Introduction
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) arises from
the urothelium of the renal pelvis or ureter, and >90% of these
tumors are histopathologically categorized as urothelial carcinomas
(1). UTUC is uncommon, accounting
for ~5–10% of all cases of urothelial cancer in the United States
in 2012 (2,3). However, in recent years, the number of
patients with UTUC has been increasing in numerous countries,
including Japan (4). In total, 55%
of UTUC cases are muscle invasive at the initial diagnosis, which
is increased compared with that of bladder cancer (30%) (5,6). Radical
nephroureterectomy with bladder cuff excision is the standard
surgical treatment for localized UTUC (1,3,5). However, since postoperative local
relapse or distant metastasis occurs in 24–28% of cases, UTUC is
considered to exhibit a poor prognosis (5,7).
Therefore, the proportion of invasive muscle cancer, postoperative
relapse and distant metastasis in UTUC is increased, compared with
the proportion of that associated with bladder cancer.
Consequently, patients with UTUC have a poor prognosis, compared
with patients with bladder cancer. Additionally, compared with
bladder cancer, a limited number of studies have investigated
predictors for patients with UTUC (3,5–7). Therefore, biomarkers are required to
improve the prognosis of patinets with UTUC.
The currently recognized prognostic markers for UTUC
are mostly derived from pathological features, including
pathological grade, T stage, lymph node involvement, surgical
margin status and lymphovascular invasion (3,8).
However, to the best of our knowledge, it remains unknown which
prognostic markers are associated with the survival outcomes of
patients with UTUC.
Previously, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR)
has been reported to be a beneficial prognostic marker in numerous
types of malignancy, including lung, renal, gastric, hepatic and
colorectal cancer (9,10). With respect to urothelial carcinoma,
the majority of previous studies regarding bladder cancer (11–13) and
UTUC (14,15) have only discussed preoperative NLR.
In particular, to the best of our knowledge, the postoperative NLR
has rarely been investigated. Therefore, the present study
investigated the clinical significance of the postoperative NLR as
a prognostic marker in patients with clinically localized UTUC.
Materials and methods
Study cohort and design
The present study was approved by the Research
Ethics Committee of Kurume University (Kurume, Japan). Data of 152
patients diagnosed with localized UTUC who underwent radical
nephroureterectomy at Kurume University hospital (Kurume, Japan)
between January 2004 and December 2015 were retrospectively
reviewed. Patients were excluded according to following criteria:
i) Had received neoadjuvant chemotherapy; ii) had an active
infection, or iii) had been administered cortical steroids. A total
of 134 patients who were observed for a minimum of 6 months were
included in the analysis. A diagnosis of localized UTUC was
established by computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging,
urine cytology, and cystoscopy and/or ureteroscopy. Pathological T
(pT) stages were uniformly adjusted according to the 2009
Tumor-Node-Metastasis classification system (16). Tumor grade was assessed according to
the 1999 World Health Organization classification (17). Postoperative surveillance was
performed by physical examination, urine cytology and cystoscopy at
3-month intervals, and blood examinations and computed tomography
at 6-month intervals. Metastasis and local relapse were defined as
urothelial tumor relapse outside the residual urinary tract. The
clinicopathological characteristics of the 134 patients enrolled in
the present study, and the comparisons between the high and low NLR
groups are presented in Table I. The
median age of the patients at the time of surgery was 70 years
(range, 64–76 years) and its incidence was ~2-fold higher in male
patients compared with female patients. The median surveillance
time was 40.5 months (range, 20.8–71.3 months). Clinicopathological
variables affecting survival were analyzed, including age at the
time of surgery, sex, tumor location, the presence of
hydronephrosis, tumor diameter, pre- and postoperative NLR,
postoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) level, pT stage, tumor
grade, the presence of lymphovascular invasion, positive surgical
margins and lymph node involvement. All pathological diagnoses were
performed by a specialist pathologist at Kurume University (Kurume,
Japan). All clinicopathological data were retrieved from medical
records at the hospital.
 | Table I.Clinicopathological characteristics of
the 134 patients with UTUC. |
Table I.
Clinicopathological characteristics of
the 134 patients with UTUC.
|
| Postoperative
NLR |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Characteristics | ≥2.5 (n=35) | <2.5 (n=99) | P-valuea |
|---|
| Median age, years
(IQR) | 73 (66–77) | 70 (61–76) | 0.142 |
| Sex, n (%) |
|
|
|
| Male | 19 (54.3) | 69 (69.7) | 0.103 |
|
Female | 16 (45.7) | 30 (30.3) |
|
| Tumor location, n
(%) |
|
|
|
| Renal
pelvis | 19 (54.3) | 55 (55.6) | 0.312 |
|
Ureter | 16 (45.7) | 44 (44.4) |
|
| Hydronephrosis, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
Yes | 21 (60.0) | 62 (62.6) | 0.784 |
| No | 14 (40.0) | 37 (37.4) |
|
| Median tumor size,
cm (IQR) | 3.0 (1.5–3.6) | 2.5 (1.7–3.5) | 0.353 |
| pT stage, n
(%)(16) |
|
|
|
|
pT1/T2 | 15 (42.9) | 65 (65.7) | 0.019b |
|
pT3/T4 | 20 (57.1) | 34 (34.3) |
|
| Lymph node
involvement, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
pNx/N0 | 28 (80.0) | 89 (89.9) | 0.146 |
|
pN1 | 7 (20.0) | 10 (10.1) |
|
| Tumor grade, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
G1/G2 | 19 (54.3) | 70 (70.7) | 0.081 |
| G3 | 16 (45.7) | 29 (29.3) |
|
| Lymphovascular
invasion, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
Yes | 18 (52.9) | 30 (30.9) | 0.024b |
| No | 16 (47.1) | 67 (69.1) |
|
| Surgical margins, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
Positive | 5 (14.3) | 7 (7.1) | 0.219 |
|
Negative | 30 (85.7) | 92 (92.9) |
|
| Postoperative CRP
level, mg/dl, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
≥0.3 | 12 (36.4) | 7 (7.5) |
<0.001b |
|
<0.3 | 21 (63.6) | 86 (92.5) |
|
| Median
postoperative leucocytes per µl (IQR) | 5,600
(4,800–7,100) | 5,100
(4,300–6,000) | 0.061 |
| Median
postoperative neutrophils per µl (IQR) | 3,694
(3,014–4,807) | 2,736
(2,112–3,321) |
<0.001b |
| Median
postoperative lymphocytes per µl (IQR) | 1,222
(972–1,440) | 1,819
(1,505–2,129) |
<0.001b |
NLR
The NLR was derived by dividing the absolute
neutrophil count by the absolute lymphocyte count in peripheral
blood. A high NLR (≥2.5) was defined according to previous studies
(12,18). Receiver operating characteristic
(ROC) curves were plotted of the postoperative NLR for the
evaluation of overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival
(CSS) rates. The area under the curves of postoperative NLR for OS
and CSS were 0.617 and 0.656, respectively. The postoperative NLR
threshold was 2.67 for OS and CSS. The sensitivity of postoperative
NLR for OS and CSS was 40.0 and 52.9% respectively, and the
specificity was 87.6 and 89% respectively. Additionally, the NLR
threshold according to the ROC curves was 2.67. In the majority of
previous studies on urothelial carcinoma, the NLR threshold has
been in the range 2.2–3.0 (9,12,14,18).
