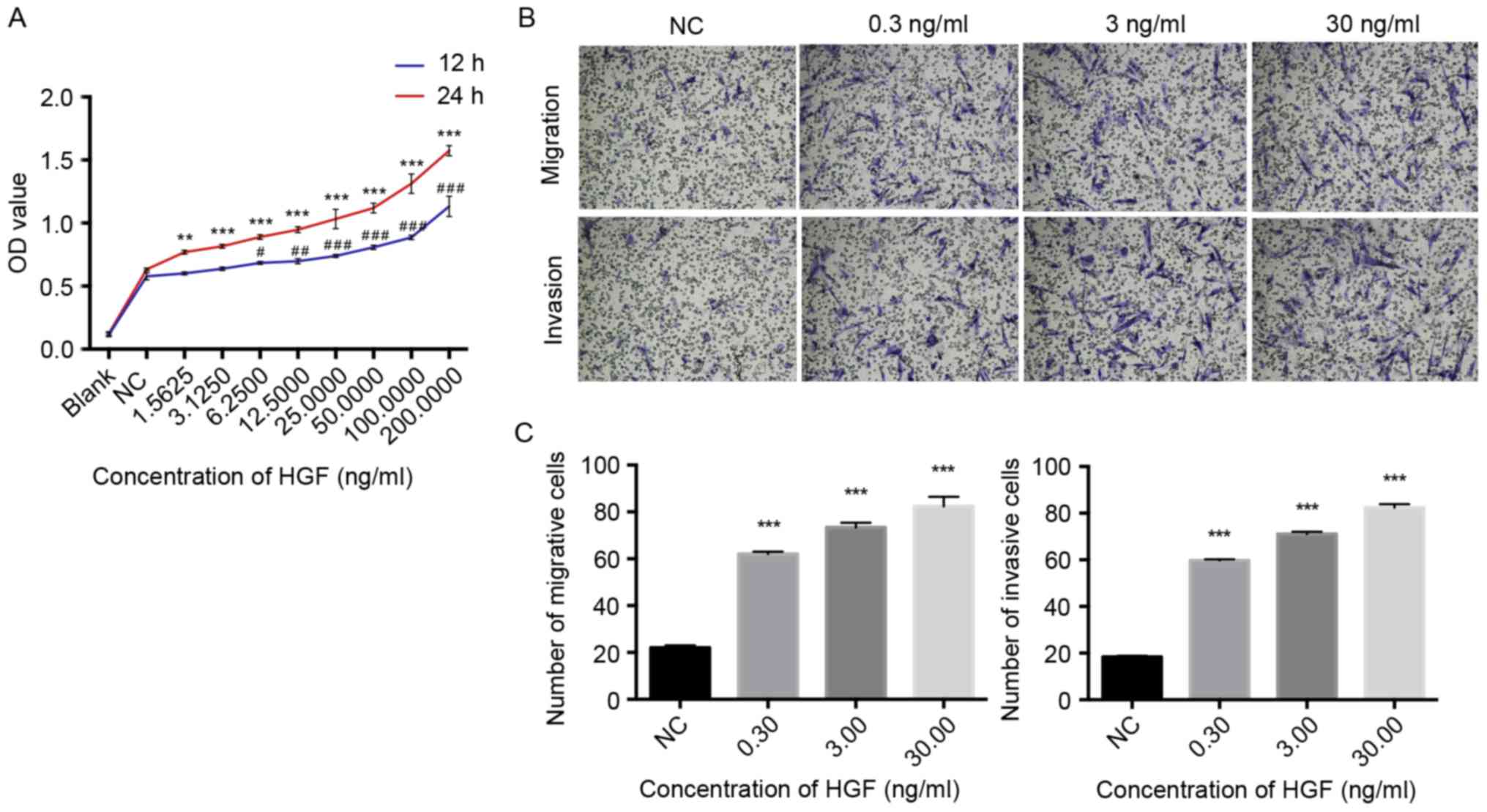
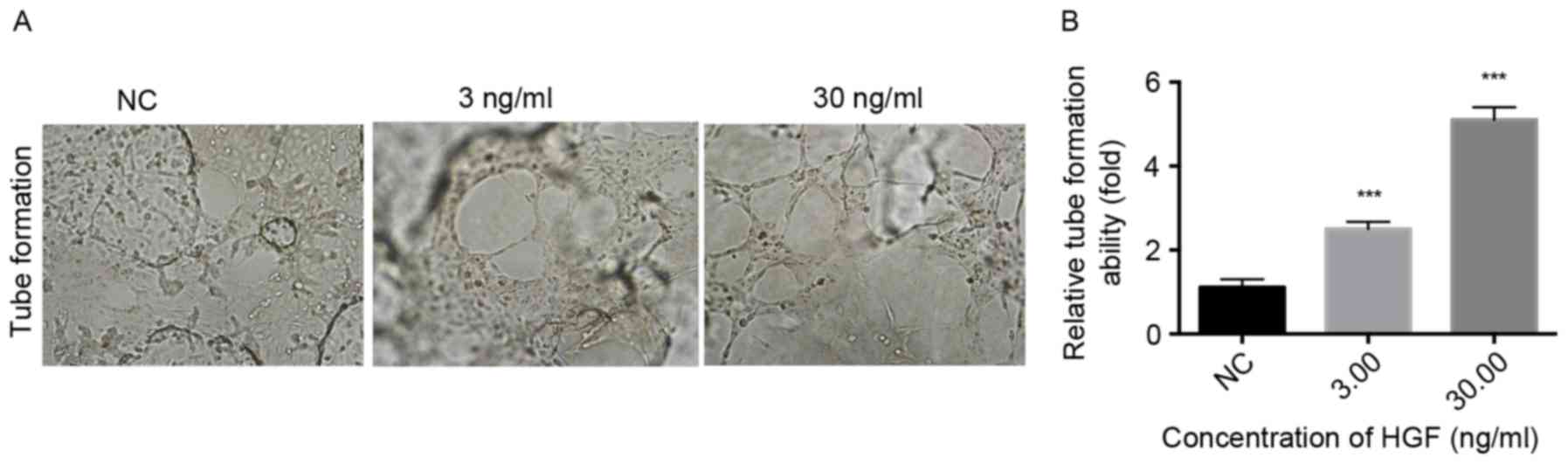
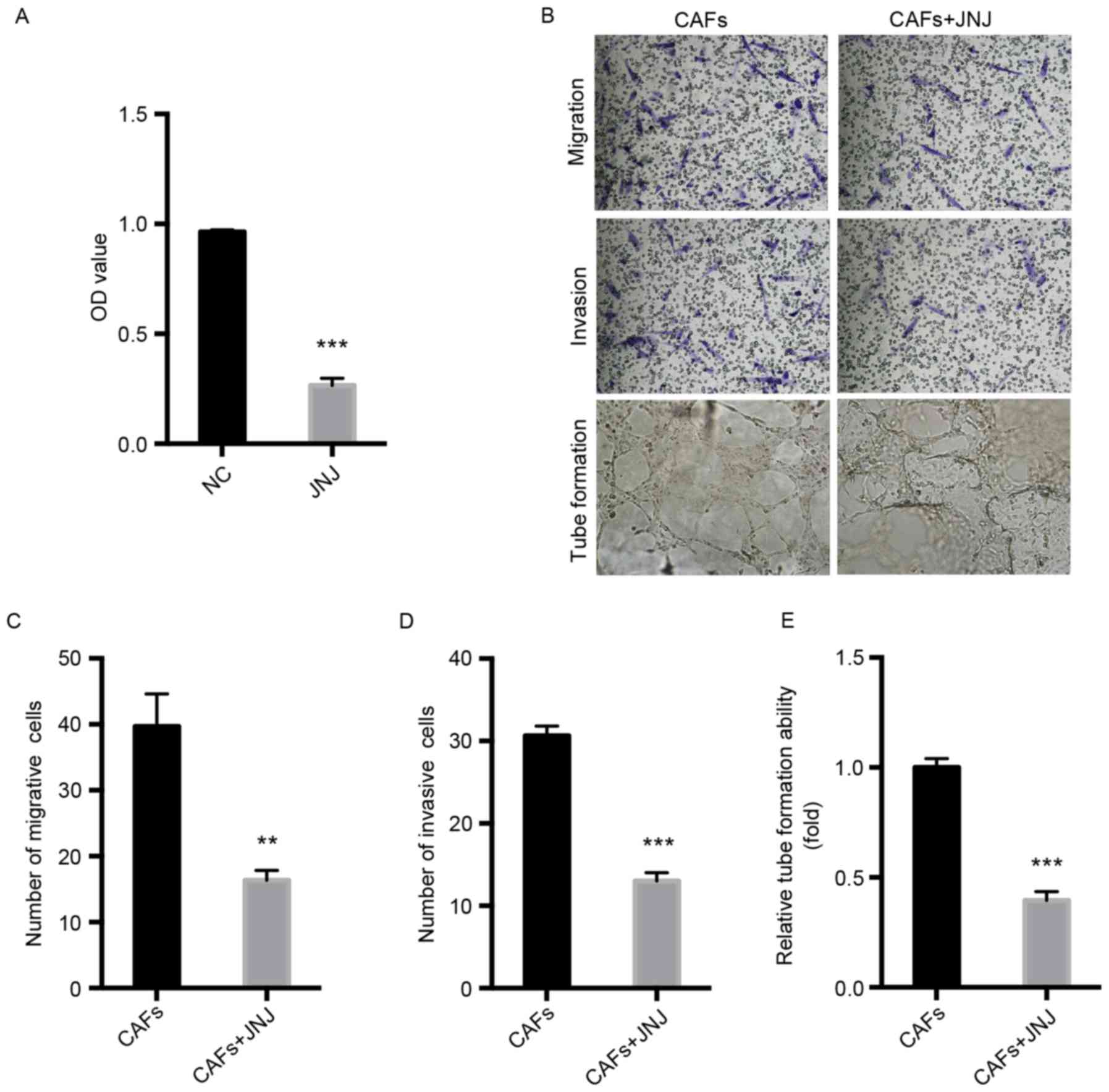
|
1
|
Roberts TJ, Colevas AD, Hara W, Holsinger
FC, Oakley-Girvan I and Divi V: Number of positive nodes is
superior to the lymph node ratio and American Joint Committee on
Cancer N staging for the prognosis of surgically treated head and
neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer. 122:1388–1397. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sipos B, Klapper W, Kruse ML, Kalthoff H,
Kerjaschki D and Klöppel G: Expression of lymphangiogenic factors
and evidence of intratumoral lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic
endocrine tumors. Am J Pathol. 165:1187–1197. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alphonso A and Alahari SK: Stromal cells
and integrins: Conforming to the needs of the tumor
microenvironment. Neoplasia. 11:1264–1271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fullár A, Kovalszky I, Bitsche M, Romani
A, Schartinger VH, Sprinzl GM, Riechelmann H and Dudás J: Tumor
cell and carcinoma-associated fibroblast interaction regulates
matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 318:1517–1527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P:
Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: A diabolic liaison
driving cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:195–208.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumar D, Kandl C, Hamilton CD, Shnayder Y,
Tsue TT, Kakarala K, Ledgerwood L, Sun XS, Huang HJ, Girod D and
Thomas SM: Mitigation of tumor-associated fibroblast-facilitated
head and neck cancer progression with anti-hepatocyte growth factor
