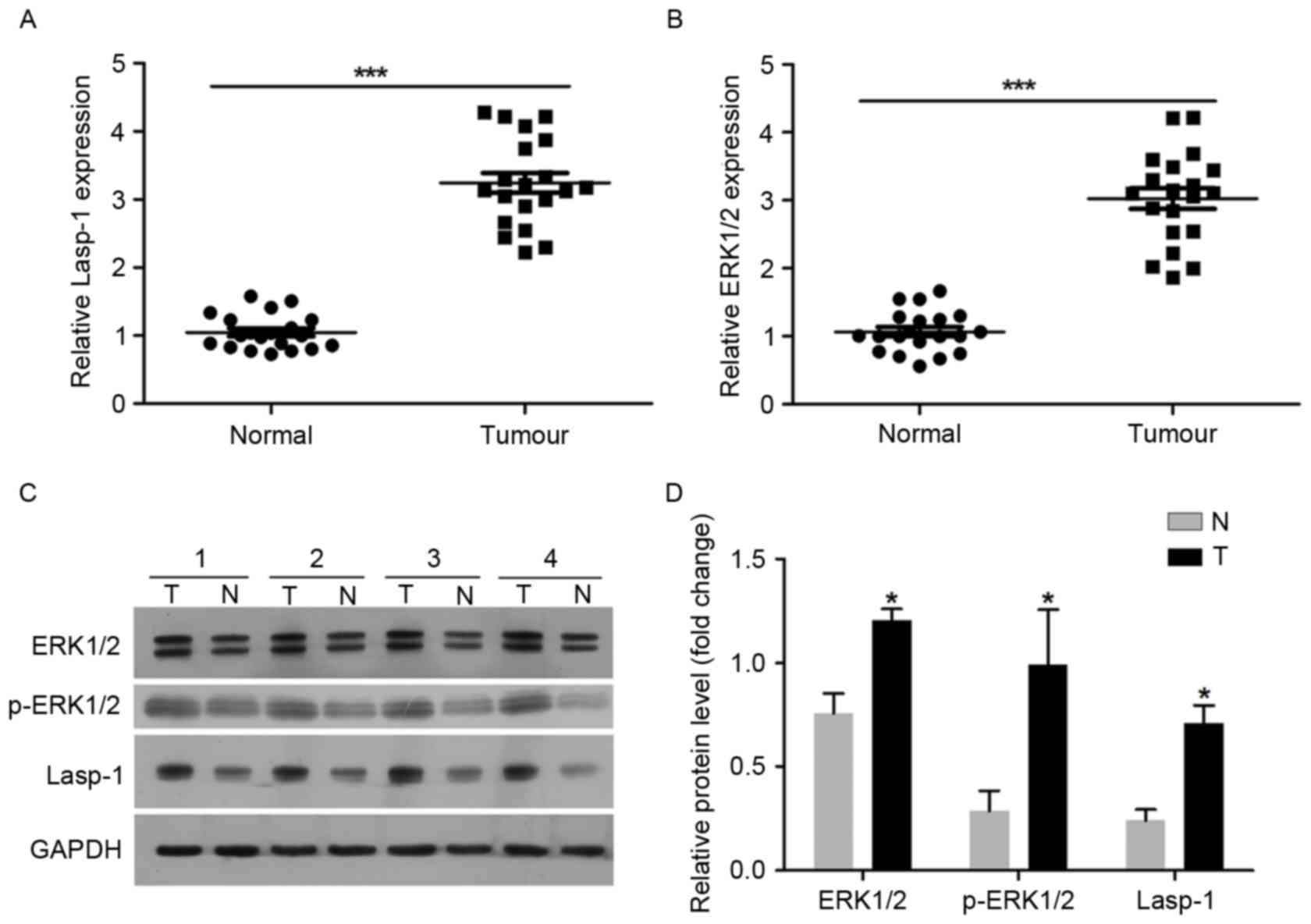
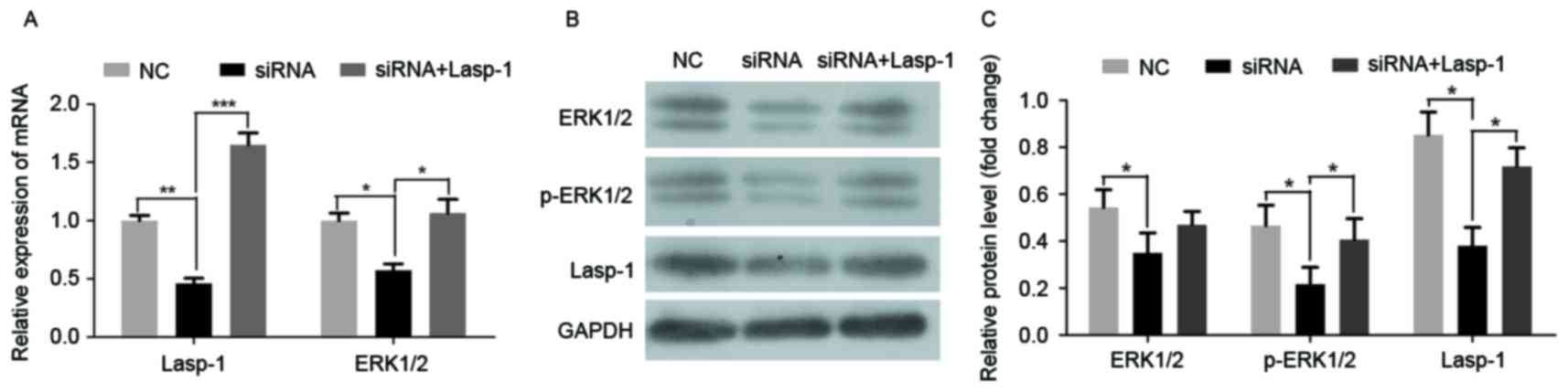
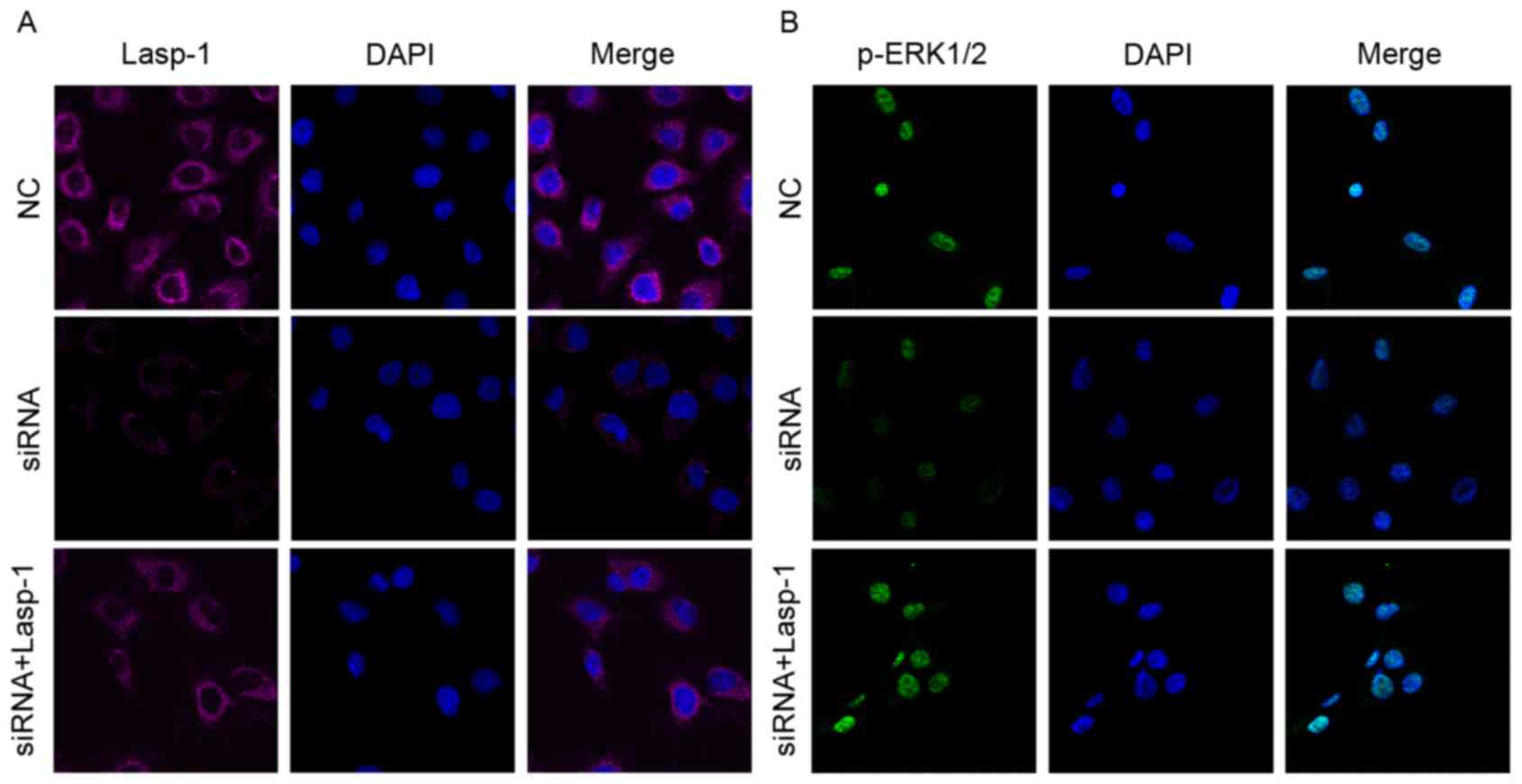
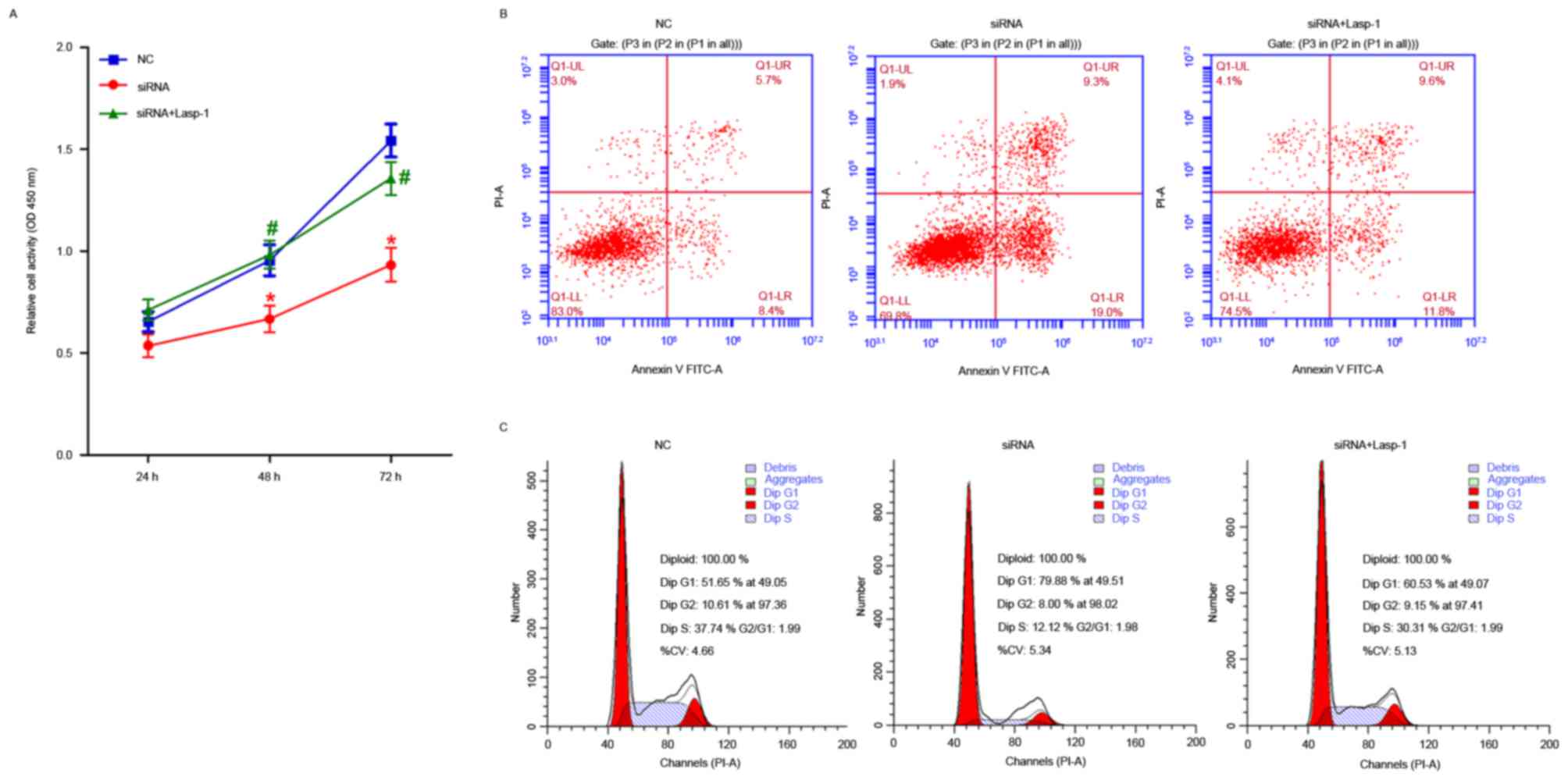
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quintero E, Carrillo M, Leoz ML, Cubiella
J, Gargallo C, Lanas A, Bujanda L, Gimeno-García AZ,
Hernández-Guerra M, Nicolás-Pérez D, et al: Risk of advanced
neoplasia in first-degree relatives with colorectal cancer: A large
multicenter cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 13:e10020082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krbal L, Hanušová V, Soukup J, John S,
Matoušková P and Ryška A: Contribution of in vitro comparison of
colorectal carcinoma cells from primary and metastatic lesions to
elucidation of mechanisms of tumor progression and response to
anticancer therapy. Tumour Biol. 37:9565–9578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan WJ, Chew MH, Tan IB, Law JH, Zhao R,
Acharyya S, Mao YL, Fernandez LG, Loi CT and Tang CL: Palliative
surgical intervention in metastatic colorectal carcinoma: A
prospective analysis of quality of life. Colorectal Dis.
