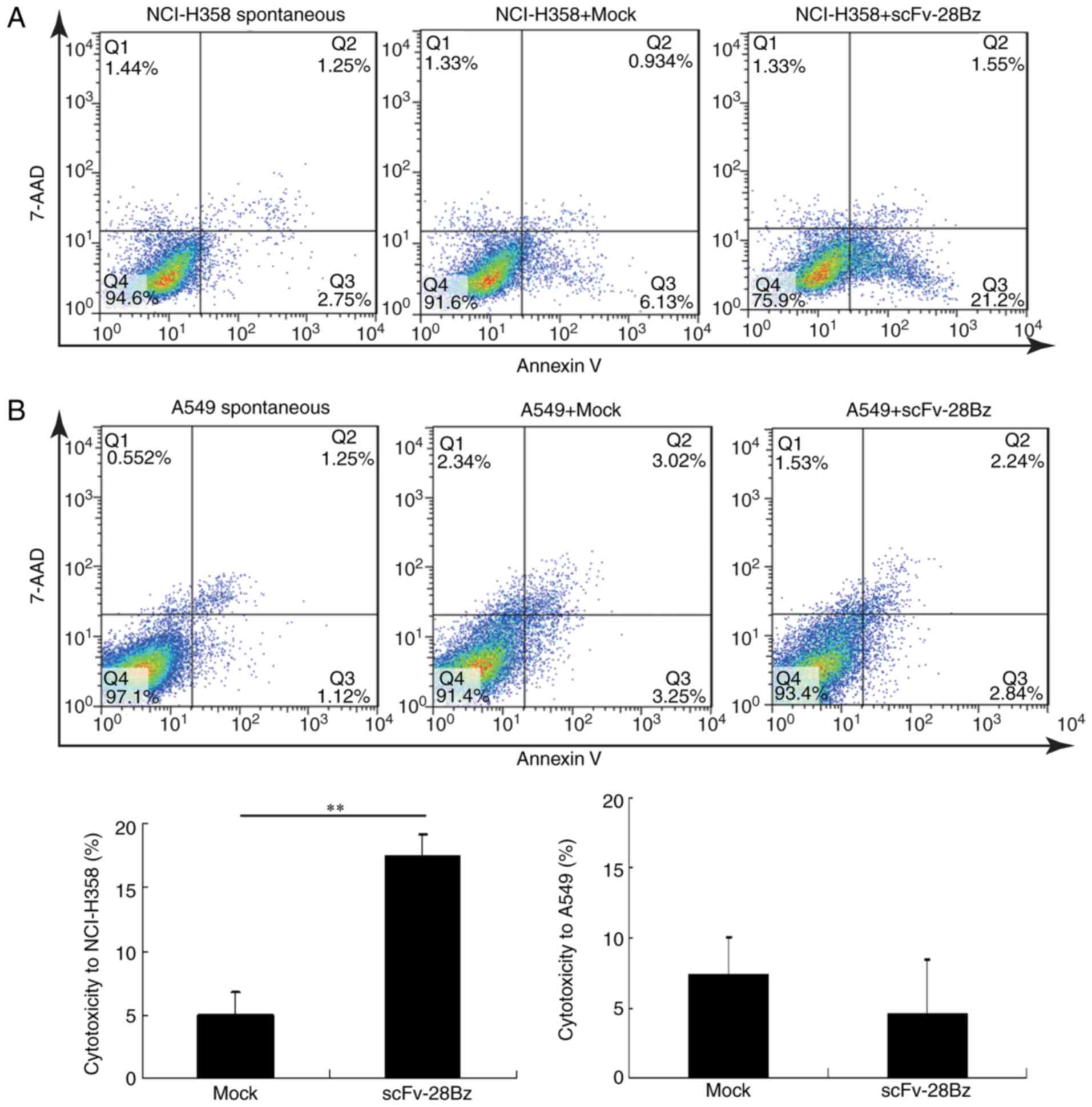
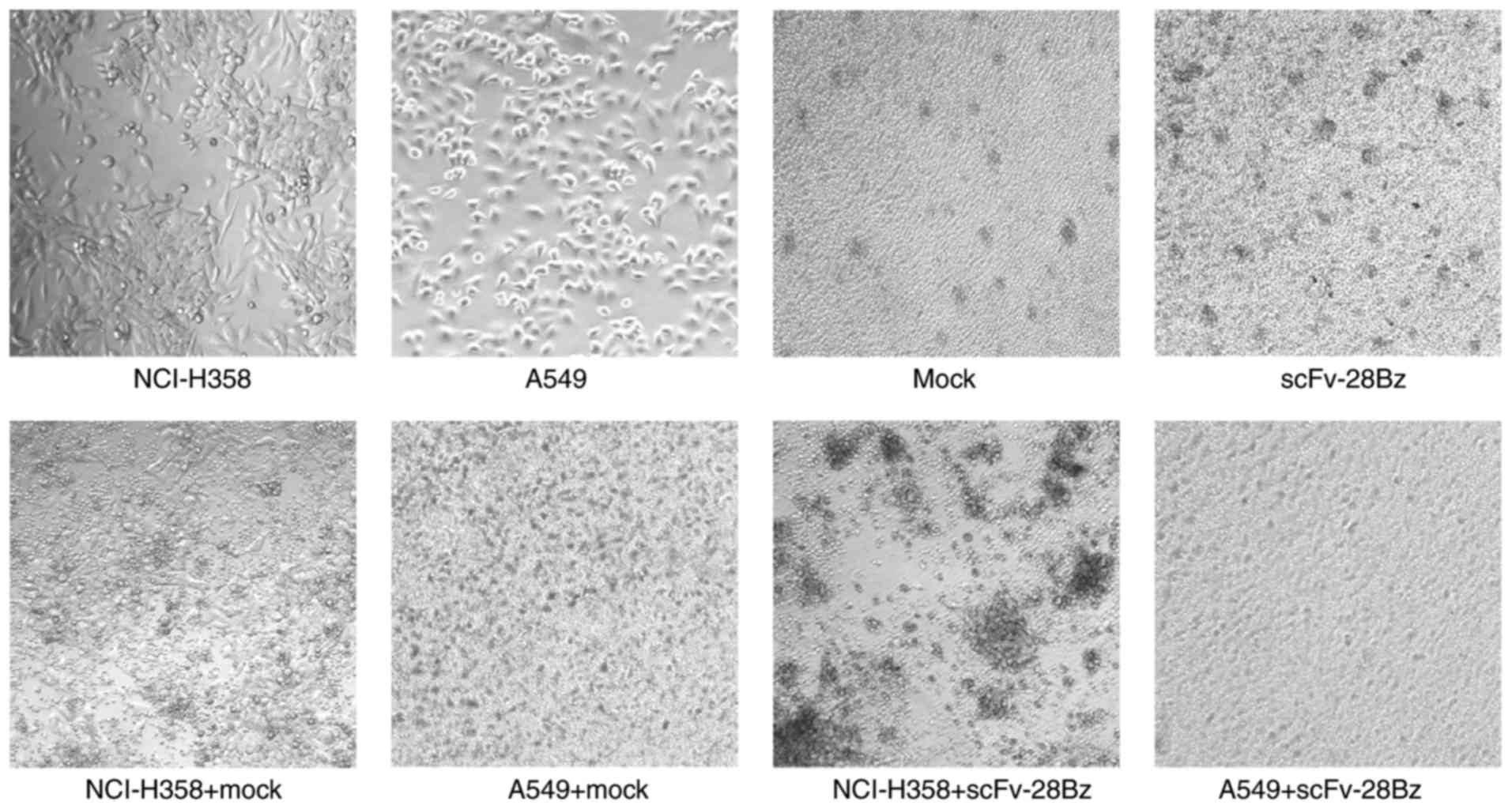
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanoue LT and Detterbeck FC: New TNM
classification for non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 9:413–423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Hassan OU, Yang YW and
Buchanan P: Lung cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1856:189–210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eshhar Z, Waks T, Gross G and Schindler
DG: Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes
through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding
domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and
T-cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:720–724. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kochenderfer JN and Rosenberg SA: Treating
B-cell cancer with T cells expressing anti-CD19 chimeric antigen
receptors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:267–276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Johnson LA and June CH: Driving
gene-engineered T cell immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Res. 27:38–58.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Wu Z, Liu Y and Han W: New
development in CAR-T cell therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 10:532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cooper LJ, Topp MS, Serrano LM, Gonzalez
S, Chang WC, Naranjo A, Wright C, Popplewell L, Raubitschek A,
Forman SJ and Jensen MC: T-cell clones can be rendered specific for
CD19: Toward the selective augmentation of the
graft-versus-B-lineage leukemia effect. Blood. 101:1637–1644. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stirrups R: CAR T-cells for relapsed
B-cell ALL in children and young adults. Lancet Oncol. 19:e1442018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gilbert JA: CAR T-cells for relapsed
B-cell ALL in adults. Lancet Oncol. 19:e1432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zuo BL, Yan B, Zheng GX, Xi WJ, Zhang X,
Yang AG and Jia LT: Targeting and suppression of HER3-positive
breast cancer by T lymphocytes expressing a heregulin chimeric
antigen receptor. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 67:393–401. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Byrd TT, Fousek K, Pignata A, Szot C,
Samaha H, Seaman S, Dobrolecki L, Salsman VS, Oo HZ, Bielamowicz K,
et al: TEM8/ANTXR1-Specific CAR T cells as a targeted therapy for
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 78:489–500. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Banerjee K, Kumar S, Ross KA, Gautam S,
Poelaert B, Nasser MW, Aithal A, Bhatia R, Wannemuehler MJ,
Narasimhan B, et al: Emerging trends in the immunotherapy of
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 417:35–46. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park YP, Jin L, Bennett KB, Wang D,
Fredenburg KM, Tseng JE, Chang LJ, Huang J and Chan EKL: CD70 as a
