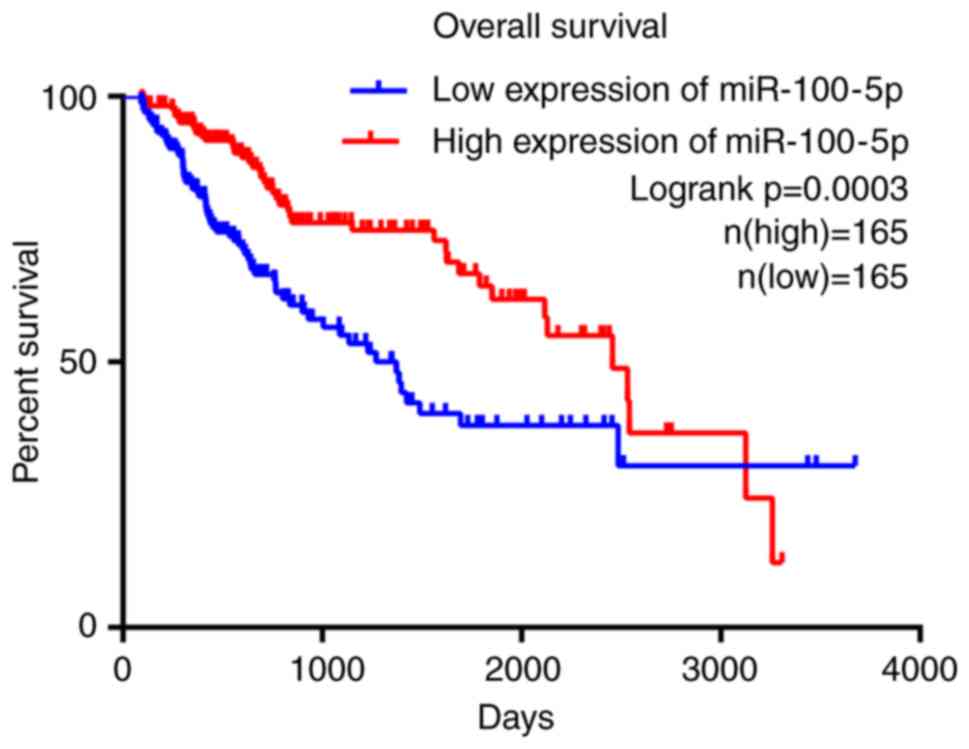
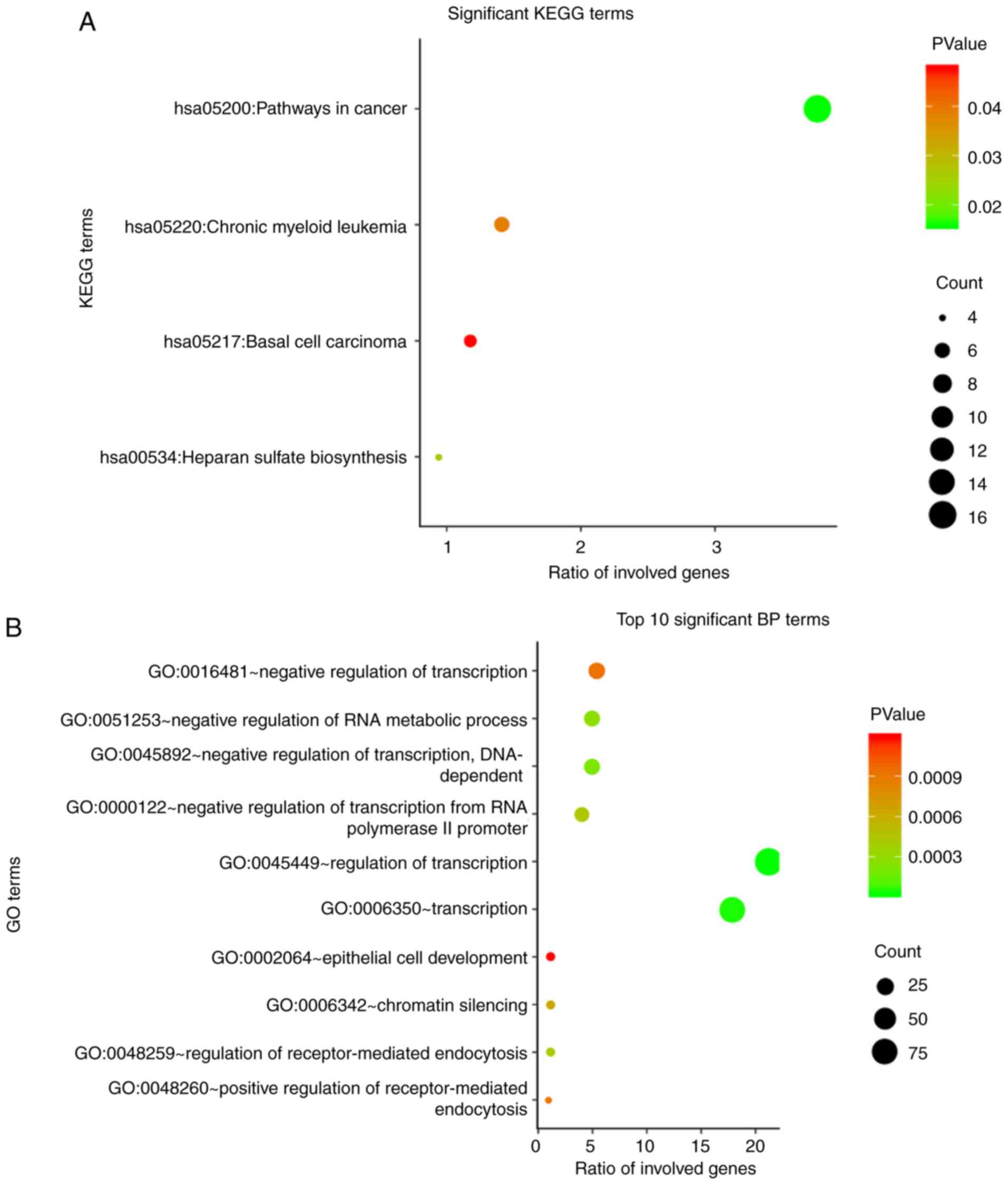
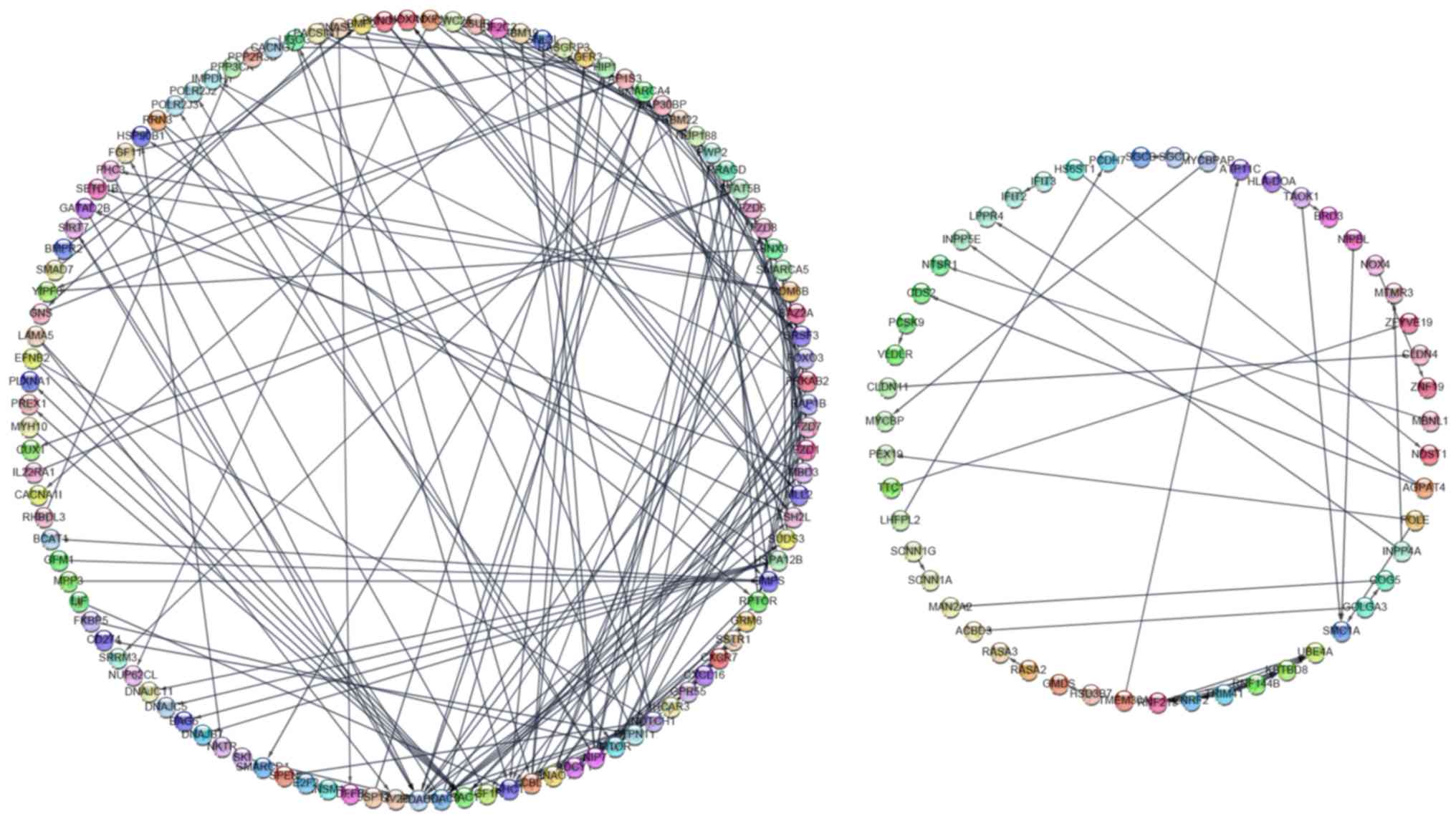
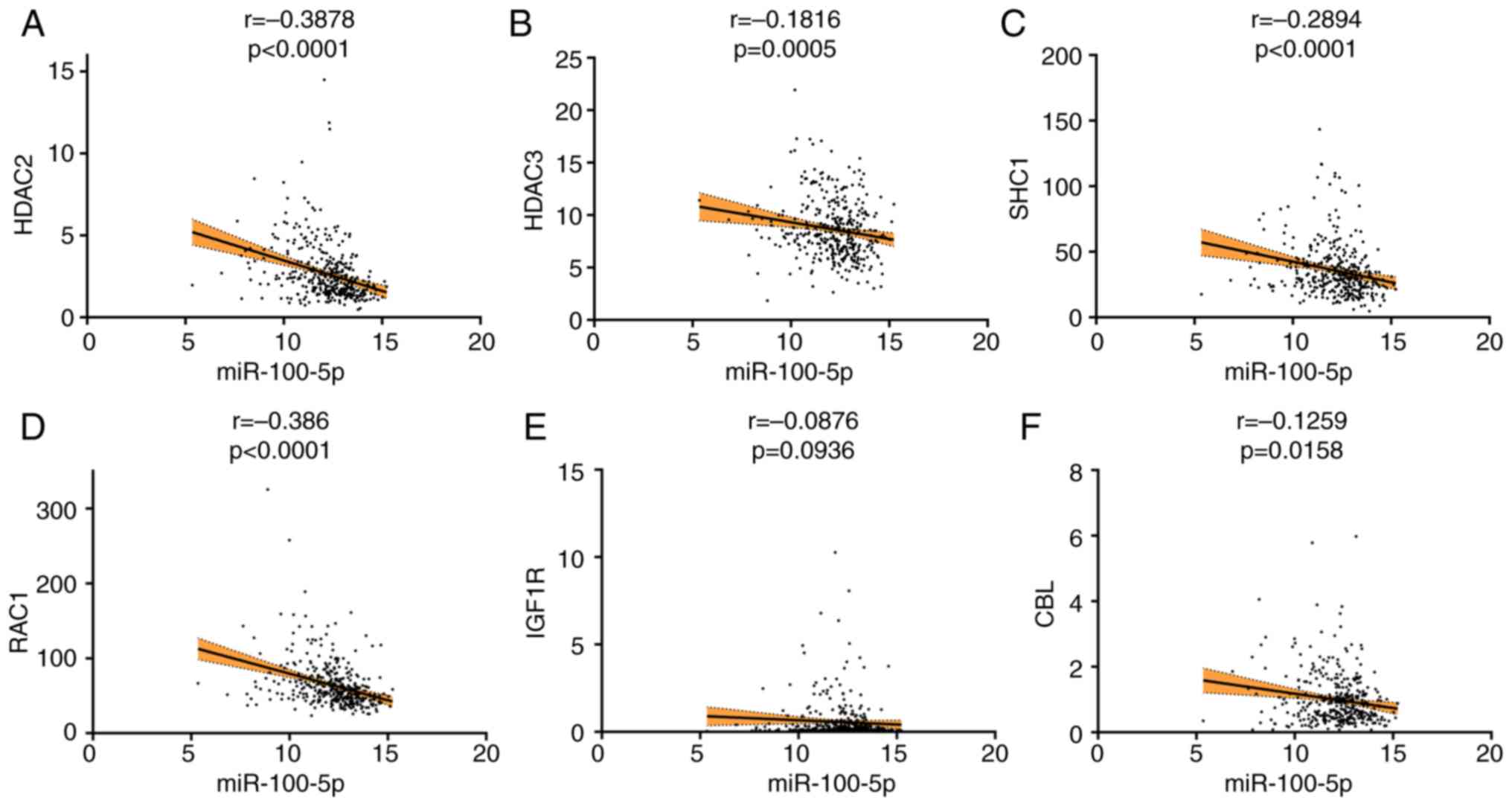
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kudo M: Systemic therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma: 2017 update. Oncology. 93 (Suppl
1):S135–S146. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Aguilar C, Mano M and Eulalio A: MicroRNAs
at the Host-bacteria interface: Host defense or bacterial offense.
Trends Microbiol. 27:206–218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mollaei H, Safaralizadeh R and Rostami Z:
MicroRNA replacement therapy in cancer. J Cell Physiol.
234:12369–12384. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li TT, Gao X, Gao L, Gan BL, Xie ZC, Zeng
JJ and Chen G: Role of upregulated miR-136-5p in lung
adenocarcinoma: A study of 1242 samples utilizing bioinformatics
analysis. Pathol Res Pract. 214:750–766. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao L, Li SH, Tian YX, Zhu QQ, Chen G,
Pang YY and Hu XH: Role of downregulated miR-133a-3p expression in
bladder cancer: A bioinformatics study. Onco Targets Ther.
10:3667–3683. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He D, Yue Z, Li G, Chen L, Feng H and Sun
J: Low serum levels of miR-101 are associated with poor prognosis
of colorectal cancer patients after curative resection. Med Sci
Monit. 24:7475–7481. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng Y, Tan K and Huang H: Long noncoding