18:357–363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grunewald TG, Kammerer U, Schulze E,
Schindler D, Honig A, Zimmer M and Butt E: Silencing of LASP-1
influences zyxin localization, inhibits proliferation and reduces
migration in breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:974–982. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vaman VSA, Poppe H, Houben R, Grunewald
TG, Goebeler M and Butt E: LASP1, a newly identified melanocytic
protein with a possible role in melanin release, but not in
melanoma progression. PLoS One. 10:e01292192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang F, Zhou X, Du S, Zhao Y, Ren W, Deng
Q, Wang F and Yuan J: LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (LASP-1)
overexpression was associated with aggressive phenotype and poor
prognosis in clear cell renal cell cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1005572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng J, Wang F, Lu S and Wang X: LASP-1,
regulated by miR-203, promotes tumor proliferation and
aggressiveness in human non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Mol Pathol.
100:116–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hailer A, Grunewald TG, Orth M, Reiss C,
Kneitz B, Spahn M and Butt E: Loss of tumor suppressor mir-203
mediates overexpression of LIM and SH3 protein 1 (LASP1) in
high-risk prostate cancer thereby increasing cell proliferation and
migration. Oncotarget. 5:4144–4153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Z, Chen Y, Wang X, Zhang H, Zhang Y,
Gao Y, Weng M, Wang L, Liang H, Li M, et al: LASP-1 induces
proliferation, metastasis and cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase
in gallbladder cancer by down-regulating S100P via the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Cancer Lett. 372:239–250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Payton S: Bladder cancer: LASP-1-a
promising urine marker for detection of bladder cancer. Nat Rev
Urol. 9:2402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ardelt P, Grünemay N, Strehl A, Jilg C,
Miernik A, Kneitz B and Butt E: LASP-1, a novel urinary marker for
detection of bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 31:1591–1598. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Orth MF, Cazes A, Butt E and Grunewald TG:
An update on the LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (LASP1): A versatile
structural, signaling, and biomarker protein. Oncotarget. 6:26–42.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salvi A, Bongarzone I, Ferrari L, Abeni E,
Arici B, De Bortoli M, Scuri S, Bonini D, Grossi I, Benetti A, et
al: Molecular characterization of LASP-1 expression reveals
vimentin as its new partner in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 46:1901–1912. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Li W, Jin X, Cui S and Zhao L: LIM
and SH3 protein 1, a promoter of cell proliferation and migration,
is a novel independent prognostic indicator in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 49:974–983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao L, Wang H, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang X, Wang
S, Sun X, Li J, Deng Y, Jiang Y and Ding Y: Promotion of colorectal
cancer growth and metastasis by the LIM and SH3 domain protein 1.
