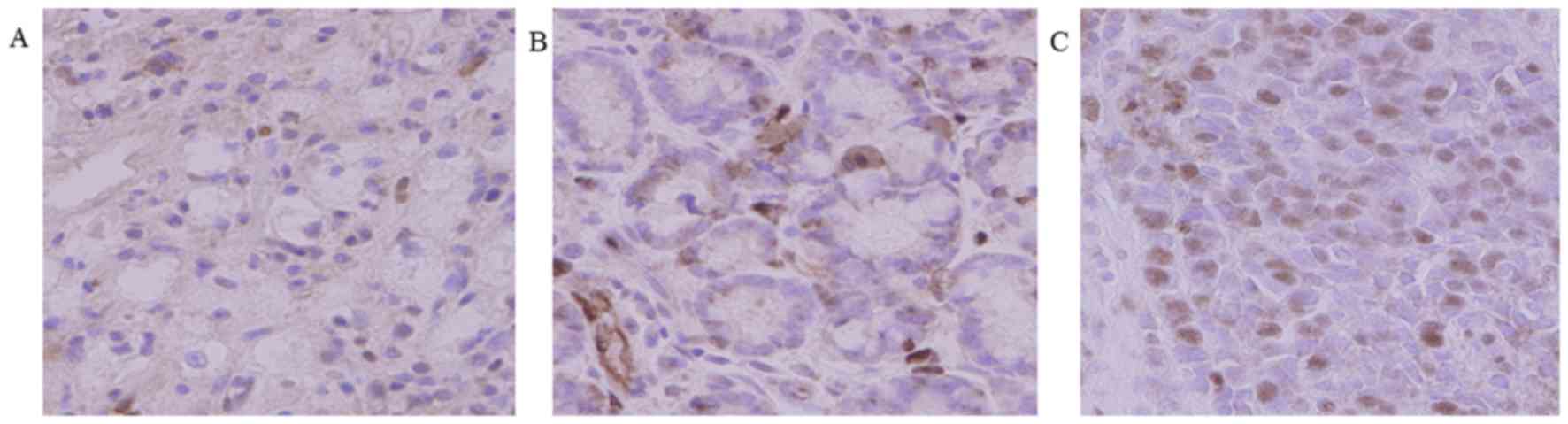
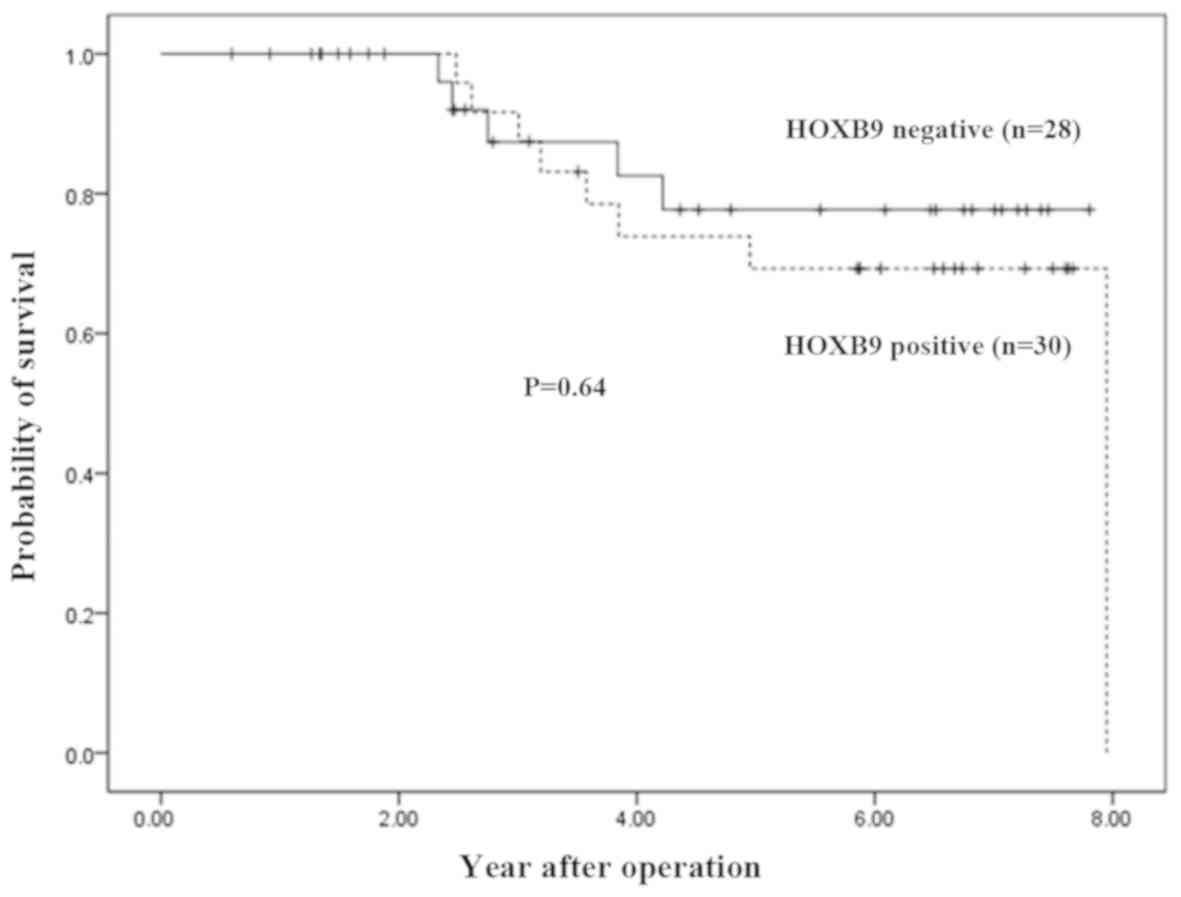
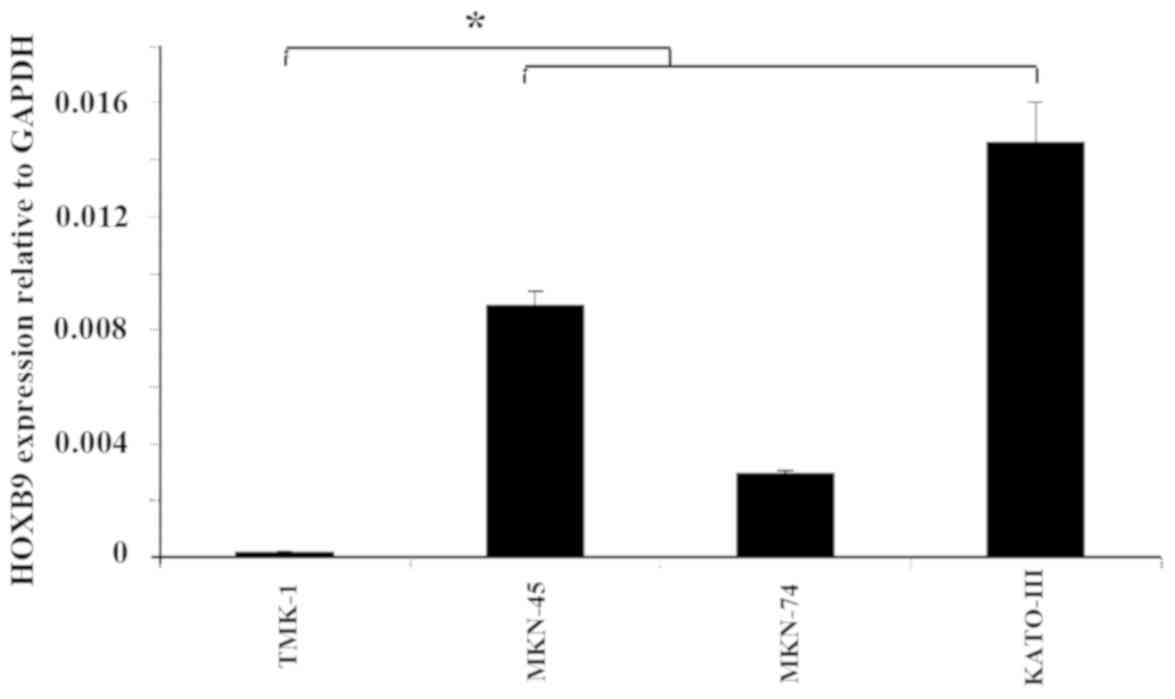
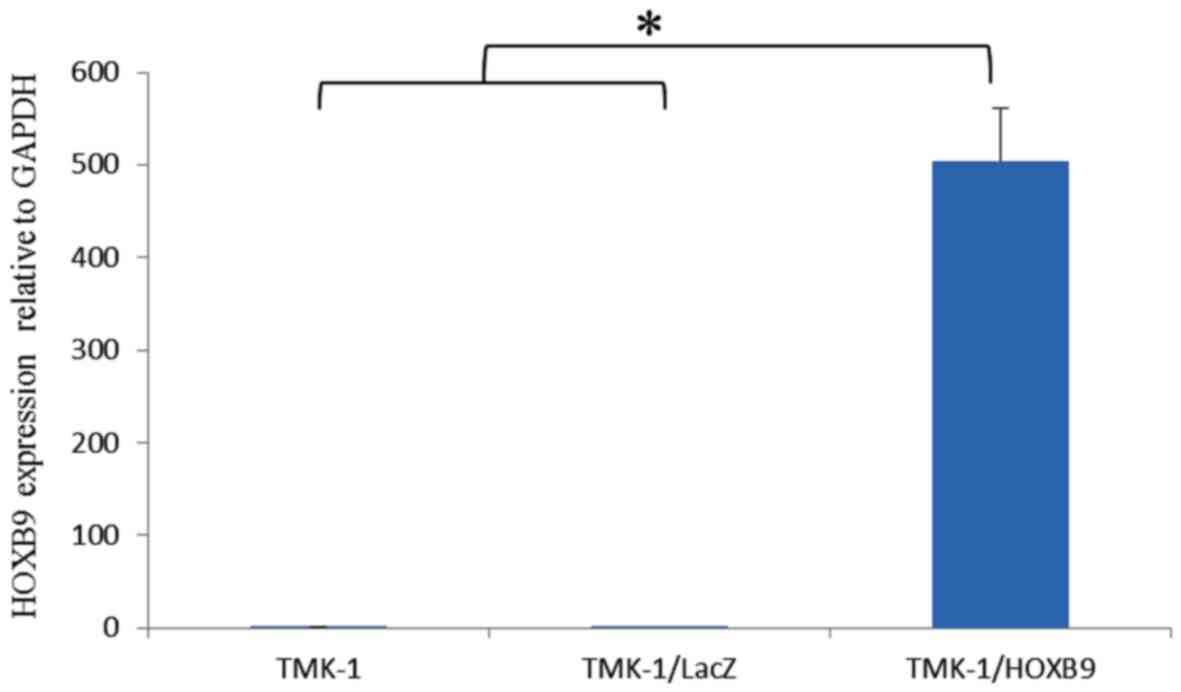
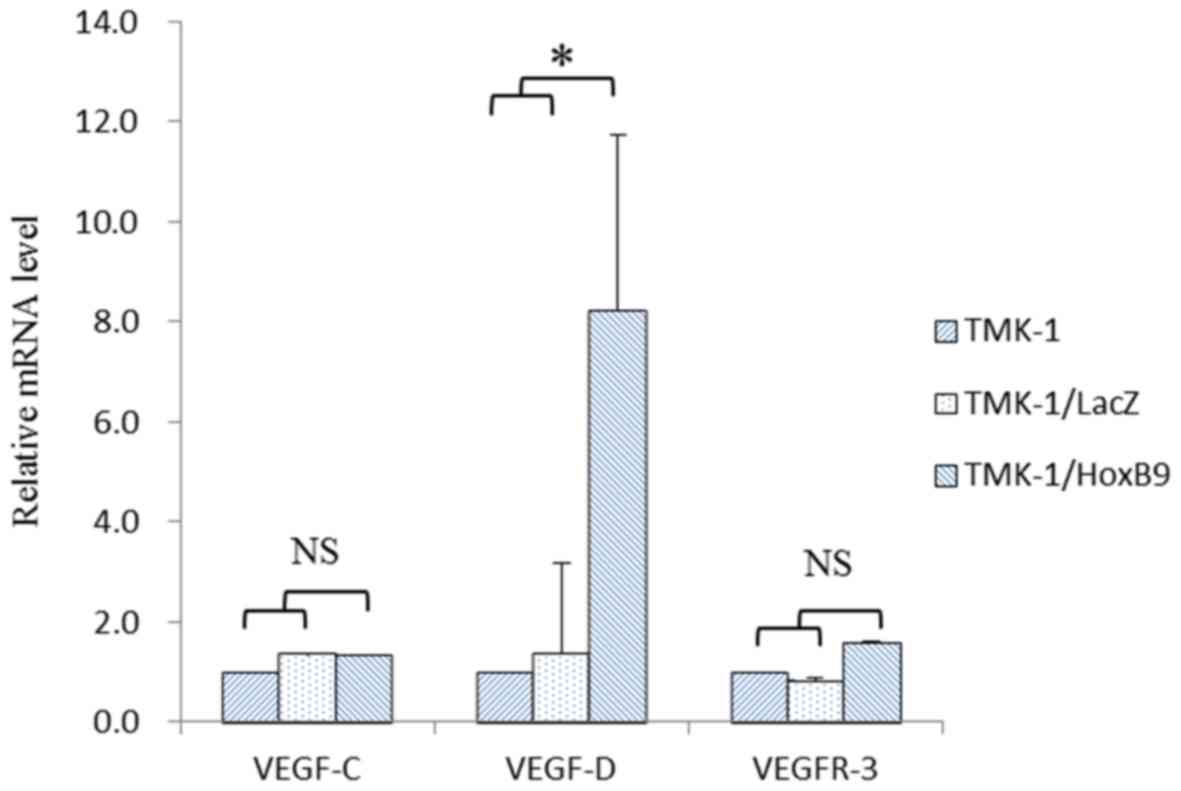
|
1
|
Sano T, Sasako M, Kinoshita T and Maruyama
K: Recurrence of early gastric cancer. Follow-up of 1475 patients
and review of the Japanese literature. Cancer. 72:3174–3178. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association
Registration Committee, ; Maruyama K, Kaminishi M, Hayashi K, Isobe
Y, Honda I, Katai H, Arai K, Kodera Y and Nashimoto A: Gastric
cancer treated in 1991 in Japan: Data analysis of nationwide
registry. Gastric Cancer. 9:51–66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, Ono H,
Nakanishi Y, Shimoda T and Kato Y: Incidence of lymph node
metastasis from early gastric cancer: Estimation with a large
number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer. 3:219–225.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abate-Shen C: Deregulated homeobox gene
