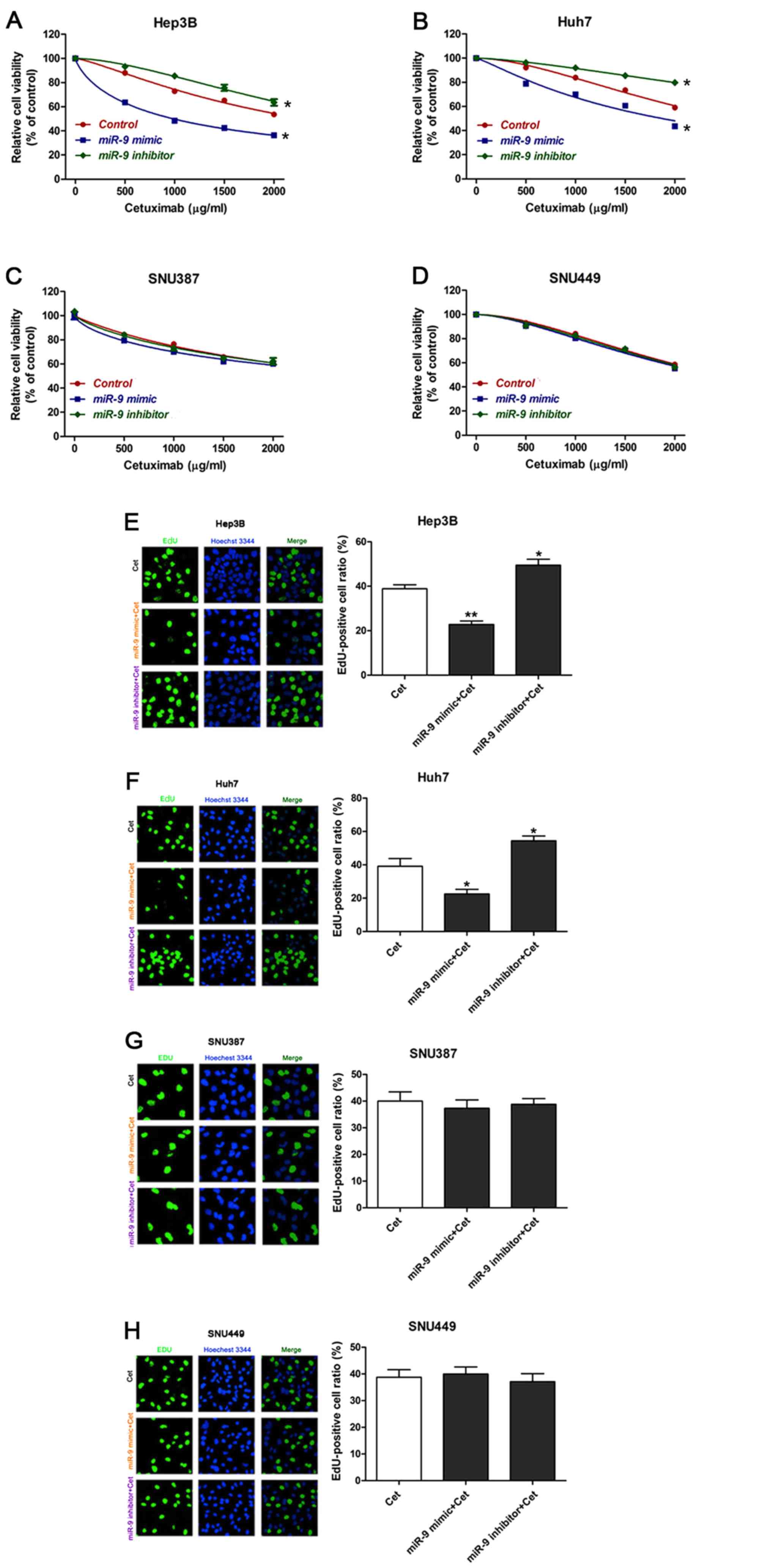
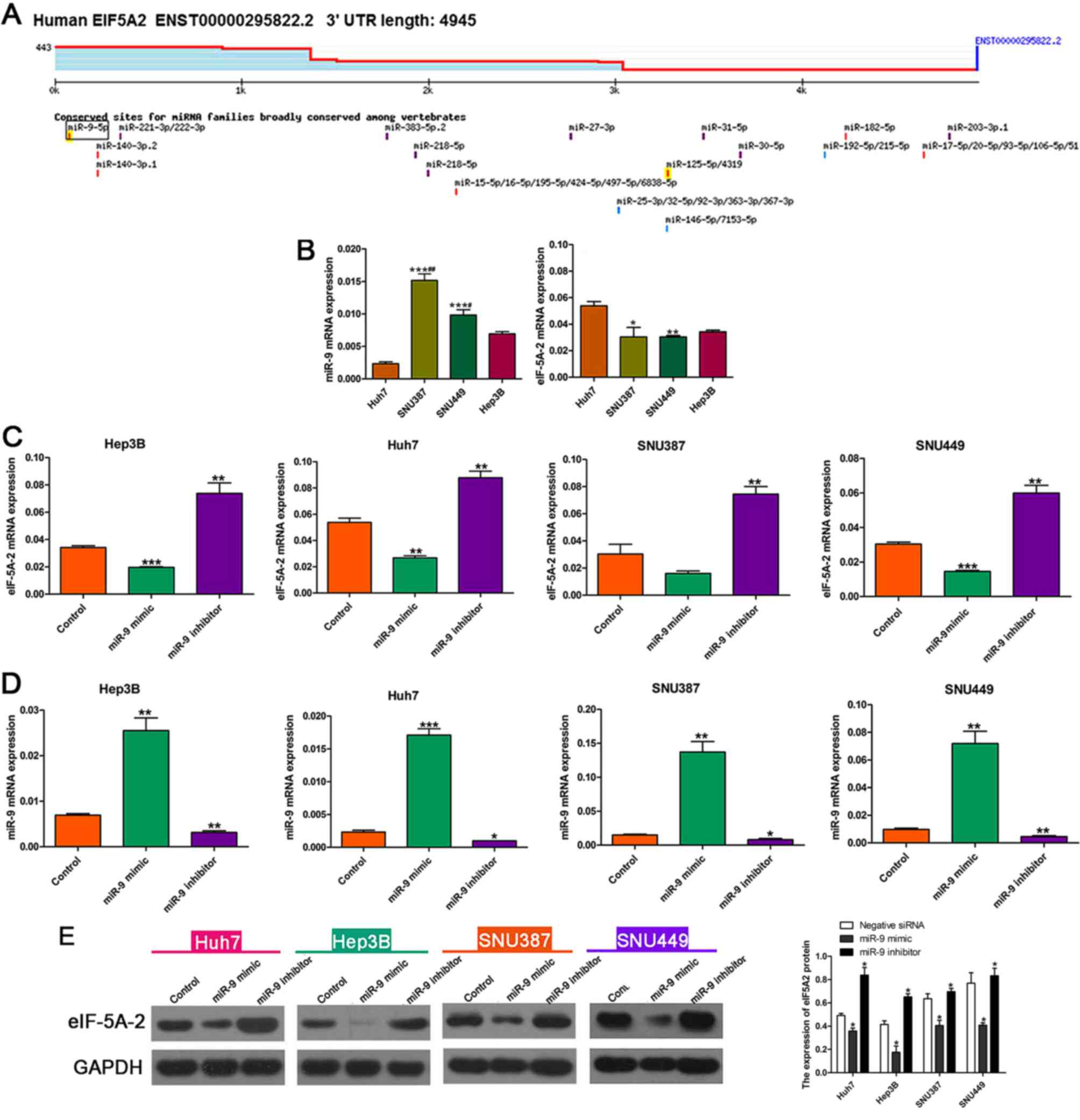
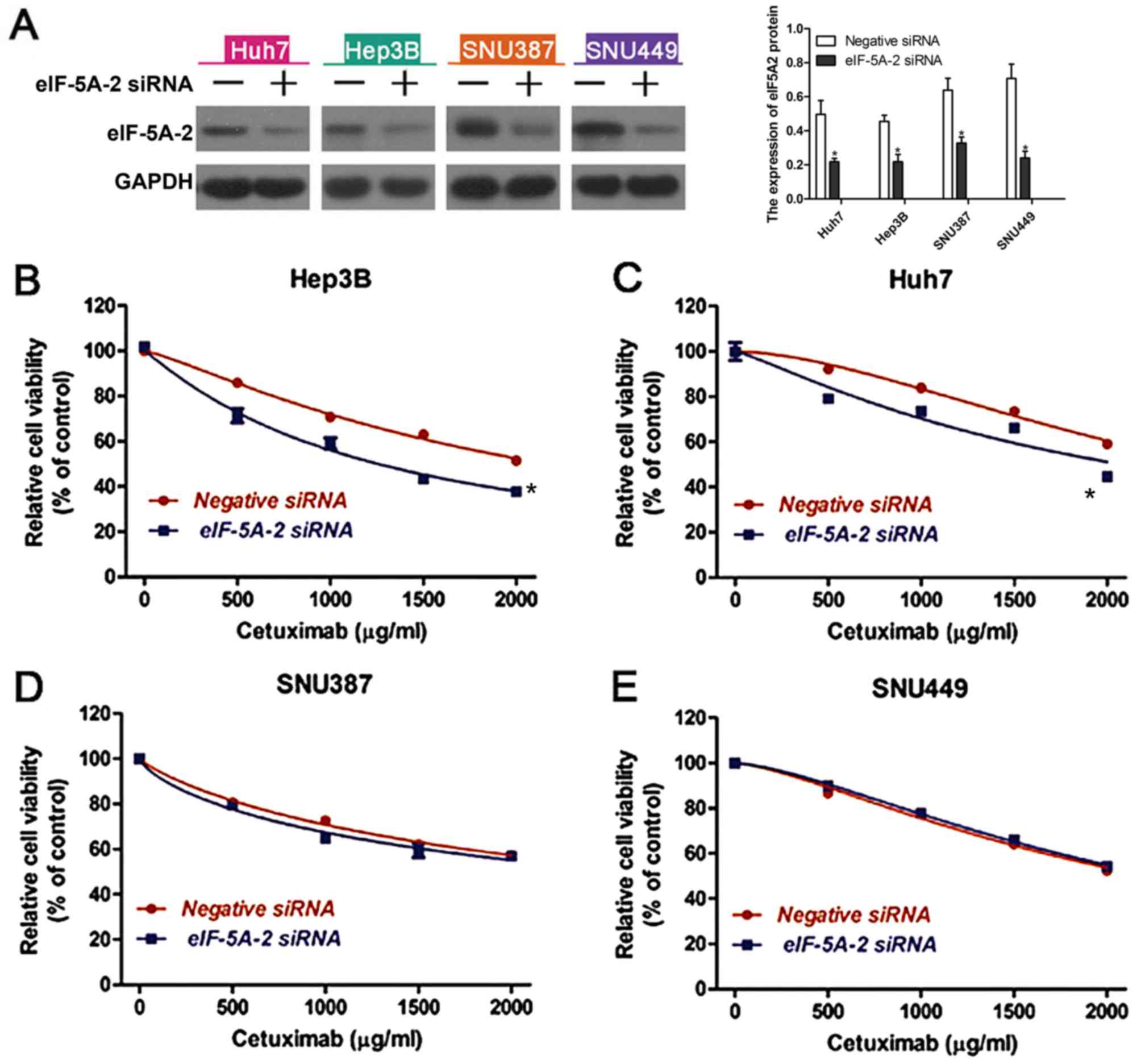
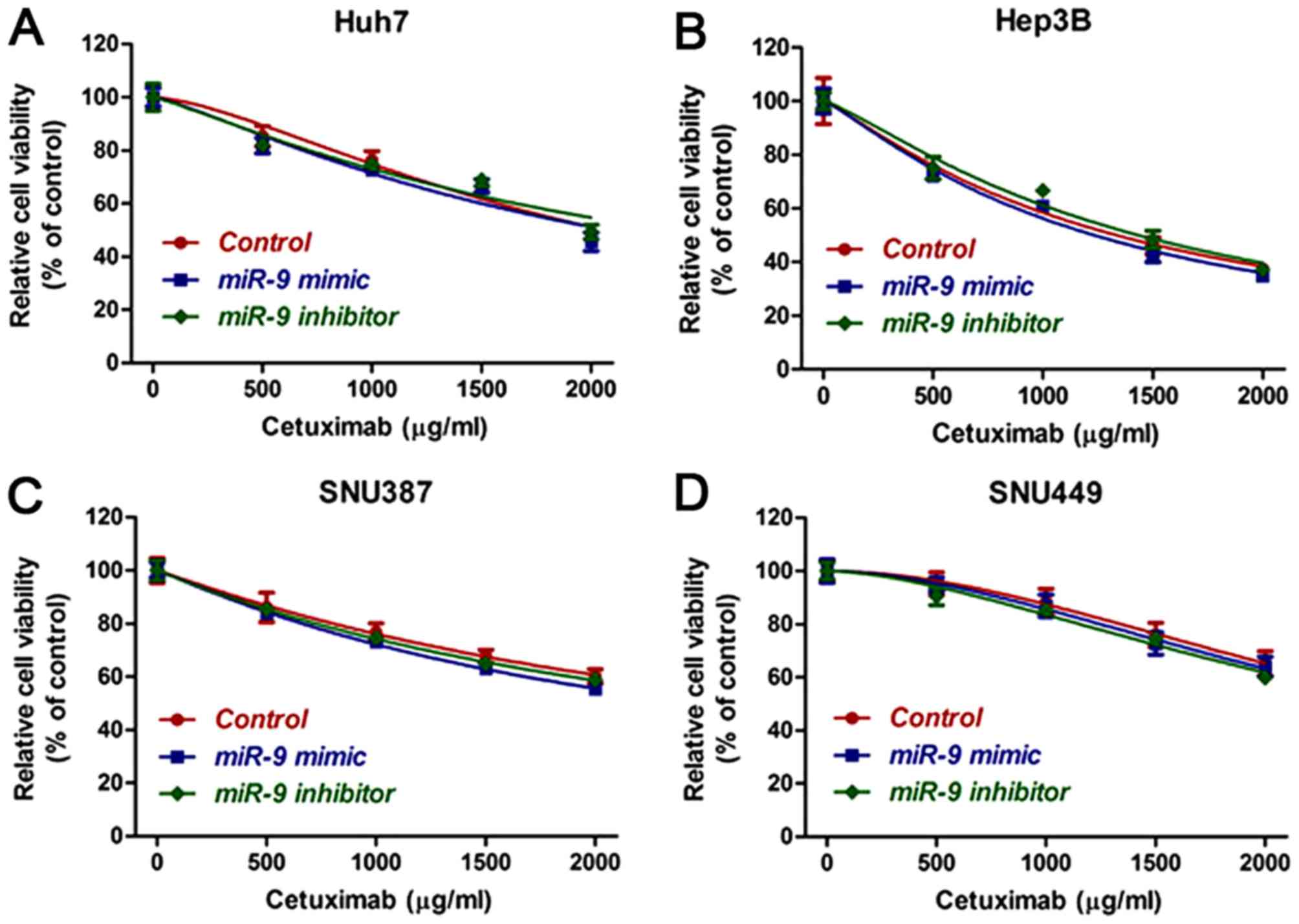
|
1
|
Faloppi L, Scartozzi M, Maccaroni E, Di
Pietro Paolo M, Berardi R, Del Prete M and Cascinu S: Evolving
strategies for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: From
clinical-guided to molecularly-tailored therapeutic options. Cancer
Treat Rev. 37:169–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sapisochin G, de Sevilla EF, Echeverri J
and Charco R: Management of ‘very early’ hepatocellular carcinoma
on cirrhotic patients. World J Hepatol. 6:766–775. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thomas RK: Overcoming drug resistance in
ALK-rearranged lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 370:1250–1251. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Selcuklu SD, Donoghue MT, Rehmet K, de
Souza Gomes M, Fort A, Kovvuru P, Muniyappa MK, Kerin MJ, Enright
AJ and Spillane C: MicroRNA-9 inhibition of cell proliferation and