target for chimeric antigen receptor T cells in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 78:145–150. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Till BG, Jensen MC, Wang J, Qian X, Gopal
AK, Maloney DG, Lindgren CG, Lin Y, Pagel JM, Budde LE, et al:
CD20-specific adoptive immunotherapy for lymphoma using a chimeric
antigen receptor with both CD28 and 4-1BB domains: Pilot clinical
trial results. Blood. 119:3940–3950. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fesnak AD, June CH and Levine BL:
Engineered T cells: The promise and challenges of cancer
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:566–581. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kalos M, Levine BL, Porter DL, Katz S,
Grupp SA, Bagg A and June CH: T cells with chimeric antigen
receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in
patients with advanced leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 3:95ra732011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee DW, Kochenderfer JN, Stetler-Stevenson
M, Cui YK, Delbrook C, Feldman SA, Fry TJ, Orentas R, Sabatino M,
Shah NN, et al: T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors
for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children and young adults: A
phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet. 385:517–528. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brentjens RJ, Davila ML, Riviere I, Park
J, Wang X, Cowell LG, Bartido S, Stefanski J, Taylor C, Olszewska
M, et al: CD19-targeted T cells rapidly induce molecular remissions
in adults with chemotherapy-refractory acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 5:177ra382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Correction: Mesothelin-specific chimeric
antigen receptor mRNA-engineered T cells induce antitumor activity
in solid malignancies. Cancer Immunol Res. 3:2172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brentjens RJ, Santos E, Nikhamin Y, Yeh R,
Matsushita M, La Perle K, Quintás-Cardama A, Larson SM and Sadelain
M: Genetically targeted T cells eradicate systemic acute
lymphoblastic leukemia xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5426–5435.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K and Honjo
T: Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin
gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 11:3887–3895.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N and
Honjo T: Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by
disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying
immunoreceptor. Immunity. 11:141–151. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y, Okazaki T,
Honjo T and Minato N: Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the
escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1
blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12293–12297. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taube JM, Klein A, Brahmer JR, Xu H, Pan
