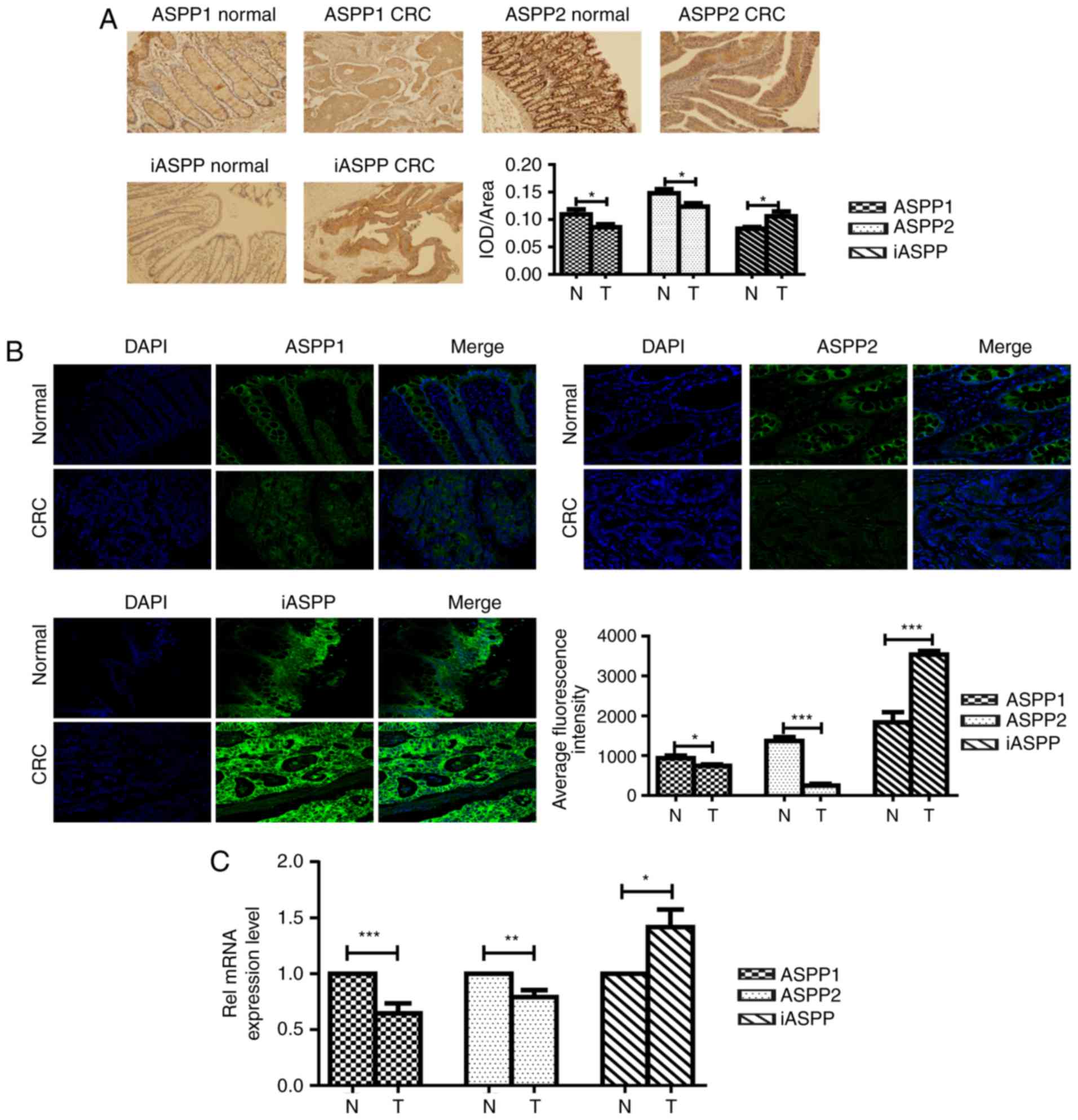
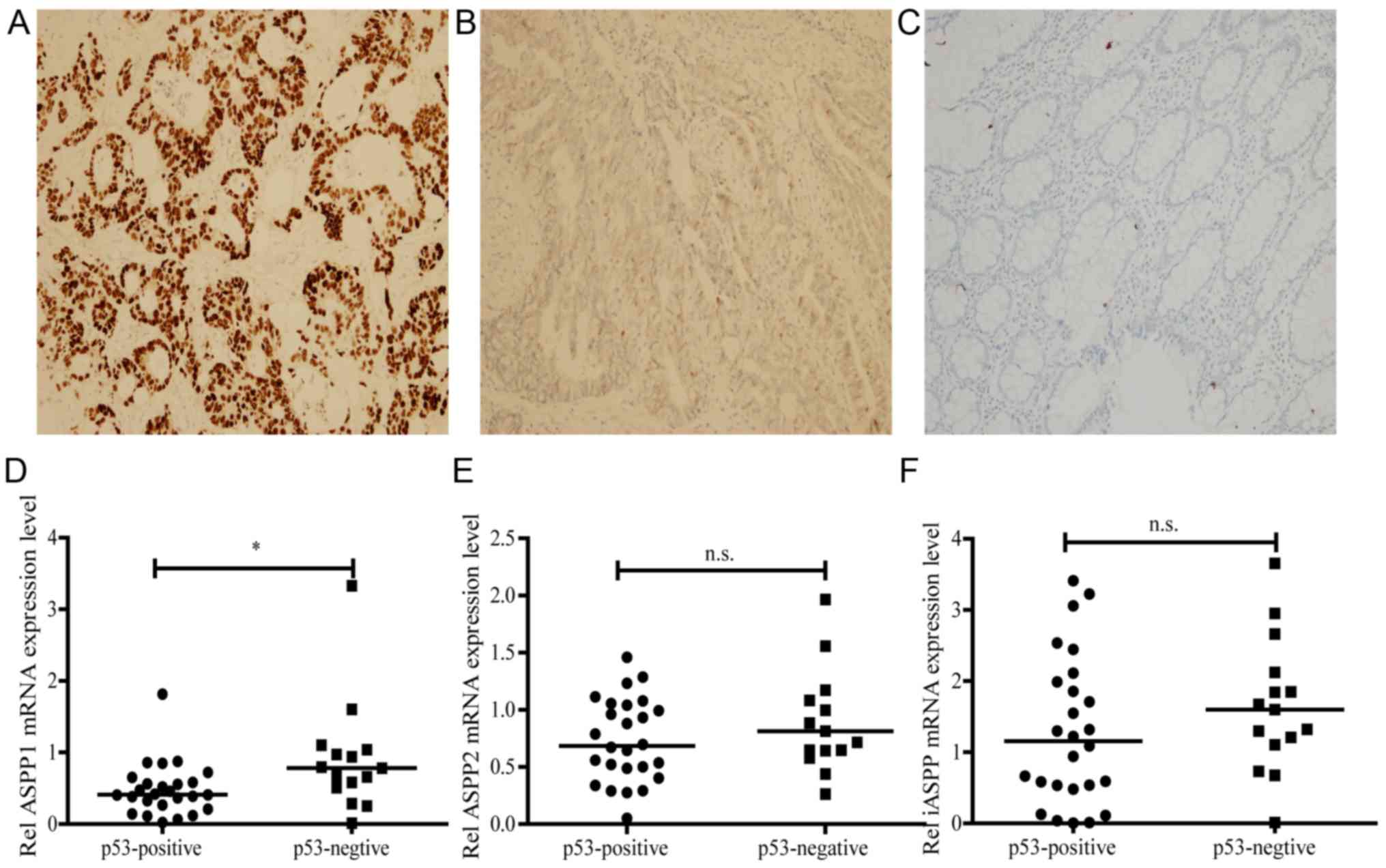
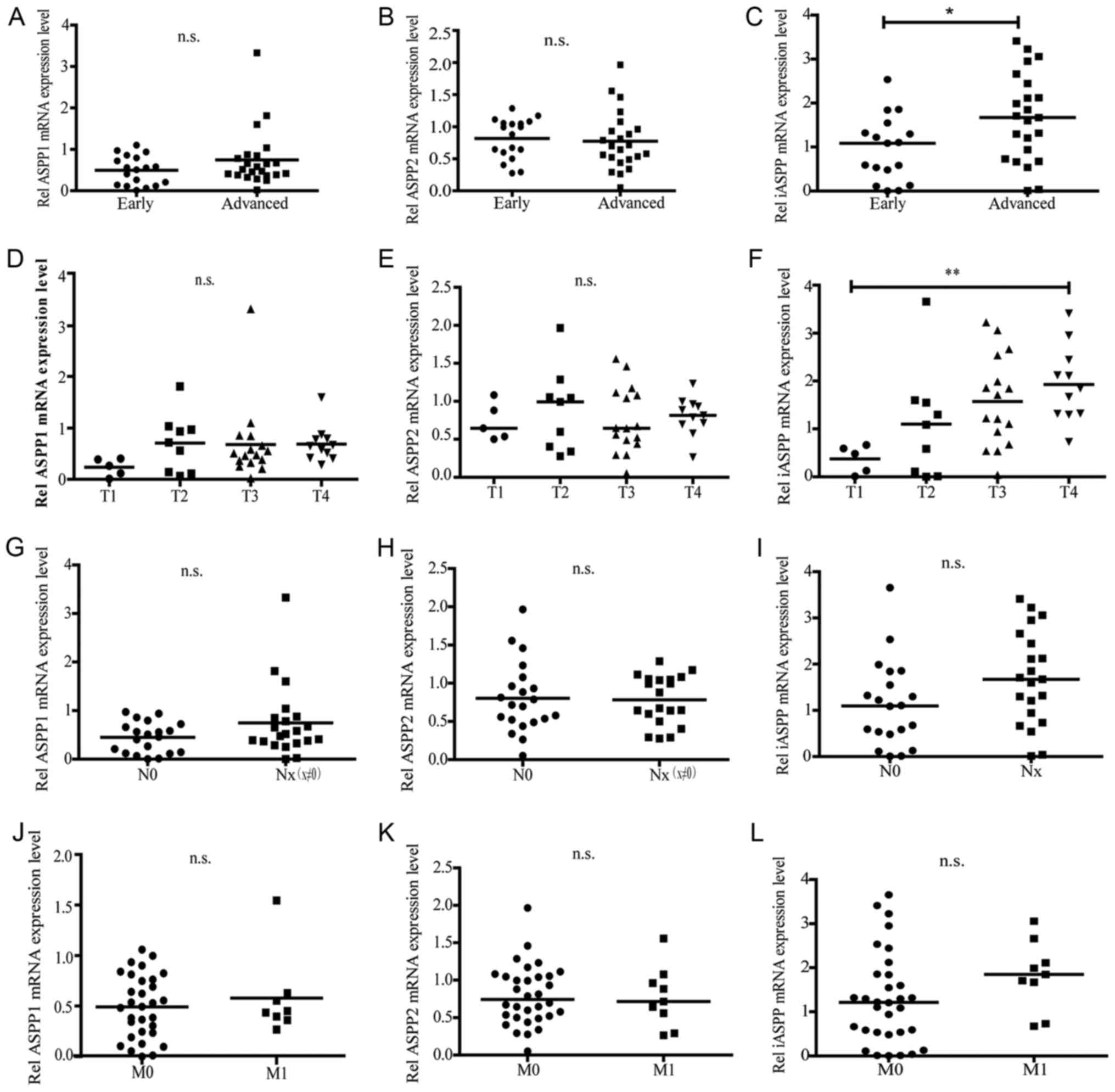
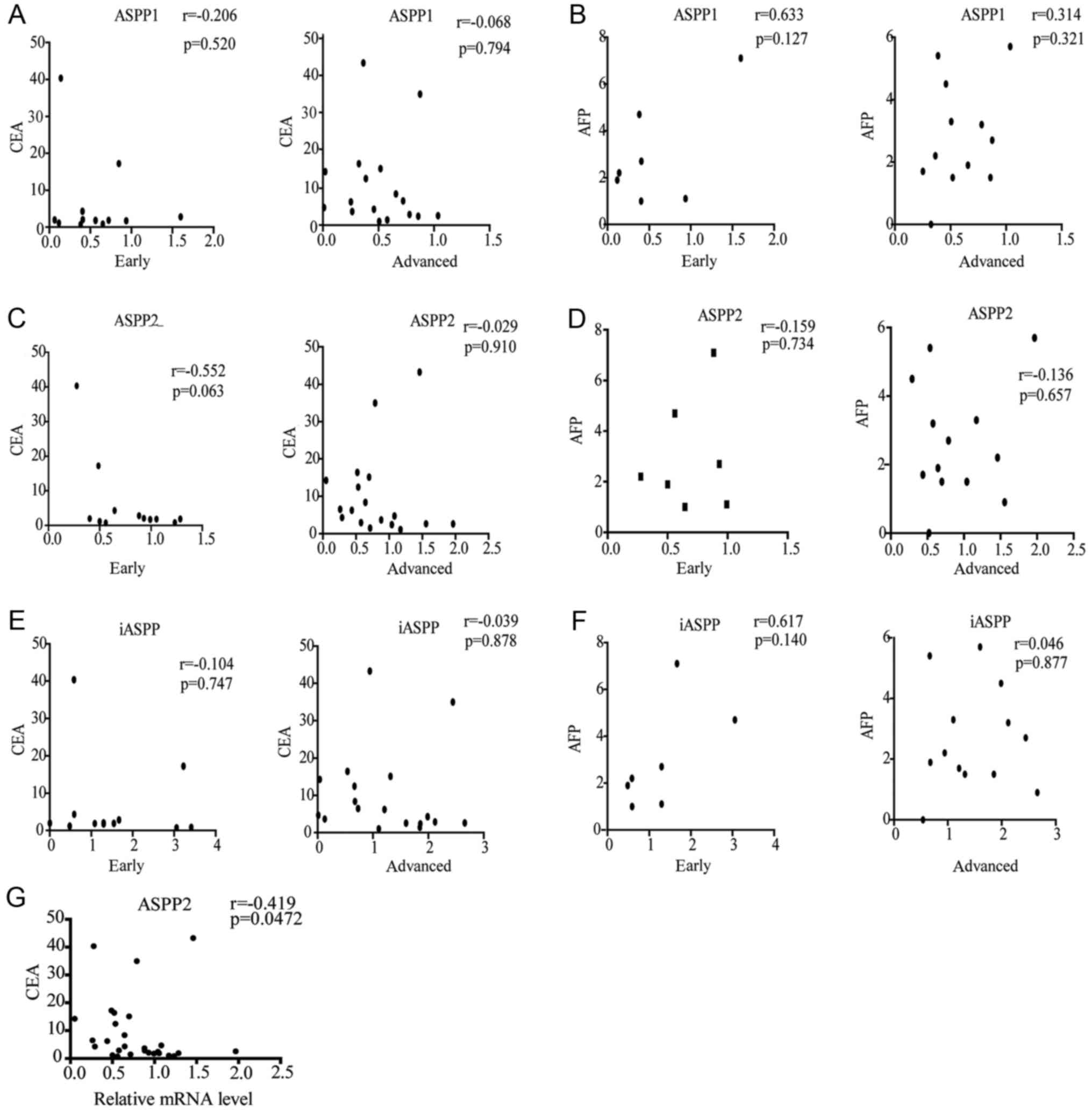
|
1
|
Haggar FA and Boushey RP: Colorectal
cancer epidemiology: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk
factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 22:191–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shah TA: Colonic cancer; presentation and
management in a surgical unit at allied hospital faisalabad. Prof
Med J. 23:251–256. 2016.
|
|
3
|
Croce CM: Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J
Med. 358:502–511. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Trigiante G and Lu X: ASPP [corrected] and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:217–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chao C, Saito S, Kang J, Anderson CW,
Appella E and Xu Y: p53 transcriptional activity is essential for
p53-dependent apoptosis following DNA damage. EMBO J. 19:4967–4975.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vousden KH and Lu X: Live or let die: The
cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:594–604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and
Harris CC: p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 253:49–53.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Starks AM, Martin DN, Dorsey TH, Boersma
BJ, Wallace TA and Ambs S: Household income is associated with the
p53 mutation frequency in human breast tumors. PLoS One.
8:e573612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soussi T, Kato S, Levy PP and Ishioka C:
Reassessment of the TP53 mutation database in human disease by data
mining with a library of TP53 missense mutations. Hum Mutat.
