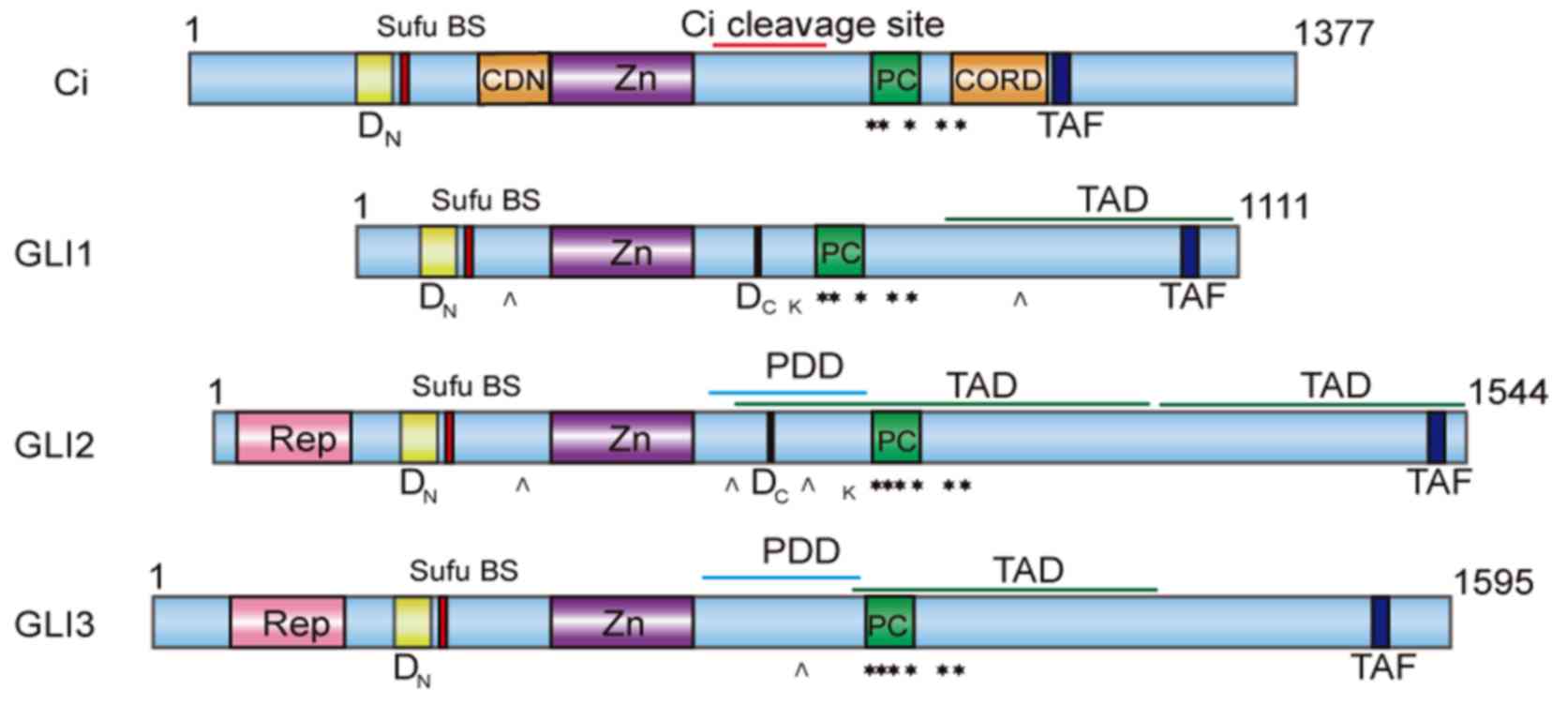
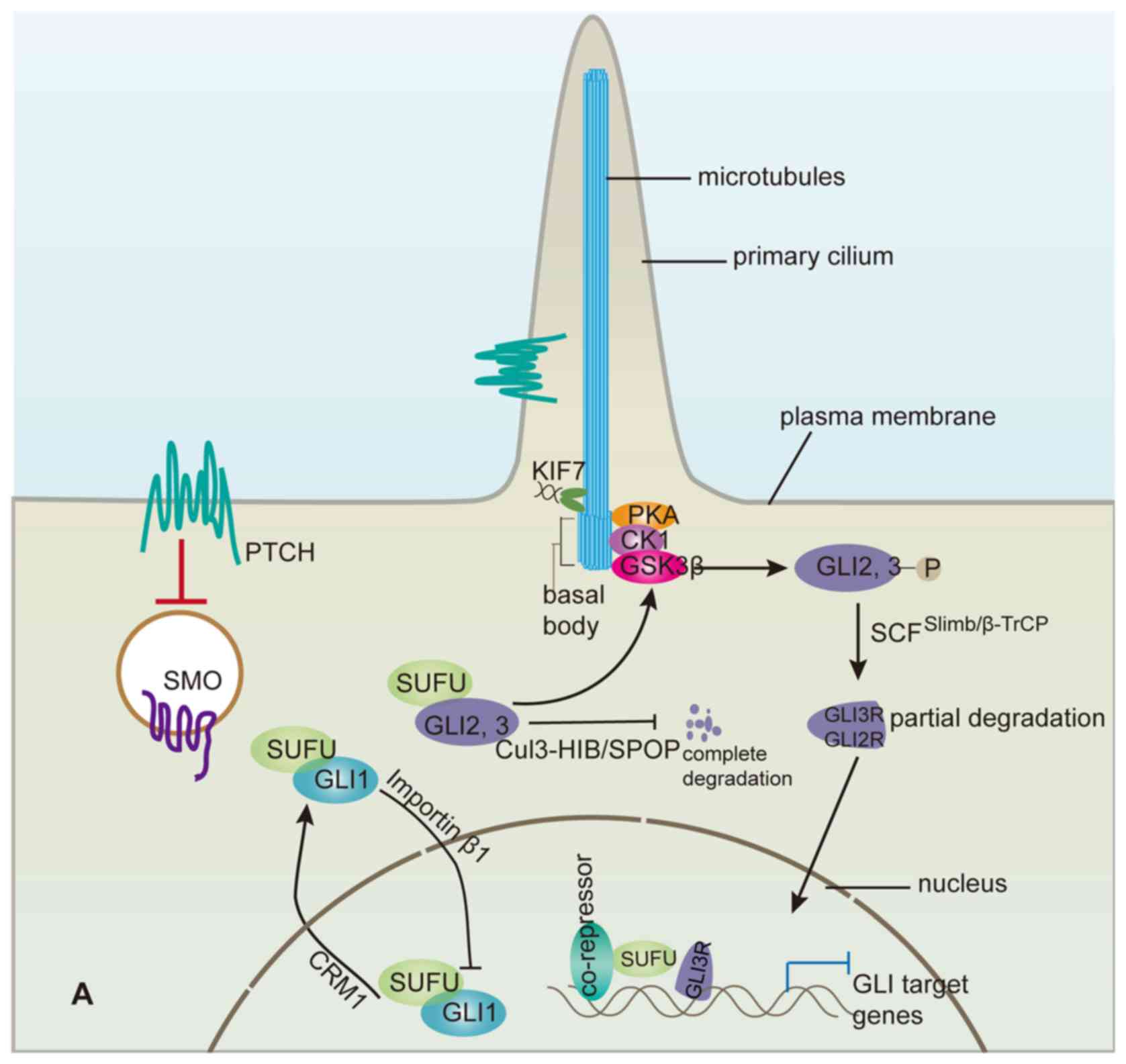
|
1
|
Nüsslein-Volhard C and Wieschaus E:
Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila.
Nature. 287:795–801. 1980. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Briscoe J and Thérond PP: The mechanisms
of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:416–429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ingham PW, Nakano Y and Seger C:
Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa.