Therefore, the present study considered that 2.5 was a reasonable
threshold. The preoperative NLR was measured prior to any tumor
manipulation, including ureteroscopy or retrograde pyelography. The
postoperative NLR was measured 1–2 months after surgery. In cases
requiring adjuvant chemotherapy, the postoperative NLR was measured
prior to adjuvant chemotherapy.
Statistical analysis
Mann-Whitney U test and χ2 test were used to assess
differences between the high and low postoperative NLR groups. The
statistical analysis data are presented as the median and
interquartile range for continuous variables or the proportion of
events for categorical variables. Spearman's correlation
coefficient was analyzed between the preoperative NLR and
postoperative NLR. Survival curves were estimated using the
Kaplan-Meier method and compared with a log-rank test. Survival
data were collected on December 31, 2016. Patients where contact
was lost during follow-up were evaluated at the date of last
contact. Patients who were alive on December 31, 2016 were assessed
for OS rate. CSS rate was calculated from the date of surgery to
the date of cancer-associated mortality. Patients were assessed at
the date of mortality if they succumbed to mortality from other
causes. OS was calculated from the date of surgery to the date of
mortality from any cause. Univariate and multivariate analyses were
performed using Cox proportional hazards regression models. All
statistical analyses were conducted using JMP software for Windows
(v.12.0.1; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Effect of Kaplan-Meier on pT stage
distribution
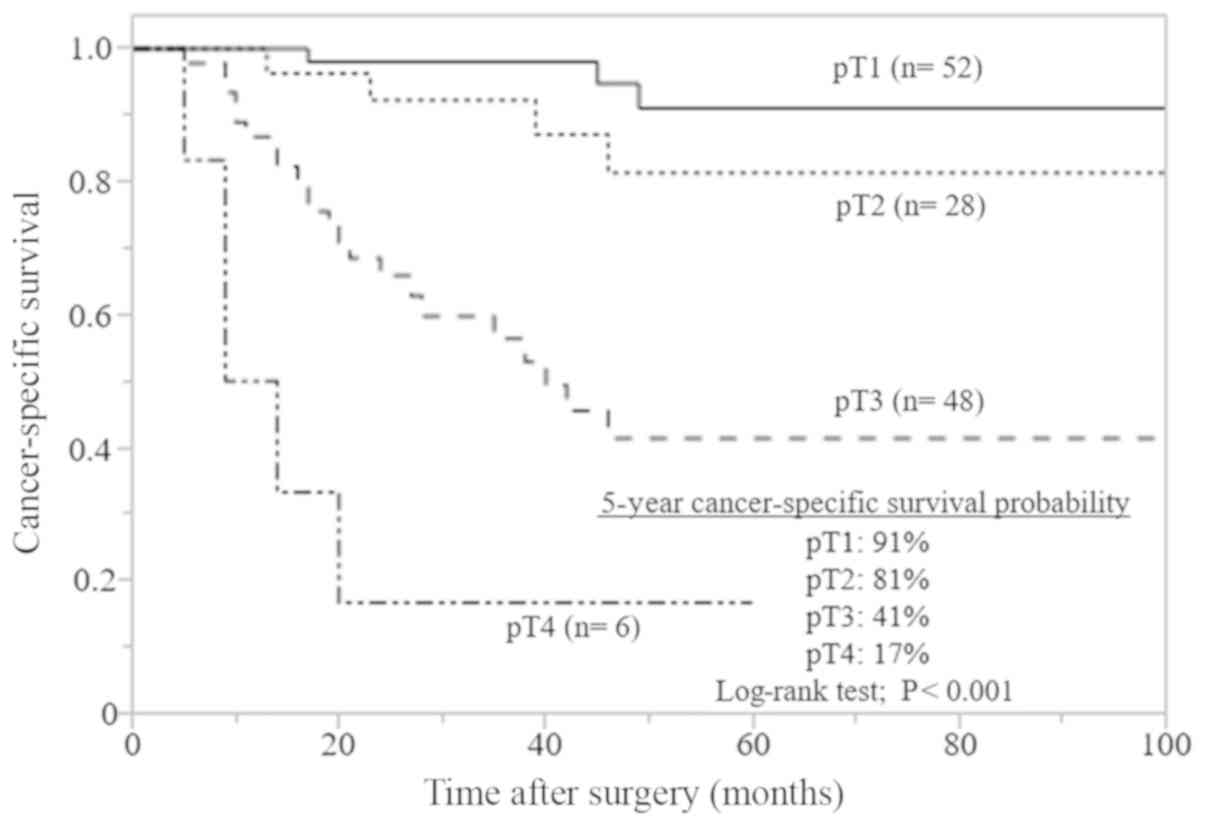
The pT stage distribution was as follows: T1
(including Ta and Tis), 38.8%; T2, 20.9%; T3, 35.8% and T4, 4.5%.