25:6–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ and Bond GL:
The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 7:979–987. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi Y, Han Y, Xie F, Wang A, Feng X, Li N,
Guo H and Chen D: ASPP2 enhances oxaliplatin (L-OHP)-induced
colorectal cancer cell apoptosis in a p53-independent manner by
inhibiting cell autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 19:535–543. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mak VC, Lee L, Siu MK, Wong OG, Lu X, Ngan
HY, Wong ES and Cheung AN: Downregulation of ASPP2 in
choriocarcinoma contributes to increased migratory potential
through Src signaling pathway activation. Carcinogenesis.
34:2170–2177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schittenhelm MM, Illing B, Ahmut F, Rasp
KH, Blumenstock G, Döhner K, Lopez CD and Kampa-Schittenhelm KM:
Attenuated expression of apoptosis stimulating protein of p53-2
(ASPP2) in human acute leukemia is associated with therapy failure.
PLoS One. 8:e801932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song B, Bian Q, Zhang YJ, Shao CH, Li G,
Liu AA, Jing W, Liu R, Zhou YQ, Jin G and Hu XG: Downregulation of
ASPP2 in pancreatic cancer cells contributes to increased
resistance to gemcitabine through autophagy activation. Mol Cancer.
14:1772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meng WD, Chu RX, Wang BZ, Wang LP, Ma LL
and Wang LX: Infection à Helicobacter pylori et les expressions de
l'apoptose liée à p53, PAES et PPEEE dans le cancer gastrique et
des lésions précancéreuses. Pathol Biol. 61:199–202. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Shi G, Yuan H, Zhou T, Zhang Q, Zhu
H and Wang X: Abnormal expression pattern of the ASPP family of
proteins in human non-small cell lung cancer and regulatory
functions on apoptosis through p53 by iASPP. Oncol Rep. 28:133–140.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mori T, Okamoto H, Takahashi N, Ueda R and
Okamoto T: Aberrant overexpression of 53BP2 mRNA in lung cancer
cell lines. FEBS Lett. 465:124–128. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lossos IS, Natkunam Y, Levy R and Lopez
CD: Apoptosis stimulating protein of p53 (ASPP2) expression differs
in diffuse large B-cell and follicular center lymphoma: Correlation
with clinical outcome. Leuk Lymphoma. 43:2309–2317. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu B, Guo H, Zhao J, Wang C, Wu G, Pang M,
Tong X, Bu F, Liang A, Hou S, et al: Increased expression of iASPP,
regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein-mediated NF-κB activation,
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 139:2183–2194.e5.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim KH, Yang SS, Yoon YS, Lim SB, Yu CS
and Kim JC: Validation of the seventh edition of the American joint
committee on cancer tumor-node-metastasis (AJCC TNM) staging in
patients with stage II and stage III colorectal carcinoma: Analysis
of 2511 cases from a medical centre in Korea. Colorectal Dis.
13:e220–e226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sgroi DC, Teng S, Robinson G, LeVangie R,
Hudson JR Jr and Elkahloun AG: In vivo gene expression profile
analysis of human breast cancer progression. Cancer Res.
59:5656–5661. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anzai H, Kazama S, Kiyomatsu T, Nishikawa
T, Tanaka T, Tanaka J, Hata K, Kawai K, Yamaguchi H, Nozawa H, et
al: Alpha-fetoprotein-producing early rectal carcinoma: A rare case
report and review. World J Surg Oncol. 13:1802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Michl M, Stintzing S, von Weikersthal
Fischer L, Decker T, Kiani A, Vehling-Kaiser U, Al-Batran SE,
Heintges T, Lerchenmueller C, Kahl C, et al: CEA response is
associated with tumor response and survival in patients with KRAS
exon 2 wild-type and extended RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal
cancer receiving first-line FOLFIRI plus cetuximab or bevacizumab
(FIRE-3 trial). Ann Oncol. 27:1565–1572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huo YR, Glenn D, Liauw W, Power M, Zhao J
and Morris DL: Evaluation of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) density
as a prognostic factor for percutaneous ablation of pulmonary
colorectal metastases. Eur Radiol. 27:128–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kong F, Shi X, Li H, Li P, Yu J, Li X,
Chen J, Sun Y and Jia Y: Increased expression of iASPP correlates
with poor prognosis in FIGO IA2-IIA cervical adenocarcinoma
following a curative resection. Am J Cancer Res.