Nat Rev Genet. 12:393–406. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich
LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM, Quinn AG, Myers RM, Cox DR, Epstein EH Jr
and Scott MP: Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the
basal cell nevus syndrome. Science. 272:1668–1671. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG,
Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A, Vorechovsky I, Holmberg E,
Unden AB, Gillies S, et al: Mutations of the human homolog of
Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
Cell. 85:841–851. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barakat MT, Humke EW and Scott MP:
Learning from Jekyll to control Hyde: Hedgehog signaling in
development and cancer. Trends Mol Med. 16:337–348. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Q, Gao G and Luo S: Hedgehog
signaling pathway and ovarian cancer. Chin J Cancer Res.
25:346–353. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zeng C, Wang Y, Lu Q, Chen J, Zhang J, Liu
T, Lv N and Luo S: SPOP suppresses tumorigenesis by regulating
Hedgehog/Gli2 signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 33:752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi C, Huang D, Lu N, Chen D, Zhang M, Yan
Y, Deng L, Lu Q, Lu H and Luo S: Aberrantly activated Gli2-KIF20A
axis is crucial for growth of hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts
poor prognosis. Oncotarget. 7:26206–26219. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin K, Lim A, Zhao C, Sahoo D, Pan Y,
Spiekerkoetter E, Liao JC and Beachy PA: Hedgehog signaling
restrains bladder cancer progression by eliciting stromal
production of urothelial differentiation factors. Cancer Cell.
26:521–533. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fei DL, Sanchez-Mejias A, Wang Z, Flaveny
C, Long J, Singh S, Rodriguez-Blanco J, Tokhunts R, Giambelli C,
Briegel KJ, et al: Hedgehog signaling regulates bladder cancer
growth and tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 72:4449–4458. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rimkus TK, Carpenter RL, Qasem S, Chan M
and Lo HW: Targeting the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway: Review
of smoothened and GLI inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 8:pii: E22.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hui CC and Angers S: Gli proteins in
development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:513–537. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Svärd J, Heby-Henricson K, Persson-Lek M,
Rozell B, Lauth M, Bergström A, Ericson J, Toftgård R and Teglund
S: Genetic elimination of suppressor of fused reveals an essential
repressor function in the mammalian hedgehog signaling pathway. Dev
Cell. 10:187–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Préat T: Characterization of suppressor of
fused, a complete suppressor of the fused segment polarity gene of
Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 132:725–736. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Babcock DT, Shi S, Jo J, Shaw M, Gutstein
HB and Galko MJ: Hedgehog signaling regulates nociceptive
sensitization. Curr Biol. 21:1525–1533. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teperino R, Amann S, Bayer M, McGee SL,
Loipetzberger A, Connor T, Jaeger C, Kammerer B, Winter L, Wiche G,
et al: Hedgehog partial agonism drives Warburg-like metabolism in
muscle and brown fat. Cell. 151:414–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teperino R, Aberger F, Esterbauer H, Riobo
N and Pospisilik JA: Canonical and non-canonical Hedgehog
signalling and the control of metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
33:81–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hooper JE: Distinct pathways for autocrine
and paracrine Wingless signalling in Drosophila embryos. Nature.
372:461–464. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pham A, Therond P, Alves G, Tournier FB,
Busson D, Lamour-Isnard C, Bouchon BL, Préat T and Tricoire H: The
suppressor of fused gene encodes a novel PEST protein involved in
Drosophila segment polarity establishment. Genetics. 140:587–598.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Monnier V, Dussillol F, Alves G,
Lamour-Isnard C and Plessis A: Suppressor of fused links fused and
Cubitus interruptus on the hedgehog signalling pathway. Curr Biol.