Gut. 59:1226–1235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao L, Wang H, Sun X and Ding Y:
Comparative proteomic analysis identifies proteins associated with
the development and progression of colorectal carcinoma. FEBS J.
277:4195–4204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Li Z, Chu B, Zhang F, Zhang Y, Ke
F, Chen Y, Xu Y, Liu S, Zhao S, et al: Upregulated LASP-1
correlates with a malignant phenotype and its potential therapeutic
role in human cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:8305–8315. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang H, Shi J, Luo Y, Liao Q, Niu Y, Zhang
F, Shao Z, Ding Y and Zhao L: LIM and SH3 protein 1 induces
TGFβ-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal
cancer by regulating S100A4 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5835–5847. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin YH, Park ZY, Lin D, Brahmbhatt AA, Rio
MC, Yates JR III and Klemke RL: Regulation of cell migration and
survival by focal adhesion targeting of Lasp-1. J Cell Biol.
165:421–432. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang H, An H, Wang B, Liao Q, Li W, Jin X,
Cui S, Zhang Y, Ding Y and Zhao L: miR-133a represses tumour growth
and metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting LIM and SH3
protein 1 and inhibiting the MAPK pathway. Eur J Cancer.
49:3924–3935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu L, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang G, Ding Y and
Zhao L: Tumor suppressor miR-1 restrains epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma via the MAPK and
PI3K/AKT pathway. J Transl Med. 12:2442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tomasetto C, Moog-Lutz C, Régnier CH,
Schreiber V, Basset P and Rio MC: Lasp-1 (MLN 50) defines a new LIM
protein subfamily characterized by the association of LIM and SH3
domains. FEBS Lett. 373:245–249. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kay BK: SH3 domains come of age. FEBS
Lett. 586:2606–2608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hammarström A, Berndt KD, Sillard R,
Adermann K and Otting G: Solution structure of a
naturally-occurring zinc-peptide complex demonstrates that the
N-terminal zinc-binding module of the Lasp-1 LIM domain is an
independent folding unit. Biochemistry. 35:12723–12732. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pappas CT, Bliss KT, Zieseniss A and
Gregorio CC: The Nebulin family: An actin support group. Trends
Cell Biol. 21:29–37. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mihlan S, Reiß C, Thalheimer P, Herterich
S, Gaetzner S, Kremerskothen J, Pavenstädt HJ, Lewandrowski U,
Sickmann A and Butt E: Nuclear import of LASP-1 is regulated by
phosphorylation and dynamic protein-protein interactions. Oncogene.
32:2107–2113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Raman D, Sai J, Neel NF, Chew CS and
Richmond A: LIM and SH3 protein-1 modulates CXCR2-mediated cell
migration. PLoS One. 5:e100502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Celeghini C, Voltan R, Rimondi E, Gattei V
and Zauli G: Perifosine selectively induces cell cycle block and
modulates retinoblastoma and E2F1 protein levels in p53 mutated
leukemic cell lines. Invest New Drugs. 29:392–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park SJ, Yang SW and Kim BC: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induces cell cycle arrest by activating atypical
cyclin-dependent kinase 5 through up-regulation of Smad3-dependent
p35 expression in human MCF10A mammary epithelial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 472:502–507. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chaudhary P, Sharma R, Sahu M, Vishwanatha
JK, Awasthi S and Awasthi YC: 4-Hydroxynonenal induces G2/M phase
cell cycle arrest by activation of the ataxia telangiectasia
mutated and Rad3-related protein (ATR)/checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1)
signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 288:20532–20546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|