In total, 34% of patients had tumor grade 3. Kaplan-Meier curves
for CSS stratified according to pT stage are presented in Fig. 1. Advanced pT stage (≥T3) was
associated with a significantly reduced survival, compared with
early pT stage (T1 and T2; P<0.001).
Clinicopathological characteristics
and survival analysis of postoperative NLR
The median pre- and postoperative NLRs were 2.03
(1.62–2.75) and 1.72 (1.34–2.59), respectively. The pre- and
postoperative NLRs were elevated in 41 (30.6%) and 35 patients
(26.1%), respectively (data not shown). A high postoperative NLR of
≥2.5 was significantly associated with a high postoperative CRP
level of ≥0.3 mg/dl (P<0.001), an advanced pT stage (≥T3;
P=0.019) and positive lymphovascular invasion (P=0.024) in the
surgical specimens (Table I). The
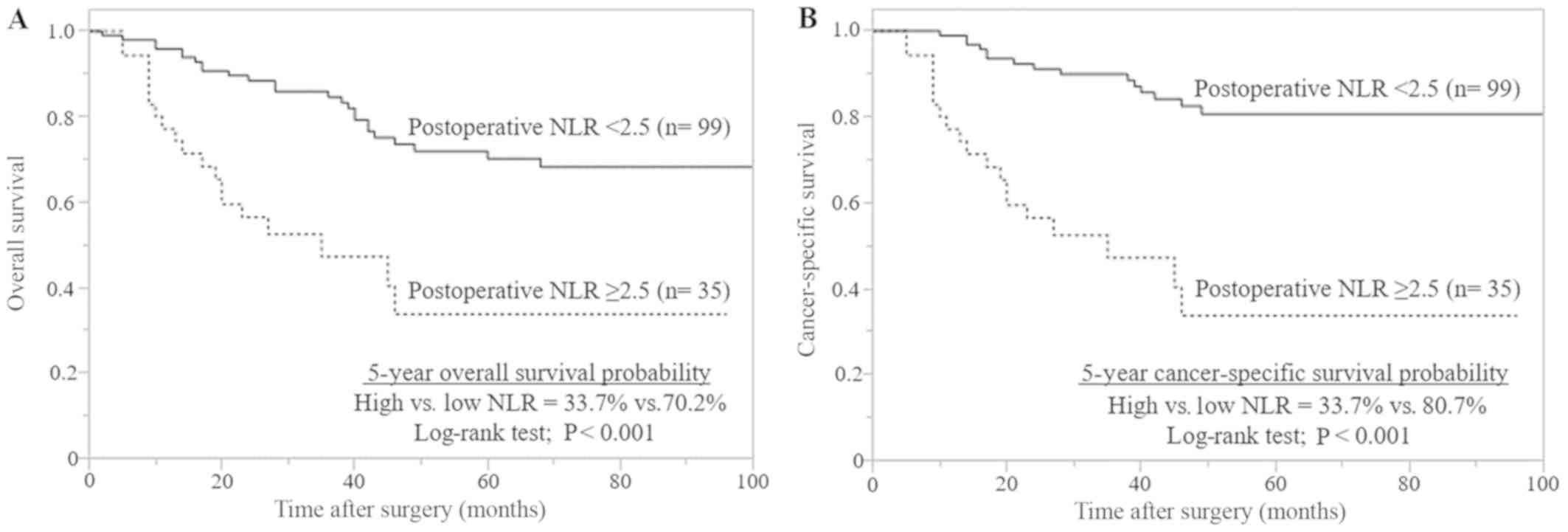
median OS and CSS times for patients with a high postoperative NLR
were both 35 months. The median OS and CSS times for patients with
a low postoperative NLR were not reached. The 5-year OS and CSS
rates in patients with a high postoperative NLR were both 33.7%,
and the 5-year OS and CSS rates for patients with a low
postoperative NLR were 70.2 and 80.7%, respectively. The
Kaplan-Meier curves demonstrated that a high postoperative NLR is
associated with significantly reduced OS and CSS rates, compared
with a low postoperative NLR (both P<0.001; Fig. 2).
