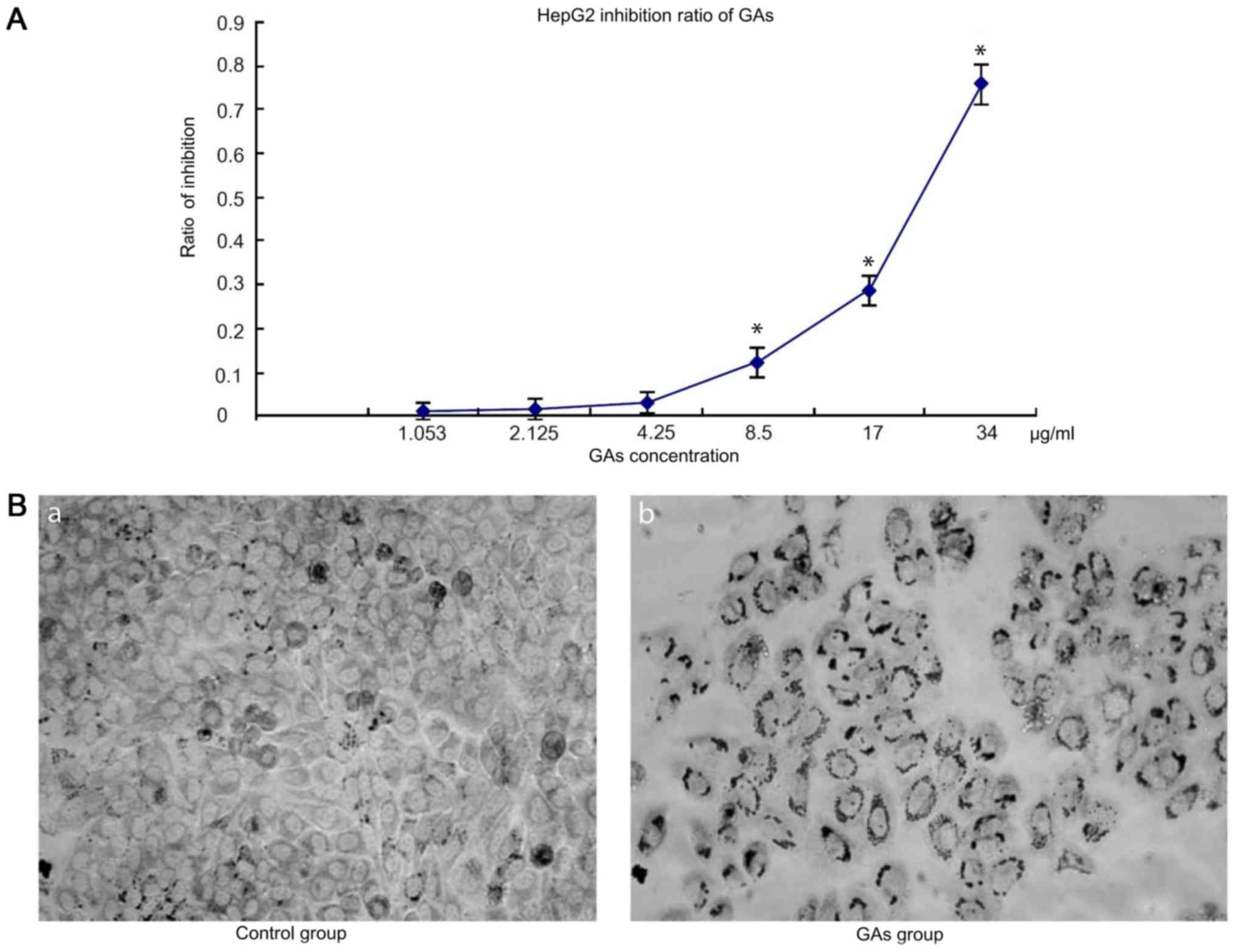
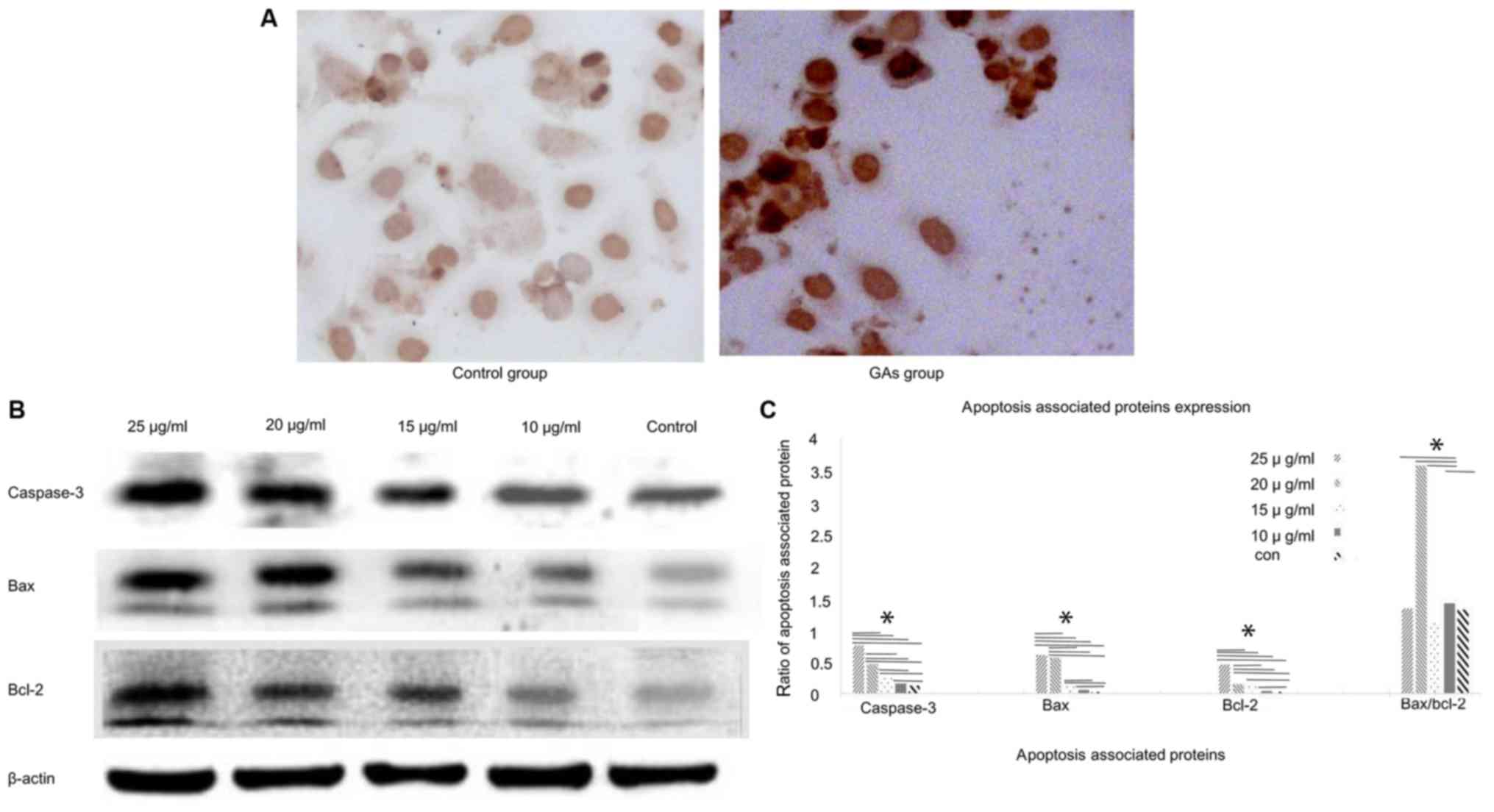
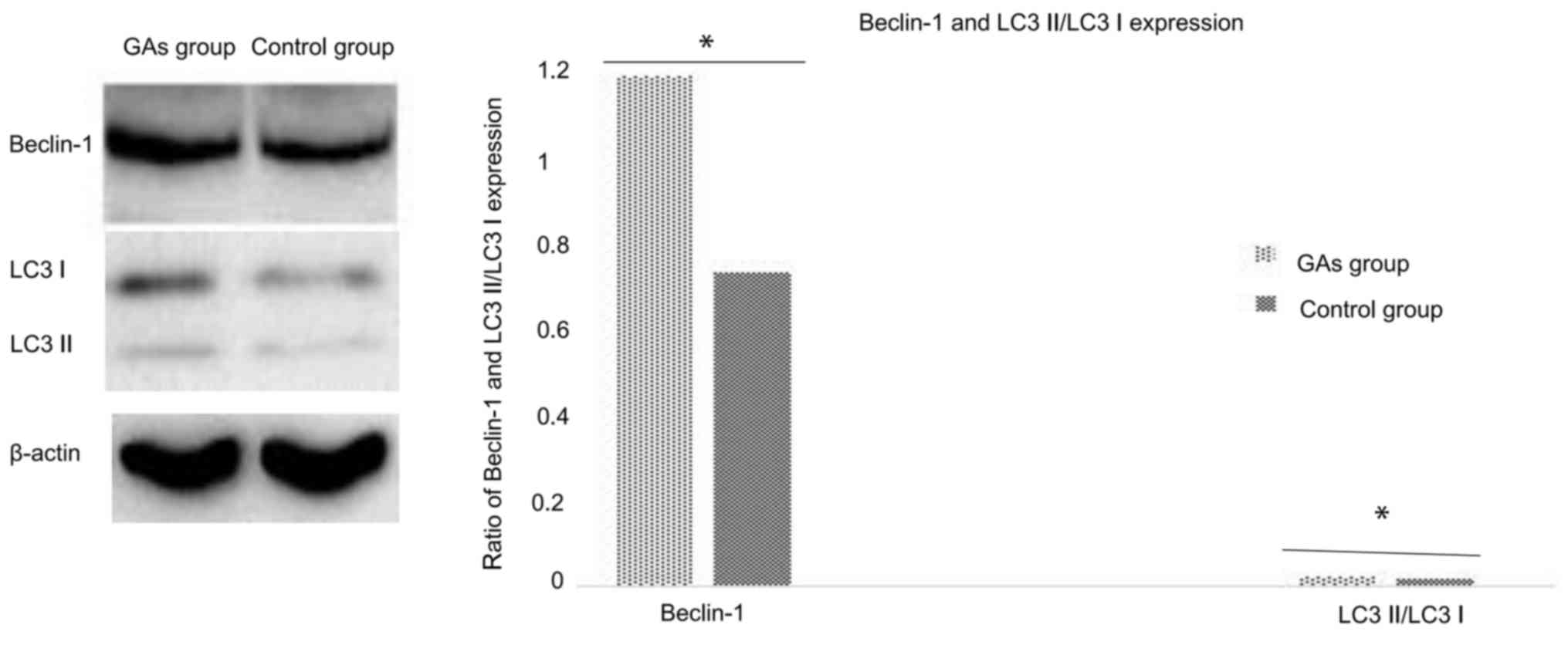
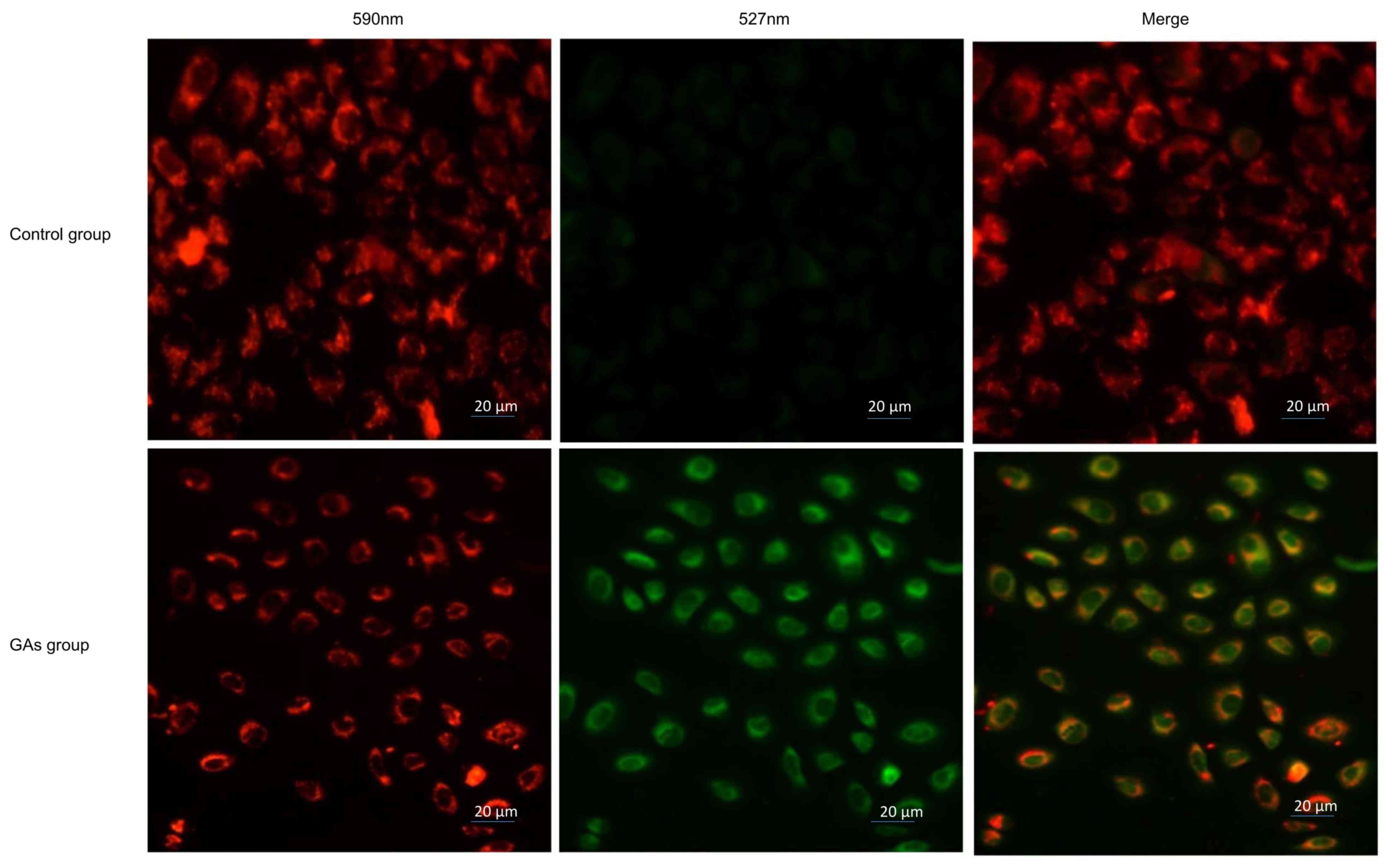
|
1
|
Shimizuguchi T, Nihei K, Okano T,
Machitori Y, Ito K and Karasawa K: A comparison of clinical
outcomes between three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and
intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Int J Clin
Oncol. 22:373–379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verma V, Moreno AC and Lin SH: Advances in
radiotherapy management of esophageal cancer. J Clin Med. 5:pii:
E91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang Y, Hu Y and Wang H: Targeting
antitumor immune response for enhancing the efficacy of
photodynamic therapy of cancer: Recent advances and future
perspectives. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:52740842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yeku O and Slovin SF: Immune therapy for
prostate cancer. Cancer J. 22:334–341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Friese CR, Li Y, Bondarenko I, Hofer TP,
Ward KC, Hamilton AS, Deapen D, Kurian AW and Katz SJ: Chemotherapy
decisions and patient experience with the recurrence score assay
for early-stage breast cancer. Cancer. 123:43–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lohiya V, Aragon-Ching JB and Sonpavde G:
Role of chemotherapy and mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy
in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Med
Insights Oncol. 10 Suppl 1:S57–S66. 2016.
