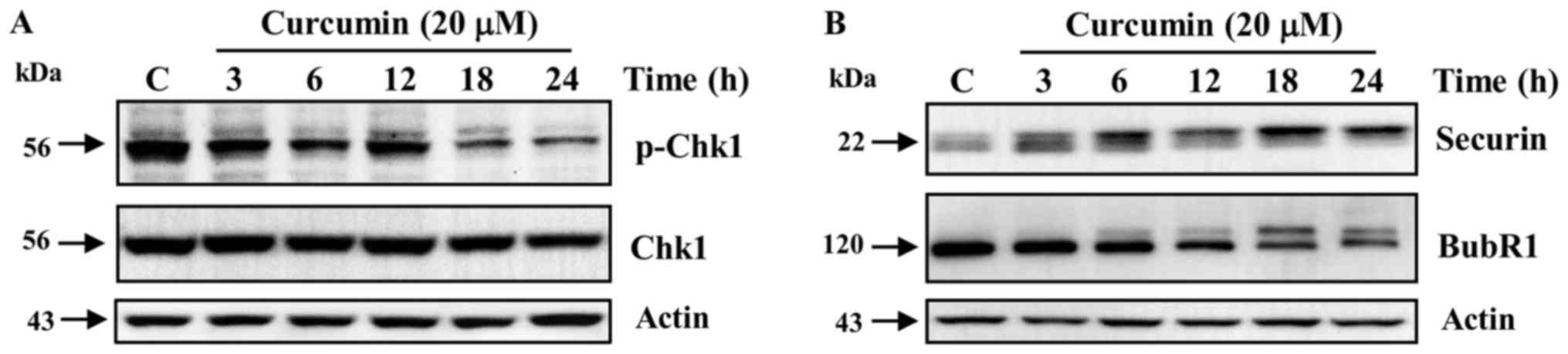
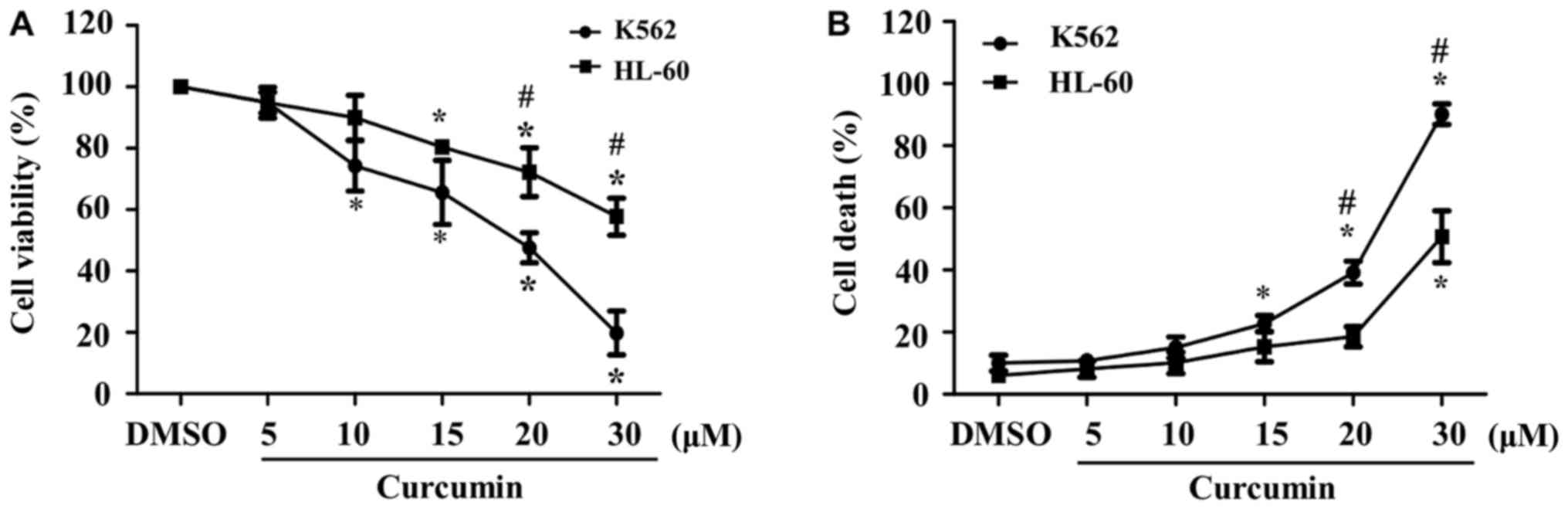
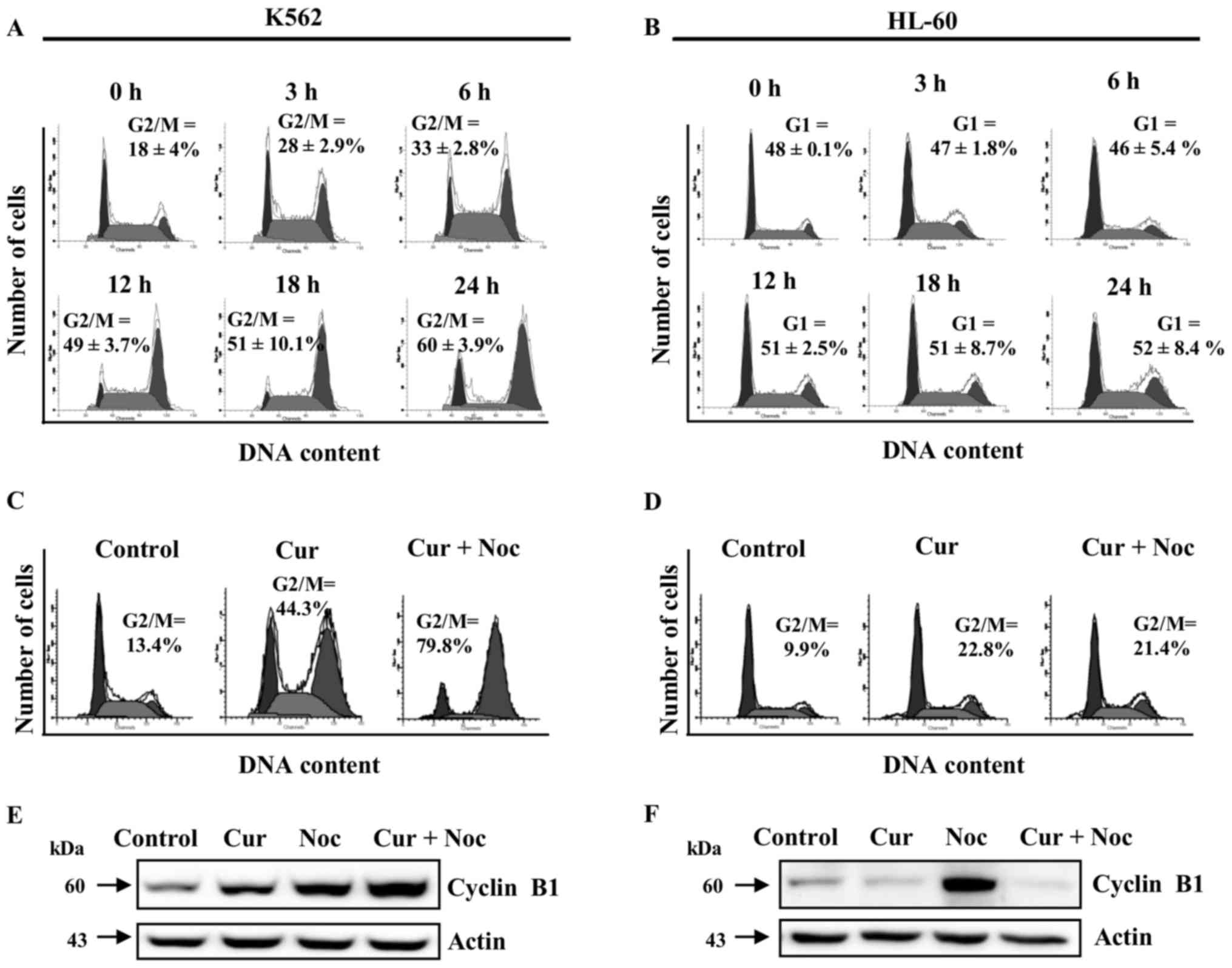
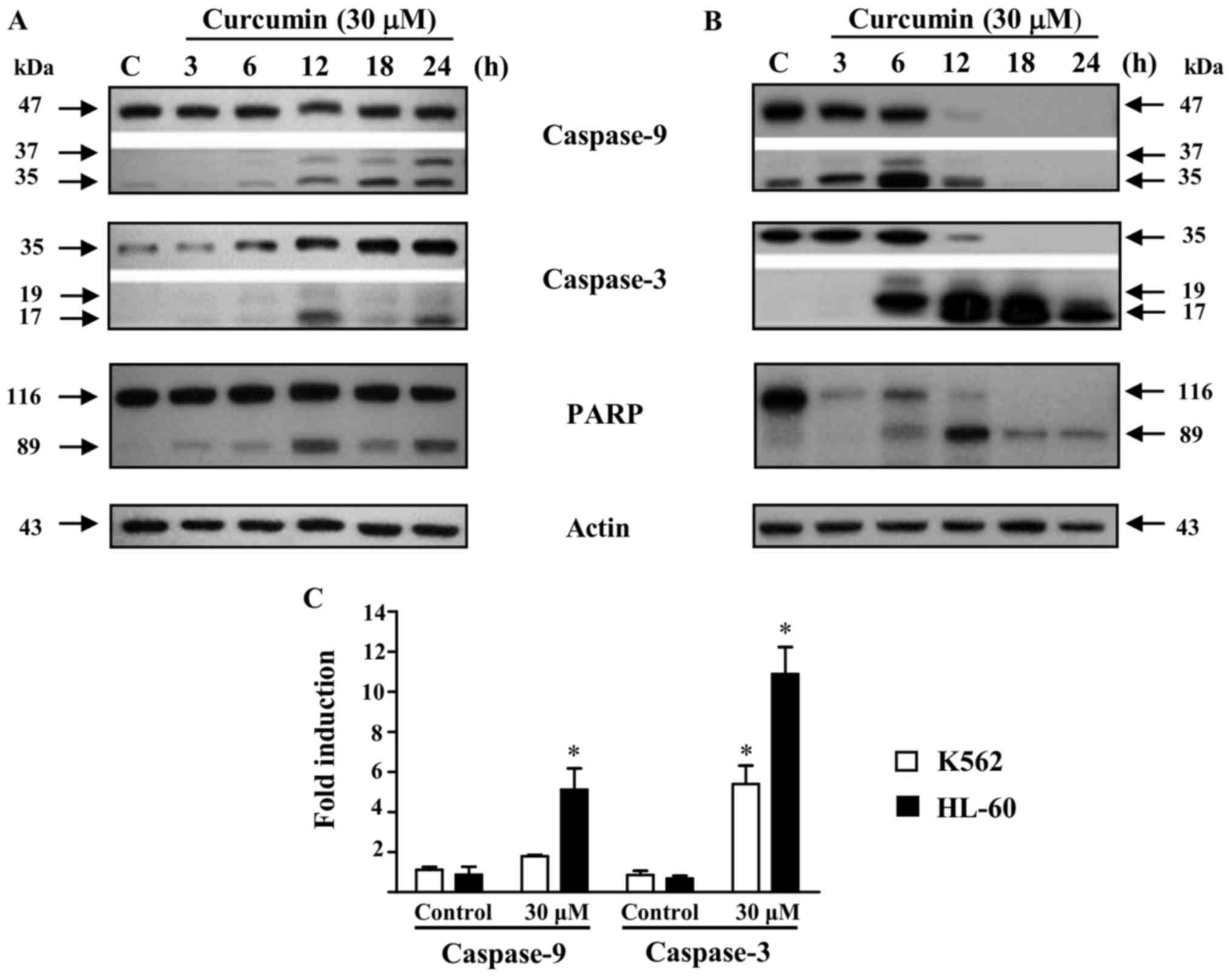
|
1
|
Shakibaei M, Buhrmann C, Kraehe P, Shayan
P, Lueders C and Goel A: Curcumin chemosensitizes 5-fluorouracil
resistant MMR-deficient human colon cancer cells in high density
cultures. PLoS One. 9:e853972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fan Z, Duan X, Cai H, Wang L, Li M, Qu J,
Li W, Wang Y and Wang J: Curcumin inhibits the invasion of lung
cancer cells by modulating the PKCα/Nox-2/ROS/ATF-2/MMP-9 signaling
pathway. Oncol Rep. 34:691–698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferreira LC, Arbab AS, Jardim-Perassi BV,
Borin TF, Varma NR, Iskander AS, Shankar A, Ali MM and Zuccari DA:
Effect of curcumin on pro-angiogenic factors in the xenograft model
of breast cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 15:1285–1296. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang AC, Lin SY, Su CC, Lin SS, Ho CC,
Hsia TC, Chiu TH, Yu CS, Ip SW, Lin TP and Chung JG: Effects of
curcumin on N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl) nitrosamine (DHPN)-induced lung
and liver tumorigenesis in BALB/c mice in vivo. In Vivo.