8:583–586. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Delattre M, Briand S, Paces-Fessy M and
Blanchet-Tournier MF: The Suppressor of fused gene, involved in
Hedgehog signal transduction in Drosophila, is conserved in
mammals. Dev Genes Evol. 209:294–300. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pearse RV II, Collier LS, Scott MP and
Tabin CJ: Vertebrate homologs of Drosophila suppressor of fused
interact with the gli family of transcriptional regulators. Dev
Biol. 212:323–336. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ding Q, Fukami Si, Meng X, Nishizaki Y,
Zhang X, Sasaki H, Dlugosz A, Nakafuku M and Hui Cc: Mouse
suppressor of fused is a negative regulator of sonic hedgehog
signaling and alters the subcellular distribution of Gli1. Curr
Biol. 9:1119–1122. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Simon-Chazottes D, Paces-Fessy M,
Lamour-Isnard C, Guénet JL and Blanchet-Tournier MF: Genomic
organization, chromosomal assignment, and expression analysis of
the mouse suppressor of fused gene (Sufu) coding a Gli protein
partner. Mamm Genome. 11:614–621. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stone DM, Murone M, Luoh S, Ye W, Armanini
MP, Gurney A, Phillips H, Brush J, Goddard A, de Sauvage FJ and
Rosenthal A: Characterization of the human suppressor of fused, a
negative regulator of the zinc-finger transcription factor Gli. J
Cell Sci. 112:4437–4448. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rasheed BK, McLendon RE, Friedman HS,
Friedman AH, Fuchs HE, Bigner DD and Bigner SH: Chromosome 10
deletion mapping in human gliomas: A common deletion region in
10q25. Oncogene. 10:2243–2246. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gray IC, Phillips SM, Lee SJ, Neoptolemos
JP, Weissenbach J and Spurr NK: Loss of the chromosomal region
10q23-25 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 55:4800–4803.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cherry AL, Finta C, Karlström M, Jin Q,
Schwend T, Astorga-Wells J, Zubarev RA, Del Campo M, Criswell AR,
de Sanctis D, et al: Structural basis of SUFU-GLI interaction in
human Hedgehog signalling regulation. Acta Crystallogr D Biol
Crystallogr. 69:2563–2579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Fu L, Qi X, Zhang Z, Xia Y, Jia
J, Jiang J, Zhao Y and Wu G: Structural insight into the mutual
recognition and regulation between Suppressor of Fused and Gli/Ci.
Nat Commun. 4:26082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee Y, Kawagoe R, Sasai K, Li Y, Russell
HR, Curran T and McKinnon PJ: Loss of suppressor-of-fused function
promotes tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 26:6442–6447. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ogino S, Gulley ML, den Dunnen JT and
Wilson RB: Association for Molecular Patholpogy Training and
Education Committtee: Standard mutation nomenclature in molecular
diagnostics: Practical and educational challenges. J Mol Diagn.
9:1–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brugières L, Remenieras A, Pierron G,
Varlet P, Forget S, Byrde V, Bombled J, Puget S, Caron O, Dufour C,
et al: High frequency of germline SUFU mutations in children with
desmoplastic/nodular medulloblastoma younger than 3 years of age. J
Clin Oncol. 30:2087–2093. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ng D, Stavrou T, Liu L, Taylor MD, Gold B,
Dean M, Kelley MJ, Dubovsky EC, Vezina G, Nicholson HS, et al:
Retrospective family study of childhood medulloblastoma. Am J Med
Genet A. 134:399–403. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Taylor MD, Liu L, Raffel C, Hui CC,
Mainprize TG, Zhang X, Agatep R, Chiappa S, Gao L, Lowrance A, et
al: Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma. Nat Genet.
31:306–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Smith MJ, Beetz C, Williams SG, Bhaskar
SS, O'Sullivan J, Anderson B, Daly SB, Urquhart JE, Bholah Z, Oudit
D, et al: Germline mutations in SUFU cause Gorlin
syndrome-associated childhood medulloblastoma and redefine the risk
associated with PTCH1 mutations. J Clin Oncol. 32:4155–4161. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Slade I, Murray A, Hanks S, Kumar A,
Walker L, Hargrave D, Douglas J, Stiller C, Izatt L and Rahman N:
Heterogeneity of familial medulloblastoma and contribution of
germline PTCH1 and SUFU mutations to sporadic medulloblastoma. Fam
Cancer. 10:337–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brugières L, Pierron G, Chompret A,
Paillerets BB, Di Rocco F, Varlet P, Pierre-Kahn A, Caron O, Grill
J and Delattre O: Incomplete penetrance of the predisposition to
medulloblastoma associated with germ-line SUFU mutations. J Med
Genet. 47:142–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Heby-Henricson K, Bergström A, Rozell B,
Toftgård R and Teglund S: Loss of Trp53 promotes medulloblastoma
development but not skin tumorigenesis in Sufu heterozygous mutant
mice. Mol Carcinog. 51:754–760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Svärd J, Rozell B, Toftgård R and Teglund
S: Tumor suppressor gene co-operativity in compound Patched1 and
suppressor of fused heterozygous mutant mice. Mol Carcinog.
