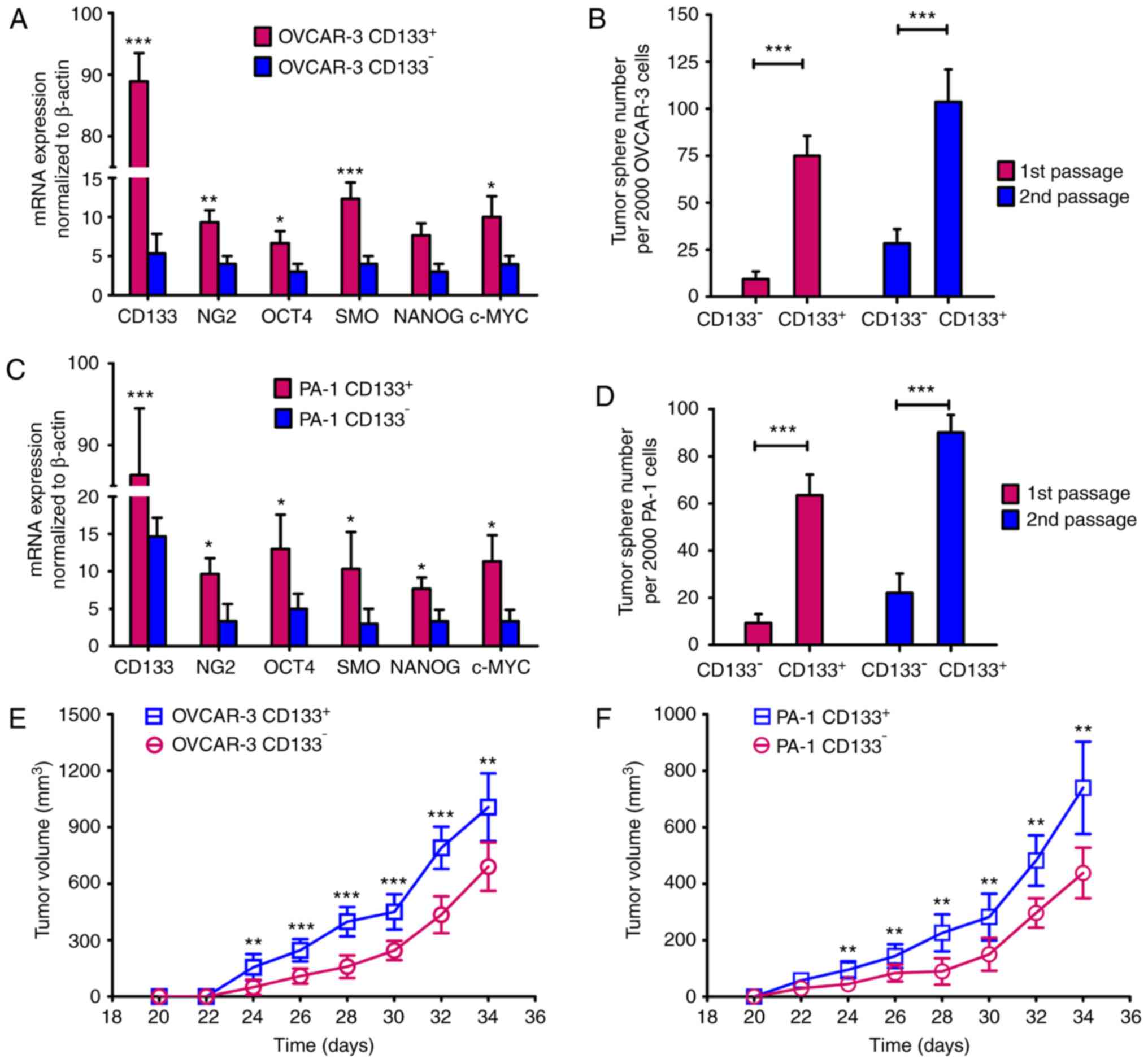
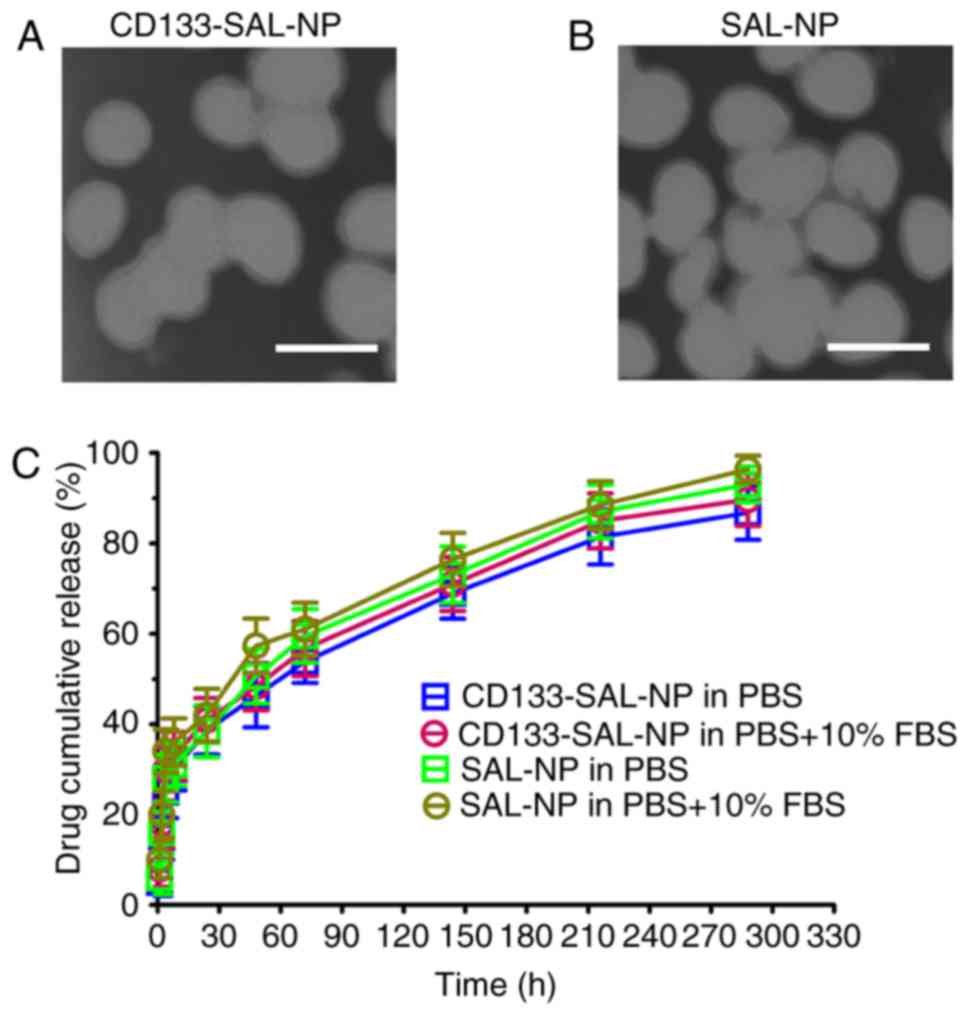
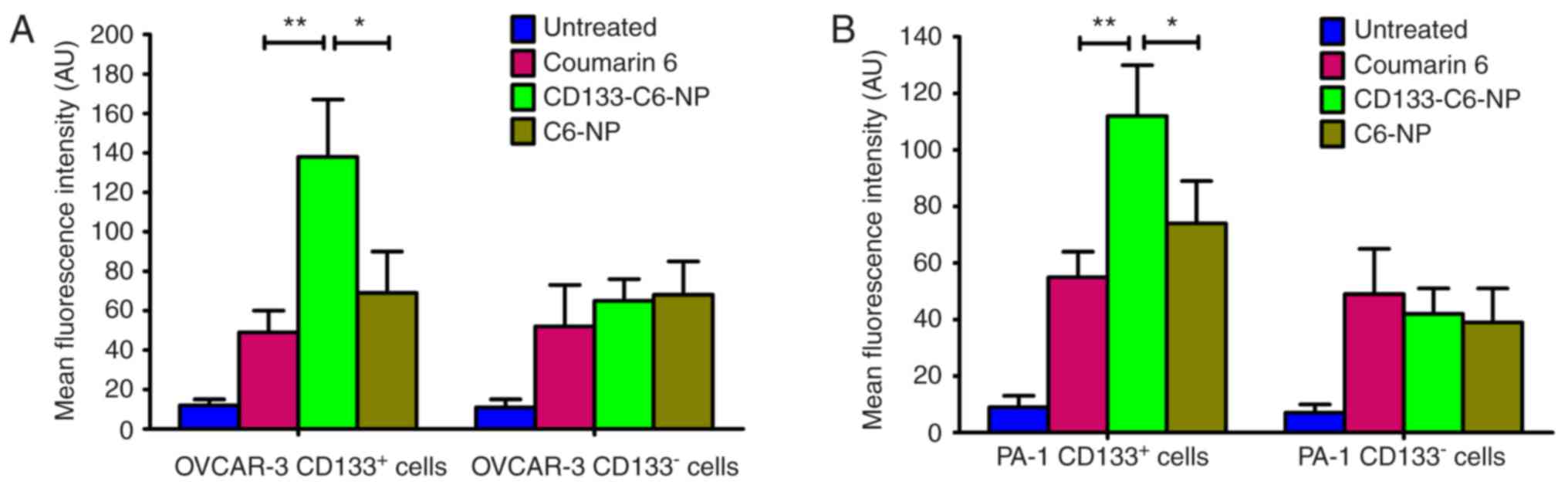
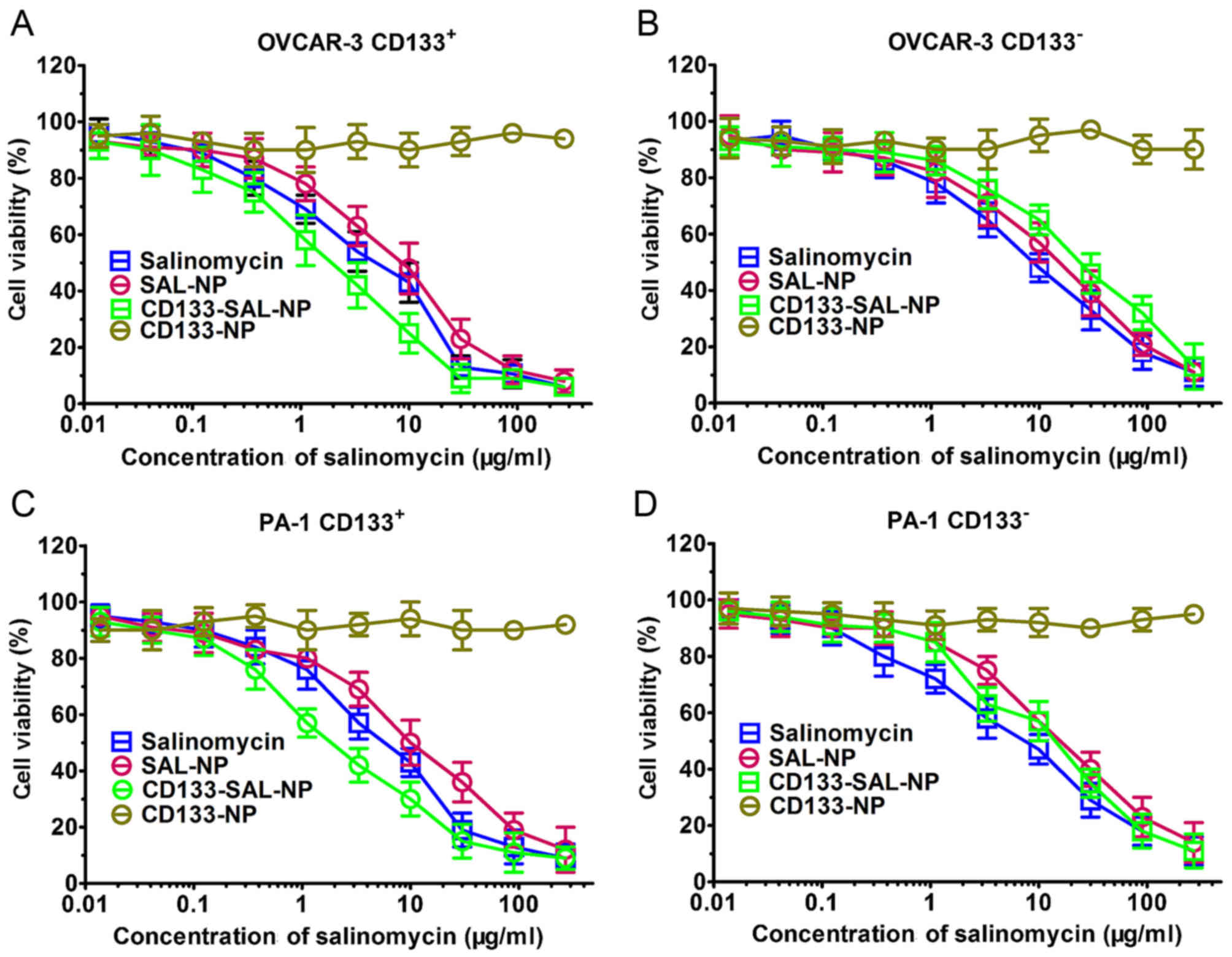
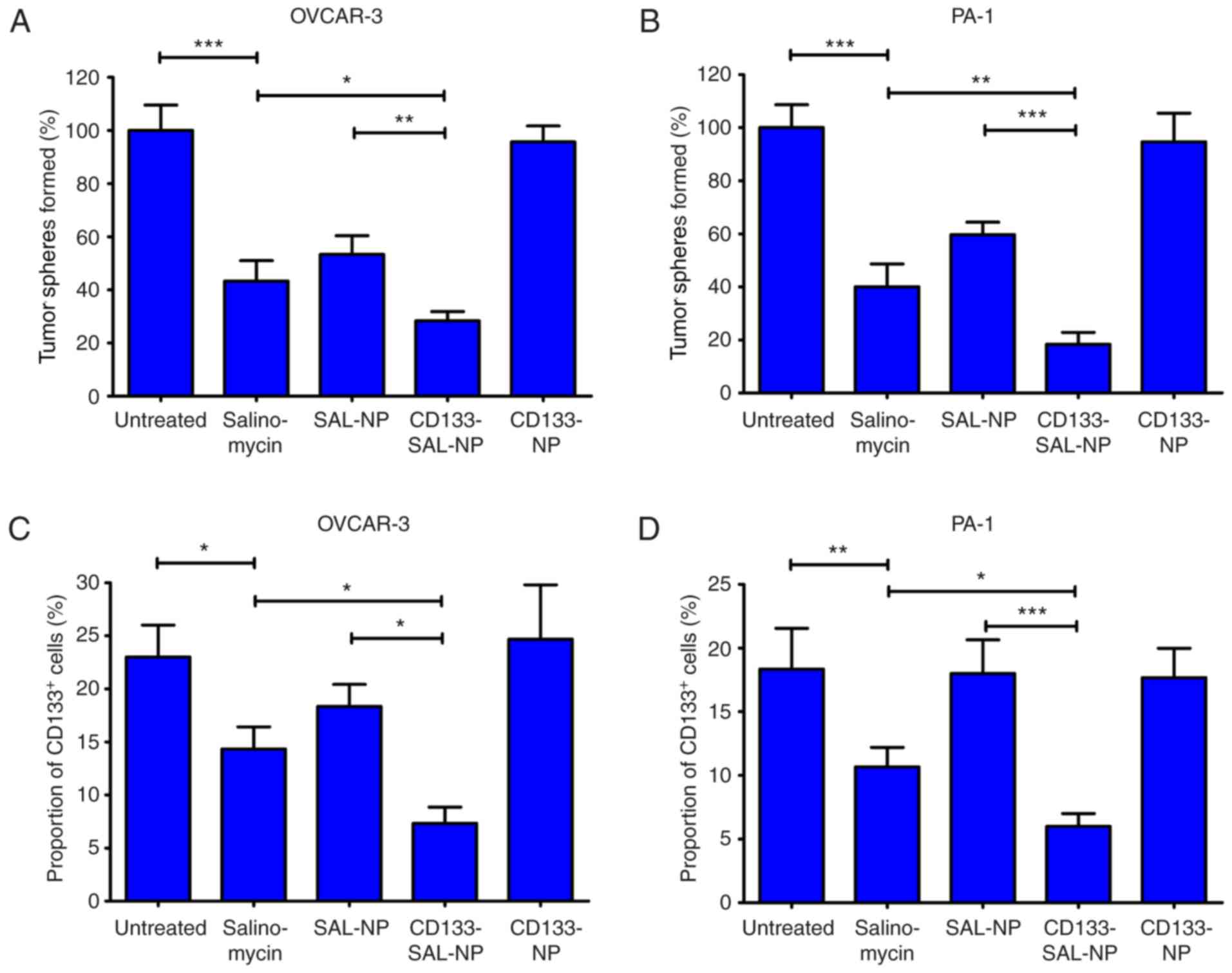
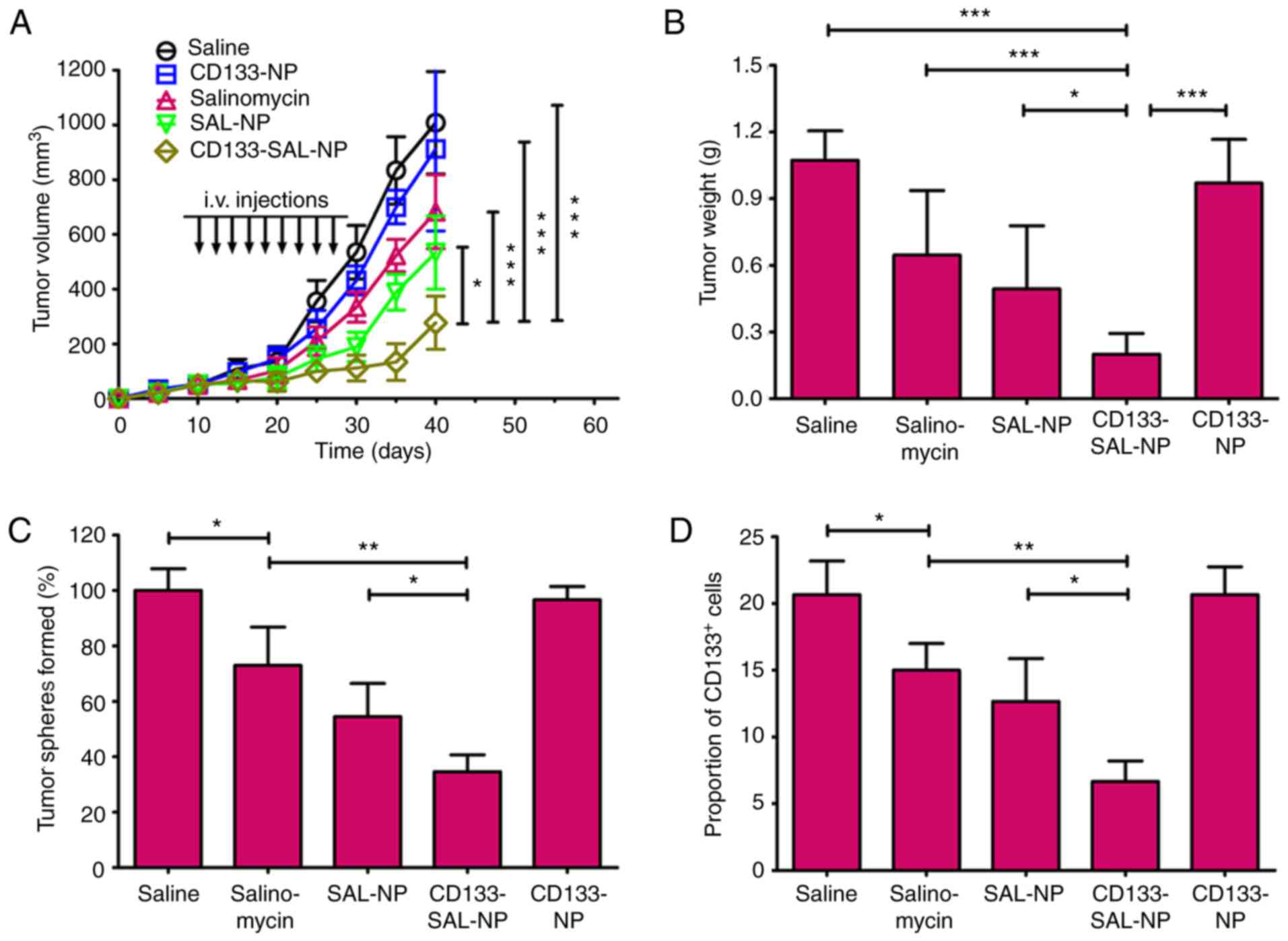
|
1
|
Baba T, Convery PA, Matsumura N, Whitaker
RS, Kondoh E, Perry T, Huang Z, Bentley RC, Mori S, Fujii S, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of CD133 and tumorigenicity of
CD133+ ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:209–218. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou BB, Zhang H, Damelin M, Geles KG,