|
|
7
|
Sun Y, Guan Z, Liang L, Cheng Y, Zhou J,
Li J and Xu Y: NF-κB signaling plays irreplaceable roles in
cisplatin-induced bladder cancer chemoresistance and tumor
progression. Int J Oncol. 48:225–234. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsu YL, Hung JY, Tsai EM, Wu CY, Ho YW,
Jian SF, Yen MC, Chang WA, Hou MF and Kuo PL: Benzyl butyl
phthalate increases the chemoresistance to
doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide by increasing breast cancer-associated
dendritic cell-derived CXCL1/GROalpha and S100A8/A9. Oncol Rep.
34:2889–2900. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thoenes L, Hoehn M, Kashirin R, Ogris M,
Arnold GJ, Wagner E and Guenther M: In vivo chemoresistance of
prostate cancer in metronomic cyclophosphamide therapy. J
Proteomics. 73:1342–1354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oh J, Hwang IH, Hong CE, Lyu SY and Na M:
Inhibition of fatty acid synthase by ginkgolic acids from the
leaves of Ginkgo biloba and their cytotoxic activity. J Enzyme
Inhib Med Chem. 28:565–568. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang H, Zhou CC, Feng Y, Dai LN, Chen J,
Chen SX, Li XY, Liu YR and Zhang P: The effect of ginkgolic acids
on multidrug resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Hua Xi Kou
Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:668–671. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fuzzati N, Pace R and Villa F: A simple
HPLC-UV method for the assay of ginkgolic acids in Ginkgo biloba
extracts. Fitoterapia. 74:247–256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Long R, Yin R and Zhen Y: Partial
purification and analysis of allergenicity, immunogenicity of
Ginkgo biloba L. pollen. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 23:429–432.
1992.(In Chines). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chao JC and Chu CC: Effects of Ginkgo
biloba extract on cell proliferation and cytotoxicity in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 10:37–41.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee JH, Kim YG, Ryu SY, Cho MH and Lee J:
Ginkgolic acids and Ginkgo biloba extract inhibit Escherichia coli
O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. Int J Food
Microbiol. 174:47–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thompson AJ, McGonigle I, Duke R, Johnston
GA and Lummis SC: A single amino acid determines the toxicity of
Ginkgo biloba extracts. FASEB J. 26:1884–1891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma J, Duan W, Han S, Lei J, Xu Q, Chen X,
Jiang Z, Nan L, Li J, Chen K, et al: Ginkgolic acid suppresses the
development of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting pathways driving
lipogenesis. Oncotarget. 6:20993–21003. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bu X, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Wang M, Li M and
Yan Y: Recombinant Newcastle disease virus (rL-RVG) triggers
autophagy and apoptosis in gastric carcinoma cells by inducing ER
stress. Am J Cancer Res. 6:924–936. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bu XF, Wang MB, Zhang ZJ, Zhao YH, Li M
and Yan YL: Autophagy is involved in recombinant Newcastle disease
virus (rL-RVG)-induced cell death of stomach adenocarcinoma cells
in vitro. Int J Oncol. 47:679–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kania E, Pajak B, O'Prey J, Gonzalez
Sierra P, Litwiniuk A, Urbańska K, Ryan KM and Orzechowski A:
Verapamil treatment induces cytoprotective autophagy by modulating
cellular metabolism. FEBS J. 284:1370–1387. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anding AL and Baehrecke EH: Autophagy in
cell life and cell death. Curr Top Dev Biol. 114:67–91. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YJ, Lee GJ, Yi SS, Heo SH, Park CR,
Nam HS, Cho MK and Lee SH: Cisplatin and resveratrol induce
apoptosis and autophagy following oxidative stress in malignant
mesothelioma cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 97:96–107. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumari KK and Setty OH: Protective effect
of Phyllanthus fraternus against mitochondrial dysfunction induced
by co-administration of cisplatin and cyclophosphamide. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 44:179–188. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hackenberg T, Juul T, Auzina A, Gwizdz S,
Malolepszy A, Van Der Kelen K, Dam S, Bressendorff S, Lorentzen A,
Roepstorff P, et al: Catalase and NO CATALASE ACTIVITY1 promote
autophagy-dependent cell death in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell.