48:408–419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Koch A, Waha A, Hartmann W, Milde U,
Goodyer CG, Sörensen N, Berthold F, Digon-Söntgerath B, Krätzschmar
J, Wiestler OD and Pietsch T: No evidence for mutations or altered
expression of the Suppressor of Fused gene (SUFU) in primitive
neuroectodermal tumours. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 30:532–539.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scott DK, Straughton D, Cole M, Bailey S,
Ellison DW and Clifford SC: Identification and analysis of tumor
suppressor loci at chromosome 10q23.3-10q25.3 in medulloblastoma.
Cell Cycle. 5:2381–2389. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zabidi MA and Stark A: Regulatory
enhancer-core-promoter communication via transcription factors and
cofactors. Trends Genet. 32:801–814. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Spurrell CH, Dickel DE and Visel A: The
ties that bind: Mapping the dynamic enhancer-promoter interactome.
Cell. 167:1163–1166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aavikko M, Li SP, Saarinen S, Alhopuro P,
Kaasinen E, Morgunova E, Li Y, Vesanen K, Smith MJ, Evans DG, et
al: Loss of SUFU function in familial multiple meningioma. Am J Hum
Genet. 91:520–526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lim CB, Prêle CM, Cheah HM, Cheng YY,
Klebe S, Reid G, Watkins DN, Baltic S, Thompson PJ and Mutsaers SE:
Mutational analysis of hedgehog signaling pathway genes in human
malignant mesothelioma. PLoS One. 8:e666852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tostar U, Malm CJ, Meis-Kindblom JM,
Kindblom LG, Toftgård R and Undén AB: Deregulation of the hedgehog
signalling pathway: A possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in
human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Pathol.
208:17–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yin WC, Li ZJ and Hui CC: BCC or not: Sufu
keeps it in check. Oncoscience. 2:77–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schulman JM, Oh DH, Sanborn JZ, Pincus L,
McCalmont TH and Cho RJ: Multiple hereditary infundibulocystic
basal cell carcinoma syndrome associated with a germline SUFU
mutation. JAMA Dermatol. 152:323–327. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Reifenberger J, Wolter M, Knobbe CB,
Köhler B, Schönicke A, Scharwächter C, Kumar K, Blaschke B, Ruzicka
T and Reifenberger G: Somatic mutations in the PTCH, SMOH, SUFUH
and TP53 genes in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Br J Dermatol.
152:43–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mann K, Magee J, Guillaud-Bataille M,
Blondel C, Bressac-de Paillerets B, Yeatman J and Winship I:
Multiple skin hamartomata: A possible novel clinical presentation
of SUFU neoplasia syndrome. Fam Cancer. 14:151–155. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sheng T, Li C, Zhang X, Chi S, He N, Chen
K, McCormick F, Gatalica Z and Xie J: Activation of the hedgehog
pathway in advanced prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 3:292004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pastorino L, Ghiorzo P, Nasti S,
Battistuzzi L, Cusano R, Marzocchi C, Garrè ML, Clementi M and
Scarrà GB: Identification of a SUFU germline mutation in a family
with Gorlin syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 149A:1539–1543. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ruel L and Thérond PP: Variations in
Hedgehog signaling: Divergence and perpetuation in Sufu regulation
of Gli. Genes Dev. 23:1843–1848. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
McDermott A, Gustafsson M, Elsam T, Hui
CC, Emerson CP Jr and Borycki AG: Gli2 and Gli3 have redundant and
context-dependent function in skeletal muscle formation.
