|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anjum K, Shagufta BI, Abbas SQ, Patel S,
Khan I, Shah SAA, Akhter N and Hassan SSU: Current status and
future therapeutic perspectives of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)
therapy: A review. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:681–689. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu ZJ, Liu HL, Zhou HC and Wang GC: TIPE2
inhibits hypoxia-induced wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation and
EMT in Glioma cells. Oncol Res. 24:255–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Xu C, Gao M, Ding B, Wei X and Ji N:
Reduced expression of Jumonji, AT-rich interactive domain 2
(JARID2) in glioma inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo.
Oncol Res. 25:365–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang S, Hui Y, Li X and Jia Q: Silencing
of lncRNA-CCDC26 restrains the growth and migration of glioma cells
in vitro and in vivo via targeting miR-203. Oncol Res. Jun
9–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ji S, Zhang B, Kong Y, Ma F and Hua Y:
MiR-326 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth through down regulating
NOB1. Oncol Res. 25:853–861. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li H, Xiang Z, Liu Y, Xu B and Tang J:
MicroRNA-133b inhibits proliferation, cellular migration, and
invasion via targeting LASP1 in hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncol Res.
25:1269–1282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Li J, Yu Z, Sun R and Kan Q:
MiR-935 promotes liver cancer cell proliferation and migration by
targeting SOX7. Oncol Res. 25:427–435. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang G, Fu Y, Liu G, Ye Y and Zhang X:
miR-218 inhibits proliferation, migration, and EMT of gastric
cancer cells by targeting WASF3. Oncol Res. 25:355–364. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen X and Chen J: MiR-3188 regulates cell
proliferation, apoptosis, and migration in breast cancer by
targeting TUSC5 and regulating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Oncol Res. May 26–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang T, Ma G, Zhang Y, Huo H and Zhao Y:
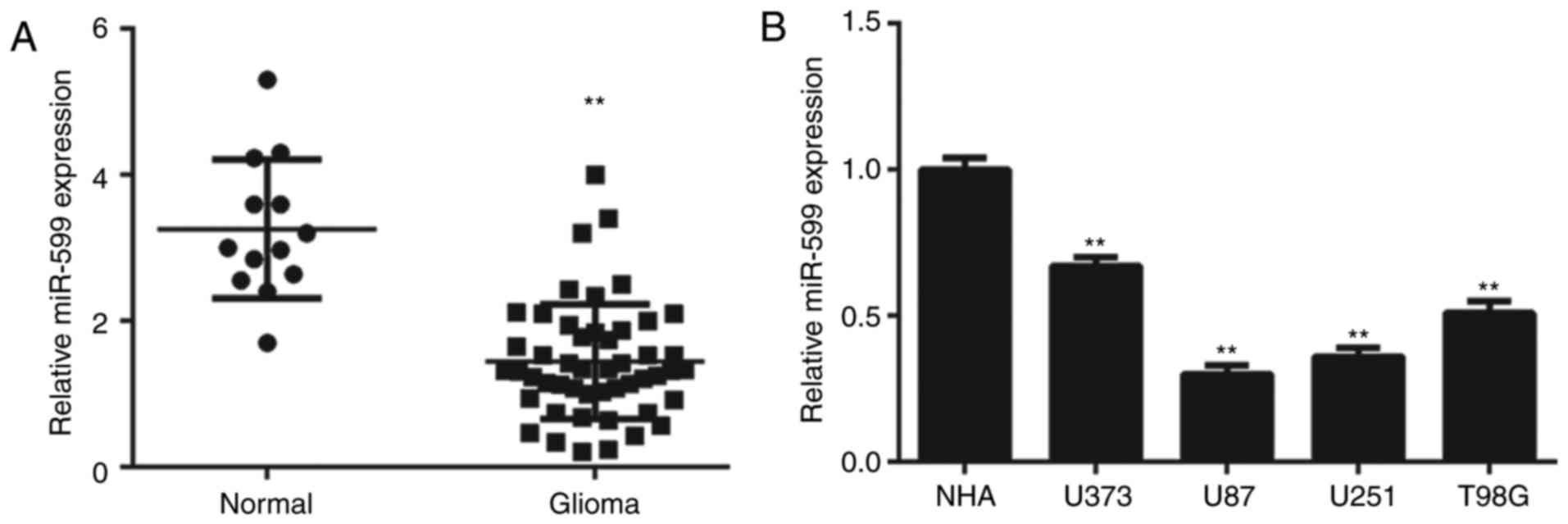
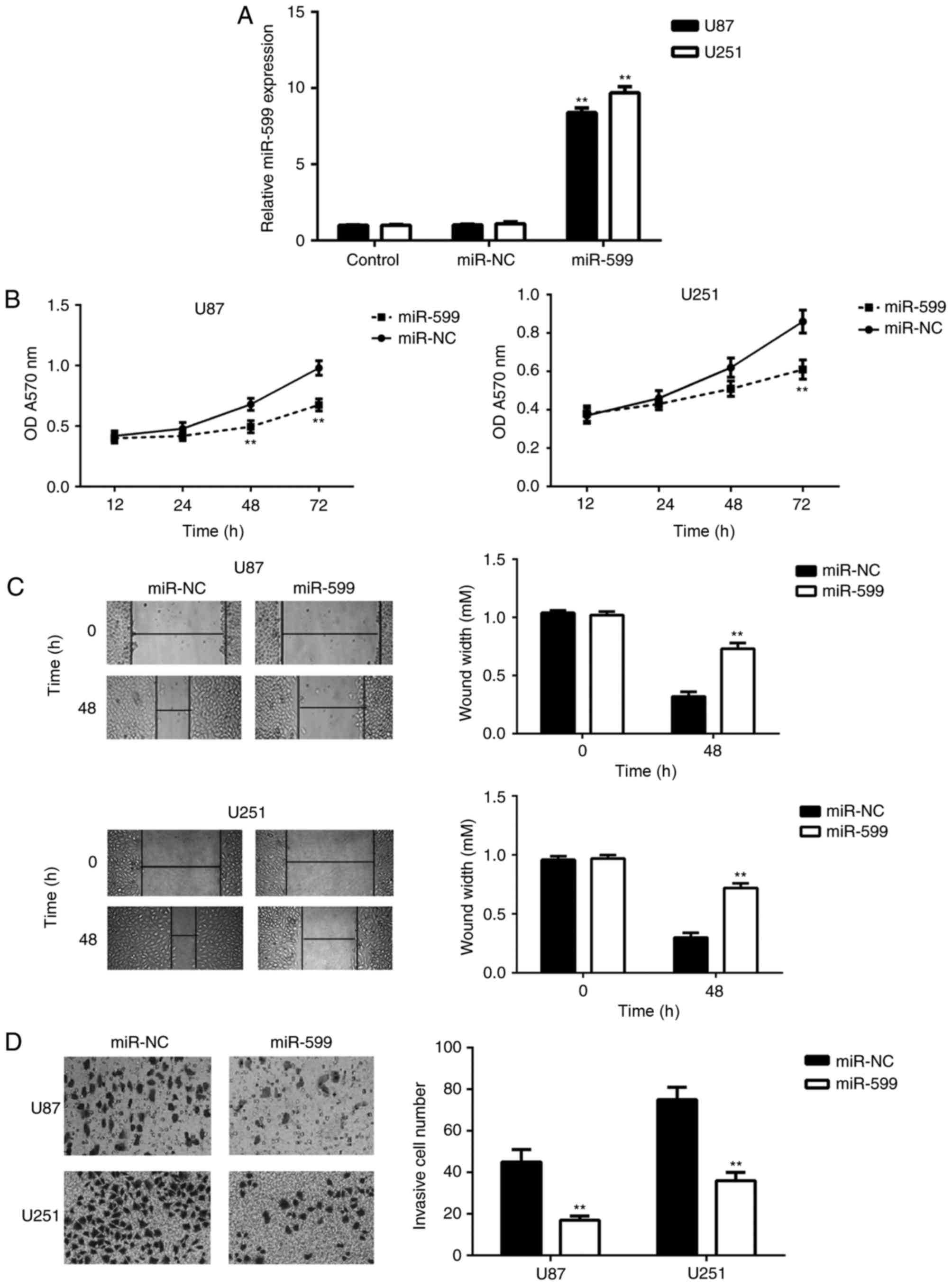
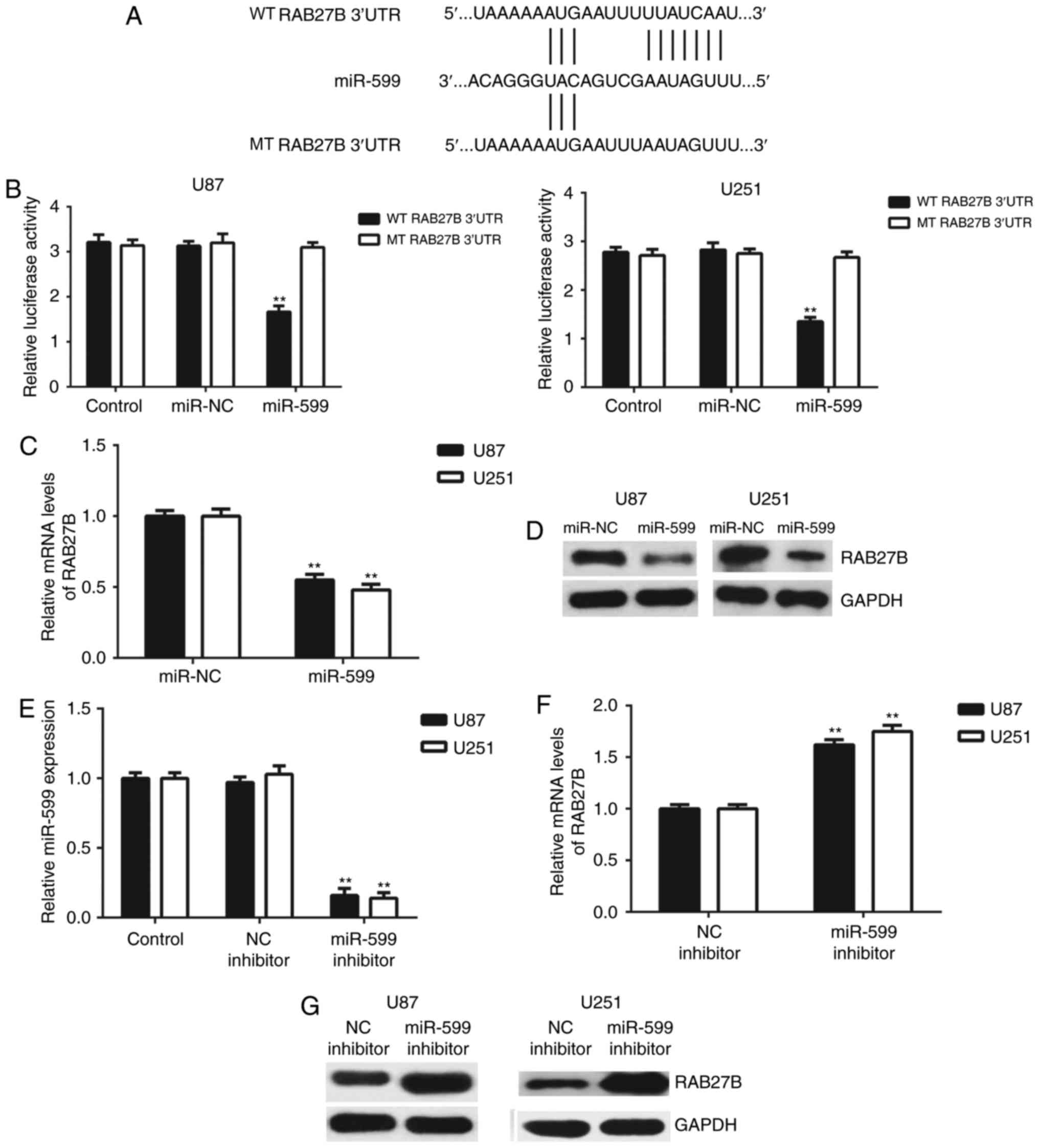
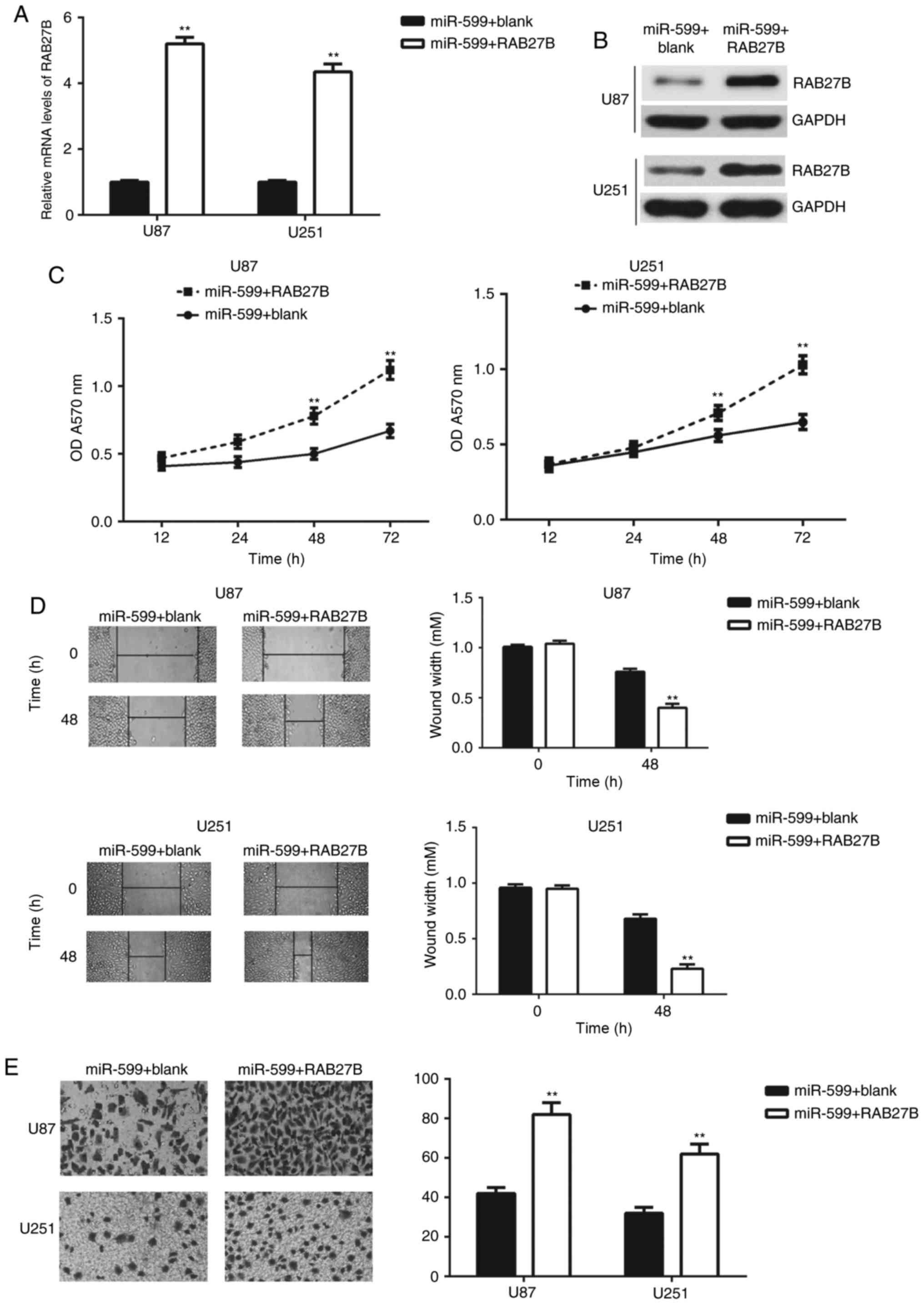
miR-599 inhibits proliferation and invasion of glioma by targeting
periostin. Biotechnol Lett. 39:1325–1333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen D, Guo J, Miki T, Tachibana M and
Gahl WA: Molecular cloning and characterization of rab27a and
