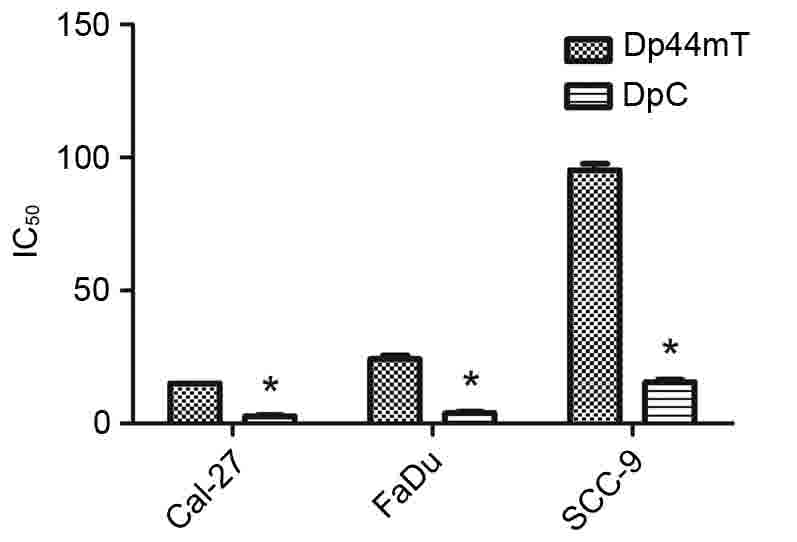
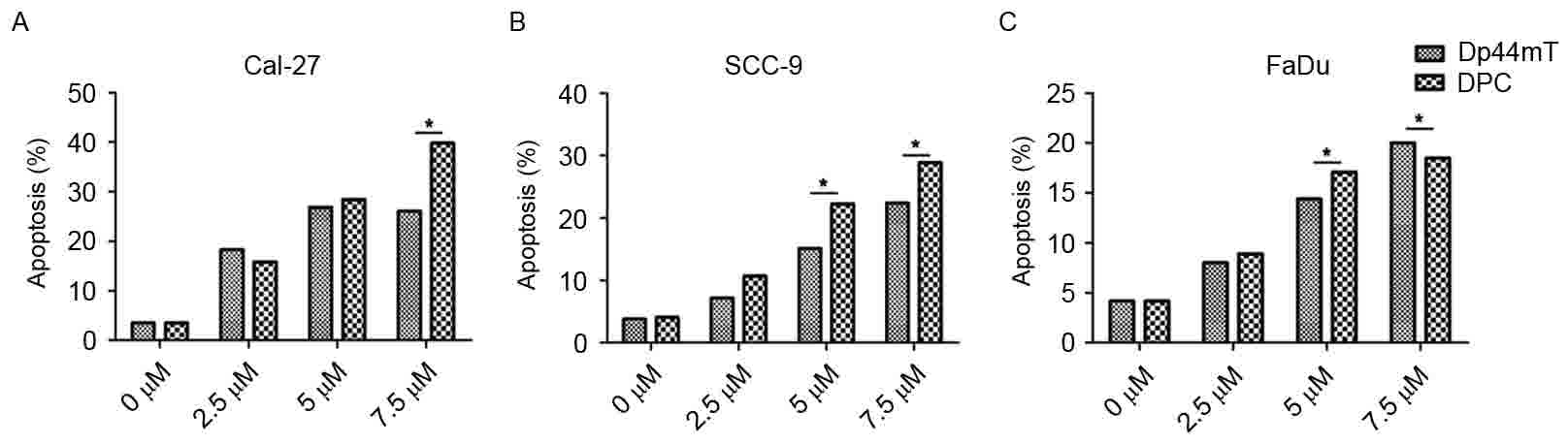
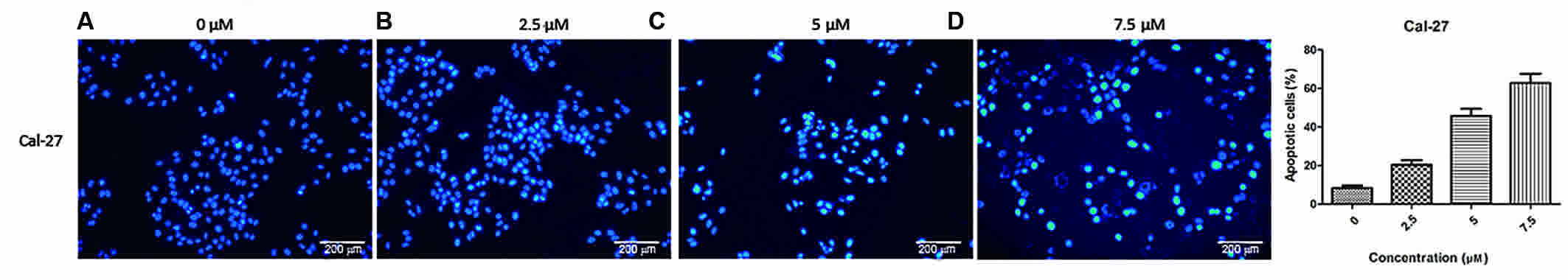
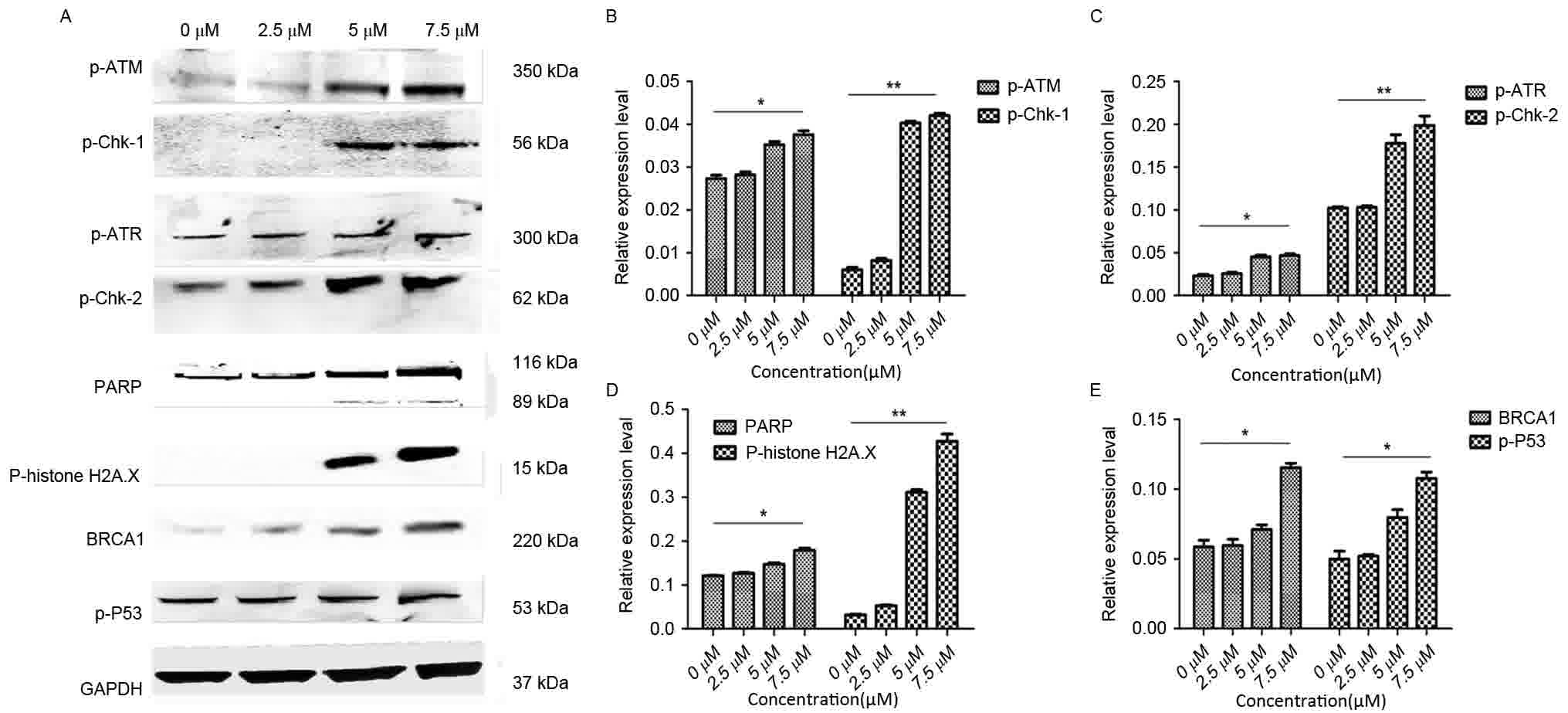
|
1
|
D'Cruz A, Lin T, Anand AK, Atmakusuma D,
Calaguas MJ, Chitapanarux I, Cho BC, Goh BC, Guo Y, Hsieh WS, et
al: Consensus recommendations for management of head and neck
cancer in Asian countries: A review of international guidelines.