Univariate and multivariate
analysis
Univariate analysis revealed that advanced pT stage
(≥T3), positive lymph node involvement, high-grade tumors, positive
lymphovascular invasion, positive surgical margins, high
postoperative CRP levels, and high pre- and postoperative NLRs were
significantly associated with OS and CSS. Multivariate analysis
identified a high postoperative NLR as an independent prognostic
marker for OS and CSS (both P<0.001). Additionally, advanced pT
stage (≥T3; P=0.042 and P=0.009, respectively) and positive
surgical margins (P=0.002 and P<0.001, respectively) were
identified as independent prognostic factors for OS and CSS
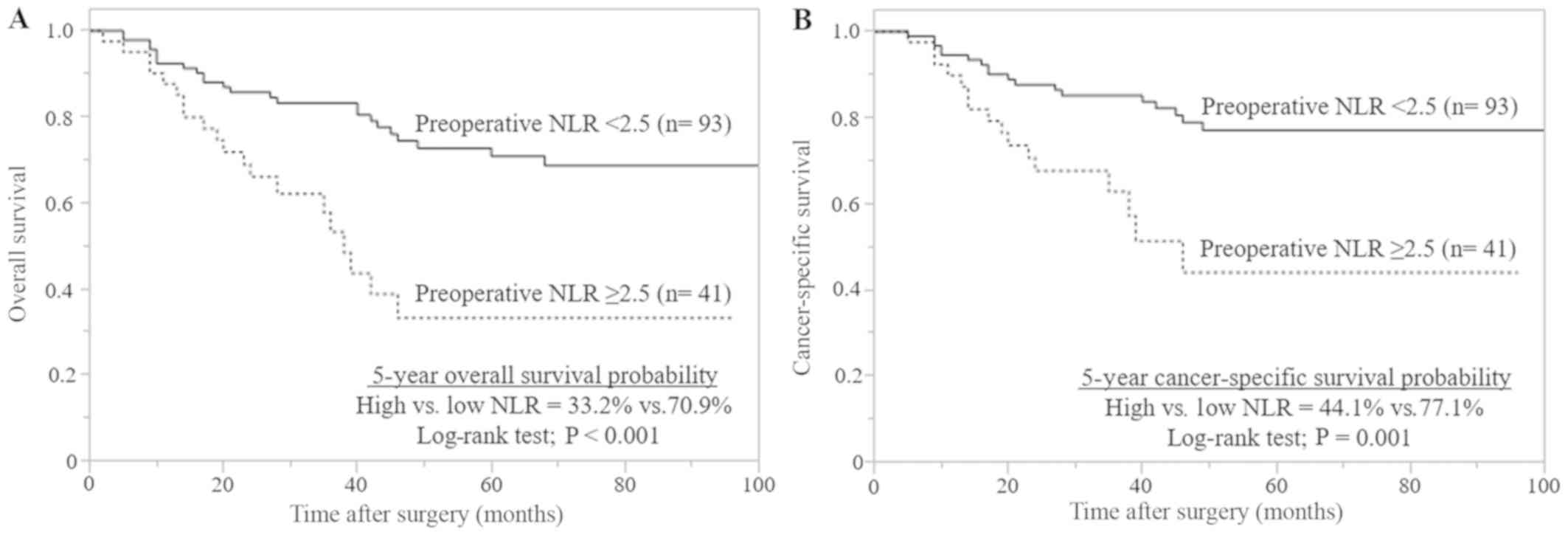
(Table II). A high preoperative NLR
was significantly associated with poor survival, compared with low
preoperative NLR (Fig. 3) and the
Spearman correlation coefficient demonstrated a significant
correlation between the preoperative and postoperative NLR
(r=0.529, P<0.001; data not shown). However, a high preoperative
NLR was not a significant prognostic marker according to the
multivariate analysis (Table
II).
 | Table II.Univariate and multivariate analyses
of clinicopathological factors influencing OS and CSS for the 134
patients with UTUC. |
Table II.
Univariate and multivariate analyses
of clinicopathological factors influencing OS and CSS for the 134
patients with UTUC.
|
| OS | CSS |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
|
| Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis | Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Factor | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|
| Age (≥70
years) | 1.71
(0.94–3.24) | 0.081 | – | – | 1.13
(0.58–2.26) | 0.717 | – | – |
| Sex (male) | 0.74
(0.40–1.39) | 0.327 | – | – | 0.54
(0.27–1.08) | 0.079 | – | – |
| Tumor location
(ureter) | 1.10
(0.61–1.97) | 0.761 | – | – | 1.02
(0.52–2.01) | 0.947 | – | – |
| Tumor diameter | 1.22
(0.97–1.51) | 0.084 | – | – | 1.38
(1.08–1.75) | 0.010a | 0.91
(0.69–1.19) | 0.519 |
| Hydronephrosis
(yes) | 1.02
(0.56–1.88) | 0.957 | – | – | 1.26
(0.63–2.63) | 0.518 | – | – |
| pT stage (pT3 or
higher) (16) | 4.41
(2.40–8.36) |
<0.001a | 2.42
(1.04–5.57) | 0.042a | 9.01
(4.11–22.60) |
<0.001a | 4.47
(1.44–15.10) | 0.009a |
| Lymph node
involvement (positive) | 5.36
(2.74–9.96) |
<0.001a | 1.81
(0.74–4.42) | 0.190 | 7.39
(3.57–14.70) |
<0.001a | 2.07
(0.81–5.40) | 0.131 |
| Tumor grade
(G3) | 2.00
(1.09–3.61) | 0.026a | 0.76
(0.38–1.51) | 0.436 | 2.96
(1.50–5.89) | 0.002a | 0.85
(0.39–1.83) | 0.667 |
| Lymphovascular
invasion (positive) | 3.66
(2.02–6.76) |
<0.001a | 1.51
(0.63–3.49) | 0.349 | 7.25
(3.48–16.50) |
<0.001a | 2.53
(0.84–7.84) | 0.098 |
| Surgical margins
(positive) | 8.17
(3.76–16.30) |
<0.001a | 4.62
(1.81–11.30) | 0.002a | 9.97
(4.32–21.10) |
<0.001a | 6.83
(2.40–19.30) |
<0.001a |
| Preoperative NLR
(≥2.5) | 2.95
(1.59–5.41) |
<0.001a | 1.02
(0.47–2.19) | 0.961 | 2.95
(1.47–5.87) | 0.003a | 0.62
(0.26–1.43) | 0.257 |
| Postoperative NLR
(≥2.5) | 3.54
(1.91–6.51) |
<0.001a | 4.66
(2.11–10.00) |
<0.001a | 5.63
(2.83–11.40) |
<0.001a | 10.90
(4.32–28.40) |
<0.001a |
| Postoperative CRP
level (≥0.3 mg/dl) | 3.23
(1.63–6.05) | 0.001a | 1.29
(0.60–2.63) | 0.504 | 3.69