Development. 132:345–357. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Pan Y, Wang C and Wang B: Phosphorylation
of Gli2 by protein kinase A is required for Gli2 processing and
degradation and the Sonic Hedgehog-regulated mouse development. Dev
Biol. 326:177–189. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Goetz SC and Anderson KV: The primary
cilium: A signalling centre during vertebrate development. Nat Rev
Genet. 11:331–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wen X, Lai CK, Evangelista M, Hongo JA, de
Sauvage FJ and Scales SJ: Kinetics of hedgehog-dependent
full-length Gli3 accumulation in primary cilia and subsequent
degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 30:1910–1922. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Endoh-Yamagami S, Evangelista M, Wilson D,
Wen X, Theunissen JW, Phamluong K, Davis M, Scales SJ, Solloway MJ,
de Sauvage FJ and Peterson AS: The mammalian Cos2 homolog Kif7
plays an essential role in modulating Hh signal transduction during
development. Curr Biol. 19:1320–1326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cheung HO, Zhang X, Ribeiro A, Mo R,
Makino S, Puviindran V, Law KK, Briscoe J and Hui CC: The kinesin
protein Kif7 is a critical regulator of Gli transcription factors
in mammalian hedgehog signaling. Sci Signal. 2:ra292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu X, Wang X, Du W, Chen L, Wang G, Cui
Y, Liu Y, Dou Z, Wang H, Zhang P, et al: Suppressor of fused (Sufu)
represses Gli1 transcription and nuclear accumulation, inhibits
glioma cell proliferation, invasion and vasculogenic mimicry,
improving glioma chemo-sensitivity and prognosis. Oncotarget.
5:11681–11694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Szczepny A, Wagstaff KM, Dias M, Gajewska
K, Wang C, Davies RG, Kaur G, Ly-Huynh J, Loveland KL and Jans DA:
Overlapping binding sites for importin b1 and suppressor of fused
(SuFu) on glioma-associated oncogene homologue 1 (Gli1) regulate
its nuclear localization. Biochem J. 461:469–476. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shi Q, Han Y and Jiang J: Suppressor of
fused impedes Ci/Gli nuclear import by opposing Trn/Kapb2 in
Hedgehog signaling. J Cell Sci. 127:1092–1103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Han Y, Shi Q and Jiang J: Multisite
interaction with Sufu regulates Ci/Gli activity through distinct
mechanisms in Hh signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:6383–6388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang C, Pan Y and Wang B: Suppressor of
fused and Spop regulate the stability, processing and function of
Gli2 and Gli3 full-length activators but not their repressors.
Development. 137:2001–2009. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tempé D, Casas M, Karaz S,
Blanchet-Tournier MF and Concordet JP: Multisite protein kinase A
and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta phosphorylation leads to Gli3
ubiquitination by SCFbetaTrCP. Mol Cell Biol. 26:4316–4326. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang B and Li Y: Evidence for the direct
involvement of {beta}TrCP in Gli3 protein processing. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:33–38. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pan Y, Bai CB, Joyner AL and Wang B: Sonic
hedgehog signaling regulates Gli2 transcriptional activity by
suppressing its processing and degradation. Mol Cell Biol.
26:3365–3377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang B, Fallon JF and Beachy PA:
Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an
anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate
limb. Cell. 100:423–434. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tukachinsky H, Lopez LV and Salic A: A
mechanism for vertebrate Hedgehog signaling: Recruitment to cilia
and dissociation of SuFu-Gli protein complexes. J Cell Biol.
