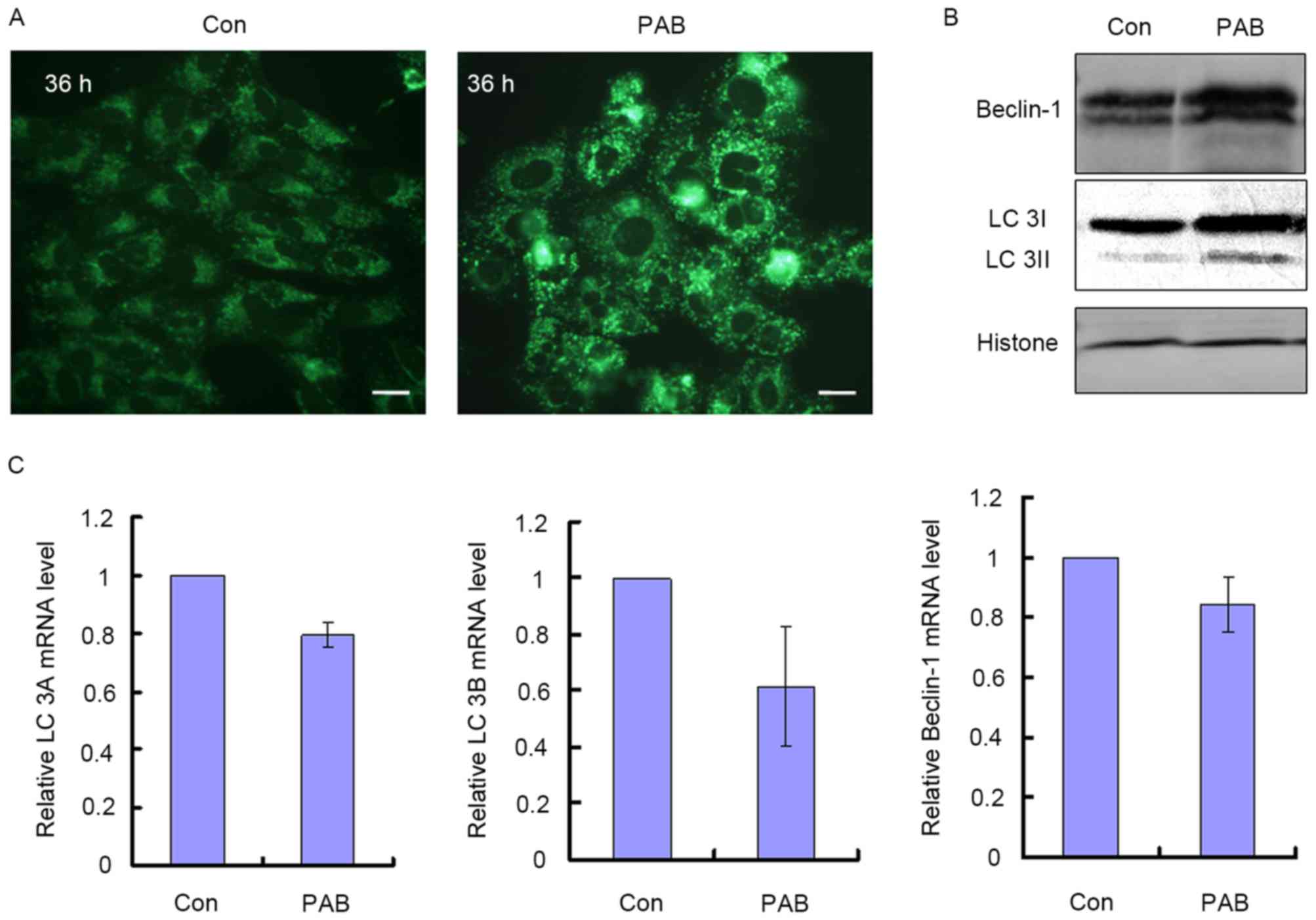
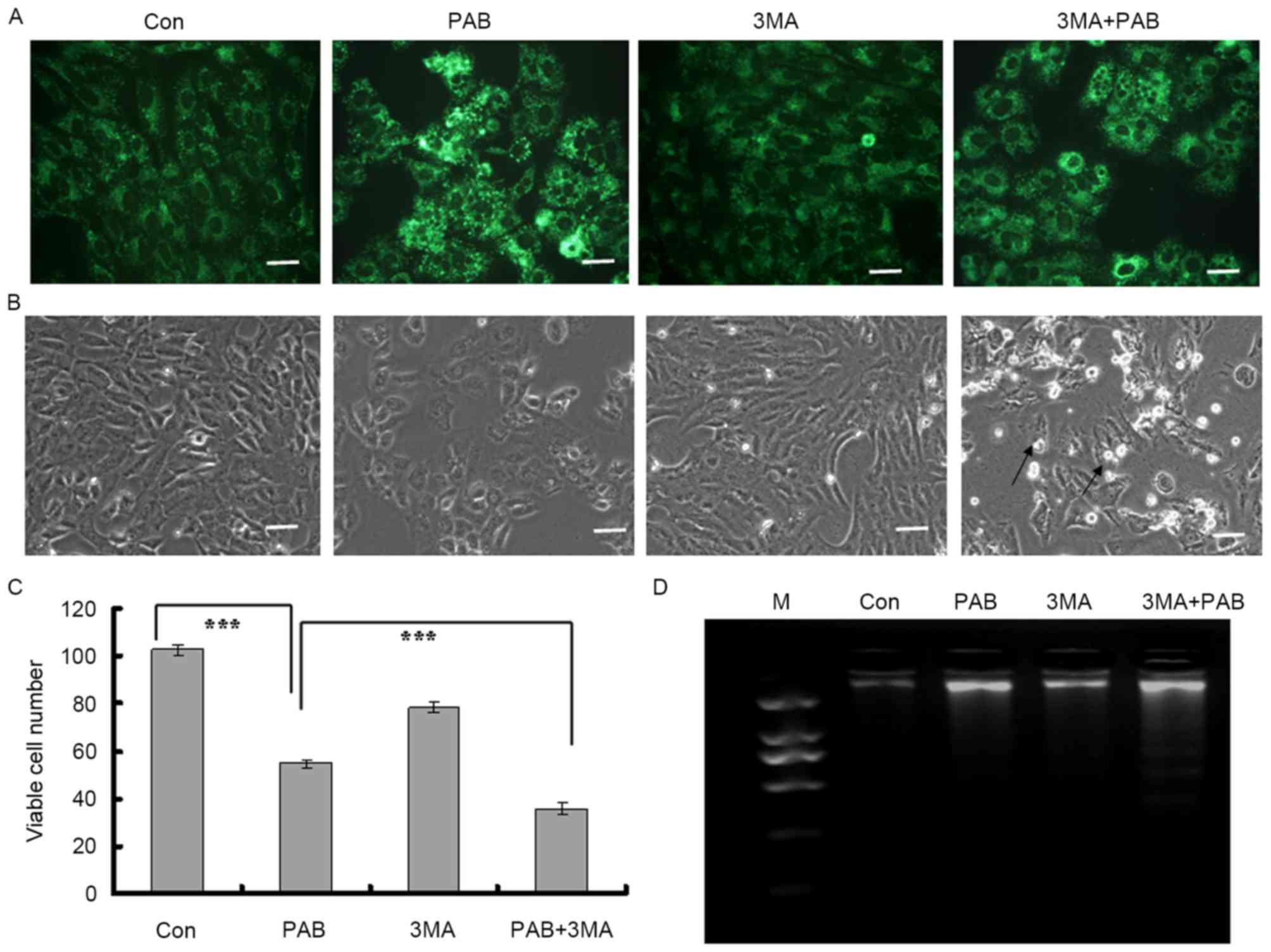
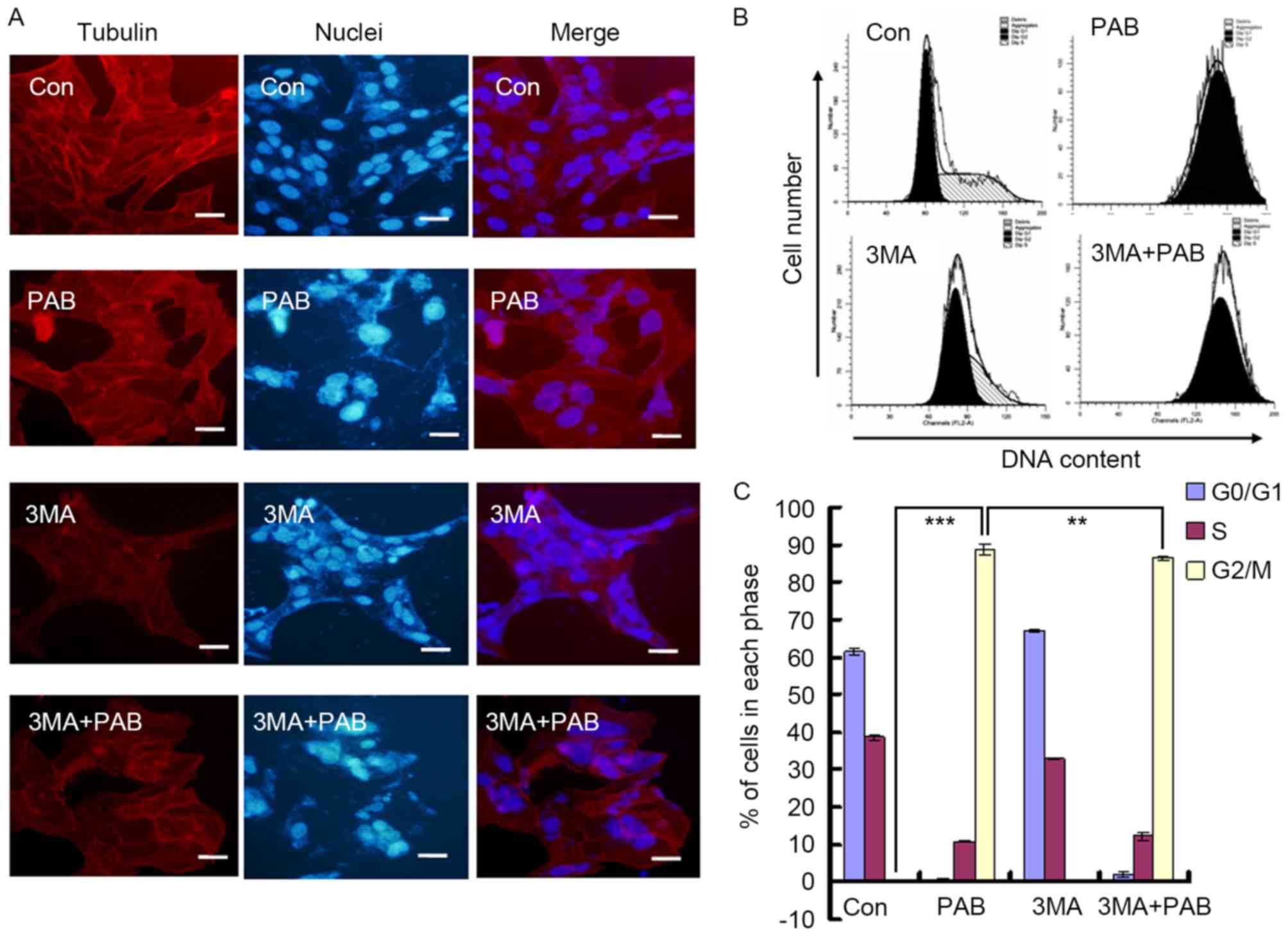
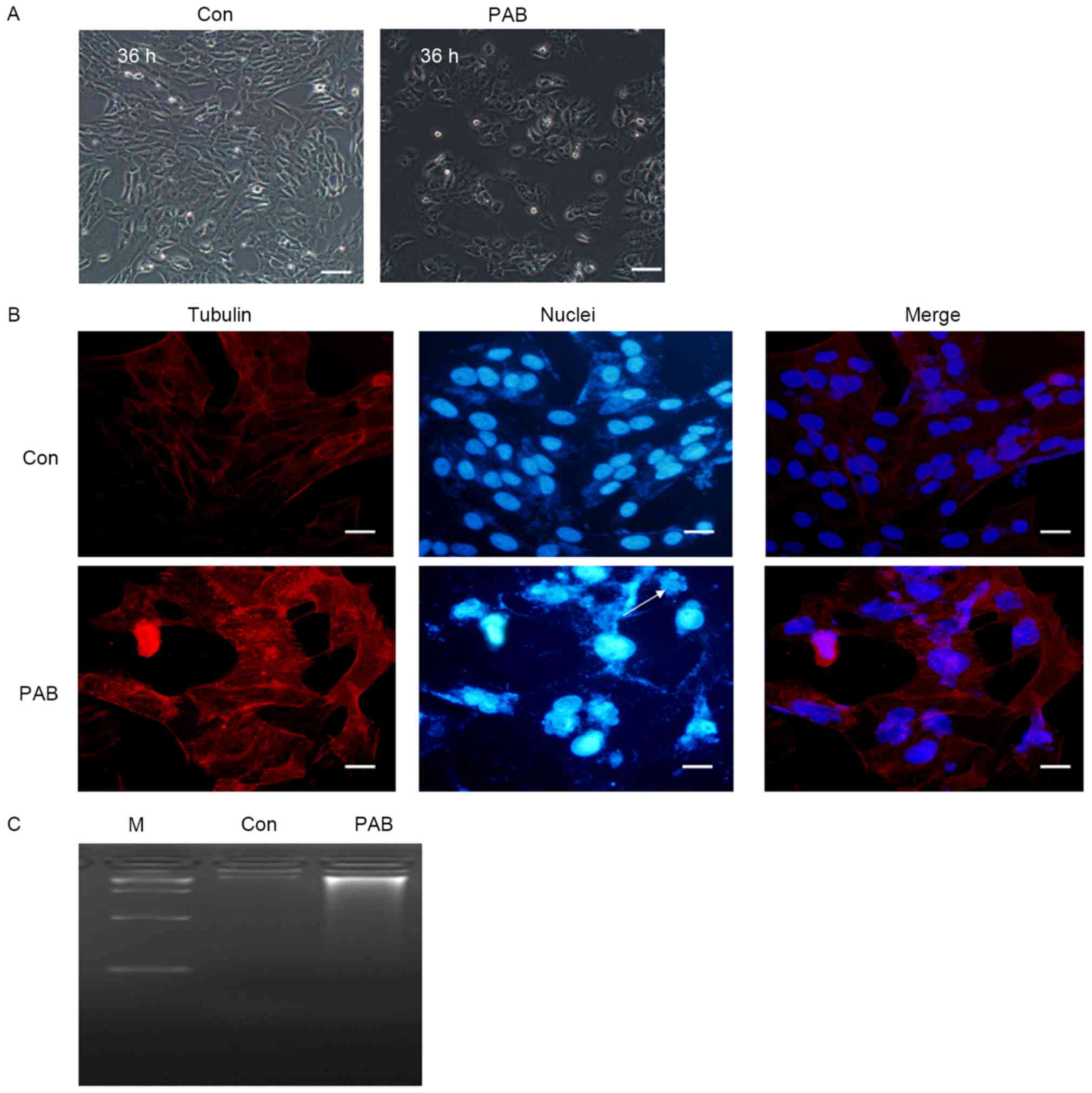
|
1
|
Gong X, Wang M, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Involvement of JNK-initiated p53 accumulation and
phosphorylation of p53 in pseudolaric acid B induced cell death.
Exp Mol Med. 38:428–434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gong XF, Wang MW, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces apoptosis through p53 and
Bax/Bcl-2 pathways in human melanoma A375-S2 cells. Arch Pharm Res.
28:68–72. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pan DJ, Li ZL, Hu CQ, Chen K, Chang JJ and
Lee KH: The cytotoxic principles of Pseudolarix kaempferi:
Pseudolaric acid-A and -B and related derivatives. Planta Med.