(1.72–7.47) | 0.001a | 1.25
(0.54–2.78) | 0.600 |
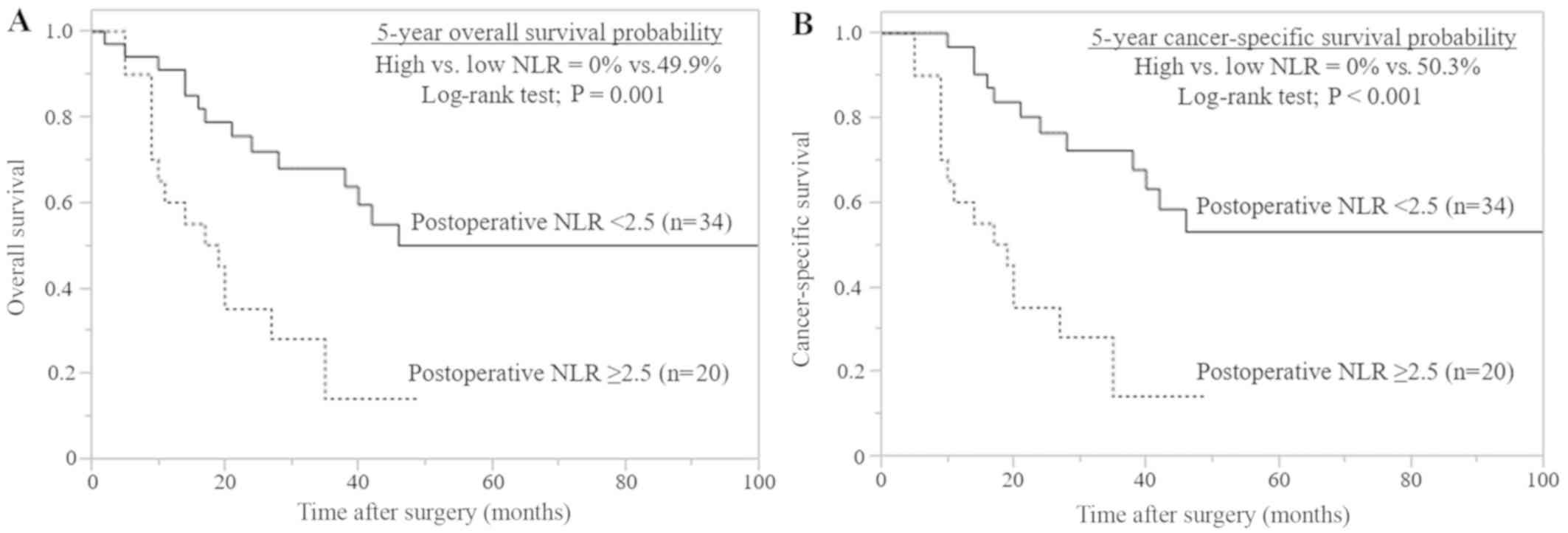
Similar results were obtained for the 54 patients
(40.3%) with advanced pT stage (≥T3). In total, 20/54 (37.0%)
patients had a high postoperative NLR (data not shown). In the
Kaplan-Meier analysis, a high postoperative NLR of ≥2.5 was
significantly associated with a reduced OS (P=0.001) and CSS
(P<0.001), compared with a low postoperative NLR (Fig. 4). Multivariate analysis identified
high postoperative NLR as a significant independent prognostic
marker for OS (P=0.002) and CSS (P<0.001; Table III).
 | Table III.Univariate and multivariate analysis
of clinicopathological factors influencing OS and CSS in the 54
patients with advanced pathological T stage (≥T3). |
Table III.
Univariate and multivariate analysis
of clinicopathological factors influencing OS and CSS in the 54
patients with advanced pathological T stage (≥T3).
|
| OS | CSS |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
|
| Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis | Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Factor | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value | HR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|
| Age (≥70
years) | 1.00
(0.48–2.15) | 0.999 | – | – | 0.88
(0.41–1.92) | 0.747 | – | – |
| Sex (male) | 0.59
(0.28–1.26) | 0.17 | – | – | 0.50
(0.23–1.10) | 0.083 | – | – |
| Tumor location
(ureter) | 1.97
(0.90–4.17) | 0.09 | – | – | 1.95
(0.85–4.25) | 0.109 | – | – |
| Tumor diameter | 1.05
(0.79–1.38) | 0.731 | – | – | 1.12
(0.83–1.48) | 0.452 | – | – |
| Hydronephrosis
(yes) | 1.46
(0.70–3.20) | 0.318 | – | – | 1.32
(0.62–2.94) | 0.476 | – | – |
| Lymph node
involvement (positive) | 2.69
(1.28–5.63) | 0.010a | 1.43
(0.56–3.66) | 0.449 | 2.73
(1.26–5.88) | 0.011a | 1.49
(0.56–3.92) | 0.420 |
| Tumor grade
(G3) | 1.53
(0.73–3.34) | 0.263 | – | – | 1.89
(0.87–4.42) | 0.109 | – | – |
| Lymphovascular
invasion (positive) | 4.36
(1.66–15.00) | 0.002a | 2.61
(0.79–10.30) | 0.118 | 5.79
(1.98–24.70) |
<0.001a | 3.82
(1.04–18.50) | 0.043a |
| Surgical margins
(positive) | 5.86
(2.50–13.10) |
<0.001a | 4.99
(1.88–13.30) | 0.002a | 6.06
(2.48–14.00) |
<0.001a | 6.00
(2.09–17.50) | 0.001a |
| Preoperative NLR
(≥2.5) | 1.60
(0.75–3.34) | 0.22 | – | – | 1.59
(0.73–3.43) | 0.238 | – | – |
| Postoperative NLR
(≥2.5) | 3.27
(1.52–7.14) | 0.003a | 4.17
(1.68–10.70) | 0.002a | 4.07
(1.84–9.28) |
<0.001a | 6.29
(2.37–17.80) |
<0.001a |
| Postoperative CRP
level (≥0.3 mg/dl) | 2.93
(1.30–6.22) | 0.011 | 1.00
(0.42–2.32) | 0.999 | 2.86
(1.22–6.28) | 0.018 | 0.82
(0.33–1.95) | 0.664 |
Clinicopathological characteristics
and survival analysis of advanced pT stage
In total, 29/54 (53.7%) patients with advanced pT
stage (≥T3) received adjuvant chemotherapy (Table IV). Cisplatin-based chemotherapy in
various combinations was the most commonly administered therapy. A
total of 19 patients (65.5%) received cisplatin plus gemcitabine; 6
patients (20.7%) received methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin
and cisplatin; 3 patients (10.3%) received carboplatin plus
gemcitabine; and 1 patient (3.5%) received gemcitabine plus
paclitaxel. The median number of chemotherapy cycles was two.
