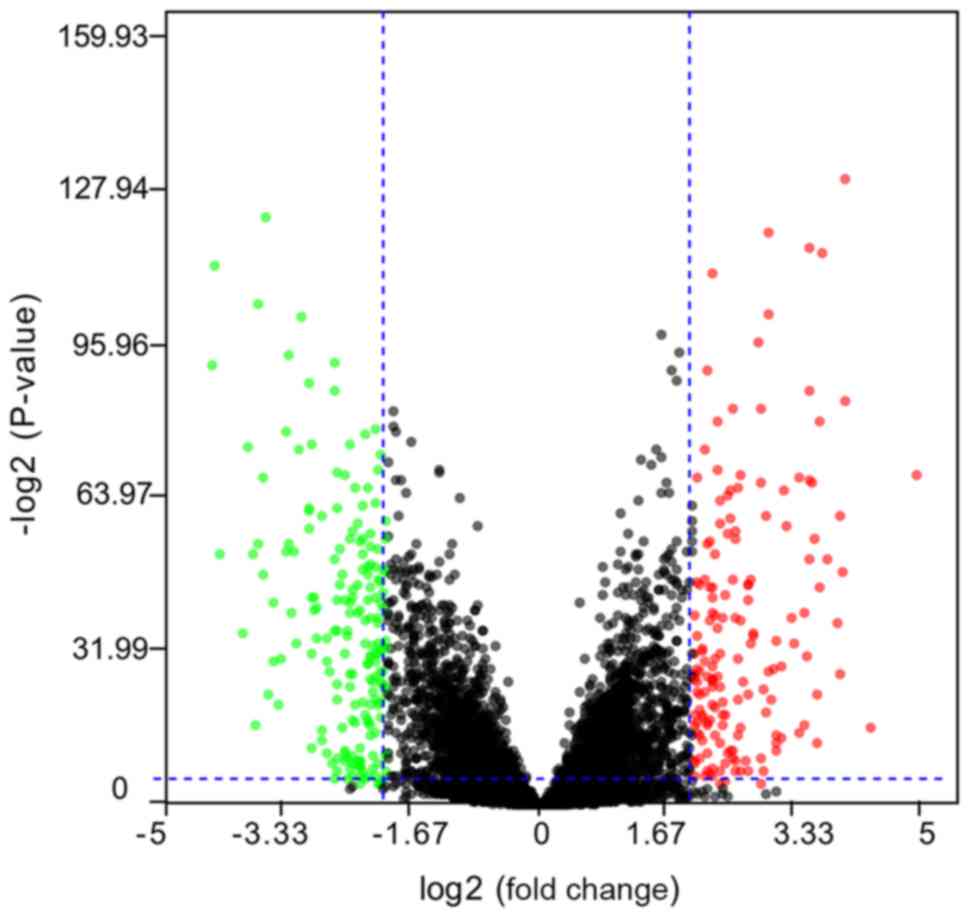
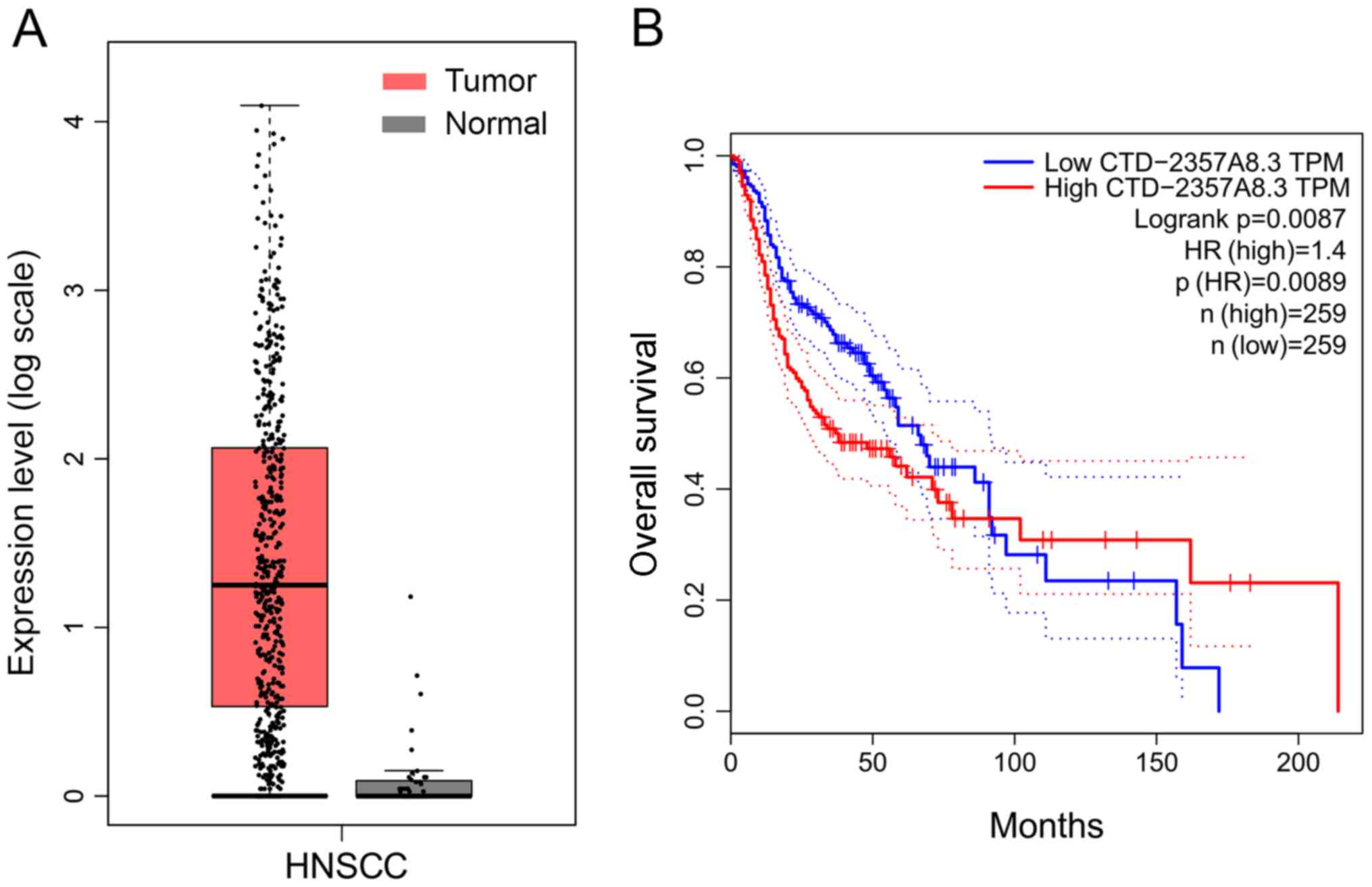
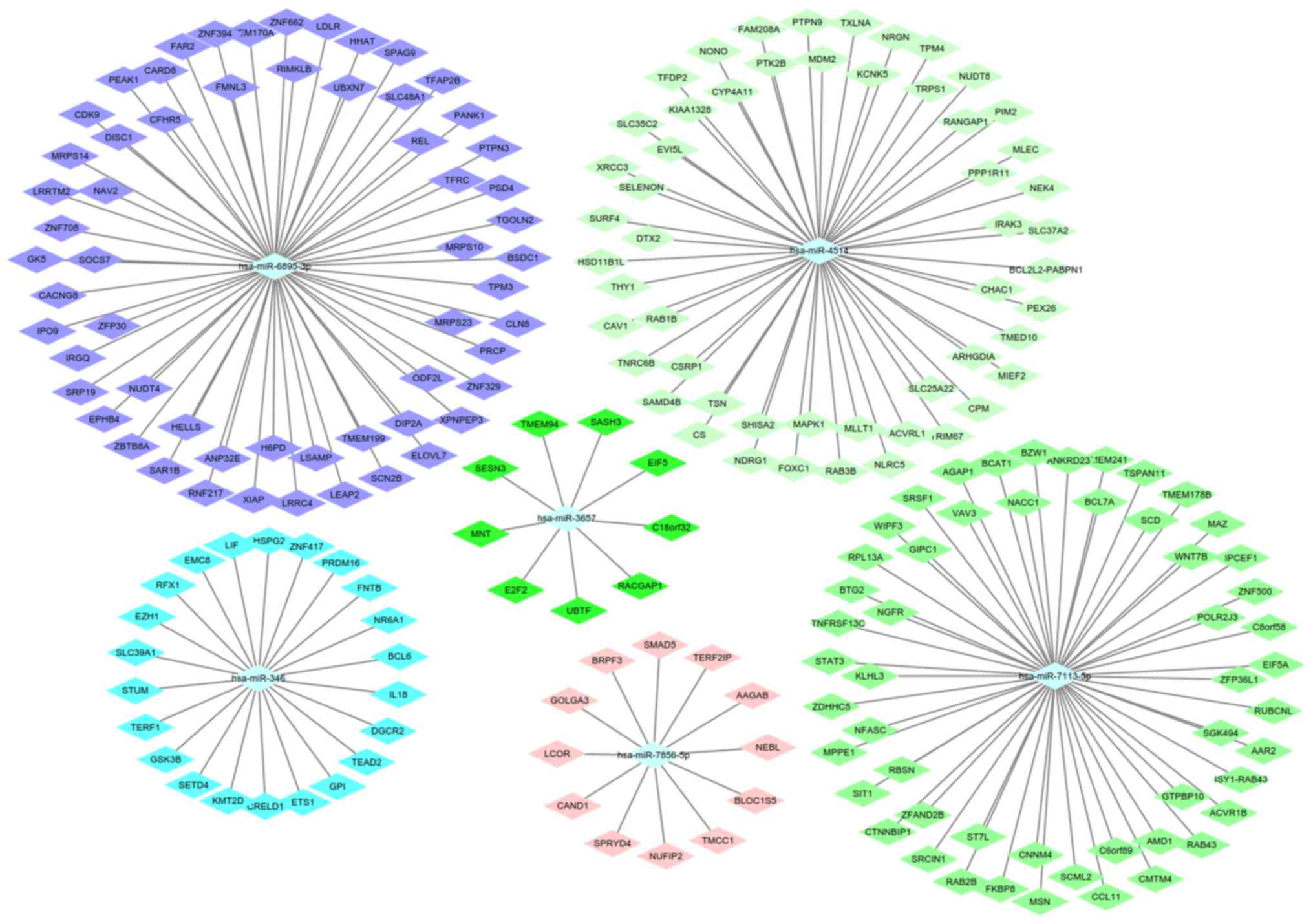
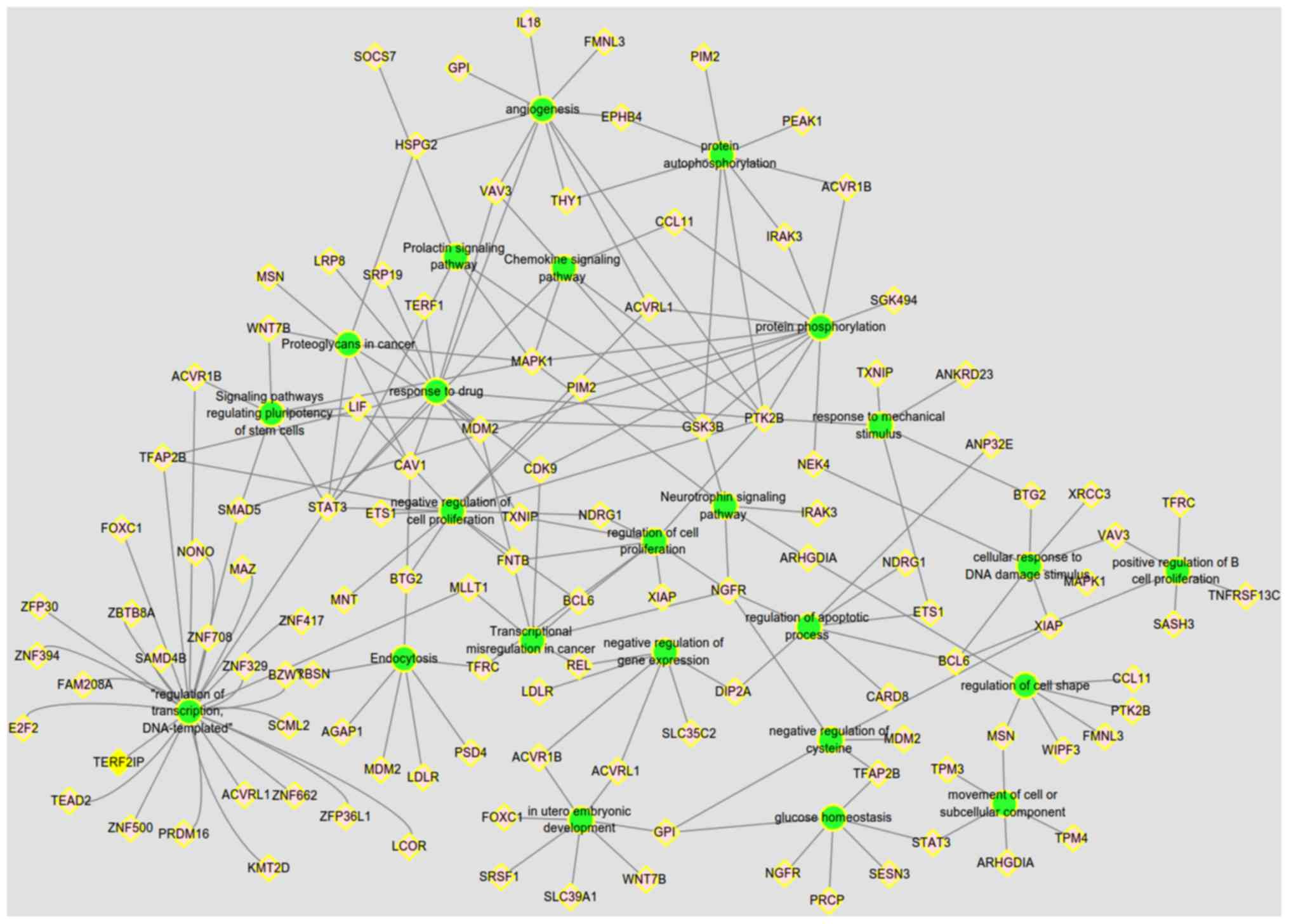
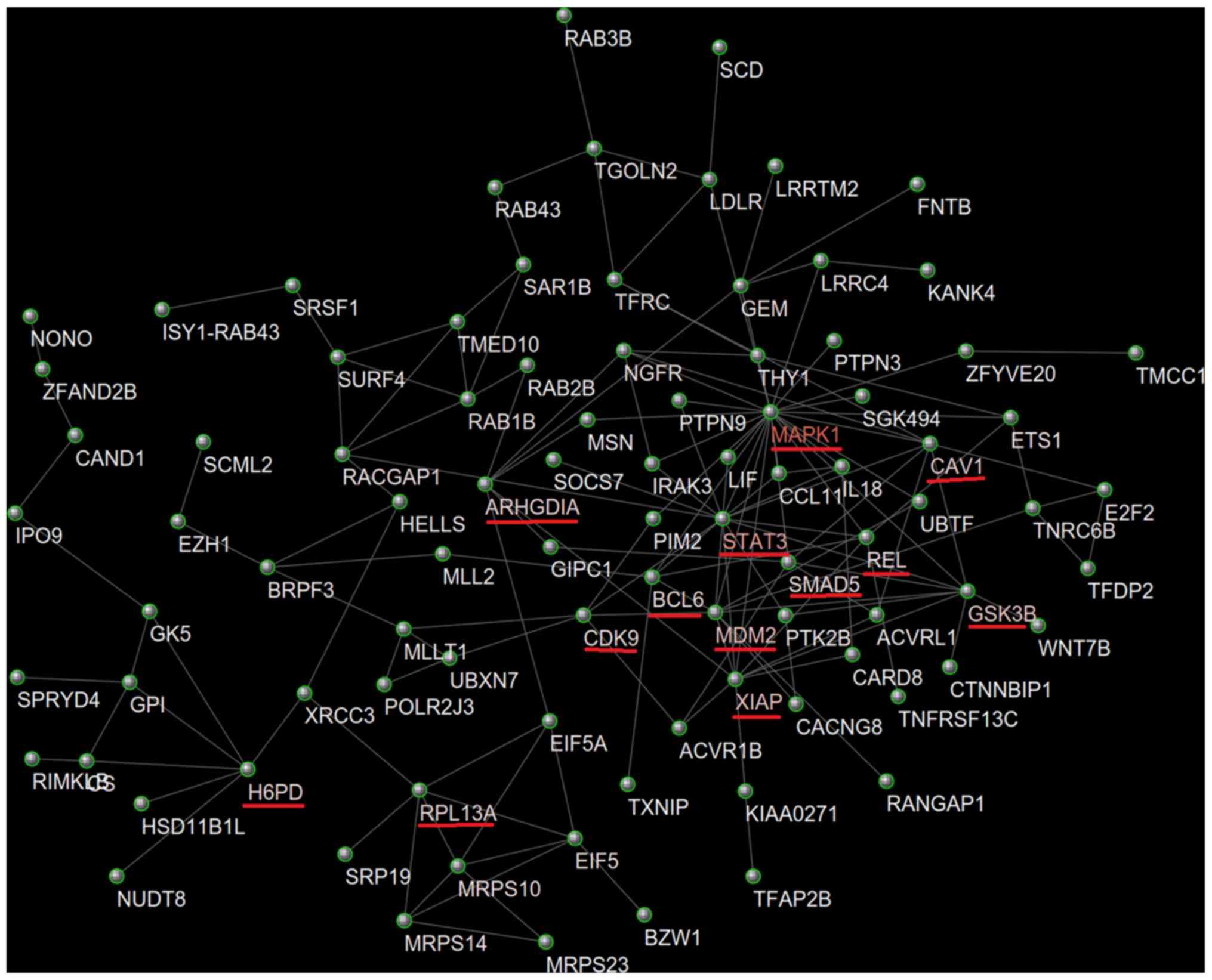
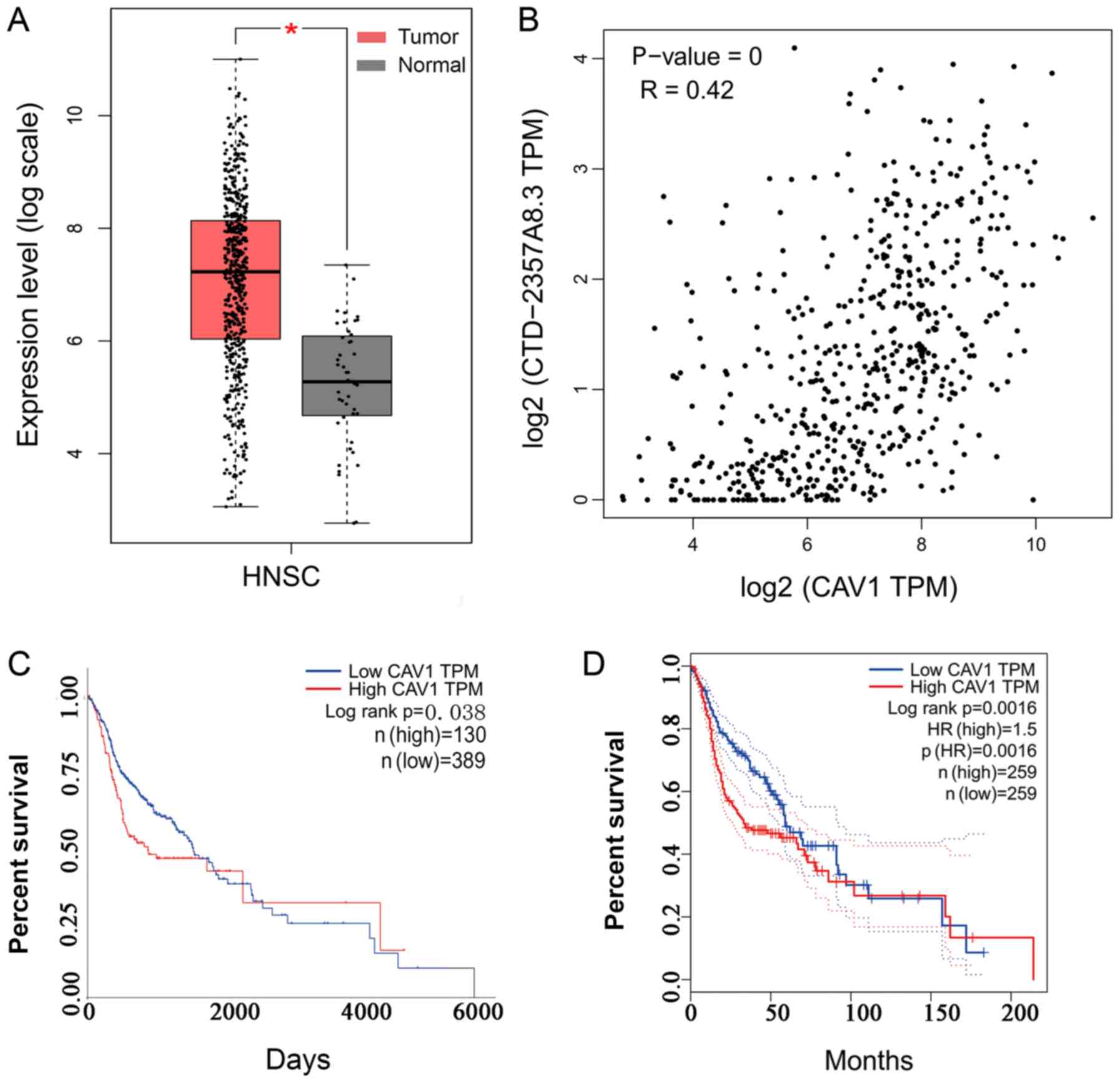
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goossens N, Nakagawa S, Sun X and Hoshida
Y: Cancer biomarker discovery and validation. Transl Cancer Res.
4:256–269. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nat Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li T, Mo X, Fu L, Xiao B and Guo J:
Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs on gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:8601–8612. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park S, Lee M, Chun CH and Jin EJ: The