RNA HAGLROS regulates apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer
cells via sponging miR-100 to target ATG5 expression. J Cell
Biochem. 120:3922–3933. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu G, Zhou W, Pan X, Sun Y, Xu H, Shi P,
Li J, Gao L and Tian X: miR-100 reverses cisplatin resistance in
breast cancer by suppressing HAX-1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
47:2077–2087. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun X, Liu X, Wang Y, Yang S, Chen Y and
Yuan T: miR-100 inhibits the migration and invasion of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting IGF1R. Oncol Lett.
15:8333–8338. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi DB, Wang YW, Xing AY, Gao JW, Zhang H,
Guo XY and Gao P: C/EBPα-induced miR-100 expression suppresses
tumor metastasis and growth by targeting ZBTB7A in gastric cancer.
Cancer Lett. 369:376–385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen P, Zhao X and Ma L: Downregulation of
microRNA-100 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 383:49–58. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou HC, Fang JH, Luo X, Zhang L, Yang J,
Zhang C and Zhuang SM: Downregulation of microRNA-100 enhances the
ICMT-Rac1 signaling and promotes metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 5:12177–12188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou HC, Fang JH, Shang LR, Zhang ZJ, Sang
Y, Xu L, Yuan Y, Chen MS, Zheng L, Zhang Y and Zhuang SM: MicroRNAs
miR-125b and miR-100 suppress metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by disrupting the formation of vessels that encapsulate
tumour clusters. J Pathol. 240:450–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ge YY, Shi Q, Zheng ZY, Gong J, Zeng C,
Yang J and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-100 promotes the autophagy of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the expression of mTOR
and IGF-1R. Oncotarget. 5:6218–6228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pan WY, Zeng JH, Wen DY, Wang JY, Wang PP,
Chen G and Feng ZB: Oncogenic value of microRNA-15b-5p in
hepatocellular carcinoma and a bioinformatics investigation. Oncol
Lett. 17:1695–1713. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Gao Y and Huang J: Interleukin-8
Gene-251 A/T (rs4073) polymorphism and coronary artery disease
risk: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 25:1645–1655. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Xin G and Sun D: Serum exosomal
miR-328, miR-575, miR-134 and miR-671-5p as potential biomarkers
for the diagnosis of Kawasaki disease and the prediction of
therapeutic outcomes of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Exp
Ther Med. 16:2420–2432. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C and
Leslie C: Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts
functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol.
11:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G,
Kostoulas N, Vlachos IS, Vergoulis T, Reczko M, Filippidis C,
Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-microT web server v5.0:
Service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W169–W173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsu SD, Chu CH, Tsou AP, Chen SJ, Chen HC,
Hsu PW, Wong YH, Chen YH, Chen GH and Huang HD: miRNAMap 2.0:
Genomic maps of microRNAs in metazoan genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36
(Database Issue). D165–D169. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Tsang JS, Ebert MS and van Oudenaarden A:
Genome-wide dissection of microRNA functions and cotargeting
networks using gene set signatures. Mol Cell. 38:140–153. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vejnar CE, Blum M and Zdobnov EM: miRmap
web: Comprehensive microRNA target prediction online. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:W165–W168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anders G, Mackowiak SD, Jens M, Maaskola
J, Kuntzagk A, Rajewsky N, Landthaler M and Dieterich C: doRiNA: A
database of RNA interactions in post-transcriptional regulation.
Nucleic Acids Res 40 (Database Issue). D180–D186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X and El Naqa IM: Prediction of both
conserved and nonconserved microRNA targets in animals.
Bioinformatics. 24:325–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Loher P and Rigoutsos I: Interactive
exploration of RNA22 microRNA target predictions. Bioinformatics.
28:3322–3323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Calderón-González KG, Hernández-Monge J,
Herrera-Aguirre ME and Luna-Arias JP: Bioinformatics tools for
proteomics data interpretation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 919:281–341.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
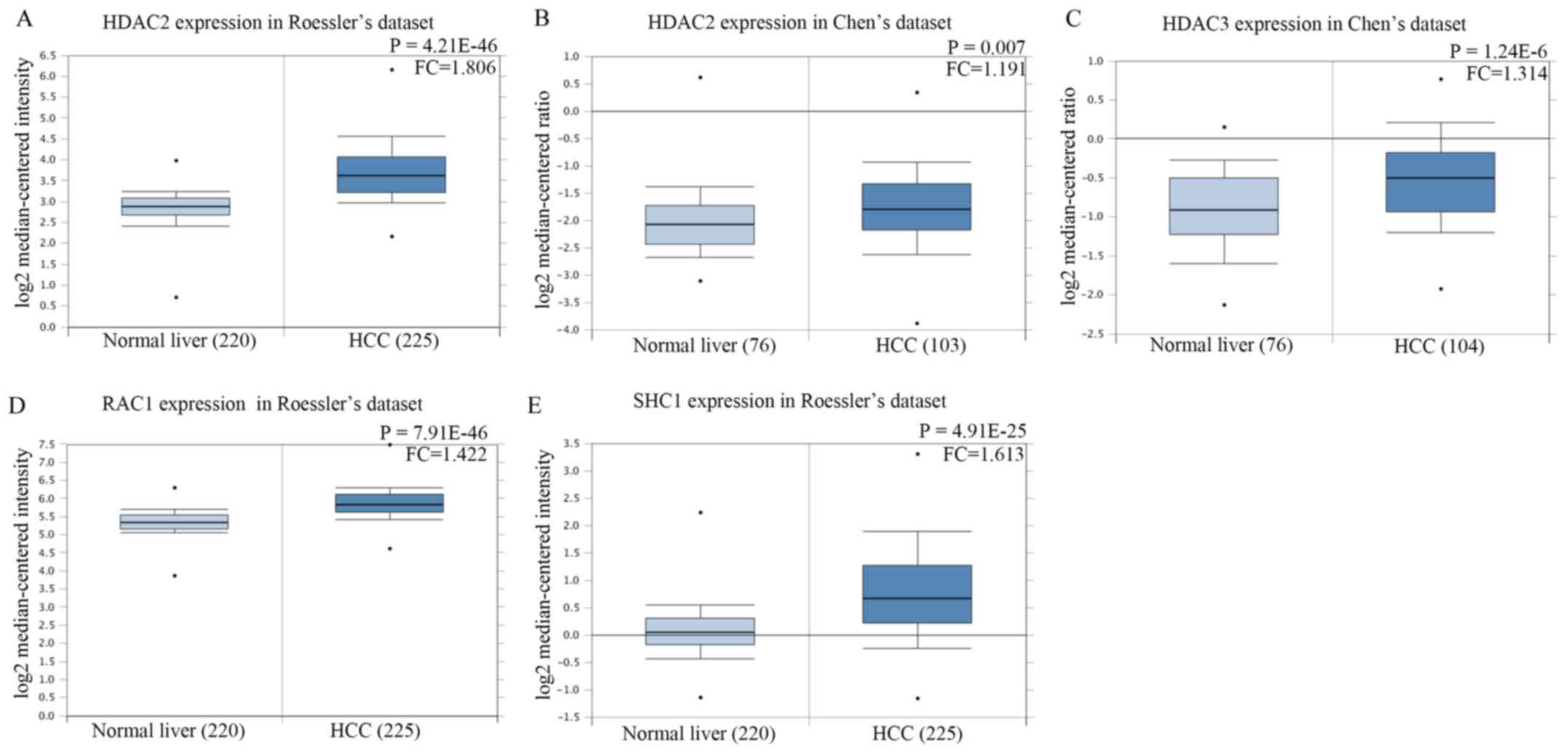
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye
QH, Lee JS, Thorgeirsson SS, Sun Z, Tang ZY, Qin LX and Wang XW: A
unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor
relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer
Res. 70:10202–10212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, Fan ST, Barry C,
Higgins J, Lai KM, Ji J, Dudoit S, Ng IO, et al: Gene expression
patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell. 13:1929–1939. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
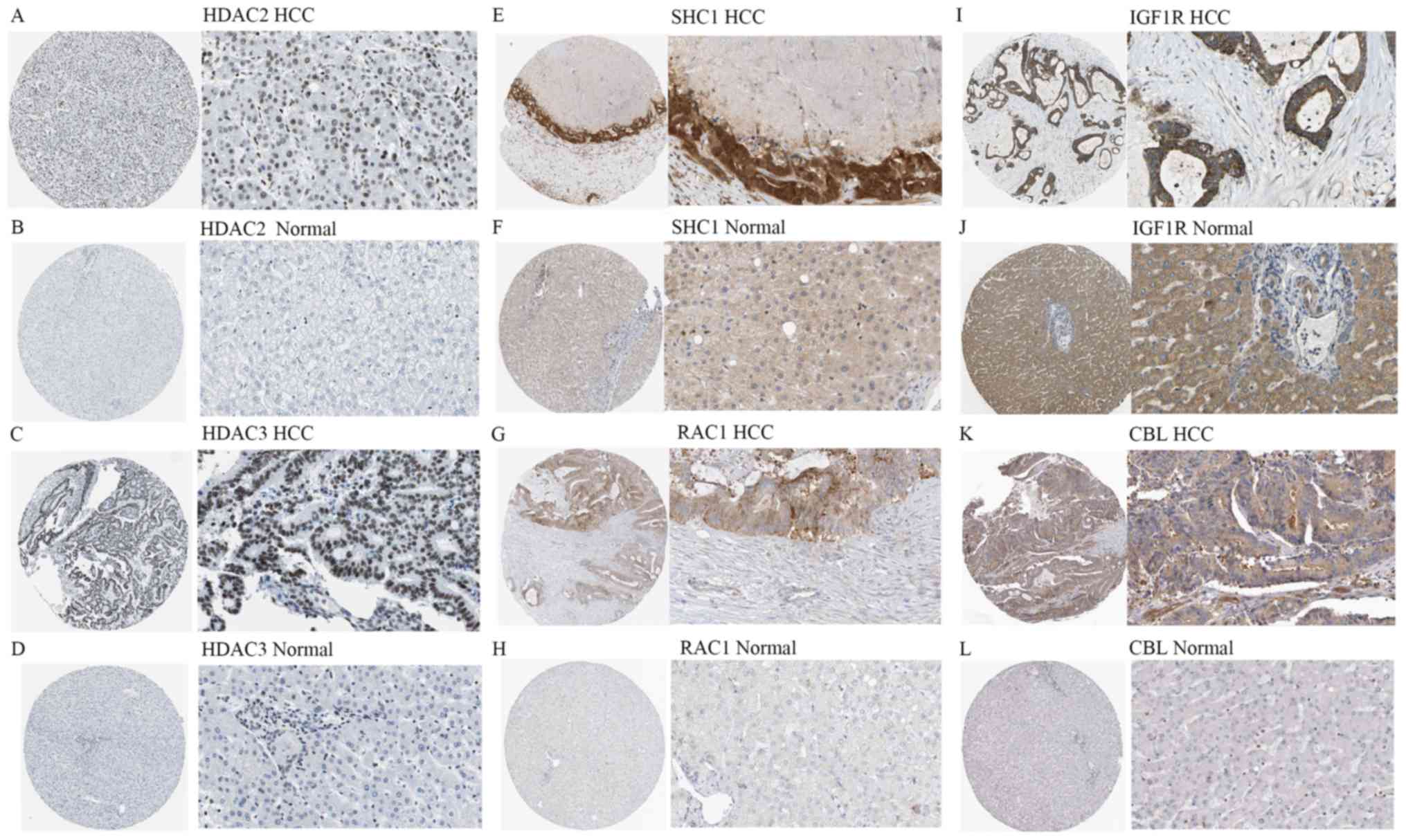
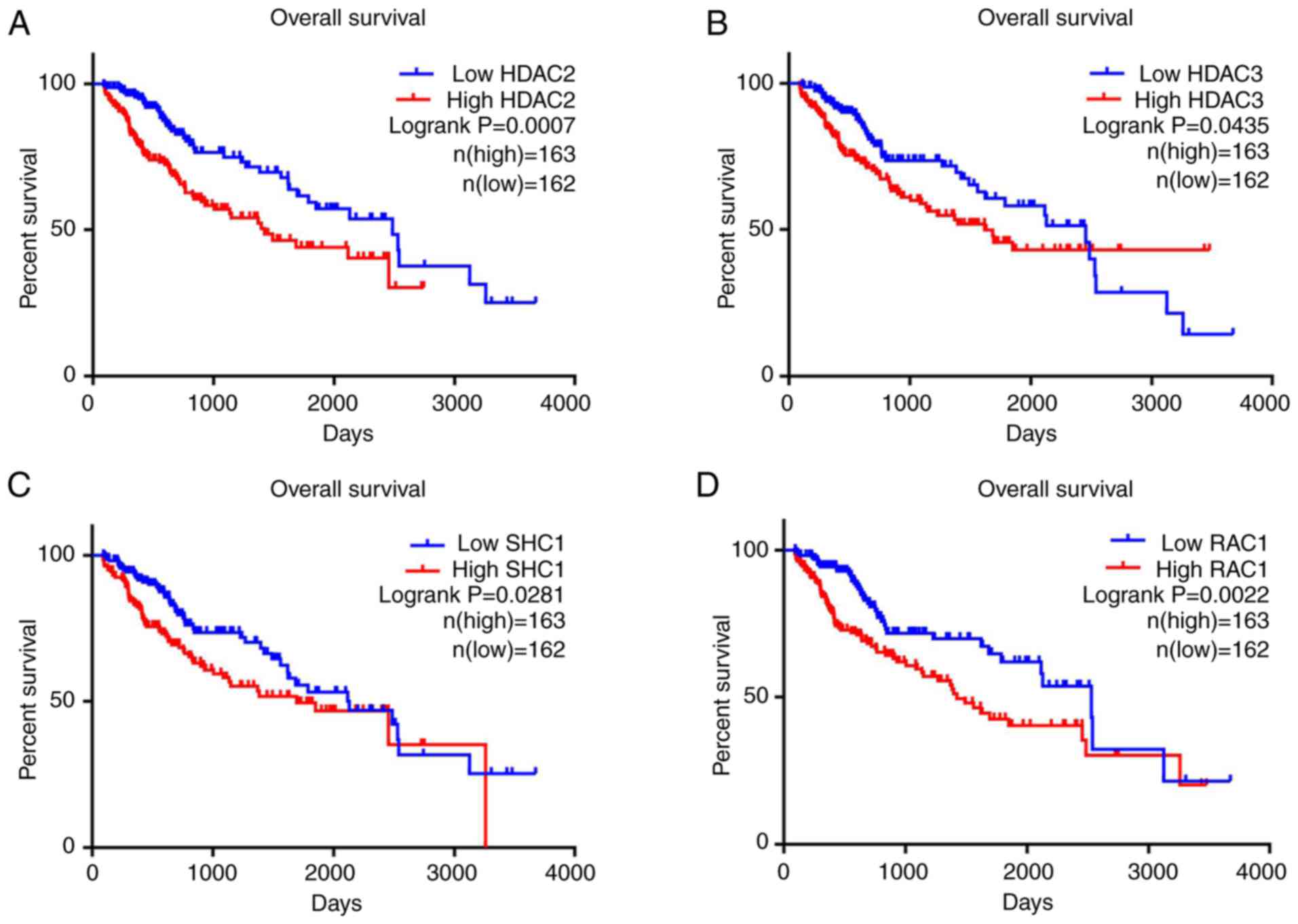
Uhlen M, Zhang C, Lee S, Sjöstedt E,
Fagerberg L, Bidkhori G, Benfeitas R, Arif M, Liu Z, Edfors F, et
al: A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science.