expression in cancer: Cause or consequence? Nat Rev Cancer.
2:777–785. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hatzis P, van der Flier LG, van Driel MA,
Guryev V, Nielsen F, Denissov S, Nijman IJ, Koster J, Santo EE,
Welboren W, et al: Genome-wide pattern of TCF7L2/TCF4 chromatin
occupancy in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2732–2744.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Zhang XH, Kim JY,
Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Gerald WL and Massagué J: WNT/TCF signaling
through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis.
Cell. 138:51–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hayashida T, Takahashi F, Chiba N,
Brachtel E, Takahashi M, Godin-Heymann N, Gross KW, Vivanco Md,
Wijendran V, Shioda T, et al: HOXB9, a gene overexpressed in breast
cancer, promotes tumorigenicity and lung metastasis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:1100–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Seki H, Hayashida T, Jinno H, Hirose S,
Sakata M, Takahashi M, Maheswaran S, Mukai M and Kitagawa Y: HOXB9
expression promoting tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis is
associated with clinical outcomes in breast cancer patients. Ann
Surg Oncol. 19:1831–1840. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang L, Xu Y and Zou L: Overexpressed
homeobox B9 regulates oncogenic activities by transforming growth
factor-β1 in gliomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:272–279.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hoshino Y, Hayashida T, Hirata A,
Takahashi H, Chiba N, Ohmura M, Wakui M, Jinno H, Hasegawa H,
Maheswaran S, et al: Bevacizumab terminates homeobox B9-induced
tumor proliferation by silencing microenvironmental communication.
Mol Cancer. 13:1022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pak KH, Jo A, Choi HJ, Choi Y, Kim H and
Cheong JH: The different role of intratumoral and peritumoral
lymphangiogenesis in gastric cancer progression and prognosis. BMC
Cancer. 15:4982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takahashi S: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for
antiangiogenic tumor therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1785–1788. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM classification of malignant tumours. (7th). Wiley-Blackwell.
(Hoboken, Oxford). 2009.
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bouhlel MA, Lambert M and David-Cordonnier
MH: Targeting transcription factor binding to DNA by competing with
DNA binders as an approach for controlling gene expression. Curr
Top Med Chem. 15:1323–1358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sha S, Gu Y, Xu B, Hu H, Yang Y, Kong X
and Wu K: Decreased expression of HOXB9 is related to poor overall
survival in patients with gastric carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis.
45:422–429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|