X, Kim JH, Chen L, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL and Anders RA:
Association of PD-1, PD-1 ligands, and other features of the tumor
immune microenvironment with response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:5064–5074. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R and Freeman
GJ: The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in
regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol. 8:239–245.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1,
a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Inoue Y, Yoshimura K, Mori K, Kurabe N,
Kahyo T, Mori H, Kawase A, Tanahashi M, Ogawa H, Inui N, et al:
Clinical significance of PD-L1 and PD-L2 copy number gains in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:32113–32128. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita
I, Dosaka-Akita H and Nishimura M: B7-H1 expression on non-small
cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5094–5100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Akbay EA, Koyama S, Carretero J, Altabef
A, Tchaicha JH, Christensen CL, Mikse OR, Cherniack AD, Beauchamp
EM, Pugh TJ, et al: Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to
immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov.
3:1355–1363. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DS, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crinò L,
Eberhardt We, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes EE,
Holgado E, et al: Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced
squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
373:123–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N,
Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L,
et al: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 372:2018–2028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M,
Kowanetz M, Vansteenkiste J, Mazieres J, Park K, Smith D,
Artal-Cortes A, Lewanski C, et al: Atezolizumab versus docetaxel
for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer
(POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled
trial. Lancet. 387:1837–1846. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Suarez ER, de Chang K, Sun J, Sui J,
Freeman GJ, Signoretti S, Zhu Q and Marasco WA: Chimeric antigen
receptor T cells secreting anti-PD-L1 antibodies more effectively
regress renal cell carcinoma in a humanized mouse model.
Oncotarget. 7:34341–34355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cherkassky L, Morello A, Villena-Vargas J,
Feng Y, Dimitrov DS, Jones DR, Sadelain M and Adusumilli PS: Human
CAR T cells with cell-intrinsic PD-1 checkpoint blockade resist
tumor-mediated inhibition. J Clin Invest. 126:3130–3144. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kobold S, Grassmann S, Chaloupka M,
Lampert C, Wenk S, Kraus F, Rapp M, Düwell P, Zeng Y, Schmollinger
JC, et al: Impact of a new fusion receptor on PD-1-mediated
immunosuppression in adoptive T cell therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst.
107:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu X, Ranganathan R, Jiang S, Fang C, Sun
J, Kim S, Newick K, Lo A, June CH, Zhao Y and Moon EK: A chimeric
switch-receptor targeting PD1 augments the efficacy of
second-generation CAR T cells in advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res.
76:1578–1590. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Davila ML, Riviere I, Wang X, Bartido S,
Park J, Curran K, Chung SS, Stefanski J, Borquez-Ojeda O, Olszewska
M, et al: Efficacy and toxicity management of 19–28z CAR T cell
therapy in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med.
6:224ra252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Savoldo B, Ramos CA, Liu E, Mims MP,
Keating MJ, Carrum G, Kamble RT, Bollard CM, Gee AP, Mei Z, et al:
CD28 costimulation improves expansion and persistence of chimeric
antigen receptor-modified T cells in lymphoma patients. J Clin
Invest. 121:1822–1826. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Long AH, Haso WM, Shern JF, Wanhainen KM,
Murgai M, Ingaramo M, Smith JP, Walker AJ, Kohler ME, Venkateshwara
VR, et al: 4-1BB costimulation ameliorates T cell exhaustion
induced by tonic signaling of chimeric antigen receptors. Nat Med.
21:581–590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zheng Z, Chinnasamy N and Morgan RA:
Protein L: A novel reagent for the detection of chimeric antigen
receptor (CAR) expression by flow cytometry. J Transl Med.
10:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sommermeyer D, Hudecek M, Kosasih PL,
Gogishvili T, Maloney DG, Turtle CJ and Riddell SR: Chimeric
antigen receptor-modified T cells derived from defined CD8+ and
CD4+ subsets confer superior antitumor reactivity in vivo.
Leukemia. 30:492–500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Cheng C, Cheng AW, Zhang
X, Li N, Xia C, Wei X, Liu X and Wang H: CRISPR-Cas9-mediated
multiplex gene editing in CAR-T cells. Cell Res. 27:154–157. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fischer K, Andreesen R and Mackensen A: An
improved flow cytometric assay for the determination of cytotoxic T
lymphocyte activity. J Immunol Methods. 259:159–169. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1
antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E and Riely GJ: New
pathologic classification of lung cancer: Relevance for clinical
practice and clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 31:992–1001. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Porter DL, Hwang WT, Frey NV, Lacey SF,
Shaw PA, Loren AW, Bagg A, Marcucci KT, Shen A, Gonzalez V, et al:
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells persist and induce sustained
remissions in relapsed refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Sci
Transl Med. 7:303ra1392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Patel SP and Kurzrock R: PD-L1 expression
as a predictive biomarker in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:847–856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
McDermott DF and Atkins MB: PD-1 as a
potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 2:662–673.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Baruch K, Deczkowska A, Rosenzweig N,
Tsitsou-Kampeli A, Sharif AM, Matcovitch-Natan O, Kertser A, David
E, Amit I and Schwartz M: PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade reduces
pathology and improves memory in mouse models of Alzheimer's
disease. Nat Med. 22:135–137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
John LB, Devaud C, Duong CP, Yong CS,
Beavis PA, Haynes NM, Chow MT, Smyth MJ, Kershaw MH and Darcy PK:
Anti-PD-1 antibody therapy potently enhances the eradication of
established tumors by gene-modified T cells. Clin Cancer Res.
19:5636–5646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS,
Loriot Y, Cruz C, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Petrylak DP, Teng SL, et
al: MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in
metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. 515:558–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Keir ME, Francisco LM and Sharpe AH: PD-1
and its ligands in T-cell immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 19:309–314.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gargett T, Yu W, Dotti G, Yvon ES, Christo
SN, Hayball JD, Lewis ID, Brenner MK and Brown MP: GD2-specific CAR
T cells undergo potent activation and deletion following antigen
encounter but can be protected from activation-induced cell death
by PD-1 blockade. Mol Ther. 24:1135–1149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Joyce JA and Fearon DT: T cell exclusion,
immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science.
348:74–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Feig C, Jones JO, Kraman M, Wells RJ,
Deonarine A, Chan DS, Connell CM, Roberts EW, Zhao Q, Caballero OL,
et al: Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated
fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:20212–20217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sharma P and Allison JP: The future of
immune checkpoint therapy. Science. 348:56–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zou W and Chen L: Inhibitory B7-family
molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:467–477. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Oncology meets
immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity. 39:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|