357(pii): eaan25072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiao XD, Qin BD, You P, Cai J and Zang YS:
The prognostic value of TP53 and its correlation with EGFR mutation
in advanced non-small cell lung cancer, an analysis based on
cBioPortal data base. Lung Cancer. 123:70–75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ryan M, Wong WC, Brown R, Akbani R, Su X,
Broom B, Melott J and Weinstein J: TCGASpliceSeq a compendium of
alternative mRNA splicing in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:D1018–D1022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang R, Lin P, Yang X, He RQ, Wu HY, Dang
YW, Gu YY, Peng ZG, Feng ZB and Chen G: Survival associated
alternative splicing events in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J
Transl Res. 10:2636–2647. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Sun N, Lu Z, Sun S, Huang J, Chen Z
and He J: Prognostic alternative mRNA splicing signature in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 393:40–51. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiao F, Bai Y, Chen Z, Li Y, Luo L, Huang
J, Yang J, Liao H and Guo L: Downregulation of HOXA1 gene affects
small cell lung cancer cell survival and chemoresistance under the
regulation of miR-100. Eur J Cancer. 50:1541–1554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo P, Xiong X, Zhang S and Peng D:
miR-100 resensitizes resistant epithelial ovarian cancer to
cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 36:3552–3558. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qin X, Yu S, Zhou L, Shi M, Hu Y, Xu X,
Shen B, Liu S, Yan D and Feng J: Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer
cell-derived exosomes increase cisplatin resistance of recipient
cells in exosomal miR-100-5p-dependent manner. Int J Nanomedicine.
12:3721–3733. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang M, Ren D, Guo W, Wang Z, Huang S, Du
H, Song L and Peng X: Loss of miR-100 enhances migration, invasion,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties in
prostate cancer cells through targeting Argonaute 2. Int J Oncol.
45:362–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Leite KR, Sousa-Canavez JM, Reis ST,
Tomiyama AH, Camara-Lopes LH, Sañudo A, Antunes AA and Srougi M:
Change in expression of miR-let7c, miR-100, and miR-218 from high
grade localized prostate cancer to metastasis. Urol Oncol.
29:265–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang H, Wang J, Wang Z, Ruan C, Wang L
and Guo H: Serum miR-100 is a potential biomarker for detection and
outcome prediction of glioblastoma patients. Cancer Biomark.
24:43–49. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Azizmohammadi S, Azizmohammadi S, Safari
A, Kosari N, Kaghazian M, Yahaghi E and Seifoleslami M: The role
and expression of miR-100 and miR-203 profile as prognostic markers
in epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res. 8:2403–2410.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Petrelli A, Perra A, Schernhuber K,
Cargnelutti M, Salvi A, Migliore C, Ghiso E, Benetti A, Barlati S,
Ledda-Columbano GM, et al: Sequential analysis of multistage
hepatocarcinogenesis reveals that miR-100 and PLK1 dysregulation is
an early event maintained along tumor progression. Oncogene.
31:4517–4526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F,
Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP and Odenthal M: MicroRNA gene
expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:1223–1232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Y, Gao Y, Shi W, Zhai D, Rao Q, Jia
X, Liu J, Jiao X and Du Z: Profiles of differential expression of
circulating microRNAs in hepatitis B virus-positive small
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 15:171–180. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tsai CT, Zulueta MML and Hung SC:
Synthetic heparin and heparan sulfate: Probes in defining
biological functions. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 40:152–159. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li JP and Kusche-Gullberg M: Heparan
Sulfate: Biosynthesis, structure, and function. Int Rev Cell Mol
Biol. 325:215–273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Weiss RJ, Esko JD and Tor Y: Targeting
heparin and heparan sulfate protein interactions. Org Biomol Chem.