antibody ficlatuzumab. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
141:1133–1139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sierra JR and Tsao MS: c-MET as a
potential therapeutic target and biomarker in cancer. Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 3(1 Suppl): S21–S35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen S, Gao P, Chang Z and Xuan M: Effects
of oral cancer-associated fibroblasts on the proliferation,
migration, invasion and tube formation to human lymphatic
endothelial cells. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 33:524–528.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cao Y: Opinion emerging mechanisms of
tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:735–743. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sund M and Kalluri R: Tumor stroma derived
biomarkers in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:177–183. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
DeWever O and Mareel M: Role of tissue
stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol. 200:429–447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pupa SM, Ménard S, Forti S and Tagliabue
E: New insights into the role of extracellular matrix during tumor
onset and progression. J Cell Physiol. 192:259–267. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Routray S, Sunkavali A and Bari KA:
Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts, its implication in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma: A mini review. Oral Dis. 20:246–253. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao R, Björndahl MA, Gallego MI, Chen S,
Religa P, Hansen AJ and Cao Y: Hepatocyte growth factor is a
lymphangiogenic factor with an indirect mechanism of action. Blood.
107:3531–3536. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gibot L, Galbraith T, Kloos B, Das S,
Lacroix DA, Auger FA and Skobe M: Cell-based approach for 3D
reconstruction of lymphatic capillaries in vitro reveals distinct
functions of HGF and VEGF-C in lymphangiogenesis. Biomaterials.
78:129–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Bacco F, Luraghi P, Medico E, Reato G,
Girolami F, Perera T, Gabriele P, Comoglio PM and Boccaccio C:
Induction of MET by ionizing radiation and its role in
radioresistance and invasive growth of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:645–661. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen YJ, Tsai RK, Wu WC, He MS, Kao YH and
Wu WS: Enhanced PKCδ and ERK signaling mediate cell migration of
retinal pigment epithelial cells synergistically induced by HGF and
EGF. PLoS One. 7:e449372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simpson DR, Mell LK and Cohen EE:
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 51:291–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rogers SJ, Box C, Harrington KJ, Nutting
C, Rhys-Evans P and Eccles SA: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
signalling pathway as a therapeutic target in squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
9:769–790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, Kim BH, Park JK,
Kim HK, Kim JS and Oh SC: Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes
metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and
MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|