lncRNA, nespas, is associated with osteoarthritis progression and
serves as a potential new prognostic biomarker. Cartilage.
10:148–156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang R, Ma Z, Feng L, Yang Y, Tan C, Shi
Q, Lian M, He S, Ma H and Fang J: LncRNA MIR31HG targets HIF1A and
P21 to facilitate head and neck cancer cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis by promoting cell-cycle progression. Mol Cancer.
17:1622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Wu C, Zhang C, Li Z, Zhu T, Chen
J, Ren Y, Wang X, Zhang L and Zhou X: TGF-β-induced STAT3
overexpression promotes human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
invasion and metastasis through malat1/miR-30a interactions. Cancer
Lett. 436:52–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45((W1)):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vlachos IS and Hatzigeorgiou AG:
Functional analysis of miRNAs using the DIANA tools online suite.
Methods Mol Biol. 1517:25–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Vlachos IS and
Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-TarBase and DIANA suite tools: Studying
experimentally supported microRNA targets. Curr Protoc
Bioinformatics. 55:12.14.1–12.14.18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA
binding sites. PLoS One. 13:e02062392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41((Database Issue)): D808–D815. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scardoni G, Tosadori G, Faizan M, Spoto F,
Fabbri F and Laudanna C: Biological network analysis with
CentiScaPe: Centralities and experimental dataset integration.
F1000Res. 3:1392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun M and Kraus WL: From discovery to
function: The expanding roles of long non-coding RNAs in physiology
and disease. Endocr Rev. er00009999. 2015.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Song W, Sun Y, Lin J and Bi X: Current
research on head and neck cancer-associated long noncoding RNAs.
Oncotarget. 9:1403–1425. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Parton RG and Simons K: The multiple faces
of caveolae. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:185–194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Salem AF, Bonuccelli G, Bevilacqua G,
Arafat H, Pestell RG, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 promotes
pancreatic cancer cell differentiation and restores membranous
E-cadherin via suppression of the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Cycle. 10:3692–3700. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nimri L, Barak H, Graeve L and Schwartz B:
Restoration of caveolin-1 expression suppresses growth,
membrane-type-4 metalloproteinase expression and
metastasis-associated activities in colon cancer cells. Mol
Carcinog. 52:859–870. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Joo HJ, Oh DK, Kim YS, Lee KB and Kim SJ:
Increased expression of caveolin-1 and microvessel density
correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 93:291–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu W, Yin NC, Liu H and Nan KJ: Cav-1
promote lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through lncRNA
HOTAIR. Gene. 641:335–340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|