identification of novel miR-9 targets by transcriptome profiling in
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:29516–29528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song Y, Li J, Zhu Y, Dai Y, Zeng T, Liu L,
Li J, Wang H, Qin Y, Zeng M, et al: MicroRNA-9 promotes tumor
metastasis via repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:11669–11680. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui EH, Li HJ, Hua F, Wang B, Mao W, Feng
XR, Li JY and Wang X: Serum microRNA 125b as a diagnostic or
prognostic biomarker for advanced NSCLC patients receiving
cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:309–313. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perell K, Vincent M, Vainer B, Petersen
BL, Federspiel B, Møller AK, Madsen M, Hansen NR, Friis-Hansen L,
Nielsen FC and Daugaard G: Development and validation of a microRNA
based diagnostic assay for primary tumor site classification of
liver core biopsies. Mol Oncol. 9:68–77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xin H, Li X, Yang B, Zhang L, Han Z and
Han C: Blood-based multiple-microRNA assay displays a better
diagnostic performance than single-microRNA assay in the diagnosis
of breast tumor. Tumour Biol. 35:12635–12643. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti
KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu SM, Chen CM, Jiang ZY, Yuan B, Ji M,
Wu FH and Jin J: MicroRNA-185 inhibits cell proliferation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting Six2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1712–1719.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deng B, Qu L, Li J, Fang J, Yang S, Cao Z,
Mei Z and Sun X: MiRNA-211 suppresses cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting SPARC in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 6:266792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo LM, Pu Y, Han Z, Liu T, Li YX, Liu M,
Li X and Tang H: MicroRNA-9 inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth
through regulation of NF-kappaB1. FEBS J. 276:5537–5546. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsai KW, Liao YL, Wu CW, Hu LY, Li SC,
Chan WC, Ho MR, Lai CH, Kao HW, Fang WL, et al: Aberrant
hypermethylation of miR-9 genes in gastric cancer. Epigenetics.
6:1189–1197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Qi M, Li S, Qi T, Mei H, Huang K,
Zheng L and Tong Q: microRNA-9 targets matrix metalloproteinase 14
to inhibit invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1454–1466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng L, Qi T, Yang D, Qi M, Li D, Xiang
X, Huang K and Tong Q: microRNA-9 suppresses the proliferation,
invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through targeting
cyclin D1 and Ets1. PLoS One. 8:e557192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muraoka T, Soh J, Toyooka S, Maki Y, Shien
K, Furukawa M, Ueno T, Tanaka N, Yamamoto H, Asano H, et al: Impact
of aberrant methylation of microRNA-9 family members on non-small
cell lung cancers. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:185–189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Zhao H, Tang D, Wu J, Yao G and
Zhang Q: Overexpressions of microRNA-9 and microRNA-200c in human
breast cancers are associated with lymph node metastasis. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 28:283–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu S, Jia S and Xu P: MicroRNA-9 as a
novel prognostic biomarker in human laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:5523–5528. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou X, Marian C, Makambi KH, Kosti O,
Kallakury BV, Loffredo CA and Zheng YL: MicroRNA-9 as potential
biomarker for breast cancer local recurrence and tumor estrogen
receptor status. PLoS One. 7:e390112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu L, Chen H, Zhou D, Li D, Bai R, Zheng
S and Ge W: MicroRNA-9 up-regulation is involved in colorectal
cancer metastasis via promoting cell motility. Med Oncol.