25:4616–4626. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang XM, Wang YF, Li YY and Ma HL: Thermal
stability of ginkgolic acids from Ginkgo biloba and the effects of
ginkgol C17:1 on the apoptosis and migration of SMMC7721 cells.
Fitoterapia. 98:66–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou C, Li X, Du W, Feng Y, Kong X, Li Y,
Xiao L and Zhang P: Antitumor effects of ginkgolic acid in human
cancer cell occur via cell cycle arrest and decrease the Bcl-2/Bax
ratio to induce apoptosis. Chemotherapy. 56:393–402. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schaaf MB, Keulers TG, Vooijs MA and
Rouschop KM: LC3/GABARAP family proteins: Autophagy-(un)related
functions. FASEB J. 30:3961–3978. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qi Z, Dong W, Shi W, Wang R, Zhang C, Zhao
Y, Ji X, Liu KJ and Luo Y: Bcl-2 phosphorylation triggers autophagy
switch and reduces mitochondrial damage in limb remote ischemic
conditioned rats after ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res.
6:198–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Münz C: Autophagy proteins in phagocyte
endocytosis and exocytosis. Front Immunol. 8:11832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nascimbeni AC, Codogno P and Morel E:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate in the regulation of autophagy
membrane dynamics. FEBS J. 284:1267–1278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lemasters JJ: Variants of mitochondrial
autophagy: Types 1 and 2 mitophagy and micromitophagy (Type 3).
Redox Biol. 2:749–754. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim J and Hurria A: Determining
chemotherapy tolerance in older patients with cancer. J Natl Compr
Canc Netw. 11:1494–1502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kalsi T, Babic-Illman G, Ross PJ, Maisey
NR, Hughes S, Fields P, Martin FC, Wang Y and Harari D: The impact
of comprehensive geriatric assessment interventions on tolerance to
chemotherapy in older people. Br J Cancer. 112:1435–1444. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lara-Guerra H and Roth JA: Gene therapy
for lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncog. 21:115–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang X, Qian Z, Chen J, Zhu W and Xie J:
Study on antitumor activities of ginkgolic acids from Ginkgo
sarcotestas in vitro. Zhong Yao Cai. 27:40–42. 2004.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou CC, Du W, Wen Z, Li JY and Zhang P:
Effects of natural plant ginkgolic acids on the apoptosis of human
Hep-2 cancer cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 40:459–461.
2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P,
Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS, Baba M, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA,
Ballabio A, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of
assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy.
4:151–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wesselborg S and Stork B: Autophagy signal
transduction by ATG proteins: From hierarchies to networks. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 72:4721–4757. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Levine B, Sinha SC and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kale J, Osterlund EJ and Andrews DW: BCL-2
family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell
Death Differ. 25:65–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lomonosova E and Chinnadurai G: BH3-only
proteins in apoptosis and beyond: An overview. Oncogene. 27 Suppl
1:S2–S19. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yousefi S, Perozzo R, Schmid I, Ziemiecki
A, Schaffner T, Scapozza L, Brunner T and Simon HU:
Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis.
Nat Cell Biol. 8:1124–1132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gong A, Ye S, Xiong E, Guo W, Zhang Y,
Peng W, Shao G, Jin J, Zhang Z, Yang J and Gao J: Autophagy
contributes to ING4-induced glioma cell death. Exp Cell Res.
319:1714–1723. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|