Oral Oncol. 49:872–877. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quach P, Gutierrez E, Basha MT, Kalinowski
DS, Sharpe PC, Lovejoy DB, Bernhardt PV, Jansson PJ and Richardson
DR: Methemoglobin formation by triapine,
di-2-pyridylketone-4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT), and
other anticancer thiosemicarbazones: Identification of novel
thiosemicarbazones and therapeutics that prevent this effect. Mol
Pharmacol. 82:105–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Molinolo AA, Amornphimoltham P, Squarize
CH, Castilho RM, Patel V and Gutkind JS: Dysregulated molecular
networks in head and neck carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol. 45:324–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bian X, Xu ZG, Lu CM, Tang PZ and Luo J:
Cancer and surgica l treatment impact the qua lity of life in
patients w ith head and neck cancer. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou
Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 40:606–610. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Padmanabhan H, Brookes MJ and Iqbal T:
Iron and colorectal cancer: Evidence from in vitro and animal
studies. Nutr Rev. 73:308–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miljuš G, Malenković V, Đukanovic B,
Kolundžić N and Nedić O: IGFBP-3/transferrin/transferrin receptor 1
complexes as principal mediators of IGFBP-3 delivery to colon cells
in non-cancer and cancer tissues. Exp Mol Pathol. 98:431–438. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dragset MS, Poce G, Alfonso S,
Padilla-Benavides T, Ioerger TR, Kaneko T, Sacchettini JC, Biava M,
Parish T, Argüello JM, et al: A novel antimycobacterial compound
acts as an intracellular iron chelator. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 59:2256–2264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang BA, Kovačević Ž, Park KC, Kalinowski
DS, Jansson PJ, Lane DJ, Sahni S and Richardson DR: Molecular
functions of the iron-regulated metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1845:1–19. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Richardson DR, Sharpe PC, Lovejoy DB,
Senaratne D, Kalinowski DS, Islam M and Bernhardt PV: Dipyridyl
thiosemicarbazone chelators with potent and selective antitumor
activity form iron complexes with redox activity. J Med Chem.
49:6510–6521. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jansson PJ, Kalinowski DS, Lane DJ,
Kovacevic Z, Seebacher NA, Fouani L, Sahni S, Merlot AM and
Richardson DR: The renaissance of polypharmacology in the
development of anti-cancer therapeutics: Inhibition of the ‘Triad
of Death’ in cancer by Di-2-pyridylketone thiosemicarbazones.
Pharmacol Res. 100:255–260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu Y, Suryo Rahmanto Y and Richardson DR:
Bp44mT: An orally active iron chelator of the thiosemicarbazone
class with potent anti-tumour efficacy. Br J Pharmacol.
165:148–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuan J, Lovejoy DB and Richardson DR:
Novel di-2-pyridyl-derived iron chelators with marked and selective
antitumor activity: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Blood.
104:1450–1458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Whitnall M, Howard J, Ponka P and
Richardson DR: A class of iron chelators with a wide spectrum of
potent antitumor activity that overcomes resistance to
chemotherapeutics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:14901–14906. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanaka T, Huang X, Jorgensen E, Traganos
F, Darzynkiewicz Z and Albino AP: ATM activation accompanies
histone H2AX phosphorylation in A549 cells upon exposure to tobacco
smoke. BMC Cell Biol. 8:262007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hamre D, Bernstein J and Donovick R: The
chemotherapy of experimental tuberculosis. II. Thiosemicarbazones
and analogues in experimental tuberculosis in the mouse. J
Bacteriol. 59:675–860. 1950.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Richardson DR, Tran EH and Ponka P: The
potential of iron chelators of the pyridoxal isonicotinoyl
hydrazone class as effective antiproliferative agents. Blood.
86:4295–4306. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Richardson DR and Milnes K: The potential
of iron chelators of the pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone class as
effective antiproliferative agents II: The mechanism of action of
ligands derived from salicylaldehyde benzoyl hydrazone and
2-hydroxy-1-naphthylaldehyde benzoyl hydrazone. Blood.
89:3025–3038. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Darnell G and Richardson DR: The potential
of iron chelators of the pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone class as
effective antiproliferative agents III: The effect of the ligands
on molecular targets involved in proliferation. Blood. 94:781–792.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao J and Richardson DR: The potential of
iron chelators of the pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone class as
effective antiproliferative agents, IV: The mechanisms involved in
inhibiting cell-cycle progression. Blood. 98:842–850. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pahontu E, Julea F, Rosu T, Purcarea V,
Chumakov Y, Petrenco P and Gulea A: Antibacterial, antifungal and
in vitro antileukaemia activity of metal complexes with
thiosemicarbazones. J Cell Mol Med. 19:865–878. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu TH, Cao SW and Yu YY: Synthesis,
characterization and biological evaluation of paeonol
thiosemicarbazone analogues as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. Int
J Biol Macromol. 62:589–595. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gan C, Cui J, Su S, Lin Q, Jia L, Fan L
and Huang Y: Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of some
steroidal thiosemicarbazones, semicarbazones and hydrozones.