Compared with those who underwent surgical treatment alone,
patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy exhibited poorer
pathological features, including positive lymph node involvement
(P=0.003) and positive lymphovascular invasion (P=0.010; Table IV). Additionally, adjuvant
chemotherapy did not significantly improve OS (P=0.167) or CSS
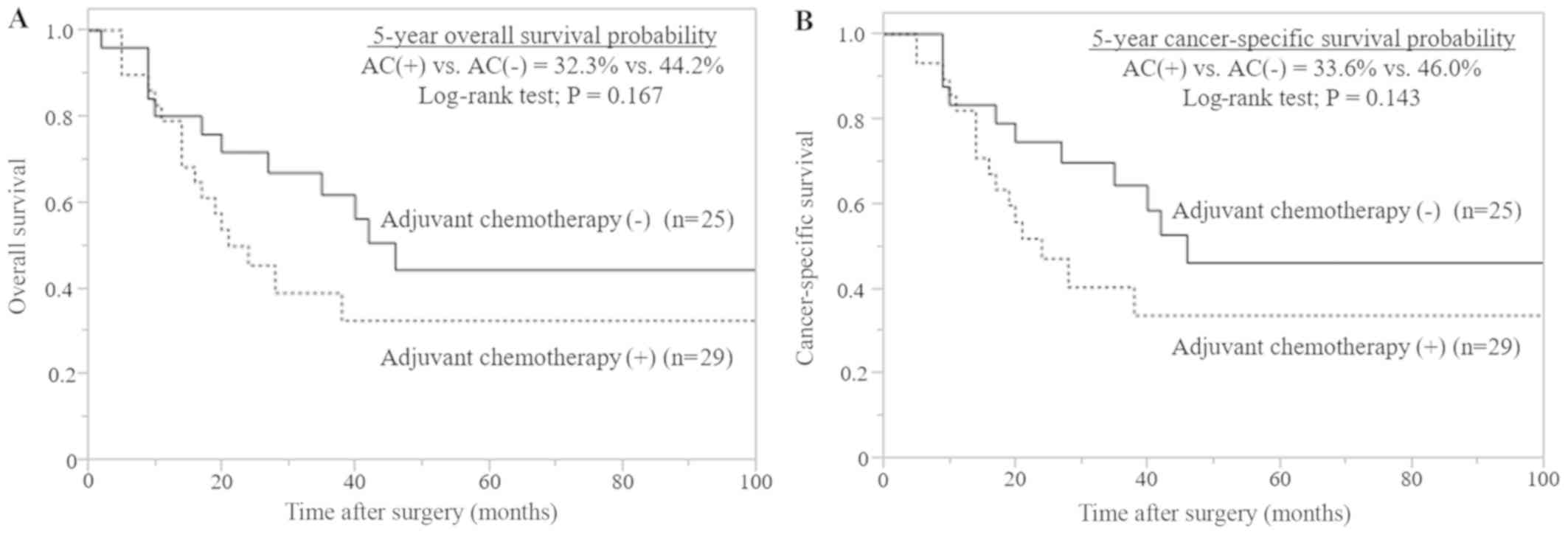
rates (P=0.143; Fig. 5) in patients
with advanced pT stage (≥T3).
 | Table IV.Clinicopathological characteristics
of the 54 patients with advanced pathological T stage (≥T3)
according to administration of adjuvant chemotherapy. |
Table IV.
Clinicopathological characteristics
of the 54 patients with advanced pathological T stage (≥T3)
according to administration of adjuvant chemotherapy.
|
| Adjuvant
chemotherapy |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
|
Characteristics | Yes (n=29) | No (n=25) |
P-valuea |
|---|
| Median age, years
(IQR) | 70 (64–75) | 74 (67–78) | 0.099 |
| Sex, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
Male | 16 (55.2) | 17 (68) | 0.407 |
|
Female | 13 (44.8) | 8 (32) |
|
| Tumor location, n
(%) |
|
|
|
| Renal
pelvis | 18 (62.1) | 19 (76) | 0.380 |
|
Ureter | 11 (37.9) | 6 (24) |
|
| Hydronephrosis, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
Yes | 20 (69) | 12 (48) | 0.167 |
| No | 9 (31) | 13 (52) |
|
| Median tumor size,
cm (IQR) | 3.2 (2.3–4.4) | 3.5 (2.0–4.1) | 0.748 |
| pT stage, n (%)
(16) |
|
|
|
|
pT3 | 24 (82.8) | 24 (96) | 0.200 |
|
pT4 | 5 (17.2) | 1 (4) |
|
| Lymph node
involvement, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
pNx/N0 | 15 (51.7) | 22 (88) | 0.003b |
|
pN1 | 14 (48.3) | 3 (12) |
|
| Tumor grade, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
G1/G2 | 10 (34.5) | 14 (56) | 0.170 |
| G3 | 19 (65.5) | 11 (44) |
|
| Lymphovascular
invasion, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
Yes | 24 (82.8) | 12 (50) | 0.010b |
| No | 5 (17.2) | 12 (50) |
|
| Surgical margins, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
Positive | 8 (27.6) | 3 (12) | 0.191 |
|
Negative | 21 (72.4) | 22 (88) |
|
Discussion
Compared with bladder cancer, there is insufficient
evidence regarding the clinical significance of neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in patients with UTUC (6,19).
Additionally, accurate preoperative staging by imaging examination
remains challenging. Currently, numerous institutions perform
nephroureterectomy without neoadjuvant chemotherapy immediately
following a diagnosis of UTUC without metastasis (20). Consequently, ~40.0% of patients are
diagnosed with advanced pT stage (≥T3) and are required to consider
adjuvant chemotherapy (5).
Therefore, it is important to investigate postoperative prognostic
markers, as well as preoperative prognostic markers in patients
with UTUC.
Previously, a number of studies reported that a high
NLR is associated with poor survival in patients with numerous
types of malignancy, including lung, renal, gastric, hepatic and
colorectal cancer (9,10). With respect to UTUC, a high NLR is
associated with a reduced prognosis, compared with a low NLR
(14,15,18).