191:415–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yue S, Chen Y and Cheng SY: Hedgehog
signaling promotes the degradation of tumor suppressor Sufu through
the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Oncogene. 28:492–499. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Raducu M, Fung E, Serres S, Infante P,
Barberis A, Fischer R, Bristow C, Thézénas ML, Finta C,
Christianson JC, et al: SCF (Fbxl17) ubiquitylation of Sufu
regulates Hedgehog signaling and medulloblastoma development. EMBO
J. 35:1400–1416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang Z, Shen L, Law K, Zhang Z, Liu X,
Hua H, Li S, Huang H, Yue S, Hui CC and Cheng SY: Suppressor of
fused chaperones Gli proteins to generate transcriptional responses
to sonic hedgehog signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 37:pii: e00421. –16.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Santos N and Reiter JF: A central region
of Gli2 regulates its localization to the primary cilium and
transcriptional activity. J Cell Sci. 127:1500–1510. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li BI, Matteson PG, Ababon MF, Nato AQ Jr,
Lin Y, Nanda V, Matise TC and Millonig JH: The orphan GPCR, Gpr161,
regulates the retinoic acid and canonical Wnt pathways during
neurulation. Dev Biol. 402:17–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pal K, Hwang SH, Somatilaka B, Badgandi H,
Jackson PK, DeFea K and Mukhopadhyay S: Smoothened determines
b-arrestin-mediated removal of the G protein-coupled receptor
Gpr161 from the primary cilium. J Cell Biol. 212:861–875. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Blair HJ, Tompson S, Liu YN, Campbell J,
MacArthur K, Ponting CP, Ruiz-Perez VL and Goodship JA: Evc2 is a
positive modulator of Hedgehog signalling that interacts with Evc
at the cilia membrane and is also found in the nucleus. BMC Biol.
9:142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yang C, Chen W, Chen Y and Jiang J:
Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by forming a complex with
Evc/Evc2. Cell Res. 22:1593–1604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Caparrós-Martín JA, Valencia M, Reytor E,
Pacheco M, Fernandez M, Perez-Aytes A, Gean E, Lapunzina P, Peters
H, Goodship JA and Ruiz-Perez VL: The ciliary Evc/Evc2 complex
interacts with Smo and controls Hedgehog pathway activity in
chondrocytes by regulating Sufu/Gli3 dissociation and Gli3
trafficking in primary cilia. Hum Mol Genet. 22:124–139. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jia J, Kolterud A, Zeng H, Hoover A,
Teglund S, Toftgård R and Liu A: Suppressor of Fused inhibits
mammalian Hedgehog signaling in the absence of cilia. Dev Biol.
330:452–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zeng H, Jia J and Liu A: Coordinated
translocation of mammalian Gli proteins and suppressor of fused to
the primary cilium. PLoS One. 5:e159002010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chen MH, Wilson CW, Li YJ, Law KK, Lu CS,
Gacayan R, Zhang X, Hui CC and Chuang PT: Cilium-independent
regulation of Gli protein function by Sufu in Hedgehog signaling is
evolutionarily conserved. Genes Dev. 23:1910–1928. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ohlmeyer JT and Kalderon D: Hedgehog
stimulates maturation of Cubitus interruptus into a labile
transcriptional activator. Nature. 396:749–753. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Paces-Fessy M, Boucher D, Petit E,
Paute-Briand S and Blanchet-Tournier MF: The negative regulator of
Gli, Suppressor of fused (Sufu), interacts with SAP18, Galectin3
and other nuclear proteins. Biochem J. 378:353–362. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cheng SY and Bishop JM: Suppressor of
Fused represses Gli-mediated transcription by recruiting the
SAP18-mSin3 corepressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:5442–5447. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lin C, Yao E, Wang K, Nozawa Y, Shimizu H,
Johnson JR, Chen JN, Krogan NJ and Chuang PT: Regulation of Sufu
activity by p66b and Mycbp provides new insight into vertebrate
Hedgehog signaling. Genes Dev. 28:2547–2563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Barnfield PC, Zhang X, Thanabalasingham V,
Yoshida M and Hui CC: Negative regulation of Gli1 and Gli2
activator function by Suppressor of fused through multiple
mechanisms. Differentiation. 73:397–405. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kogerman P, Grimm T, Kogerman L, Krause D,