5:12172015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cobleigh MA, Tabesh B, Bitterman P, Baker
J, Cronin M, Liu ML, Borchik R, Mosquera JM, Walker MG and Shak S:
Tumor gene expression and prognosis in breast cancer patients with
10 or more positive lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8623–8631.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vives V, Su J, Zhong S, Ratnayaka I, Slee
E, Goldin R and Lu X: ASPP2 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor
that cooperates with p53 to suppress tumor growth. Genes Dev.
20:1262–1267. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Samuels-Lev Y, O'Connor DJ, Bergamaschi D,
Trigiante G, Hsieh JK, Zhong S, Campargue I, Naumovski L, Crook T
and Lu X: ASPP proteins specifically stimulate the apoptotic
function of p53. Mol Cell. 8:781–794. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu ZJ, Lu X, Zhang Y, Zhong S, Gu SZ,
Zhang XB, Yang X and Xin HM: Downregulated mRNA expression of ASPP
and the hypermethylation of the 5′-untranslated region in cancer
cell lines retaining wild-type p53. FEBS Lett. 579:1587–1590. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mori S, Ito G, Usami N, Yoshioka H, Ueda
Y, Kodama Y, Takahashi M, Fong KM, Shimokata K and Sekido Y: p53
apoptotic pathway molecules are frequently and simultaneously
altered in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 100:1673–1682.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sullivan A and Lu X: ASPP: A new family of
oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. Br J Cancer. 96:196–200.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O'Neil NJ,
Trigiante G, Crook T, Hsieh JK, O'Connor DJ, Zhong S, Campargue I,
Tomlinson ML, et al: iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53
conserved from worm to human. Nat Genet. 33:162–167. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Wang M, Zhou C, Chen S and Wang
J: The expression of iASPP in acute leukemias. Leuk Res.
29:179–183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu ZJ, Zhang Y, Zhang XB and Yang X:
Abnormal mRNA expression of ASPP members in leukemia cell lines.
Leukemia. 18:8802004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lettre G, Kritikou EA, Jaeggi M, Calixto
A, Fraser AG, Kamath RS, Ahringer J and Hengartner MO: Genome-wide
RNAi identifies p53-dependent and -independent regulators of germ
cell apoptosis in C. elegans. Cell Death Differ. 11:1198–1203.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gorina S and Pavletich NP: Structure of
the p53 tumor suppressor bound to the ankyrin and SH3 domains of
53BP2. Science. 274:1001–1005. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Denoix PF: Enquete permanent dans les
centres anticancereaux. Bull Inst Natl Hyg. 1:701946.
|
|
39
|
Thomas SN, Zhu F, Schnaar RL, Alves CS and
Konstantopoulos K: Carcinoembryonic antigen and CD44 variant
isoforms cooperate to mediate colon carcinoma cell adhesion to E-
and L-selectin in shear flow. J Biol Chem. 283:15647–15655. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Konstantopoulos K and Thomas SN: Cancer
cells in transit: The vascular interactions of tumor cells. Annu
Rev Biomed Eng. 11:177–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mak VC, Lee L, Siu MK, Wong OG, Lu X, Ngan
HY, Wong ES and Cheung AN: Downregulation of ASPP1 in gestational
trophpblastic disease: Correlation with hypermethylation, apoptopic
activity and clinical outcome. Mod Pathol. 24:522–532. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thomas SN, Tong Z, Stebe KJ and
Konstantopoulos K: Identification, characterization and utilization
of tumor cell selectin ligands in the design of colon cancer
diagnostics. Biorheology. 46:207–225. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
O'Conor GT, Tatarinov YS, Abelev GI and
Uriel J: A collaborative study for the evaluation of a serologic
test for primary liver cancer. Cancer. 25:1091–1098. 1970.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smith CJ, Ajdukiewicz A and Kelleher PC:
Concanavalin-A-affinity molecular heterogeneity of human hepatoma
AFP and cord-serum AFP. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 417:69–74. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Norgaard-Pedersen R, Albrechtsen R and
Teilum G: Serum alpha-foetoprotein as a marker for endodermal sinus
tumour (yolk sac tumour) or a vitelline component of
‘teratocarcinoma’. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 83:573–589.
1975.PubMed/NCBI
|