15:5656–5668. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cassinelli G, Zaffaroni N and Lanzi C: The
heparanase/heparan sulfate proteoglycan axis: A potential new
therapeutic target in sarcomas. Cancer Lett. 382:245–254. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ling L, Tan SK, Goh TH, Cheung E, Nurcombe
V, van Wijnen AJ and Cool SM: Targeting the heparin-binding domain
of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 as a potential cancer
therapy. Mol Cancer. 14:1362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dudás J, Bocsi J, Fullár A, Baghy K, Füle
T, Kudaibergenova S and Kovalszky I: Heparin and liver heparan
sulfate can rescue hepatoma cells from topotecan action. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:7657942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gao J, Wang Y, Li W, Zhang J, Che Y, Cui
X, Sun B and Zhao G: Loss of histone deacetylase 2 inhibits
oxidative stress induced by high glucose via the HO-1/SIRT1 pathway
in endothelial progenitor cells. Gene. 678:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li Y, Zhou M, Lv X, Song L, Zhang D, He Y,
Wang M, Zhao X, Yuan X, Shi G and Wang D: Reduced activity of HDAC3
and increased acetylation of histones H3 in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol
Res. 2018:73135152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li S, Wang F, Qu Y, Chen X, Gao M, Yang J,
Zhang D, Zhang N, Li W and Liu H: HDAC2 regulates cell
proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell apoptosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma EC9706 cells. Oncol Lett.
13:403–409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Peng Z, Zhou W, Zhang C, Liu H and Zhang
Y: Curcumol controls choriocarcinoma stem-like cells self-renewal
via repression of DNA Methyltransferase (DNMT)- and histone
deacetylase (HDAC)-mediated epigenetic regulation. Med Sci Monit.
24:461–472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu L, Lin W, Zhang Q, Cao W and Liu Z:
TGF-β induces miR-30d down-regulation and podocyte injury through
Smad2/3 and HDAC3-associated transcriptional repression. J Mol Med
(Berl). 94:291–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mao QD, Zhang W, Zhao K, Cao B, Yuan H,
Wei LZ, Song MQ and Liu XS: MicroRNA-455 suppresses the oncogenic
function of HDAC2 in human colorectal cancer. Braz J Med Biol Res.
50:e61032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang Y, Zhang J, Wu T, Xu X, Cao G, Li H
and Chen X: Histone deacetylase 2 regulates the doxorubicin (Dox)
resistance of hepatocarcinoma cells and transcription of ABCB1.
Life Sci. 216:200–206. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhao H, Yu Z, Zhao L, He M, Ren J, Wu H,
Chen Q, Yao W and Wei M: HDAC2 overexpression is a poor prognostic
factor of breast cancer patients with increased multidrug
resistance-associated protein expression who received
anthracyclines therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:893–902. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cui Z, Xie M, Wu Z and Shi Y: Relationship
between histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and breast cancer. Med Sci
Monit. 24:2456–2464. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wu LM, Yang Z, Zhou L, Zhang F, Xie HY,
Feng XW, Wu J and Zheng SS: Identification of histone deacetylase 3
as a biomarker for tumor recurrence following liver transplantation
in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 5:e144602010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lebiedzinska-Arciszewska M, Oparka M,
Vega-Naredo I, Karkucinska-Wieckowska A, Pinton P, Duszynski J and
Wieckowski MR: The interplay between p66Shc, reactive oxygen
species and cancer cell metabolism. Eur J Clin Invest. 45 (Suppl
1):S25–S31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wong N, Chan A, Lee SW, Lam E, To KF, Lai
PB, Li XN, Liew CT and Johnson PJ: Positional mapping for amplified
DNA sequences on 1q21-q22 in hepatocellular carcinoma indicates
candidate genes over-expression. J Hepatol. 38:298–306. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kisielow M, Kleiner S, Nagasawa M, Faisal
A and Nagamine Y: Isoform-specific knockdown and expression of
adaptor protein ShcA using small interfering RNA. Biochem J.
363:1–5. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang L, Zhu S, Shi X and Sha W: The
silence of p66(Shc) in HCT8 cells inhibits the viability via
PI3K/AKT/Mdm-2/p53 signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:9097–9104. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yukimasa S, Masaki T, Yoshida S, Uchida N,
Watanabe S, Usuki H, Yoshiji H, Maeta T, Ebara K, Nakatsu T, et al:
Enhanced expression of p46 Shc in the nucleus and p52 Shc in the
cytoplasm of human gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 26:905–911.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Muniyan S, Chou YW, Tsai TJ, Thomes P,
Veeramani S, Benigno BB, Walker LD, McDonald JF, Khan SA, Lin FF,
et al: p66Shc longevity protein regulates the proliferation of
human ovarian cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 54:618–631. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rajendran M, Thomes P, Zhang L, Veeramani
S and Lin MF: p66Shc-a longevity redox protein in human prostate
cancer progression and metastasis: p66Shc in cancer progression and
metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:207–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yoshida S, Kornek M, Ikenaga N, Schmelzle
M, Masuzaki R, Csizmadia E, Wu Y, Robson SC and Schuppan D:
Sublethal heat treatment promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and enhances the malignant potential of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 58:1667–1680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bid HK, Roberts RD, Manchanda PK and
Houghton PJ: RAC1: An emerging therapeutic option for targeting
cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1925–1934.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cheng H, Wang W, Wang G, Wang A, Du L and
Lou W: Silencing ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1
inhibits growth and migration of hypopharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma via the P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathway. Med Sci Monit. 24:768–781. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liu B, Xiong J, Liu G, Wu J, Wen L, Zhang
Q and Zhang C: High expression of Rac1 is correlated with partial
reversed cell polarity and poor prognosis in invasive ductal
carcinoma of the breast. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177109082017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yoon C, Cho SJ, Chang KK, Park DJ, Ryeom
SW and Yoon SS: Role of Rac1 pathway in epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and cancer stem-like cell phenotypes in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 15:1106–1116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Niu X, Gao Z, Qi S, Su L, Yang N, Luan X,
Li J, Zhang Q, An Y and Zhang S: Macropinocytosis activated by
oncogenic Dbl enables specific targeted delivery of Tat/pDNA
nano-complexes into ovarian cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine.
13:4895–4911. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Poudel KR, Roh-Johnson M, Su A, Ho T,
Mathsyaraja H, Anderson S, Grady WM, Moens CB, Conacci-Sorrell M,
Eisenman RN and Bai J: Competition between TIAM1 and membranes
balances endophilin A3 activity in cancer metastasis. Dev Cell.