Undén AB, Sandstedt B, Toftgård R and Zaphiropoulos PG: Mammalian
suppressor-of-fused modulates nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of
Gli-1. Nat Cell Biol. 1:312–319. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ruiz i Altaba A, Sánchez P and Dahmane N:
Gli and hedgehog in cancer: Tumours, embryos and stem cells. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:361–372. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Humke EW, Dorn KV, Milenkovic L, Scott MP
and Rohatgi R: The output of Hedgehog signaling is controlled by
the dynamic association between Suppressor of Fused and the Gli
proteins. Genes Dev. 24:670–682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Merchant M, Vajdos FF, Ultsch M, Maun HR,
Wendt U, Cannon J, Desmarais W, Lazarus RA, de Vos AM and de
Sauvage FJ: Suppressor of fused regulates Gli activity through a
dual binding mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 24:8627–8641. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Dunaeva M, Michelson P, Kogerman P and
Toftgard R: Characterization of the physical interaction of Gli
proteins with SUFU proteins. J Biol Chem. 278:5116–5122. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chen Y, Yue S, Xie L, Pu XH, Jin T and
Cheng SY: Dual Phosphorylation of suppressor of fused (Sufu) by PKA
and GSK3beta regulates its stability and localization in the
primary cilium. J Biol Chem. 286:13502–13511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Hu G, Huang X, Rao H, Xiong
X, Luo Z, Lu Q and Luo S: Nek2A phosphorylates and stabilizes SuFu:
A new strategy of Gli2/Hedgehog signaling regulatory mechanism.
Cell Signal. 28:1304–1313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhou F, Huang D, Li Y, Hu G, Rao H, Lu Q,
Luo S and Wang Y: Nek2A/SuFu feedback loop regulates Gli-mediated
Hedgehog signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 50:373–380. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liu C, Zhou Z, Yao X, Chen P, Sun M, Su M,
Chang C, Yan J, Jiang J and Zhang Q: Hedgehog signaling
downregulates suppressor of fused through the HIB/SPOP-Crn axis in
Drosophila. Cell Res. 24:595–609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH and Yang BB:
MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis
by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:20350–20355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Long H, Wang Z, Chen J, Xiang T, Li Q,
Diao X and Zhu B: microRNA-214 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting the
suppressor-of-fused protein (Sufu). Oncotarget. 6:38705–38718.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Peng RQ, Wan HY, Li HF, Liu M, Li X and
Tang H: MicroRNA-214 suppresses growth and invasiveness of cervical
cancer cells by targeting
UDP-N-acetyl-a-D-galactosamine:polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7. J Biol Chem. 287:14301–14309.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Browne G, Dragon JA, Hong D, Messier TL,
Gordon JA, Farina NH, Boyd JR, VanOudenhove JJ, Perez AW, Zaidi SK,
et al: MicroRNA-378-mediated suppression of Runx1 alleviates the
aggressive phenotype of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 human breast
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:8825–8839. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Min TH, Kriebel M, Hou S and Pera EM: The
dual regulator Sufu integrates Hedgehog and Wnt signals in the
early Xenopus embryo. Dev Biol. 358:262–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Peng Y, Zhang X, Ma Q, Yan R, Qin Y, Zhao
Y, Cheng Y, Yang M, Wang Q, Feng X, et al: MiRNA-194 activates the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer by targeting the
negative Wnt regulator, SUFU. Cancer Lett. 385:117–127. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bari R, Hartford C, Chan WK, Vong Q, Li Y,
Gan K, Zhou Y, Cheng C, Kang G, Shurtleff S, et al: Genome-wide
single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis revealed SUFU suppression
of acute graft-versus-host disease through downregulation of HLA-DR
expression in recipient dendritic cells. Sci Rep. 5:110982015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
D'Amico D, Antonucci L, Di Magno L, Coni
S, Sdruscia G, Macone A, Miele E, Infante P, Di Marcotullio L, De
Smaele E, et al: Non-canonical Hedgehog/AMPK-mediated control of
polyamine metabolism supports neuronal and medulloblastoma cell
growth. Dev Cell. 35:21–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|