rab27b, novel human rab proteins shared by melanocytes and
platelets. Biochem Mol Med. 60:27–37. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang X, Ye X, Sun L, Gao F, Li Y, Ji X and
Wang X, Feng Y and Wang X: Downregulation of serum RAB27B confers
improved prognosis and is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
progression through PI3K-AKT-P21 signaling. Oncotarget.
8:61118–61132. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren P, Yang XQ, Zhai XL, Zhang YQ and
Huang JF: Overexpression of Rab27B is correlated with distant
metastasis and poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett.
12:1539–1545. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Wang Y, Bao Z, Zhang C, Liu Y, Cai
J and Jiang C: Hypomethylated Rab27b is a progression-associated
prognostic biomarker of glioma regulating MMP-9 to promote
invasion. Oncol Rep. 34:1503–1509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rogers TW, Toor G, Drummond K, Love C,
Field K, Asher R, Tsui A, Buckland M and Gonzales M: The 2016
revision of the WHO classification of central nervous system
tumours: Retrospective application to a cohort of diffuse gliomas.
J Neurooncol. 137:181–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xie B, Zhang C, Kang K and Jiang S:
miR-599 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and
migration by targeting TGFB2. PLoS One. 10:e01415122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian W, Wang G, Liu Y, Huang Z, Zhang C,
Ning K, Yu C, Shen Y, Wang M, Li Y, et al: The miR-599 promotes
non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion via SATB2. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 485:35–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chi MN, Guo ST, Wilmott JS, Guo XY, Yan
XG, Wang CY, Liu XY, Jin L, Tseng HY, Liu T, et al: INPP4B is
upregulated and functions as an oncogenic driver through SGK3 in a
subset of melanomas. Oncotarget. 6:39891–39907. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hendrix A, Maynard D, Pauwels P, Braems G,
Denys H, Van den Broecke R, Lambert J, Van Belle S, Cocquyt V,
Gespach C, et al: Effect of the secretory small GTPase Rab27B on
breast cancer growth, invasion, and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst.
102:866–880. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pu Y, Zhao F, Cai W, Meng X, Li Y and Cai
S: MiR-193a-3p and miR-193a-5p suppress the metastasis of human
osteosarcoma cells by down-regulating Rab27B and SRR, respectively.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 33:359–372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|