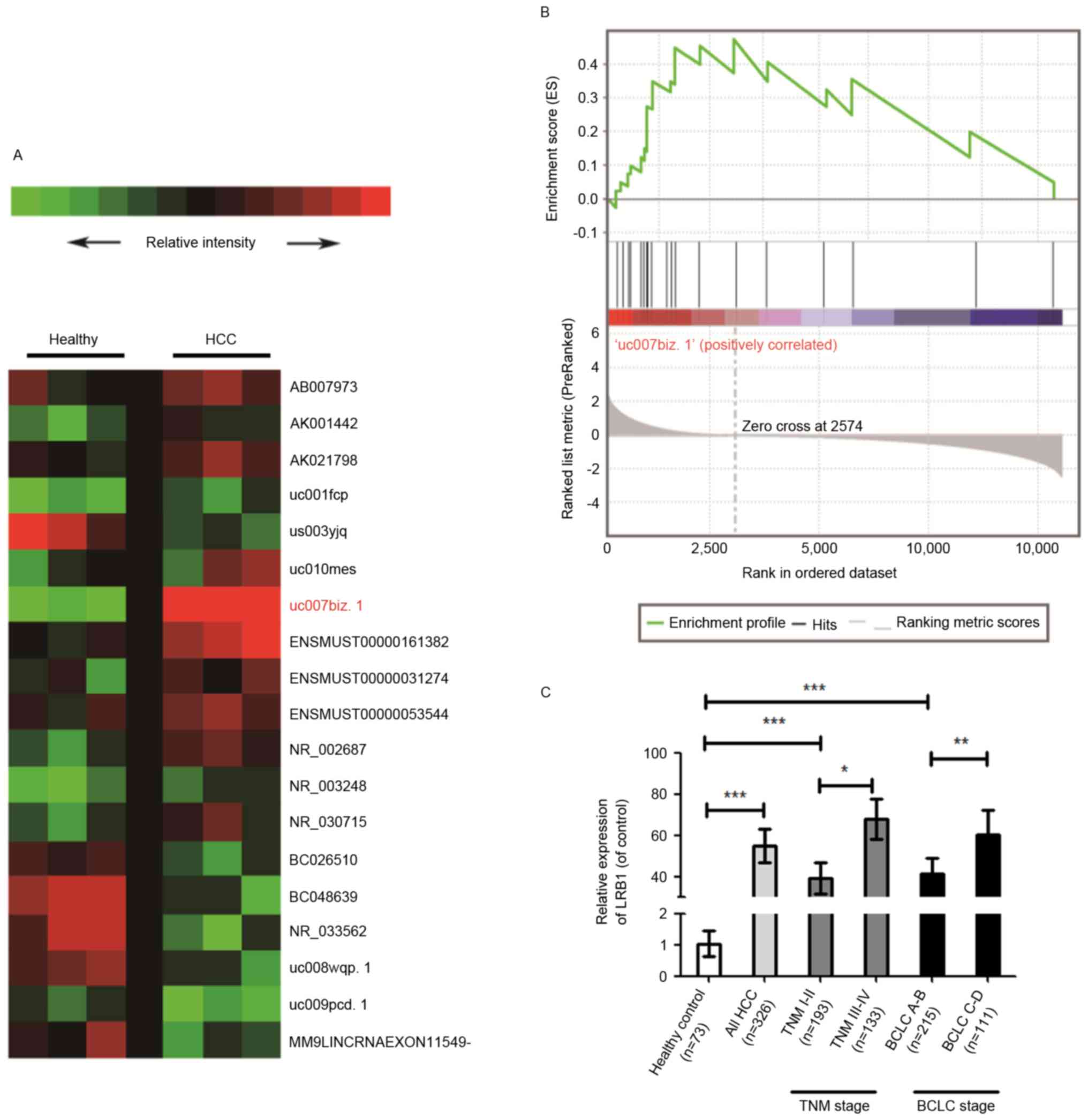
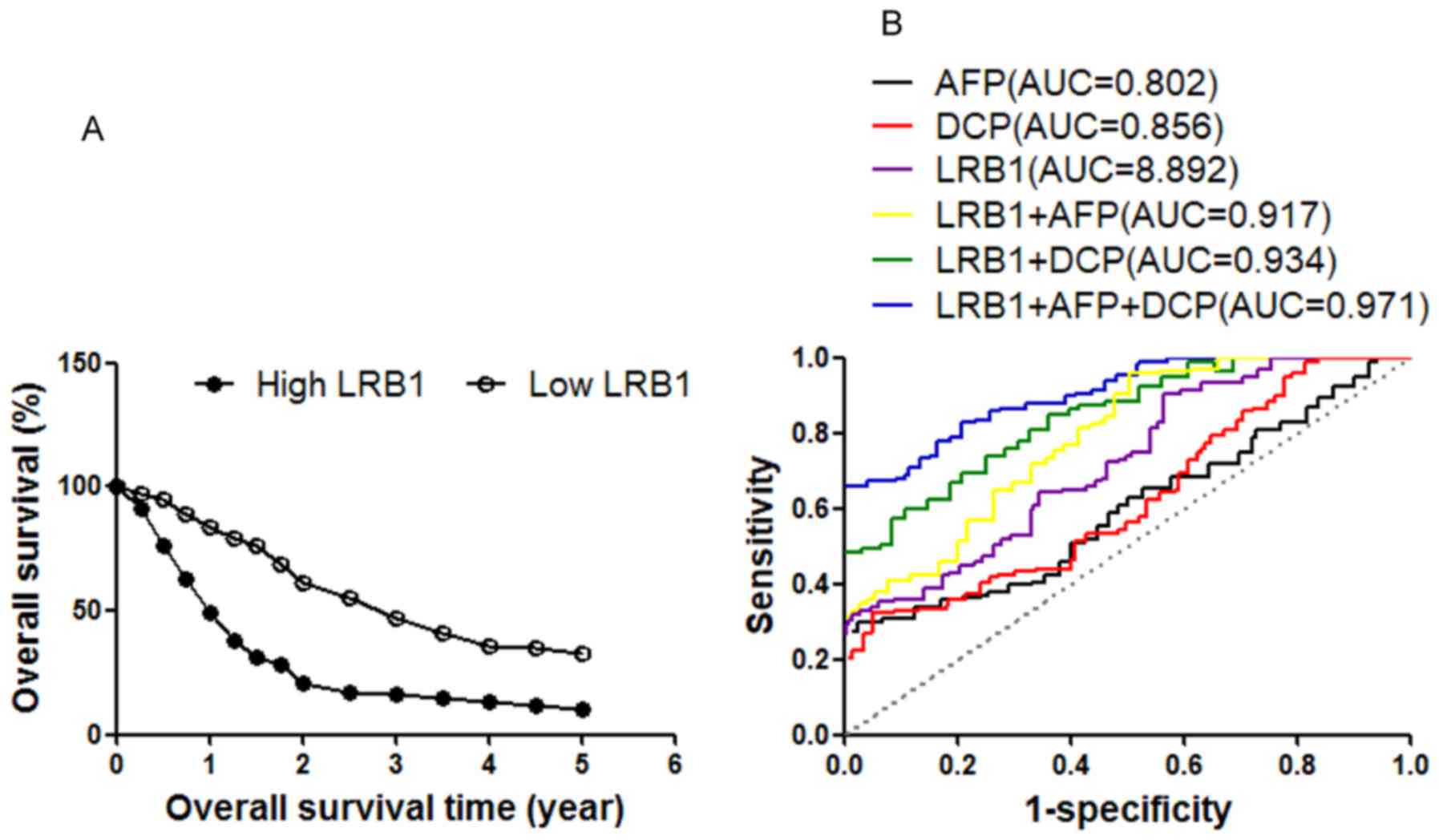
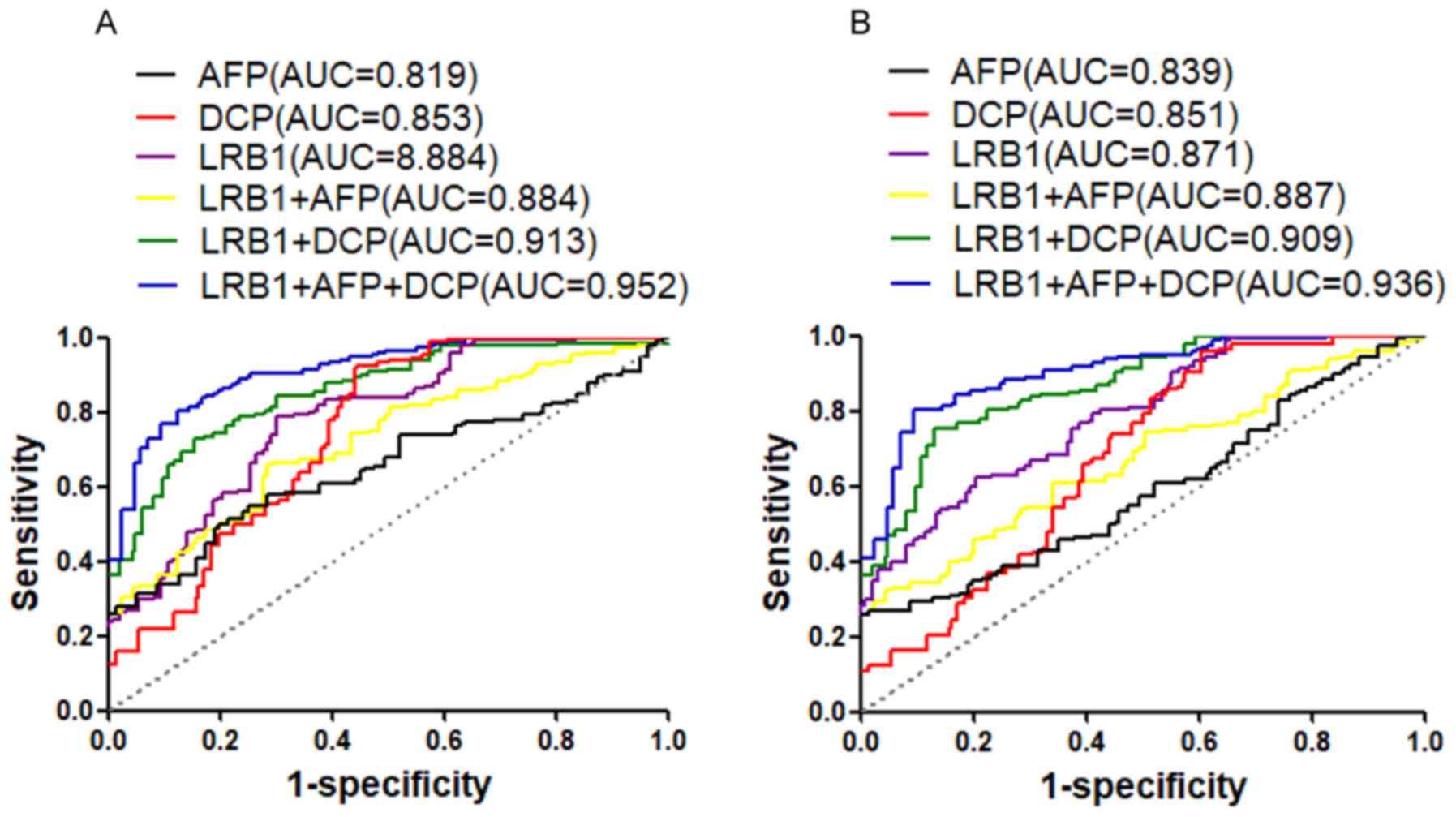
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Trépo C, Chan HL and Lok A: Hepatitis B
virus infection. Lancet. 384:2053–2063. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu LC, Cheng AL and Poon RT: Recent
advances in the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence.
Semin Liver Dis. 34:427–434. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang X, Zhang A and Sun H: Power of
metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:2072–2077. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zucman-Rossi J, Villanueva A, Nault JC and
Llovet JM: Genetic landscape and biomarkers of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 149:1226–1239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bruix J, Reig M and Sherman M:
Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 150:835–853. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frau M, Biasi F, Feo F and Pascale RM:
Prognostic markers and putative therapeutic targets for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Aspects Med. 31:179–193. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sauzay C, Petit A, Bourgeois AM, Barbare
JC, Chauffert B, Galmiche A and Houessinon A: Alpha-foetoprotein
(AFP): A multi-purpose marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin
Chim Acta. 463:39–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Liu X, Li M, Wu
Z, Liu Z, Lv Y and Wang B: Prognostic role of pre-treatment serum
AFP-L3% in hepatocellular carcinoma: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e870112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
rnas in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mohankumar S and Patel T: Extracellular
vesicle long noncoding RNA as potential biomarkers of liver cancer.