Steroids. 87:99–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie W, Xie S, Zhou Y, Tang X, Liu J, Yang
W and Qiu M: Design and synthesis of novel 5,6-disubstituted
pyridine-2,3-dione-3-thiosemicarbazone derivatives as potential
anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 81:22–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akgemci EG, Saf AO, Tasdemir HU, Türkkan
E, Bingol H, Turan SO and Akkiprik M: Spectrophotometric,
voltammetric and cytotoxicity studies of
2-hydroxy-5-methoxyacetophenone thiosemicarbazone and its
N(4)-substituted derivatives: A combined experimental-computational
study. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 136:719–725. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang N, Tai Y, Li M, Ma P, Zhao J and Niu
J: Main group bismuth(III), gallium(III) and diorganotin(IV)
complexes derived from bis(2-acetylpyrazine)thiocarbonohydrazone:
Synthesis, crystal structures and biological evaluation. Dalton
Trans. 43:5182–5189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma B, Goh BC, Tan EH, Lam KC, Soo R, Leong
SS, Wang LZ, Mo F, Chan AT, Zee B and Mok T: A multicenter phase II
trial of 3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone (3-AP,
Triapine) and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
with pharmacokinetic evaluation using peripheral blood mononuclear
cells. Invest New Drugs. 26:169–173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lovejoy DB, Jansson PJ, Brunk UT, Wong J,
Ponka P and Richardson DR: Antitumor activity of metal-chelating
compound Dp44mT is mediated by formation of a redox-active copper
complex that accumulates in lysosomes. Cancer Res. 71:5871–5880.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kovacevic Z, Chikhani S, Lovejoy DB and
Richardson DR: Novel thiosemicarbazone iron chelators induce
up-regulation and phosphorylation of the metastasis suppressor
N-myc down-stream regulated gene 1: A new strategy for the
treatment of pancreatic cancer. Mol Pharmacol. 80:598–609. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Merolla F, Mascolo M, Ilardi G, Siano M,
Russo D, Graziano V, Celetti A and Staibano S: Nucleotide excision
repair and head and neck cancers. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
21:55–69. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han Yue CD and Guo Hongliang: Advances in
DNA damage response. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 20:1775–78.
2013.
|
|
32
|
Chen Z, Zhou Q, Zou D, Tian Y, Liu B,
Zhang Y and Wu Z: Chloro-benzoquinones cause oxidative DNA damage
through iron-mediated ROS production in Escherichia coli.
Chemosphere. 135:379–386. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Melis JP, van Steeg H and Luijten M:
Oxidative DNA damage and nucleotide excision repair. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 18:2409–2419. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park JS, Na HJ, Pyo JH, Jeon HJ, Kim YS
and Yoo MA: Requirement of ATR for maintenance of intestinal stem
cells in aging Drosophila. Aging (Albany NY). 7:307–318. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tang S, Hou Y, Zhang H, Tu G, Yang L, Sun
Y, Lang L, Tang X, Du YE, Zhou M, et al: Oxidized ATM promotes
abnormal proliferation of breast CAFs through maintaining
intracellular redox homeostasis and activating the PI3K-AKT,
MEK-ERK, and Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathways. Cell Cycle.
14:1908–1924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Le NT and Richardson DR: Iron chelators
with high antiproliferative activity up-regulate the expression of
a growth inhibitory and metastasis suppressor gene: A link between
iron metabolism and proliferation. Blood. 104:2967–2975. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun J, Zhang D, Zheng Y, Zhao Q, Zheng M,
Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR: Targeting the metastasis suppressor,
NDRG1, using novel iron chelators: Regulation of stress
fiber-mediated tumor cell migration via modulation of the
ROCK1/pMLC2 signaling pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 83:454–469. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seebacher NA, Lane DJ, Jansson PJ and
Richardson DR: Glucose modulation induces lysosome formation and
increases lysosomotropic drug sequestration via the P-glycoprotein
drug transporter. J Biol Chem. 291:3796–3820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wong FC, Ng AW, Lee VH, Lui CM, Yuen KK,
Sze WK, Leung TW and Tung SY: Whole-field simultaneous
integrated-boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy for patients with
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:138–145.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|