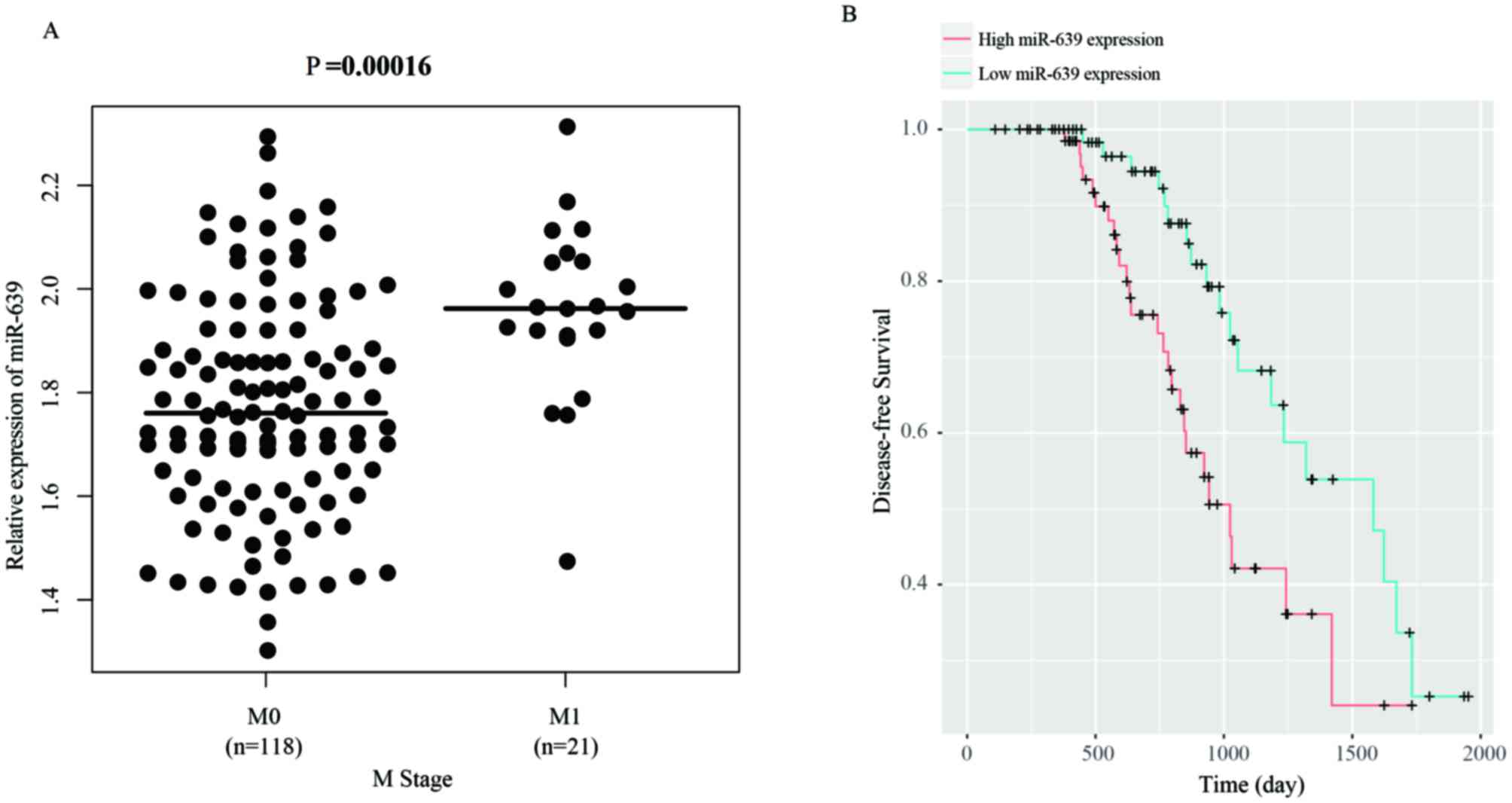
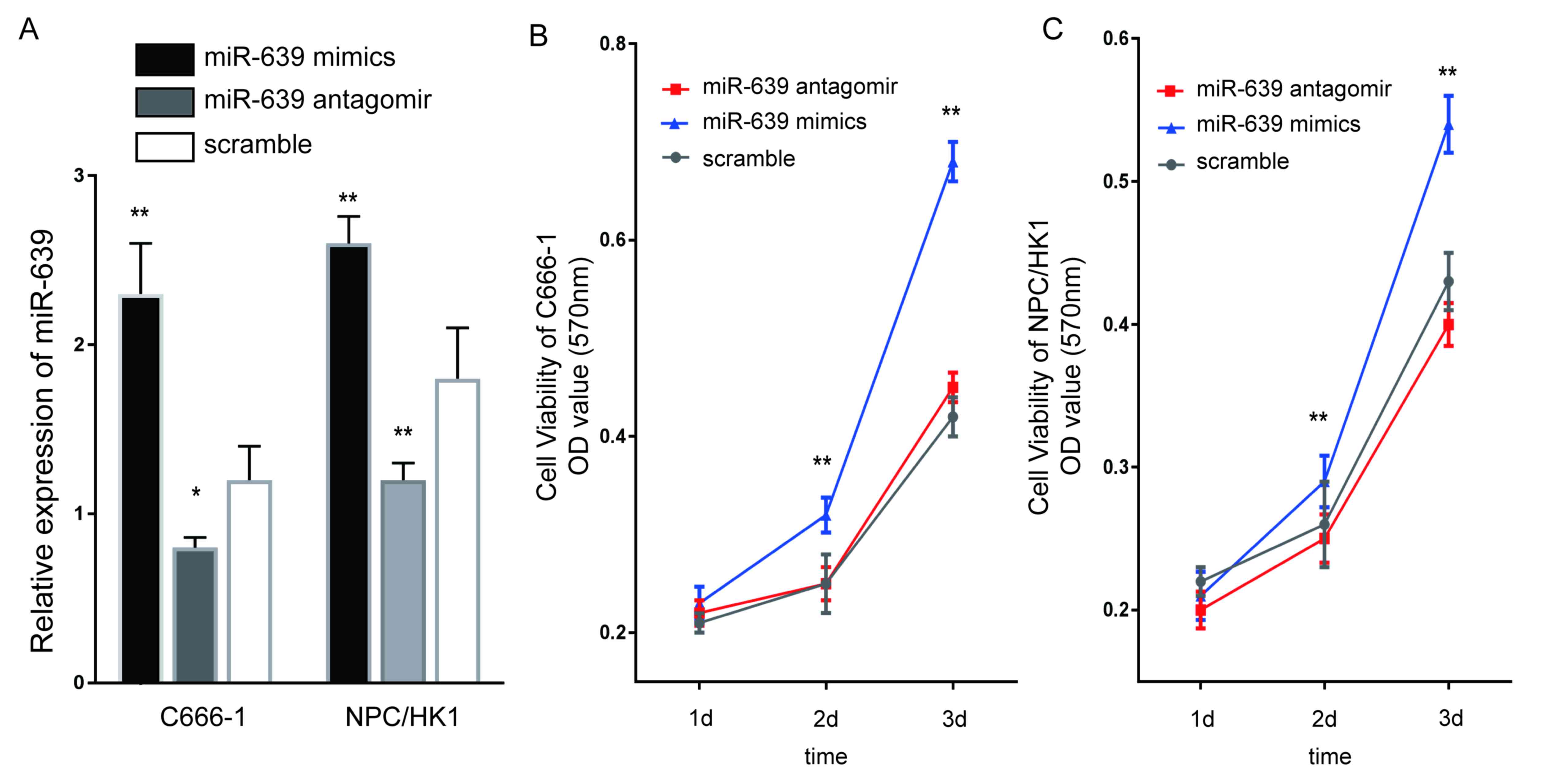
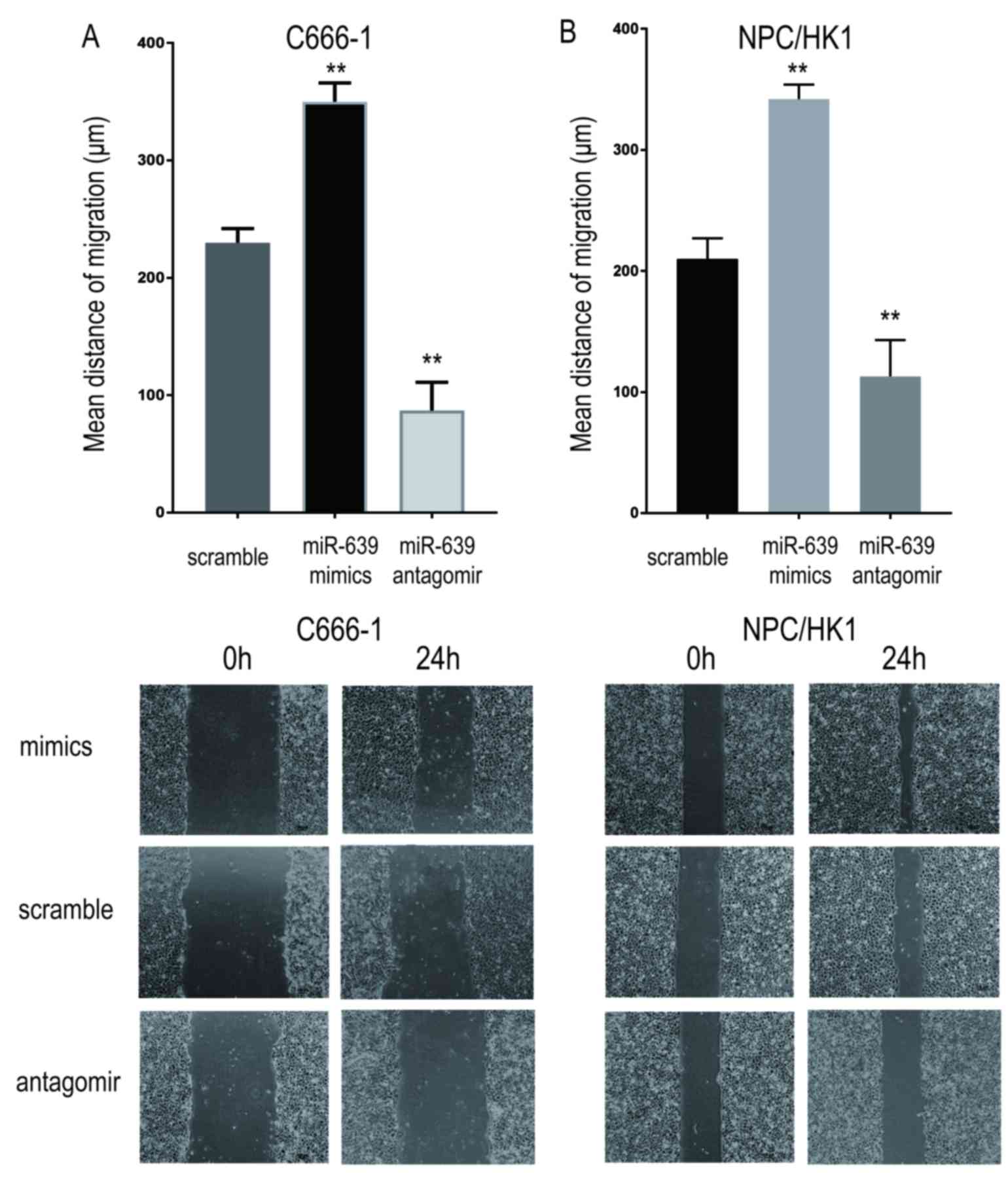
|
1
|
Mcdermott AL, Dutt SN and Watkinson JC:
The aetiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol Allied
Sci. 26:82–92. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang TR, Zhang SW, Chen WQ, Deng W, Zhang
CY, Zhou XJ and Zhai RH: Trends in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
mortality in China, 1973–2005. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:2495–2502. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lai SZ, Li WF, Chen L, Luo W, Chen YY, Liu
LZ, Sun Y, Lin AH, Liu MZ and Ma J: How does intensity-modulated
radiotherapy versus conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy
influence the treatment results in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:661–668. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma J, Mai HQ, Hong MH, Cui NJ, Lu TX, Lu
LX, Mo HY and Min HQ: Is the 1997 AJCC staging system for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma prognostically useful for Chinese patient
populations? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 50:1181–1189. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: MicroRNAs: New
tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma? Hepatology. 57:840–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gomes CC, de Sousa SF and Gomez RS:
MicroRNAs: Small molecules with a potentially role in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Curr Pharm Des. 19:1285–1291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu HL, Wu DP, Wang XF, Wang JG, Jiao F,