56:383–385. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu J, Li X, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Bcl-2 family proteins were involved in pseudolaric acid
B-induced autophagy in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells. J Pharmacol
Sci. 107:295–302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu JH, Cui Q, Jiang YY, Yang W, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces apoptosis,
senescence, and mitotic arrest in human breast cancer MCF-7. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 28:1975–1983. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu JH, Wang HJ, Li XR, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Protein tyrosine kinase, JNK, and ERK involvement
in pseudolaric acid B-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer
MCF-7 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:1069–1076. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li FF, Yi S, Wen L, He J, Yang LJ, Zhao J,
Zhang BP, Cui GH and Chen Y: Oridonin induces NPM mutant protein
translocation and apoptosis in NPM1c+ acute myeloid leukemia cells
in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:806–813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qi M, Yao G, Fan S, Cheng W, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces mitotic
catastrophe followed by apoptotic cell death in murine fibrosarcoma
L929 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 683:16–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adams JM: Ways of dying: Multiple pathways
to apoptosis. Genes Dev. 17:2481–2495. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagata S and Golstein P: The Fas death
factor. Science. 267:1449–1456. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Klekotka PA, Santoro SA, Wang H and Zutter
MM: Specific residues within the alpha 2 integrin subunit
cytoplasmic domain regulate migration and cell cycle progression
via distinct MAPK pathways. J Biol Chem. 276:32353–32361. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon S and Seger R: The extracellular
signal-regulated kinase: Multiple substrates regulate diverse
cellular functions. Growth Factors. 24:21–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee YJ, Won AJ, Lee J, Jung JH, Yoon S,
Lee BM and Kim HS: Molecular mechanism of SAHA on regulation of
autophagic cell death in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Int J Med Sci. 9:881–893. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee YZ, Yang CW, Chang HY, Hsu HY, Chen
IS, Chang HS, Lee CH, Lee JC, Kumar CR, Qiu YQ, et al: Discovery of
selective inhibitors of Glutaminase-2, which inhibit mTORC1,
activate autophagy and inhibit proliferation in cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 5:6087–6101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He H, Feng YS, Zang LH, Liu WW, Ding LQ,
Chen LX, Kang N, Hayashi T, Tashiro S, Onodera S, et al: Nitric
oxide induces apoptosis and autophagy; autophagy down-regulates NO
synthesis in physalin A-treated A375-S2 human melanoma cells. Food
Chem Toxicol. 71:128–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang ZY, Zhong T, Wang Y, Song FM and Yu
XF, Xing LP, Zhang WY, Yu JH, Hua SC and Yu XF: Human enterovirus
68 interferes with the host cell cycle to facilitate viral
production. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 7:292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong T, Zhang LY, Wang ZY, Wang Y, Song
FM, Zhang YH and Yu JH: Rheum emodin inhibits enterovirus 71 viral
replication and affects the host cell cycle environment. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 38:392–401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu YQ, Han XF, Bo JX and Ma HP:
Wedelolactone enhances osteoblastogenesis but inhibits
osteoclastogenesis through Sema3A/NRP1/PlexinA1 pathway. Front
Pharmacol. 7:3752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu J, Chen C, Xu T, Yan M, Xue B, Wang Y,
Liu C, Zhong T, Wang Z, Meng X, et al: Pseudolaric acid B activates
autophagy in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells to prevent cell death.
Oncol Lett. 11:1731–1737. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu J, Ren P, Zhong T, Wang Y, Yan M, Xue
B, Li R, Dai C, Liu C, Chen G and Yu XF: Pseudolaric acid B
inhibits proliferation in SW579 human thyroid squamous cell
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 12:7195–7202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu J, Wang Z, Ren P, Zhong T, Wang Y, Song
F, Hou J, Yu X and Hua S: Pseudolaric acid B inhibits the secretion
of hepatitis B virus. Oncol Rep. 37:519–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wong VK, Chiu P, Chung SS, Chow LM, Zhao
YZ, Yang BB and Ko BC: Pseudolaric acid B, a novel
microtubule-destabilizing agent that circumvents multidrug
resistance phenotype and exhibits antitumor activity in vivo. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:6002–6011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng Y, He D, Yao Z and Klionsky DJ: The
machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res. 24:24–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro
JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J,
Gewirtz DA, Karantza V, et al: Autophagy in malignant
transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 34:856–880. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Crighton D, Wilkinson S, O'Prey J, Syed N,
Smith P, Harrison PR, Gasco M, Garrone O, Crook T and Ryan KM:
DRAM, a p53-induced modulator of autophagy, is critical for
apoptosis. Cell. 126:121–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP and Harper
JW: Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature.
466:68–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salah FS, Ebbinghaus M, Muley VY, Zhou Z,
Al-Saadi KR, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, O'Sullivan GA, Betz H, König R,
Wang ZQ, et al: Tumor suppression in mice lacking GABARAP, an
Atg8/LC3 family member implicated in autophagy, is associated with
alterations in cytokine secretion and cell death. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tong YG, Zhang XW, Geng MY, Yue JM, Xin
XL, Tian F, Shen X, Tong LJ, Li MH, Zhang C, et al: Pseudolarix
acid B, a new tubulin-binding agent, inhibits angiogenesis by
interacting with a novel binding site on tubulin. Mol Pharmacol.
69:1226–1233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|