Grindley JC and Dirks PB: Tumour-initiating cells: Challenges and
opportunities for anticancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:806–823. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeimet AG, Reimer D, Sopper S, Boesch M,
Martowicz A, Roessler J, Wiedemair AM, Rumpold H, Untergasser G,
Concin N, et al: Ovarian cancer stem cells. Neoplasma. 59:747–755.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siclari VA and Qin L: Targeting the
osteosarcoma cancer stem cell. J Orthop Surg Res. 5:782010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao J, Li W, Guo Y and Feng SS:
Nanomedicine strategies for sustained, controlled and targeted
treatment of cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:3261–3282.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xie FY, Xu WH, Yin C, Zhang GQ, Zhong YQ
and Gao J: Nanomedicine strategies for sustained, controlled, and
targeted treatment of cancer stem cells of the digestive system.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 8:735–744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shah MM and Landen CN: Ovarian cancer stem
cells: Are they real and why are they important? Gynecol Oncol.
132:483–489. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lupia M and Cavallaro U: Ovarian cancer
stem cells: Still an elusive entity? Mol Cancer. 16:642017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 21:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yue W, Hamaï A, Tonelli G, Bauvy C,
Nicolas V, Tharinger H, Codogno P and Mehrpour M: Inhibition of the
autophagic flux by salinomycin in breast cancer
stem-like/progenitor cells interferes with their maintenance.
Autophagy. 9:714–729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gong Z, Chen D, Xie F, Liu J, Zhang H, Zou
H, Yu Y, Chen Y, Sun Z, Wang X, et al: Codelivery of salinomycin
and doxorubicin using nanoliposomes for targeting both liver cancer
cells and cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:2565–2579.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xie F, Zhang S, Liu J, Gong Z, Yang K,
Zhang H, Lu Y, Zou H, Yu Y, Chen Y, et al: Codelivery of
salinomycin and chloroquine by liposomes enables synergistic
antitumor activity in vitro. Nanomedicine (Lond). 11:1831–1846.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang J, Zhang X
and Zhang Q: The eradication of breast cancer and cancer stem cells
using octreotide modified paclitaxel active targeting micelles and
salinomycin passive targeting micelles. Biomaterials. 33:679–691.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao P, Dong S, Bhattacharyya J and Chen
M: iTEP nanoparticle-delivered salinomycin displays an enhanced
toxicity to cancer stem cells in orthotopic breast tumors. Mol
Pharm. 11:2703–2712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo J, Gao X, Su L, Xia H, Gu G, Pang Z,
Jiang X, Yao L, Chen J and Chen H: Aptamer-functionalized PEG-PLGA
nanoparticles for enhanced anti-glioma drug delivery. Biomaterials.