Numerous studies demonstrated an association between preoperative
NLR and survival (14,15,18). By
contrast, the present study aimed to investigate whether
postoperative NLR is an effective prognostic marker for patients
with clinically localized UTUC who have undergone surgical
treatment.
The postoperative NLR has been investigated as a
beneficial prognostic marker not only in urothelial carcinoma
(21,22), but also in lung and gastric cancer
(23,24). Kang et al (21), reported that early postoperative NLR
is significantly associated with poor OS and CSS rates in patients
who have undergone a radical cystectomy. Morizawa et al
(22), demonstrated that a high
postoperative NLR is associated with tumor recurrence even before a
mass is detected by imaging examination in patients who have
undergone radical cystectomy. The present results revealed that a
high early postoperative NLR was significantly associated with a
poor prognosis in patients with clinically localized UTUC. Among
those with advanced pT stage (≥T3), patients with a high
postoperative NLR exhibited a significantly reduced prognosis,
compared with those with a low postoperative NLR. Furthermore, a
high preoperative NLR was identified as a significant prognostic
marker in the present study. This may be because a high
postoperative NLR reflects only the potentially residual cancer,
including micrometastases, while preoperative NLR reflects the
primary tumor and the potential micrometastatic lesion. If the
postoperative NLR reflects micrometastases, it appears to be a
significant prognostic marker in patients with surgical
treatment.
Recently, a phase III randomized trial of
perioperative chemotherapy versus surveillance in UTUC (POUT trial,
NCT01993979) reported that adjuvant chemotherapy improved the
disease-free survival rate for patients with histologically
confirmed pT2-T4 N0-3 M0 UTUC (25).
However, it could not be accurately determined whether the primary
lesion was localized, as the current imaging modalities are not
able to detect disseminated micrometastases. In this sense, the
present study provided reasonable evidence that postoperative NLR
may be a beneficial marker to select patients who require adjuvant
therapy.
To the best of our knowledge, the mechanisms
underlying the association between a high NLR and poor survival in
patients with cancer remain unclear. A study by Mantovani et
al (26), supported the
involvement of systemic inflammation in cancer development and
progression. Features of cancer-associated inflammation involve the
secretion of inflammatory molecules, including cytokines and
prostaglandins, and the recruitment of inflammatory cells into the
tumor tissue (26). The cytokines
activate the same key transcription factors in inflammatory cells,
stromal cells and tumor cells, resulting in more inflammatory
mediators being produced and a cancer-associated inflammatory
microenvironment being generated (26). Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines
can be produced by the tumor and associated host cells, including
the leukocytes neutrophils and monocytes, and contribute to
malignant progression (26,27). Lymphocytes serve a fundamental role
in antitumor immunity (28). It has
been reported that the increasing infiltration of tumors by
lymphocytes is associated with an improved response to cytotoxic
treatment and prognosis in patients with cancer (28). Lymphopenia has been demonstrated to
be an independent predictor of poor survival in pancreatic and
renal cell cancer (29,30). Furthermore, the neutrophil response
is associated with the cancer progression process and lymphocytes
serve an important role in immune surveillance of cancer (26–30).
Therefore, the NLR represents both groups by a simple measurement
and could be an indicator of homeostasis between cancer progression
and antitumor activity.
There are several limitations of the present study.
Firstly, the present study was a retrospective non-randomized
analysis. Therefore, it may not be possible to completely avoid
selection and information bias. Secondly, only a relatively small
number of patients were included in the study. A limited in the
number of patients with UTUC were included in the study, as UTUC is
uncommon, accounting for 5–10% of all urothelial cancer cases
(2,3). Thirdly, the present study had a
relatively short median follow-up duration of 40.5 months and the
time span was relatively large. Although the timespan of the
observation period was relatively large, the data analysis was
appropriately conducted and the timespan did not affect the
analysis result. Fourthly, adjuvant chemotherapy did not exhibit a
significant benefit in terms of OS or CSS in the present study.
This may be due to the small population size, regimen variability,
patient selection bias and a small number of chemotherapy cycles.
In the present study, the NLR was measured once preoperatively and
once postoperatively. There is a tendency for a high NLR to also
reflect infection and stress, in addition to cancer (31). Therefore, it is necessary to consider
the timing of measuring the postoperative NLR.
In conclusion, a high postoperative NLR is
associated with a poor prognosis in patients with UTUC. The
postoperative NLR may be a more accurate prognostic marker,
compared with the preoperative NLR, in patients with UTUC. The
present study indicates that the postoperative NLR may be a
potential prognostic marker, in addition to pathological features.
Identifying patients with a increased chance of survival may assist
with the development of adjuvant therapy for specific subgroups of
patients to improve survival or establish individualized follow-up
protocols. However, further external validation and a prospective
multicenter trial is necessary to confirm the prognostic
significance of the postoperative NLR in patients with UTUC.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Japan Society
for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI grant no. JP18K09182).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
KN, SS and TI designed the study and revised the
manuscript. KU, MN and MM contributed to the collection, analysis
and interpretation of the data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Research
Ethics Committee of Kurume University (Fukuoka, Japan; approval no.
17303). The requirement for informed consent was waived due to the
retrospective nature of the study. The research content was
available publicly on the website of the Research Ethics Committee
of Kurume University, which ensured opportunities for participants
to opt out of the research.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
UTUC
|
upper tract urothelial carcinoma
|
|
NLR
|
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
|
|
pT
|
pathological T
|
|
CRP
|
C-reactive protein
|
|
OS
|
overall survival
|
|
CSS
|
cancer-specific survival
|
References
|
1
|
Oya M and Kikuchi E; Committee for
Establishment of Clinical Practice Guideline for Management of
Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma; Japanese Urological Association,
: Evidenced-based clinical practice guideline for upper tract
urothelial carcinoma (summary-Japanese Urological Association, 2014
edition). Int J Urol. 22:3–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Compérat E, Zigeuner
R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, Cowan NC, Böhle A, Van Rhijn BWG,
Kaasinen E, et al: European Association of Urology Guidelines on
Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Cell Carcinoma: 2015 Update. Eur
Urol. 68:868–879. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, .