29:1037–1043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Fang K, Shen H and Qian Y:
MicroRNA-9 is a ponderable index for the prognosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:17748–17756.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clement PM, Johansson HE, Wolff EC and
Park MH: Differential expression of eIF5A-1 and eIF5A-2 in human
cancer cells. FEBS J. 273:1102–1114. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee NP, Tsang FH, Shek FH, Mao M, Dai H,
Zhang C, Dong S, Guan XY, Poon RT and Luk JM: Prognostic
significance and therapeutic potential of eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 127:968–976. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang GF, Xie D, Liu JH, Luo JH, Li LJ, Hua
WF, Wu HM, Kung HF, Zeng YX and Guan X: Expression and
amplification of eIF-5A2 in human epithelial ovarian tumors and
overexpression of EIF-5A2 is a new in dependent predictor of
outcome in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
112:314–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo JH, Hua WF, Rao HL, Liao YJ, Kung HF,
Zeng YX, Guan XY, Chen W and Xie D: Overexpression of EIF-5A2
predict s tumor recurrence and progression in pTa/pT1 urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Sci. 100:896–902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He LR, Zhao HY, Li BK, Liu YH, Liu MZ,
Guan XY, Bian XW, Zeng YX and Xie D: Overexpression of eIF5A-2 is
an adverse prognostic marker of survival in stage I non-small cell
lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 129:143–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, Xie D, Chen L, Fu
L, Lau SH, Li Y, Li Y and Guan XY: Overexpression of eukaryotic
initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor
metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51:1255–1263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu W, Cai MY, Tong ZT, Dong SS, Mai SJ,
Liao YJ, Bian XW, Lin MC, Kung HF, Zeng YX, et al: Overexpression
of EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by
upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce
epithelial-mesenchymaltransition. Gut. 61:562–575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun Z, Han Q, Zhou N, Wang S, Lu S, Bai C
and Zhao RC: MicroRNA-9 enhances migration and invasion through
KLF17 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 7:884–894. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ye M, Du YL, Nie YQ, Zhou ZW, Cao J and Li
YF: Overexpression of activated leukocute cell adhesion molecule in
gastric cancer is associated with advanced stages and poor
prognosis and miR-9 deregulation. Mol Med Rep. 11:2004–2012. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie D, Ma NF, Pan ZZ, Wu HX, Liu YD, Wu
GQ, Kung HF and Guan XY: Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is associated
with metastasis of human colorectal carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
39:80–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shek FH, Fatima S and Lee NP: Implications
of the use of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A)
for prognosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Hepatol. 2012:7609282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wei JH, Cao JZ, Zhang D, Liao B, Zhong WM,
Lu J, Zhao HW, Zhang JX, Tong ZT, Fan S, et al: EIF5A2 predicts
outcome in localised invasive bladder cancer and promotes bladder
cancer cell aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer.
110:1767–1777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lou B, Fan J, Wang K, Chen W, Zhou X,
Zhang J, Lin S, Lv F and Chen Y: N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane (GC7)
enhances the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin by inhibiting
activation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2)
and preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 319:2708–2717. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu RR, Lv YS, Tang YX, Wang YF, Chen XL,
Zheng XX, Xie SZ, Cai Y, Yu J and Zhang XN: Eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 5A2 regulates the migration and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via pathways involving reactive
oxygen species. Oncotarget. 7:24348–24360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Iida M, Brand TM, Starr MM, Huppert EJ,
Luthar N, Bahrar H, Coan JP, Pearson HE, Salgia R and Wheeler DL:
Overcoming acquired resistance to cetuximab by dual targeting HER
family receptors with antibody-based therapy. Mol Cancer.
13:2422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N,
Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, et al:
Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. N Engl J Med. 354:567–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cuninham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D,
Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Best D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C,
et al: Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in
irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
351:337–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang X, Jiang R, Cui EH, Feng WM, Guo HH,
Gu DH, Tang CW, Xue T and Bao Y: N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane
enhances the chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells to cetuximab through
inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2
activation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1244–1250.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ezzoukhry Z, Louandre C, Trécherel E,
Godin C, Chauffert B, Dupont S, Diouf M, Barbare JC, Maziere JC and
Galmiche A: EGFR activation is a potential determinant of primary
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. Int J
Cancer. 131:2961–2969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen W, Shen X, Xia X, Xu G, Ma T, Bai X
and Liang T: NSC 74859-mediated inhibition of STAT3 enhances the
anti-proliferative activity of cetuximab in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 32:70–77. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|