45:738–752.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Aspenström P: Activated Rho GTPases in
cancer-the beginning of a new paradigm. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii):
E39492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ching YP, Leong VY, Lee MF, Xu HT, Jin DY
and Ng IO: P21-activated protein kinase is overexpressed in
hepatocellular carcinoma and enhances cancer metastasis involving
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation and paxillin phosphorylation.
Cancer Res. 67:3601–3608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhu S, Jin J, Gokhale S, Lu AM, Shan H,
Feng J and Xie P: Genetic alterations of TRAF proteins in human
cancers. Front Immunol. 9:21112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Reder H, Wagner S, Gamerdinger U, Sandmann
S, Wuerdemann N, Braeuninger A, Dugas M, Gattenloehner S, Klussmann
JP and Wittekindt C: Genetic alterations in human
papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma of
patients with treatment failure. Oral Oncol. 93:59–65. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sajnani K, Islam F, Smith RA, Gopalan V
and Lam AK: Genetic alterations in Krebs cycle and its impact on
cancer pathogenesis. Biochimie. 135:164–172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Jonckheere N, Vasseur R and Van Seuningen
I: The cornerstone K-RAS mutation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma:
From cell signaling network, target genes, biological processes to
therapeutic targeting. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 111:7–19. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Song X, Zeng Z, Wei H and Wang Z:
Alternative splicing in cancers: From aberrant regulation to new
therapeutics. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 75:13–22. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Climente-González H, Porta-Pardo E, Godzik
A and Eyras E: The functional impact of alternative splicing in
cancer. Cell Rep. 20:2215–2226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xie M, Dart DA, Owen S, Wen X, Ji J and
Jiang W: Insights into roles of the miR-1, −133 and −206 family in
gastric cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 36:1191–1198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Teplyuk NM, Uhlmann EJ, Gabriely G,
Volfovsky N, Wang Y, Teng J, Karmali P, Marcusson E, Peter M, Mohan
A, et al: Therapeutic potential of targeting microRNA-10b in
established intracranial glioblastoma: First steps toward the
clinic. EMBO Mol Med. 8:268–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Li W, Xie L, He X, Li J, Tu K, Wei L, Wu
J, Guo Y, Ma X, Zhang P, et al: Diagnostic and prognostic
implications of microRNAs in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 123:1616–1622. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y
and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular
carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer
Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Burchard J, Zhang C, Liu AM, Poon RT, Lee
NP, Wong KF, Sham PC, Lam BY, Ferguson MD, Tokiwa G, et al:
microRNA-122 as a regulator of mitochondrial metabolic gene network
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Sys Biol. 6:4022010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Sato F, Hatano E, Kitamura K, Myomoto A,
Fujiwara T, Takizawa S, Tsuchiya S, Tsujimoto G, Uemoto S and
Shimizu K: MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan Criteria.
PLoS One. 6:e164352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Noh JH, Chang YG, Kim MG, Jung KH, Kim JK,
Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Kim SJ, Kwon SH, et al: MiR-145 functions
as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2
in liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 335:455–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wang PR, Xu M, Toffanin S, Li Y, Llovet JM
and Russell DW: Induction of hepatocellular carcinoma by in vivo
gene targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:11264–11269. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Morita K, Shirabe K, Taketomi A, Soejima
Y, Yoshizumi T, Uchiyama H, Ikegami T, Yamashita Y, Sugimachi K,
Harimoto N, et al: Relevance of microRNA-18a and microRNA-199a-5p
to hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after living donor liver
transplantation. Liver Transpl. 22:665–676. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Shih TC, Tien YJ, Wen CJ, Yeh TS, Yu MC,
Huang CH, Lee YS, Yen TC and Hsieh SY: MicroRNA-214 downregulation
contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the
hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J Hepatol.
57:584–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wojcicka A, Swierniak M, Kornasiewicz O,
Gierlikowski W, Maciag M, Kolanowska M, Kotlarek M, Gornicka B,
Koperski L, Niewinski G, et al: Next generation sequencing reveals
microRNA isoforms in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 53:208–217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shen J, Siegel AB, Remotti H, Wang Q and
Santella RM: Identifying microRNA panels specifically associated
with hepatocellular carcinoma and its different etiologies.
Hepatoma Res. 2:151–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lou W, Liu J, Ding B, Chen D, Xu L, Ding
J, Jiang D, Zhou L, Zheng S and Fan W: Identification of potential
miRNA-mRNA regulatory network contributing to pathogenesis of
HBV-related HCC. J Transl Med. 17:72019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Murakami Y, Kubo S, Tamori A, Itami S,
Kawamura E, Iwaisako K, Ikeda K, Kawada N, Ochiya T and Taguchi YH:
Comprehensive analysis of transcriptome and metabolome analysis in
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 5:162942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ghosh A, Ghosh A, Datta S, Dasgupta D, Das
S, Ray S, Gupta S, Datta S, Chowdhury A, Chatterjee R, et al:
Hepatic miR-126 is a potential plasma biomarker for detection of
hepatitis B virus infected hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
138:2732–2744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Peng H, Ishida M, Li L, Saito A, Kamiya A,
Hamilton JP, Fu R, Olaru AV, An F, Popescu I, et al: Pseudogene
INTS6P1 regulates its cognate gene INTS6 through competitive
binding of miR-17-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:5666–5677. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhang Y, Wen DY, Zhang R, Huang JC, Lin P,
Ren FH, Wang X, He Y, Yang H, Chen G and Luo DZ: A preliminary
investigation of PVT1 on the effect and mechanisms of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from clinical data, a
meta-analysis of 840 cases and in vivo validation. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 47:2216–2232. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Shi J, Ye G, Zhao G, Wang X, Ye C,
Thammavong K, Xu J and Dong J: Coordinative control of G2/M phase
of the cell cycle by non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
PeerJ. 6:e57872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|