Vital Statistics of Japan (Volume 1~3), General Mortality.
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/database/db-hw/vs01.htmlSeptember
7–2018
|
|
5
|
Margulis V, Shariat SF, Matin SF, Kamat
AM, Zigeuner R, Kikuchi E, Lotan Y, Weizer A, Raman JD and Wood CG:
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma collaboration the upper tract
urothelial carcinoma collaboration: outcomes of radical
nephroureterectomy: A series from the upper tract urothelial
carcinoma collaboration. Cancer. 115:1224–1233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC, De Santis
M, Gakis G, Lebret T, Ribal MJ, Van der Heijden AG and Sherif A;
European Association of Urology, : EAU guidelines on
muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2013
guidelines. Eur Urol. 65:778–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rink M, Sjoberg D, Comploj E, Margulis V,
Xylinas E, Lee RK, Hansen J, Cha EK, Raman JD, Remzi M, et al: Risk
of cancer-specific mortality following recurrence after radical
nephroureterectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:4337–4344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leow JJ, Orsola A, Chang SL and Bellmunt
J: A contemporary review of management and prognostic factors of
upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:310–319.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS,
Horgan PG, McMillan DC and Clarke SJ: The systemic
inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in
patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:218–230. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B,
Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocaña A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G,
Knox JJ, Tran B, et al: Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 106:dju1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Viers BR, Boorjian SA, Frank I, Tarrell
RF, Thapa P, Karnes RJ, Thompson RH and Tollefson MK: Pretreatment
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with advanced
pathologic tumor stage and increased cancer-specific mortality
among patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder undergoing
radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 66:1157–1164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gondo T, Nakashima J, Ohno Y, Choichiro O,
Horiguchi Y, Namiki K, Yoshioka K, Ohori M, Hatano T and Tachibana
M: Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and
establishment of novel preoperative risk stratification model in
bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy. Urology.
79:1085–1091. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Krane LS, Richards KA, Kader AK, Davis R,
Balaji KC and Hemal AK: Preoperative neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio
predicts overall survival and extravesical disease in patients
undergoing radical cystectomy. J Endourol. 27:1046–1050. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tanaka N, Kikuchi E, Kanao K, Matsumoto K,
Shirotake S, Miyazaki Y, Kobayashi H, Kaneko G, Hagiwara M, Ide H,
et al: A multi-institutional validation of the prognostic value of
the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for upper tract urothelial
carcinoma treated with radical nephroureterectomy. Ann Surg Oncol.
21:4041–4048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dalpiaz O, Ehrlich GC, Mannweiler S,
Hernández JM, Gerger A, Stojakovic T, Pummer K, Zigeuner R, Pichler
M and Hutterer GC: Validation of pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte
ratio as a prognostic factor in a European cohort of patients with
upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int. 114:334–339.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours (7th edition).
Wiley-Blackwell. New Jersey, NY: 2009.
|
|
17
|
Mostofi FK, Davis CJ and Sesterhenn IA:
World Health Organization International Histological Classification
of Tumours. Histological typing of urinary bladder tumours (2nd
edition). Springer-Verlag Berlin. Heidelberg: 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Azuma T, Matayoshi Y, Odani K, Sato Y,
Sato Y, Nagase Y and Oshi M: Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte
ratio as an independent prognostic marker for patients with upper
urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer.
11:337–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC)
Meta-analysis Collaboration, . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive
bladder cancer: Update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of
individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis
collaboration. Eur Urol. 48:202–205; discussion 205–206. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fritz GA, Schoellnast H, Deutschmann HA,
Quehenberger F and Tillich M: Multiphasic multidetector-row CT
(MDCT) in detection and staging of transitional cell carcinomas of
the upper urinary tract. Eur Radiol. 16:1244–1252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang M, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH and Ku
JH: The prognostic significance of the early postoperative
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder undergoing radical cystectomy. Ann Surg
Oncol. 23:335–342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morizawa Y, Miyake M, Shimada K, Hori S,
Tatsumi Y, Nakai Y, Anai S, Tanaka N, Konishi N and Fujimoto K:
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a detection marker of tumor
recurrence in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after
radical cystectomy. Urol Oncol. 34(257): e211–257.
2016.doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.02.012.
|
|
23
|
Tanaka H, Tamura T, Toyokawa T, Muguruma
K, Miki Y, Kubo N, Sakurai K, Hirakawa K and Ohira M: Clinical
relevance of postoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) to
recurrence after adjuvant chemotherapy of S-1 for gastric cancer.
Anticancer Res. 38:3745–3751. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin F, Han A, Shi F, Kong L and Yu J: The
postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and changes in this
ratio predict survival after the complete resection of stage I
non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 9:6529–6537. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Birtle AJ, Chester JD, Jones RJ, Johnson
M, Hill M, Bryan RT, Catto J, Donovan J, French A, Harris C, et al:
Results of POUT: A phase III randomised trial of perioperative
chemotherapy versus surveillance in upper tract urothelial cancer
(UTUC). J Clin Oncol. 36 (6_suppl):407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gooden MJ, de Bock GH, Leffers N, Daemen T
and Nijman HW: The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating
lymphocytes in cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J
Cancer. 105:93–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fogar P, Sperti C, Basso D, Sanzari MC,
Greco E, Davoli C, Navaglia F, Zambon CF, Pasquali C, Venza E, et
al: Decreased total lymphocyte counts in pancreatic cancer: An
index of adverse outcome. Pancreas. 32:22–28. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saroha S, Uzzo RG, Plimack ER, Ruth K and
Al-Saleem T: Lymphopenia is an independent predictor of inferior
outcome in clear cell renal carcinoma. J Urol. 189:454–461. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Glaser R and Kiecolt-Glaser JK:
Stress-induced immune dysfunction: Implications for health. Nat Rev
Immunol. 5:243–251. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|