22:781–785. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carroll RE, Benya RV, Turgeon DK, Vareed
S, Neuman M, Rodriguez L, Kakarala M, Carpenter PM, McLaren C,
Meyskens FL Jr and Brenner DE: phase IIa clinical trial of curcumin
for the prevention of colorectal neoplasia. Cancer Prev Res.
4:354–364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Epelbaum R, Schaffer M, Vizel B, Badmaev V
and Bar-Sela G: Curcumin and gemcitabine in patients with advanced
pancreatic cancer. Nutr Cancer. 62:1137–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sha J, Li J, Wang W, Pan L, Cheng J, Li L,
Zhao H and Lin W: Curcumin induces G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis in
hormone independent prostate cancer DU-145 cells by down regulating
Notch signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:177–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun SH, Huang HC, Huang C and Lin JK:
Cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231/Her2 cells induced by
curcumin. Eur J Pharmacol. 690:22–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng C, Jiao JT, Qian Y, Guo XY, Huang J,
Dai MC, Zhang L, Ding XP, Zong D and Shao JF: Curcumin induces
G2/M arrest and triggers apoptosis via FoxO1 signaling
in U87 human glioma cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:3763–3770. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu JJ, Cai YJ and Ding J: Curcumin induces
DNA damage and caffeine insensitive cell cycle arrest in colorectal
carcinoma HCT116 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 354:247–252. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo H, Xu YM, Ye ZQ, Yu JH and Hu XY:
Curcumin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of prostate cancer
cells by regulating the expression of IkappaBalpha, c-Jun and
androgen receptor. Pharmazie. 68:431–434. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao A, Li Q, Yin P, Dong Y, Shi H, Wang L,
Ji G, Xie J and Wu D: Curcumin induces apoptosis in human gastric
carcinoma AGS cells and colon carcinoma HT-29 cells through
mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Apoptosis. 18:1391–1402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yao Q, Lin M, Wang Y, Lai Y, Hu J, Fu T,
Wang L, Lin S, Chen L and Guo Y: Curcumin induces the apoptosis of
A549 cells via oxidative stress and MAPK signaling pathways. Int J
Mol Med. 36:1118–1126. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Subramaniam D, Ramalingam S, Linehan DC,
Dieckgraefe BK, Postier RG, Houchen CW, Jensen RA and Anant S: RNA
binding protein CUGBP2/CELF2 mediates curcumin-induced mitotic
catastrophe of pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e169582011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
O'Sullivan-Coyne G, O'Sullivan GC,
O'Donovan TR, Piwocka K and McKenna SL: Curcumin induces
apoptosis-independent death in oesophageal cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 101:1585–1595. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao G, Han X, Zheng S, Li Z, Sha Y, Ni J,
Sun Z, Qiao S and Song Z: Curcumin induces autophagy, inhibits
proliferation and invasion by downregulating AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway in human melanoma cells. Oncol Rep. 35:1065–1074. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tork OM, Khaleel EF and Abdelmaqsoud OM:
Altered cell to cell communication, autophagy and mitochondrial
dysfunction in a model of hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential
protective effects of curcumin and stem cell therapy. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:8271–8279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tan TW, Tsai HR, Lu HF, Lin HL, Tsou MF,
Lin YT, Tsai HY, Chen YF and Chung JG: Curcumin-induced cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in human acute promyelocytic leukemia HL-60
cells via MMP changes and caspase-3 activation. Anticancer Res.