Song LL, Xie H, Wen XY, Shan HS, Du YX and Zhao YP: Altered miRNA
expression is associated with differentiation, invasion, and
metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) in patients
from Huaian, China. Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:657–668. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Giles KM, Brown RA, Epis MR, Kalinowski FC
and Leedman PJ: miRNA-7-5p inhibits melanoma cell migration and
invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:706–710. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Salim H, Akbar NS, Zong D, Vaculova AH,
Lewensohn R, Moshfegh A, Viktorsson K and Zhivotovsky B: miRNA-214
modulates radiotherapy response of non-small cell lung cancer cells
through regulation of p38MAPK, apoptosis and senescence. Br J
Cancer. 107:1361–1373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Z, Zeng H, Guo Y, Liu P, Pan H, Deng
A and Hu J: miRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell
proliferation by targeting c-Myc. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
29:1512010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li L, Qiu XG, Lv PW and Wang F: miR-639
promotes the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cell in
vitro. Cancer Cell Int. 14:392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schickel R, Boyerinas B, Park SM and Peter
ME: MicroRNAs: Key players in the immune system, differentiation,
tumorigenesis and cell death. Oncogene. 27:5959–5974. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu N, Chen NY, Cui RX, Li WF, Li Y, Wei
RR, Zhang MY, Sun Y, Huang BJ, Chen M, et al: Prognostic value of a
microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A microRNA
expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 13:633–641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin Z, Sun L, Chen W, Liu B, Wang Y, Fan
S, Li Y and Li J: miR-639 regulates transforming growth factor
beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human tongue
cancer cells by targeting FOXC1. Cancer Sci. 105:1288–1298. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lei ST, Shen F, Chen JW, Feng JH, Cai WS,
Shen L, Hu ZW and Xu B: miR-639 promoted cell proliferation and
cell cycle in human thyroid cancer by suppressing CDKN1A
expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1834–1840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arantes L, de Carvalho AC, Melendez ME,
Carvalho AL and Goloni-Bertollo EM: Methylation as a biomarker for
head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 50:587–592. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Belinsky SA: Gene-promoter
hypermethylation as a biomarker in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:707–717. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sebova K, Zmetakova I, Bella V, Kajo K,
Stankovicova I, Kajabova V, Krivulcik T, Lasabova Z, Tomka M,
Galbavy S and Fridrichova I: RASSF1A and CDH1 hypermethylation as
potential epimarkers in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 10:13–26.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang KP, Hao SP, Chang JH, Wu CC, Tsang
NM, Lee YS, Hsu CL, Ueng SH, Liu SC, Liu YL, et al: Macrophage
inflammatory protein-3alpha is a novel serum marker for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma detection and prediction of treatment
outcomes. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6979–6987. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Apple FS, Wu AHB, Mair J, Ravkilde J,
Panteghini M, Tate J, Pagani F, Christenson RH, Mockel M, Danne O,
et al: Future biomarkers for detection of ischemia and risk
stratification in acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chem. 51:810–824.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bakir M, Millington KA, Soysal A, Deeks
JJ, Efee S, Aslan Y, Dosanjh DP and Lalvani A: Prognostic value of
a T-cell-based, interferon-gamma biomarker in children with
tuberculosis contact. Ann Intern Med. 149:777–786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao M, Yin H and Fei ZW: Clinical
application of microRNA in gastric cancer in Eastern Asian area.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:2019–2027. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Luo HN, Tian WD, Lu J, Li G, Wang
L, Zhang B, Liang BJ, Peng XH, Lin SX, et al: Diagnostic and
prognostic value of plasma microRNA deregulation in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:1133–1142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to
mammalian P-bodies. Nat Cell Biol. 7:719–723. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ørom UA, Nielsen FC and Lund AH:
MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and
enhances their translation. Mol Cell. 30:460–471. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Büssing I, Slack FJ and Grosshans H: let-7
microRNAs in development, stem cells and cancer. Trends Mol Med.