Brief Funct Genomics. 15:249–256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M and Glavač D:
Long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers.
2017:72439682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Misawa A, Takayama K, Urano T and Inoue S:
Androgen-induced long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Socs2-As1 promotes
cell growth and inhibits apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 291:17861–1780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xue S, Li QW, Che JP, Guo Y, Yang FQ and
Zheng JH: Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA NBAT-1 is
associated with poor prognosis in patients with clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3765–3774. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pandey GK, Mitra S, Subhash S, Hertwig F,
Kanduri M, Mishra K, Fransson S, Ganeshram A, Mondal T, Bandaru S,
et al: The risk-associated long noncoding RNA NBAT-1 controls
neuroblastoma progression by regulating cell proliferation and
neuronal differentiation. Cancer Cell. 26:722–737. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; Practice Guidelines
Committee: American association for the study of liver diseases,
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 42:1208–1236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chun YH, Kim SU, Park JY, Kim DY, Han KH,
Chon CY, Kim BK, Choi GH, Kim KS, Choi JS and Ahn SH: Prognostic
value of the 7th edition of the AJCC staging system as a clinical
staging system in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J
Cancer. 47:2568–2575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Forner A, Reig ME, de Lope CR and Bruix J:
Current strategy for staging and treatment: The BCLC update and
future prospects. Semin Liver Dis. 30:61–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Subramanian A, Kuehn H, Gould J, Tamayo P
and Mesirov JP: Gsea-p: A desktop application for gene set
enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics. 23:3251–3253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singal AG, Pillai A and Tiro J: Early
detection, curative treatment, and survival rates for
hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in patients with cirrhosis: A
meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 11:e10016242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Poon D, Anderson BO, Chen LT, Tanaka K,
Lau WY, van Cutsem E, Singh H, Chow WC, Ooi LL, Chow P, et al:
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia: Consensus statement
from the asian oncology summit 2009. Lancet Oncol. 10:1111–1118.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo Y, Wang J, Zhang L, Shen S, Guo R,
Yang Y, Chen W, Wang Y, Chen G and Shuai X: Theranostical
nanosystem-mediated identification of an oncogene and highly
effective therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
63:1240–1255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cui SX, Zhang YS, Chu JH, Song ZY and Qu
XJ: Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) antagonizes the effects of
gefitinib on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 35:201–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hiraoka A, Ishimaru Y, Kawasaki H, Aibiki
T, Okudaira T, Toshimori A, Kawamura T, Yamago H, Nakahara H, Suga
Y, et al: Tumor Markers AFP, AFP-L3, and DCP in hepatocellular
carcinoma refractory to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Oncology. 89:167–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun M and Kraus WL: From discovery to
function: The expanding roles of long noncoding RNAs in physiology
and disease. Endocr Rev. 36:25–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Knoll M, Lodish HF and Sun L: Long
non-coding RNAs as regulators of the endocrine system. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 11:151–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Okugawa Y, Grady WM and Goel A: Epigenetic
alterations in colorectal cancer: Emerging biomarkers.
Gastroenterology. 149:1204–1225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Böttcher R, Croce CM,
Jenster G, Visakorpi T and Calin GA: Long noncoding RNA in
prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer. Eur Urol. 65:1140–1151. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tantai J1, Hu D1, Yang Y1 and Geng J1:
Combined identification of long non-coding RNA XIST and HIF1A-AS1
in serum as an effective screening for non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7887–7895. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin C, Shi W, Wang F, Shen X, Qi J, Cong
H, Yuan J, Shi L, Zhu B, Luo X, et al: Long non-coding RNA HULC as
a novel serum biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction of
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:51763–51772. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Amorim M, Salta S, Henrique R and Jerónimo
C: Decoding the usefulness of non-coding RNAs as breast cancer
markers. J Transl Med. 14:2652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chauhan R and Lahiri N: Tissue- and
serum-associated biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark
Cancer. 8:37–55. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|