26:4361–4371. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sarkar R, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee S, Biswas
R, Biswas J and Roy M: Curcumin augments the efficacy of antitumor
drugs used in leukemia by modulation of heat shock proteins via
HDAC6. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 33:247–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang JR, Lu F, Lu T, Dong WH, Li P, Liu
N, Ma DX and Ji CY: Inactivation of FoxM1 transcription factor
contributes to curcumin-induced inhibition of survival,
angiogenesis, and chemosensitivity in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
J Mol Med. 92:1319–1330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Y, Chang RL, Cui XX, Newmark HL and
Conney AH: Synergistic effects of curcumin on all-trans retinoic
acid- and 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation in
human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Oncol Res. 9:19–29.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Wang G, Wang L, Kang J and Wang J:
Curcumin p38-dependently enhances the anticancer activity of
valproic acid in human leukemia cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 41:210–218.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duvoix A, Morceau F, Schnekenburger M,
Delhalle S, Galteau MM, Dicato M and Diederich M: Curcumin-induced
cell death in two leukemia cell lines: K562 and Jurkat. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1010:389–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chakraborty S, Ghosh U, Bhattacharyya NP,
Bhattacharya RK and Roy M: Inhibition of telomerase activity and
induction of apoptosis by curcumin in K-562 cells. Mutat Res.
596:81–90. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jia YL, Li J, Qin ZH and Liang ZQ:
Autophagic and apoptotic mechanisms of curcumin-induced death in
K562 cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 11:918–928. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang AJ, Jiang G, Li LT and Zheng JN:
Curcumin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and
caspases activation in human melanoma cells. Mol Biol Rep.
42:267–275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Blakemore LM, Boes C, Cordell R and Manson
MM: Curcumin-induced mitotic arrest is characterized by spindle
abnormalities, defects in chromosomal congression and DNA damage.
Carcinogenesis. 34:351–360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mathur A, Abd Elmageed ZY, Liu X,
Kostochka ML, Zhang H, Abdel-Mageed AB and Mondal D: Subverting
ER-stress towards apoptosis by nelfinavir and curcumin coexposure
augments docetaxel efficacy in castration resistant prostate cancer
cells. PLoS One. 9:e1031092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng Y, Weng G, Fan J, Li Z, Wu J, Li Y,
Zheng R, Xia P and Guo K: Curcumin reduces the expression of
survivin, leading to enhancement of arsenic trioxide induced
apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome and leukemia stem-like cells.
Oncol Rep. 36:1233–1242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen J, Wanming D, Zhang D, Liu Q and Kang
J: Water-soluble antioxidants improve the antioxidant and
anticancer activity of low concentrations of curcumin in human
leukemia cells. Pharmazie. 60:57–61. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu J, Peng Y, Wu LC, Xie Z, Deng Y, Hughes
T, He S, Mo X, Chiu M, Wang QE, et al: Curcumin down-regulates DNA
methyltransferase 1 and plays an anti-leukemic role in acute
myeloid leukemia. PLoS One. 8:e559342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rao J, Xu DR, Zheng FM, Long ZJ, Huang SS,
Wu X, Zhou WH, Huang RW and Liu Q: Curcumin reduces expression of
Bcl-2, leading to apoptosis in daunorubicin-insensitive
CD34+ acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and primary
sorted CD34+ acute myeloid leukemia cells. J Transl Med.
9:712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wolanin K, Magalska A, Mosieniak G,
Klinger R, McKenna S, Vejda S, Sikora E and Piwocka K: Curcumin
affects components of the chromosomal passenger complex and induces
mitotic catastrophe in apoptosis-resistant Bcr-Abl-expressing
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 4:457–469. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sánchez Y, Simón GP, Calviño E, de Blas E
and Aller P: Curcumin stimulates reactive oxygen species production
and potentiates apoptosis induction by the antitumor drugs arsenic
trioxide and lonidamine in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 335:114–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martinez-Castillo M, Bonilla-Moreno R,
Aleman-Lazarini L, Meraz-Rios MA, Orozco L, Cedillo-Barron L,
Cordova EJ and Villegas-Sepulveda N: A subpopulation of the K562
cells are killed by curcumin treatment after G2/M arrest and
mitotic catastrophe. PLoS One. 11:e01659712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qadir MI, Naqvi ST and Muhammad SA:
Curcumin: A polyphenol with molecular targets for cancer control.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:2735–2739. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chakraborti S, Das L, Kapoor N, Das A,
Dwivedi V, Poddar A, Chakraborti G, Janik M, Basu G, Panda D, et
al: Curcumin recognizes a unique binding site of tubulin. J Med
Chem. 54:6183–6196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jackson SJ, Murphy LL, Venema RC,
Singletary KW and Young AJ: Curcumin binds tubulin, induces mitotic
catastrophe, and impedes normal endothelial cell proliferation.
Food Chem Toxicol. 60:431–438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|