32:8010–8020. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Gao J, Lu Y, Kou G, Zhang H, Fan
L, Sun Z, Guo Y and Zhong Y: Preparation and characterization of
PE38KDEL-loaded anti-HER2 nanoparticles for targeted cancer
therapy. J Control Release. 128:209–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Manjappa AS, Chaudhari KR, Venkataraju MP,
Dantuluri P, Nanda B, Sidda C, Sawant KK and Murthy RS: Antibody
derivatization and conjugation strategies: Application in
preparation of stealth immunoliposome to target chemotherapeutics
to tumor. J Control Release. 150:2–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao J, Liu W, Xia Y, Li W, Sun J, Chen H,
Li B, Zhang D, Qian W, Meng Y, et al: The promotion of siRNA
delivery to breast cancer overexpressing epidermal growth factor
receptor through anti-EGFR antibody conjugation by immunoliposomes.
Biomaterials. 32:3459–3470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao J, Sun J, Li H, Liu W, Zhang Y, Li B,
Qian W, Wang H, Chen J and Guo Y: Lyophilized HER2-specific
PEGylated immunoliposomes for active siRNA gene silencing.
Biomaterials. 31:2655–2664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagy I, Caelers A, Monge A, Bonabi S,
Huber AM and Bodmer D: NF-kappaB-dependent apoptotic hair cell
death in the auditory system. Audiol Neurotol. 12:209–220. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gao J, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Song J, Chen H, Li
W, Qian W, Deng L, Kou G, Chen J and Guo Y: EGFR-specific PEGylated
immunoliposomes for active siRNA delivery in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biomaterials. 33:270–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumari A, Yadav SK and Yadav SC:
Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems.
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 75:1–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Green MR, Manikhas GM, Orlov S, Afanasyev
B, Makhson AM, Bhar P and Hawkins MJ: Abraxane, a novel
Cremophor-free, albumin-bound particle form of paclitaxel for the
treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
17:1263–1268. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chumsri S and Burger AM: Cancer stem cell
targeted agents: Therapeutic approaches and consequences. Curr Opin
Mol Ther. 10:323–333. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao J, Chen H, Yu Y, Song J, Song H, Su X,
Li W, Tong X, Qian W, Wang H, et al: Inhibition of hepatocellular
carcinoma growth using immunoliposomes for co-delivery of
adriamycin and ribonucleotide reductase M2 siRNA. Biomaterials.
34:10084–10098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang CH, Chiou SH, Chou CP, Chen YC, Huang
YJ and Peng CA: Photothermolysis of glioblastoma stem-like cells
targeted by carbon nanotubes conjugated with CD133 monoclonal
antibody. Nanomedicine. 7:69–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shvedova AA and Kagan VE: The role of
nanotoxicology in realizing the ‘helping without harm’ paradigm of
nanomedicine: Lessons from studies of pulmonary effects of
single-walled carbon nanotubes. J Intern Med. 267:106–118. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells: Current status and evolving complexities. Cell Stem Cell.
10:717–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chaffer CL, Marjanovic ND, Lee T, Bell G,
Kleer CG, Reinhardt F, D'Alessio AC, Young RA and Weinberg RA:
Poised chromatin at the ZEB1 promoter enables breast cancer cell
plasticity and enhances tumorigenicity. Cell. 154:61–74. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|