14:400–409. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Chen X, Lin J, Lwin T, Wright G,
Moscinski LC, Dalton WS, Seto E, Wright K, Sotomayor E and Tao J:
Myc represses miR-15a/miR-16-1 expression through recruitment of
HDAC3 in mantle cell and other non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas.
Oncogene. 31:3002–3008. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Christoffersen NR, Shalgi R, Frankel LB,
Leucci E, Lees M, Klausen M, Pilpel Y, Nielsen FC, Oren M and Lund
AH: p53-independent upregulation of miR-34a during oncogene-induced
senescence represses MYC. Cell Death Differ. 17:236–245. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lei ST, Shen F, Chen JW, Feng JH, Cai WS,
Shen L, Hu ZW and Xu B: miR-639 promoted cell proliferation and
cell cycle in human thyroid cancer by suppressing CDKN1A
expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1834–1840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Qiu XG, Lv PW and Wang F: miR-639
promotes the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cell in
vitro. Cancer Cell Int. 14:392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Endo H, Muramatsu T, Furuta M, Uzawa N,
Pimkhaokham A, Amagasa T, Inazawa J and Kozaki K: Potential of
tumor-suppressive miR-596 targeting LGALS3BP as a therapeutic agent
in oral cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:560–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu S, Huang S, Ding J, Zhao Y, Liang L,
Liu T, Zhan R and He X: Multiple microRNAs modulate p21Cip1/Waf1
expression by directly targeting its 3′ untranslated region.
Oncogene. 29:2302–2308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ragusa M, Caltabiano R, Russo A, Puzzo L,
Avitabile T, Longo A, Toro MD, Di Pietro C, Purrello M and Reibaldi
M: MicroRNAs in vitreus humor from patients with ocular diseases.
Mol Vis. 19:430–440. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nordentoft I, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,
Agerbæk M, Theodorescu D, Ostenfeld MS, Hartmann A, Borre M,
Ørntoft TF and Dyrskjøt L: miRNAs associated with chemo-sensitivity
in cell lines and in advanced bladder cancer. BMC Med Genomics.
5:402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sandip KM: Unravelling the mechanism of
ERR beta behind its role as a tumor suppressor and contribution of
specific miRNAs and co-regulators in breast cancer cell lines. J
Cancer Sci Ther. 6:102014.
|
|
40
|
Smart CE, Amiri Askarian ME, Wronski A,
Dinger ME, Crawford J, Ovchinnikov DA, Vargas AC, Reid L, Simpson
PT, Song S, et al: Expression and function of the protein tyrosine
phosphatase receptor J (PTPRJ) in normal mammary epithelial cells
and breast tumors. PLoS One. 7:e407422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Spring K, Fournier P, Lapointe L, Chabot
C, Roussy J, Pommey S, Stagg J and Royal I: The protein tyrosine
phosphatase DEP-1/PTPRJ promotes breast cancer cell invasion and
metastasis. Oncogene. 34:5536–5547. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kakkoura MG, Demetriou CA, Loizidou MA,
Loucaides G, Neophytou I, Malas S, Kyriacou K and Hadjisavvas A:
MnSOD and CAT polymorphisms modulate the effect of the
Mediterranean diet on breast cancer risk among Greek-Cypriot women.
Eur J Nutr. 55:1535–1544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ralph DA, Zhao LP, Aston CE, Manjeshwar S,
Pugh TW, DeFreese DC, Gramling BA, Shimasaki CD and Jupe ER:
Age-specific association of steroid hormone pathway gene
polymorphisms with breast cancer risk. Cancer. 109:1940–1948. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu S, Huang S, Ding J, Zhao Y, Liang L,
Liu T, Zhan R and He X: Multiple microRNAs modulate p21Cip1/Waf1
expression by directly targeting its 3′untranslated region.
Oncogene. 29:2302–2308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|